OPT 114: Orbit - Contents
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Globe (Eye, eyeball)
consists of 3 coats and 3 chambers
contents of outer fibrous layer
cornea and sclera
contents of middle vascular layer (uvea)
iris, ciliary body, choroid
contents of inner neural layer
retina
What are the 3 chambers in the globe?
anterior, posterior, vitreous
another name for tenon's capsule
bulbar fascia
tenon's capsule
sheet of dense connective tissue that covers the sclera; covers tendons of the extraocular muscles as they insert into the sclera; provides a strong barrier; separates the globe from the contents of the orbit; prevents orbital infections from entering the globe
what does the tenon's capsule merge with anteriorly?
sclera and conjunctiva at limbus
what is the tenon's capsule continuous with posteriorly?
dural sheath of the optic nerve
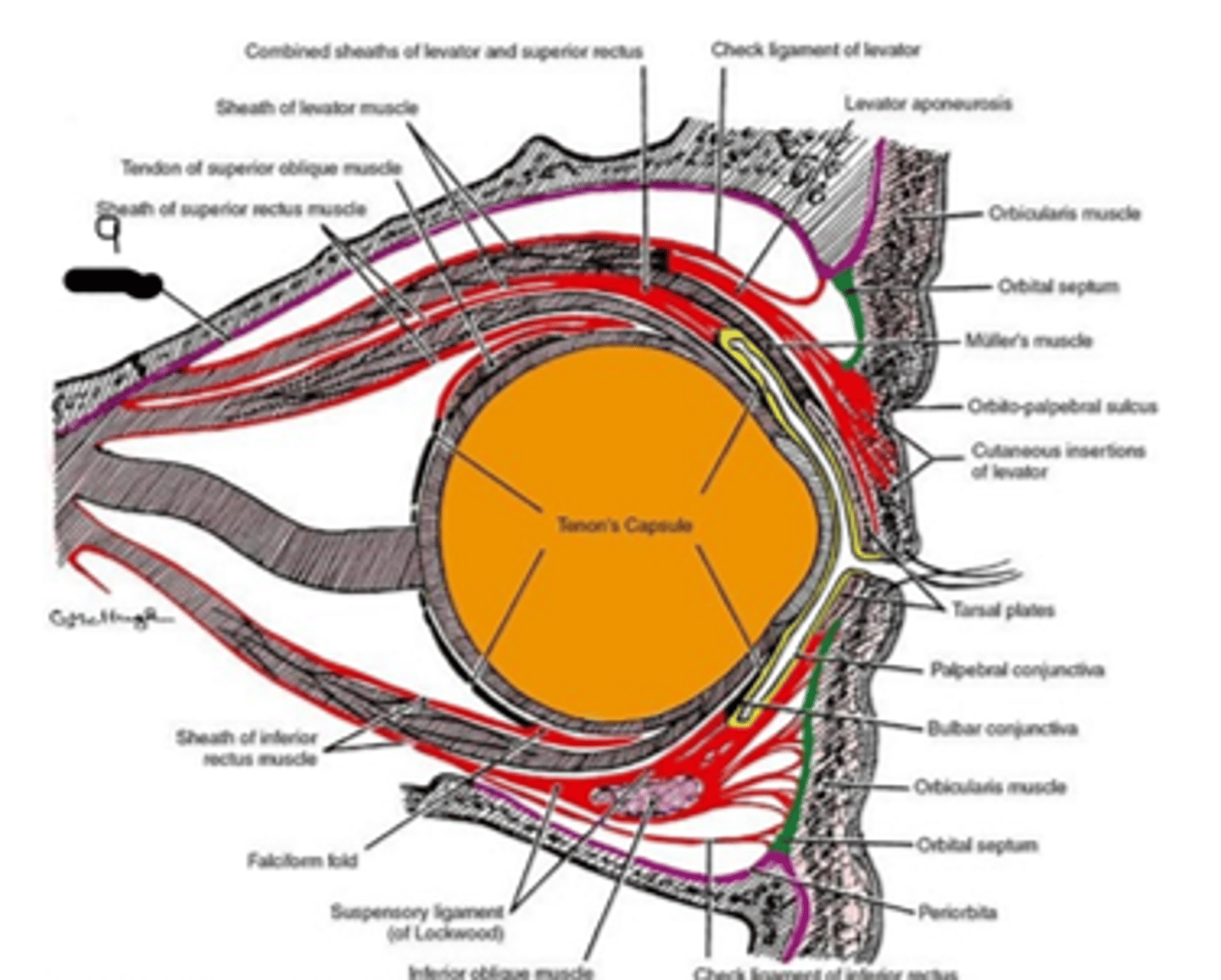
conjunctiva; tenon's capsule; sclera
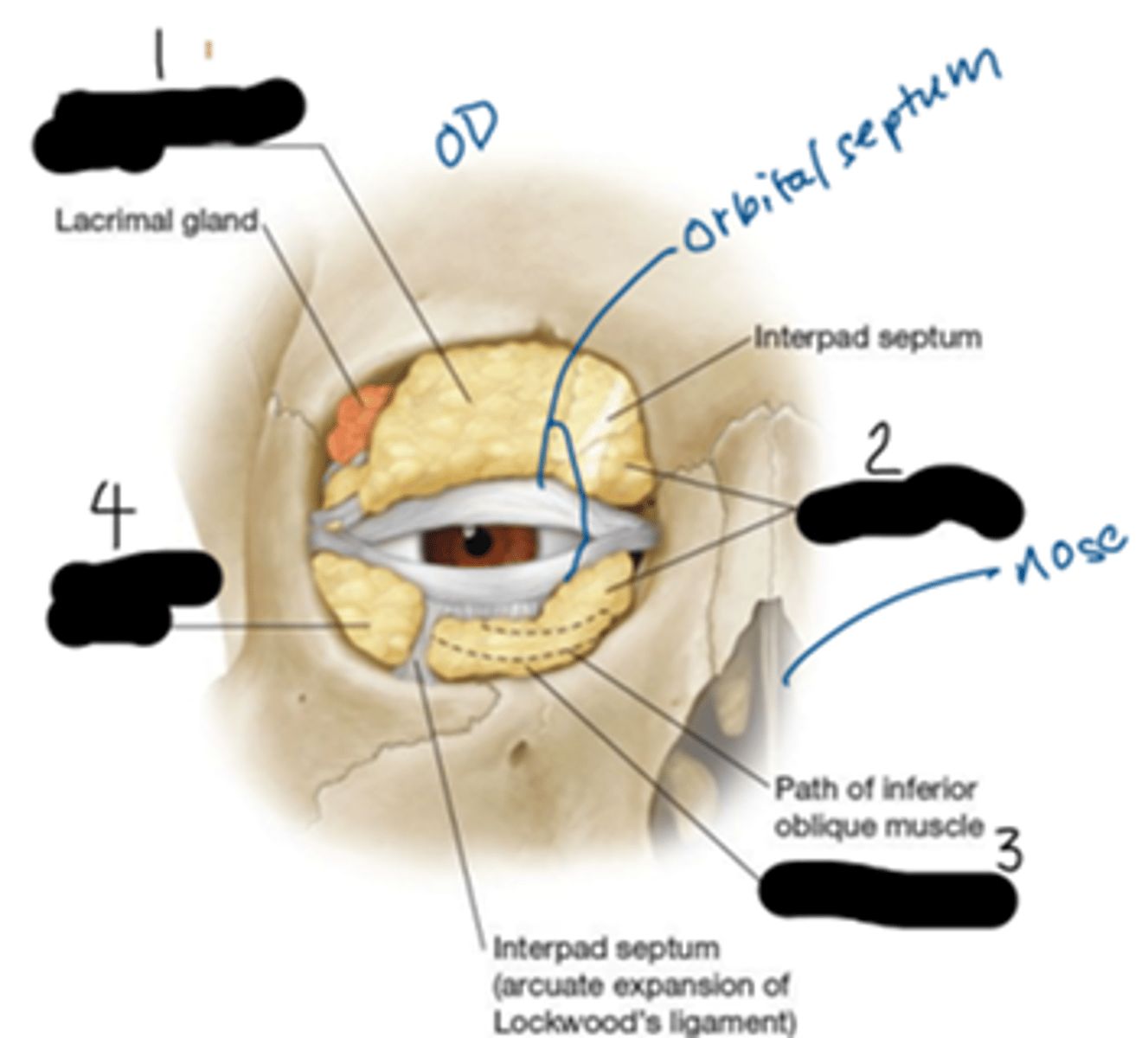
What's "1", "2", "3", respectfully?
