Tissue Integrity, FE, Psychosocial
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
6 types of burns
fire, scald, contact, electrical, chemical, radiation
Burns classified by ___ and ___
depth and extent
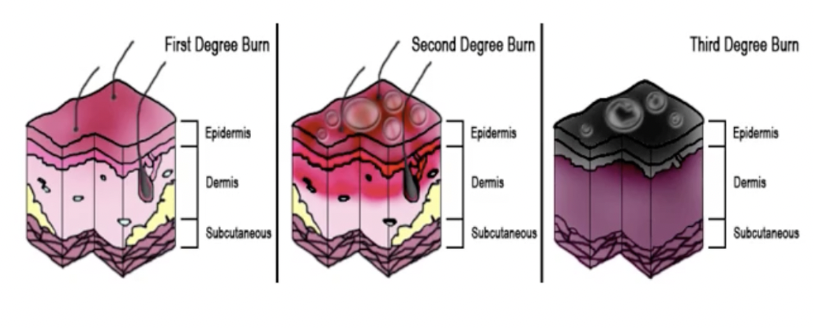
First degree wound is superficial ___ thickness on outer layer of ___
partial, epidermis
Superficial heals in ___days, like a sunburn
3-10
1st degree burn tx
pain relief and fluid
second degree burn is partial thickness of ___x2___. Has brigh red, painful and moist ____ that you dont want to pop
epidermis and dermis. blisters
2nd degree takes ____ days to heal,
10-21
Full thickness (2nd degree) is entire ___ and ___. It is ___ with dry ___. Takes ___ to heal
epidermis and dermis. mottled, blisters. 1 month
3rd degree goes to ___, even muscle and bones.
sq
3rd degree appearance is white, yellow, brown, red, and black. It is ____ and ___ with extensive ____ but no pain bc nerves destroyed
dry, leathery, edema
if 3rd degree is wider than 1.5 inches you need a
skin graft
injury degree pic
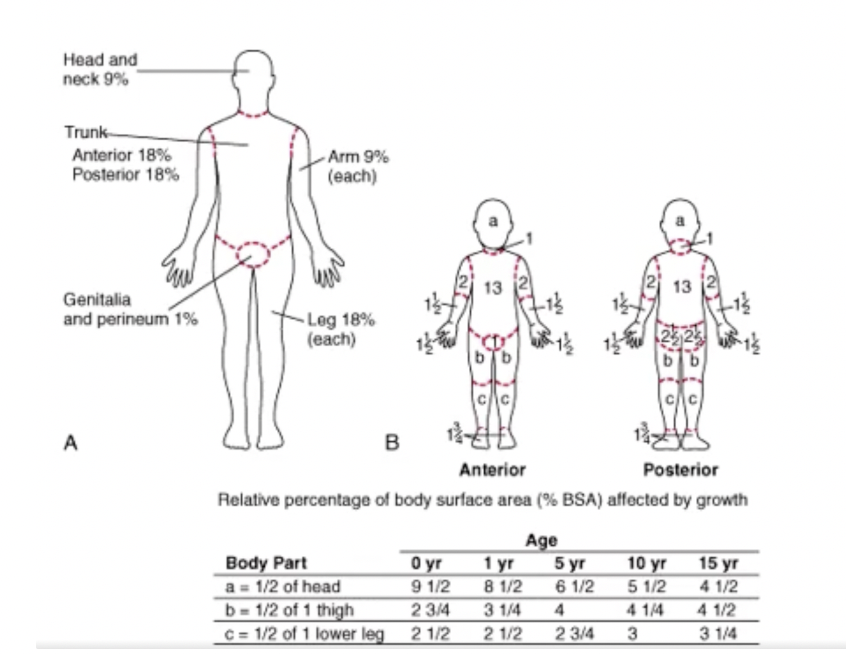
extent of burn aka
tbsa
rule of nines chart
other factors for managing burns
age, location, other injuries, preexisting conditions
even if burns themselves are first degree, can be ____ as more severe if injury to hands, face, feet, inhalation, trauma, etc
reclassified
x burns almost always require hospitalization because edema causes ____ issues
genital, urination
Most immediate threat to burn survival is
hemodynamic instability
____ level can predict which people in burn shock will benefit from plasma exchange
lactate
K is usually ___ in burns from cell destruction K spewing out.
