Ib biology HL: D.2.3 - water potential
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
water’s polar nature and it’s basic structure
oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, which results in a slight negative charge in oxygen, and a slight positive charge in hydrogen ions. it is a dipolar molecule
hydrogen bonds in the water form due to weak electrostatic attraction between the slightly positively charger hydrogen atoms and slightly negatively charged oxygen atoms
conditions for ionic compounds being soluble in water
if the force of attraction between ions and water molecules is greater than the force of attraction between oppositely charged ions, water has the ability to dissolve the substance
hydration shells
term refering to water molecules surrounding ions when in a solution. If the ion is positive, the more negative oxygen side will be pointing towards it and vice versa. their presence leads to dissolution
dissolution
the process of particles moving and becoming evenly spread out in a solvent
hypertonic
with a relative higher solute concentration
isotonic
a solution with a relatively equal solute concentration
hypotonic
a solution with a relative lower solute concentration
what happens to a cell without cell wall in a hypotonic solution
water will move into the cell as the solute concentration is higher inside. cells might burst (lysis) because of the increased pressure because the lack of cell wall means that they cannot generate positive pressure potentials
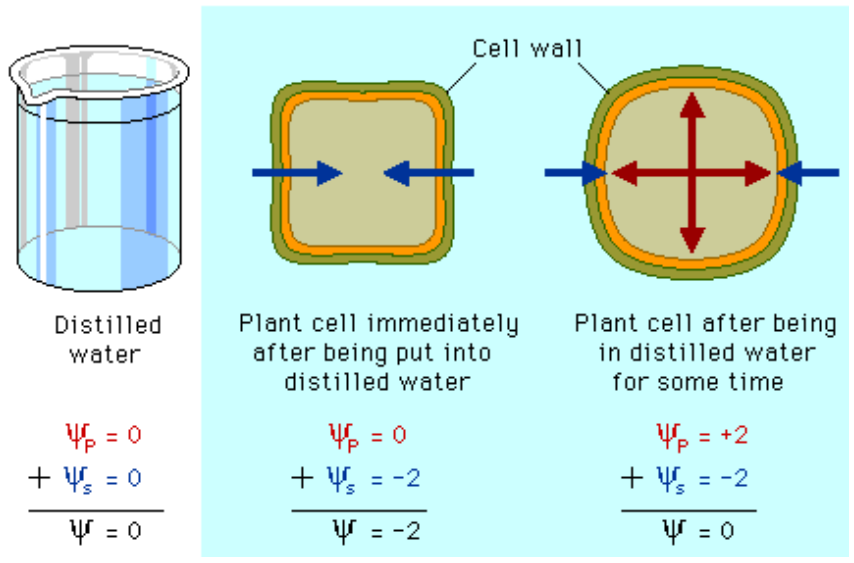
what happens to a cell with cell wall in a hypotonic solution
water will enter cell from an area of less negative solute potential to an area of more negative solute potential
The cell will experience and increase in turgor, have a larger permanent vacuole, pressure and becomes turgid.
that is it’s normal state; the osmotic pressure is equal
this causes positive internal pressure ( pressure potential) , which can offset the lower solute potential, creating an equilibrium
this is possible because of the cell wall can withstand pressure
what happens to a cell without a cell wall in a hypertonic solution
water will move out of the cell where the solute concentration is lower
the cell will shrink: it will become crenated. this can lead to tissue damage and function loss
what happens to a cell with a cell wall in a hypertonic solution
water will move out of the cell where the solute concentration is lower.
the pernament vacuole reduces in size, stop applying pressure, the plant cell will undergo plasmolysis as the cell shrinks and looses turgor pressure. it can cause irreversible damage to plant cells
osmosis
the movement of water through a semi permeable membrane from an area high water potential to low water potential. will occur until both side of the membrane have equal solute concentrations ( state of dynamic equilibrium )
medical applications of isotonic solutions
organs used in transplantations need to be stored in isotonic solutions to cushion against damage, provide the necessary nutrients and prevents water loss
isotonic fluids can be given intravenously to administer drugs directly in the bloodflow or in cases of severe dehydration
water potential
Water potential is a measure of the potential energy of water per unit of volume of water, relative to the potential energy of pure water at standard conditions (atmospheric pressure and 20 °C)
high water potential
low solute concentration
more free water molecules
more potential to leave
low water potential
high solute concentration
little free water molecules
low potential for water to leave
what influences water potential ( short answer )
pressure potential ( concentration gradient )
solute potential
surface area
temperature
distance ( the thickness of the semi permeable membrane)
pressure potential: positive and negative
physical pressure on a system:
positive pressure potential means something is increasing the pressure of the solution (eg water entering root cells). It increases water potential
negative pressure potential means the pressure of the solution is decreased ( eg transpiration at the top of the cell creating a pressure difference and pulling water up ) decreased water potential ('“pulls water in”)
solute potential
Solute potential refers to the attraction of water molecules to solute particles, which, when present, reduces the number of free water molecules and limits the movement of water.
pure water solute potential
0Kpa - the more negative, the lower the water potential
plant cells; parts involved in osmosis
cell wall: fully permeable
the wall is strong and pushes against the cytoplasm of the cell pushing against the cell wall
this causes the plant cell to develop high internal pressures in the right conditions
turgor pressure in plants
turgidity; the pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall ( caused by a large permanent vacuole )
this force exerted outward; this gives the plant rigidity
cells with a cell wall in an isotonic solution
the vacuole is not as large
the plant cell is placcid
much lesser turgor pressure
osmosis in single celled organisms
contractile vacuole; constantly pumps water out; active transport because against concentration gradient. Homeostasis: osmoregulation.
water potential formula
water potential = Solute potential + pressure potential
effect of cell wall on water potential