another name for the orbital septum
palpebral fascia
orbital septum
sheet of dense connective tissue that extends from the entire rim of the orbit to the tarsal plate; anterior barrier of the orbit; separates the eyelids and lacrimal sac from the orbit; prevents facial/eyelid/nasolacrimal system infections from entering the orbit; keeps orbital fat in place
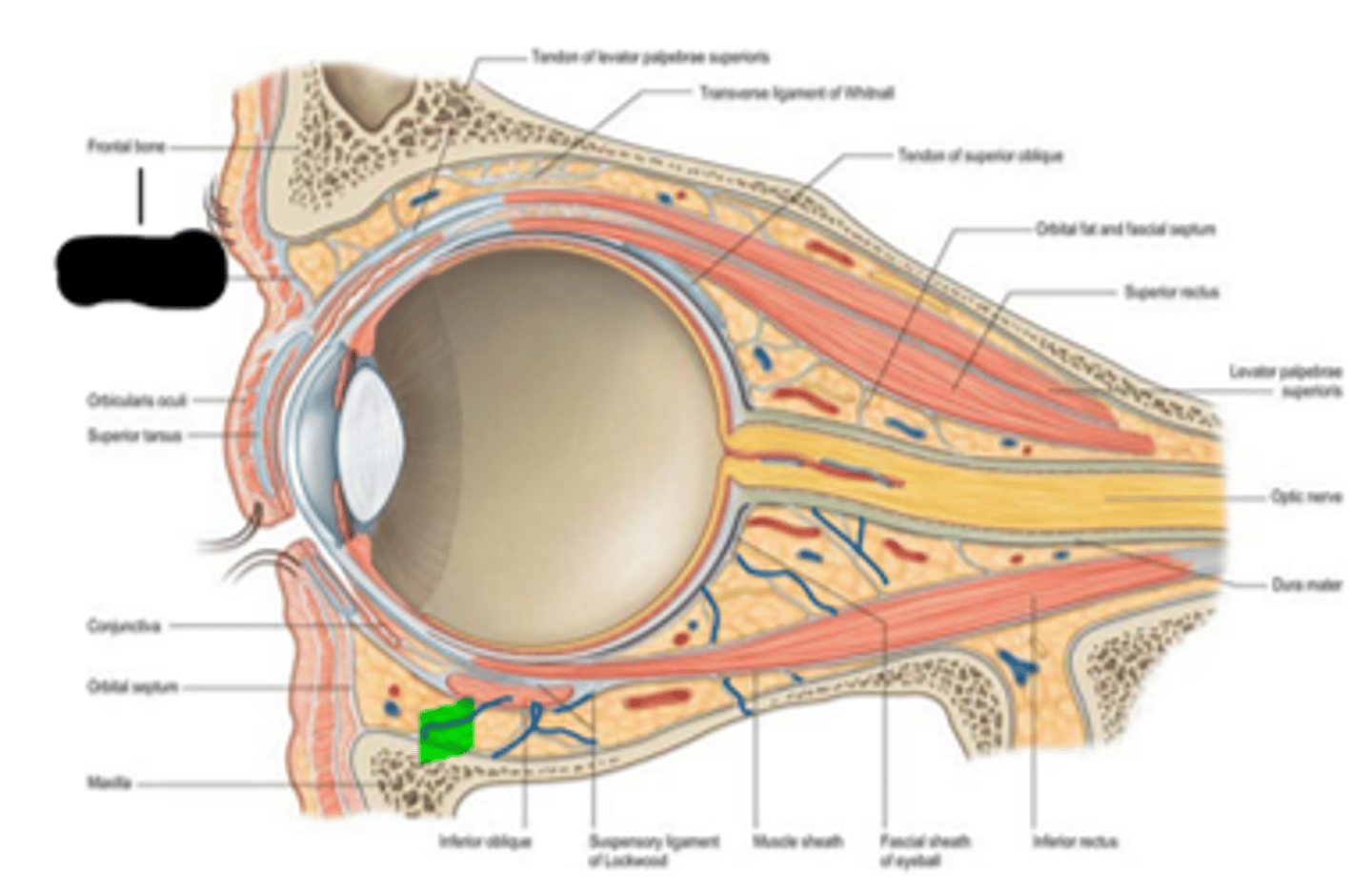
The orbital septum is continuous with the ____________ at the superior and inferior orbital rim.
periosteum
orbital septum
What's "1"?