high
smoke or chemical inhalation can lead to
microscopic lung injury
Sudden increase in ___ means ARDS risk
rr
if any smoke or chemical inhalation need to ____ prophylactically bc we anticipate they will fail in 24-48 hrs
intubate
Smoke/chemical to resp dysfunction
inhaled reacts with mucous membranes, acids produced, ulcers spasms edema
resp dysfunction from burns ss
hacking cough, drooling, dyspnea, shallow breathing, horaseness, o2 drop
hypermetabolic response in burn is dt
tissue destruction and loss of skin that holds heat
how does hypermetabolic response happen in burns
catecholamine and cortisol release, heat production to balance heat loss from no skin
hypermetabolic response def
increased o2, glucose, protein use and fat wasting
most common cause of burn death is
sepsis
first priority to thermal injury
stop fire and provide relief
immediate ____ is more important than remove clothes
submersion
autograft is ___ homograft from ____, heterograft from ____
self, human, pig
circumferential burns
encircle body and act like tourniquets
Stress def
disruptive condition from change in environment that is perceived as damaging to balance or equilibrium
stress types
physical, physiologic, psychosocial
physiologic stress type
pain and fatigue
stressor sequence
series of stressful events from initial event
chronic intermittent stressors
everyday hassles
chronic enduring stressor
poverty
Selye’s GAS/theory of adaptation stages
alarm, resistance, exhaustion
alarm stage is ____ start, resistance is ____< exhaustion is when ____ effects happen with elevated endocrine activity
sns, adaptation, negative
local adaptation syndrome
inflammatory response to repair processes at local site of tissue injury
patho of stress
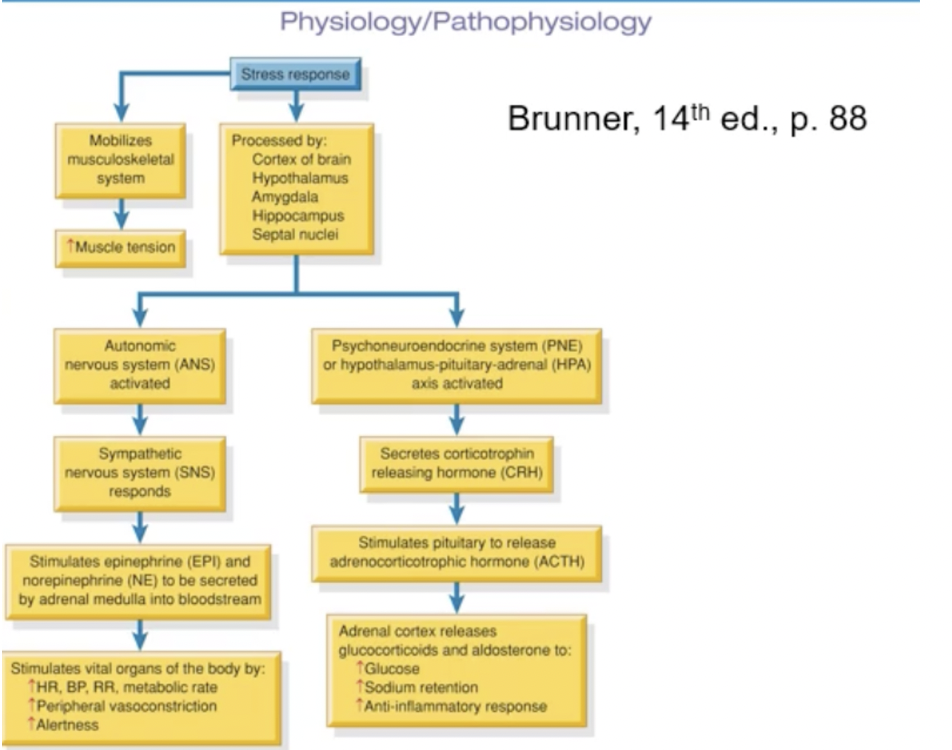
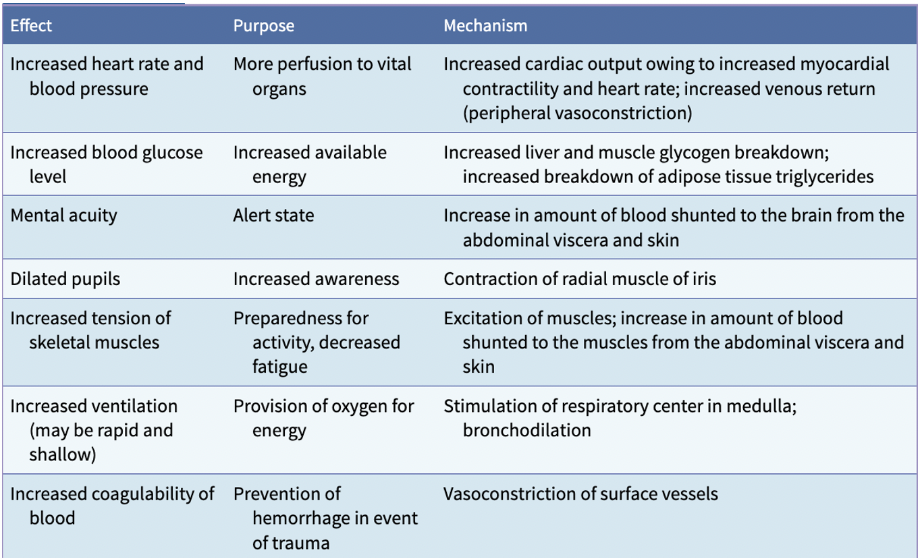
SNS/stress se
maladaptive responses to stress
goals not met, poor coping, distrurbed physiologic balance, increase illness susceptibility
psychoneuroimmunology
study of relationships of neuroendocrine system, cns, and immune system and how they affect overall health