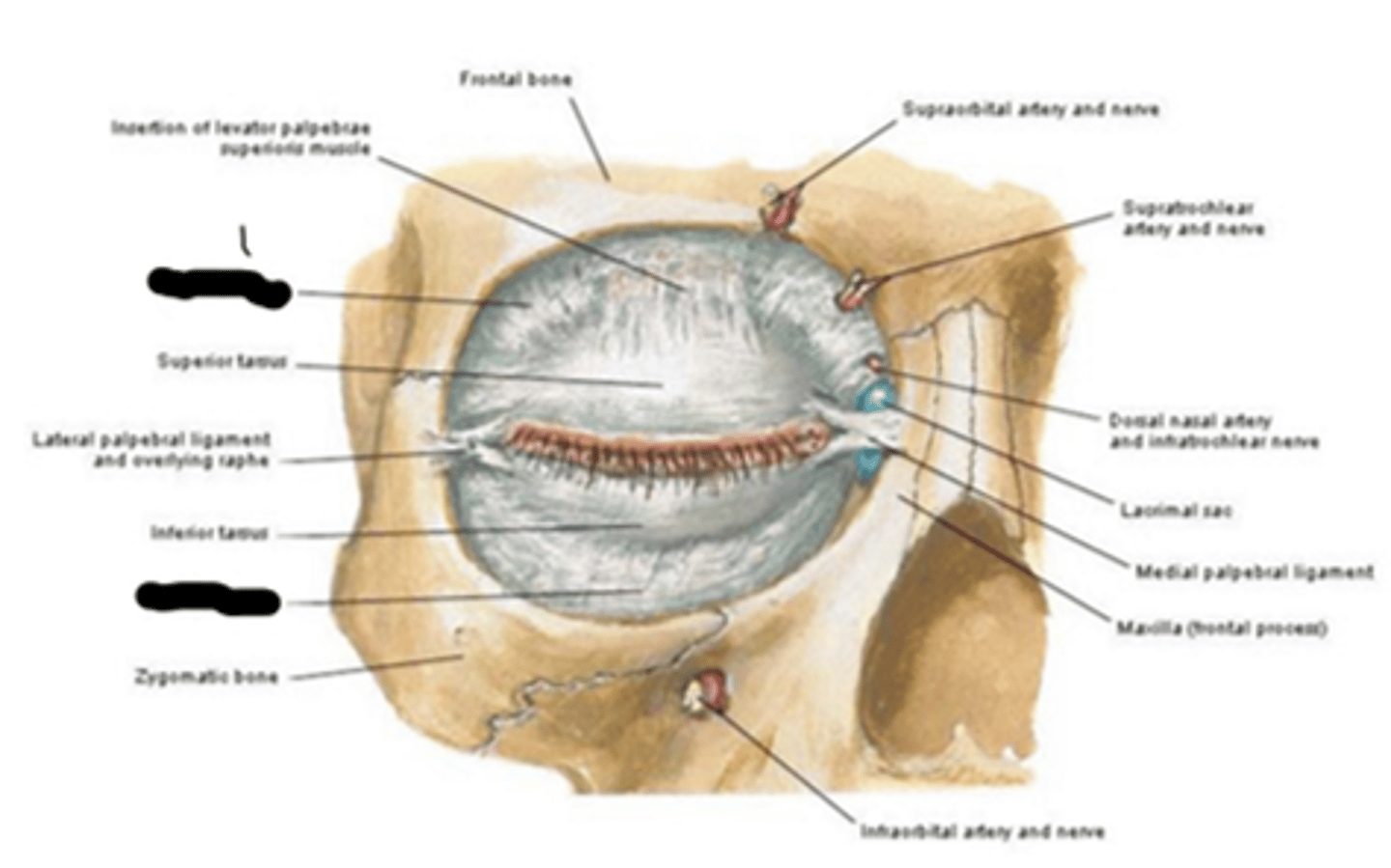
orbital septum
What's "8"?
periorbita (orbital fascia, periosteum)
sheet of dense connective tissue that covers the bones of the orbit; attachment site for muscles, tendons, and ligaments as well as support structure for vascular supply to the orbital bones
anteriorly, the periorbita is continuous with the periosteum of _________ ________ and _______ _____.
facial bones; orbital septum
posteriorly, the periorbita is continuous with the _______ _______ of the ________ _______ and forms the _______ ____________ _____.
dural sheath; optic nerve; common tendinous ring
periorbita
What's "9"?