OD risk factors
family hx, access, mental issue, peer pressure, lack of family, nature of substance, age of first use, stress, metabolism, social norms
acetaminophen tx
charcoal 4, acetylcysteine 48
acetaminophen OD steps

amphetamines effects (CNS and PNS)
increased catecholamines so hyperactive, increased dope so euphoria, sympathetic CV effects
Valium/diazepam amphetamines tx meds
sedatives and muscle relaxants, benzos HTN, charcoal for GI decontamination, defib/antidysrhythmics for dysrhythmias
Nursing Tx for amphetamines
high body heat from high metabolism so turn down temp
SSRI clinicals
AMS< ataxia, hyperpyrexia, hyperreflexia, tremor, myoclonus, ans effects, cv effects
SSRI drugs
maois, trazodone, snri, norepidope reuptake inhibitors, lithium, opioids, amphetamine/stimulants
alcohol od ss
drowsy, impaired coord, slurred speech, sudden mood change, aggression, gradiosity, stupor, coma
alcohol od tx nursing
head injury, hypoglycemia, hypoxia, hypovolemia, airway, let them sleep
suicide patho
more white matter, decreased serotonin
Biogenic amine theory
deficiency of nt (amines) in key areas of brain cause depression
top three biogenic amines
norepi, dope, serotonin
how can nt deficiecny happen
breakdown, rapid neuron firing, increased numbers/sensitivity of postsynaptic neurons
nursing tx for suicidals

suicidal 2 phase process
pt safety, underlying cause
pt safety suicide
never alone, no dangerous items
undelrying cause suicide
psych counseling
antidepressants increase norepi and serotonin in ___ membrane receptors by inhibiting serotonin reuptake in ___ space
post, pre
tricyclic antidepressants moa
block reuptake of serotonin and ne by pre
tricyclica anti (TCA) SE
CNS sedation, fatigue, suicide, visual disturbance, cv changes, dry mouth, constipation, fetal toxic, urinary retention, loss of libido
maoi moa
increase serotonin and ne concentration by reducing degredation of nt by MAO
ECT moa
artificial light to influence production of melatonin and function of catecholamine systems
ect is first line of defense for
seasonal depression