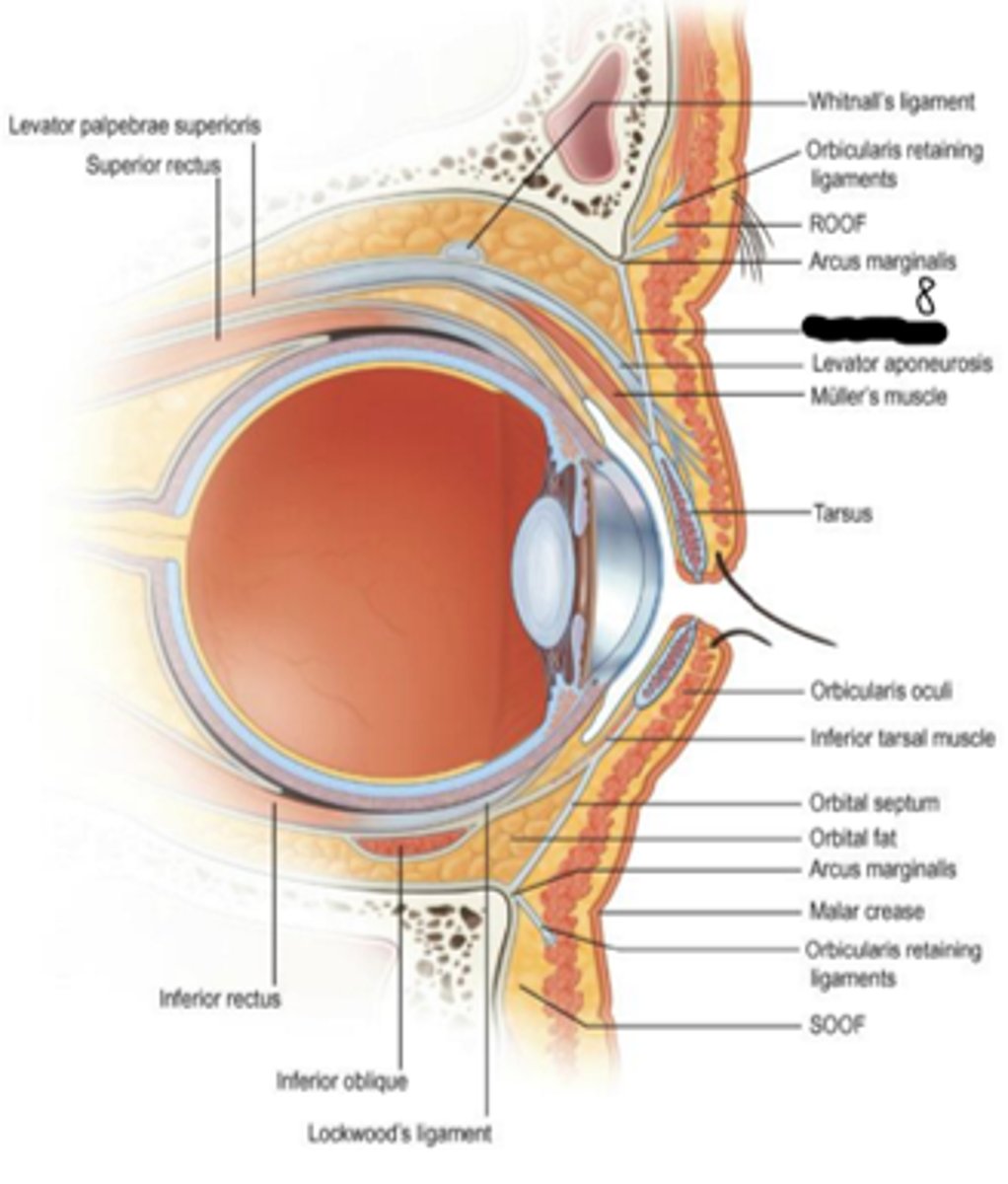
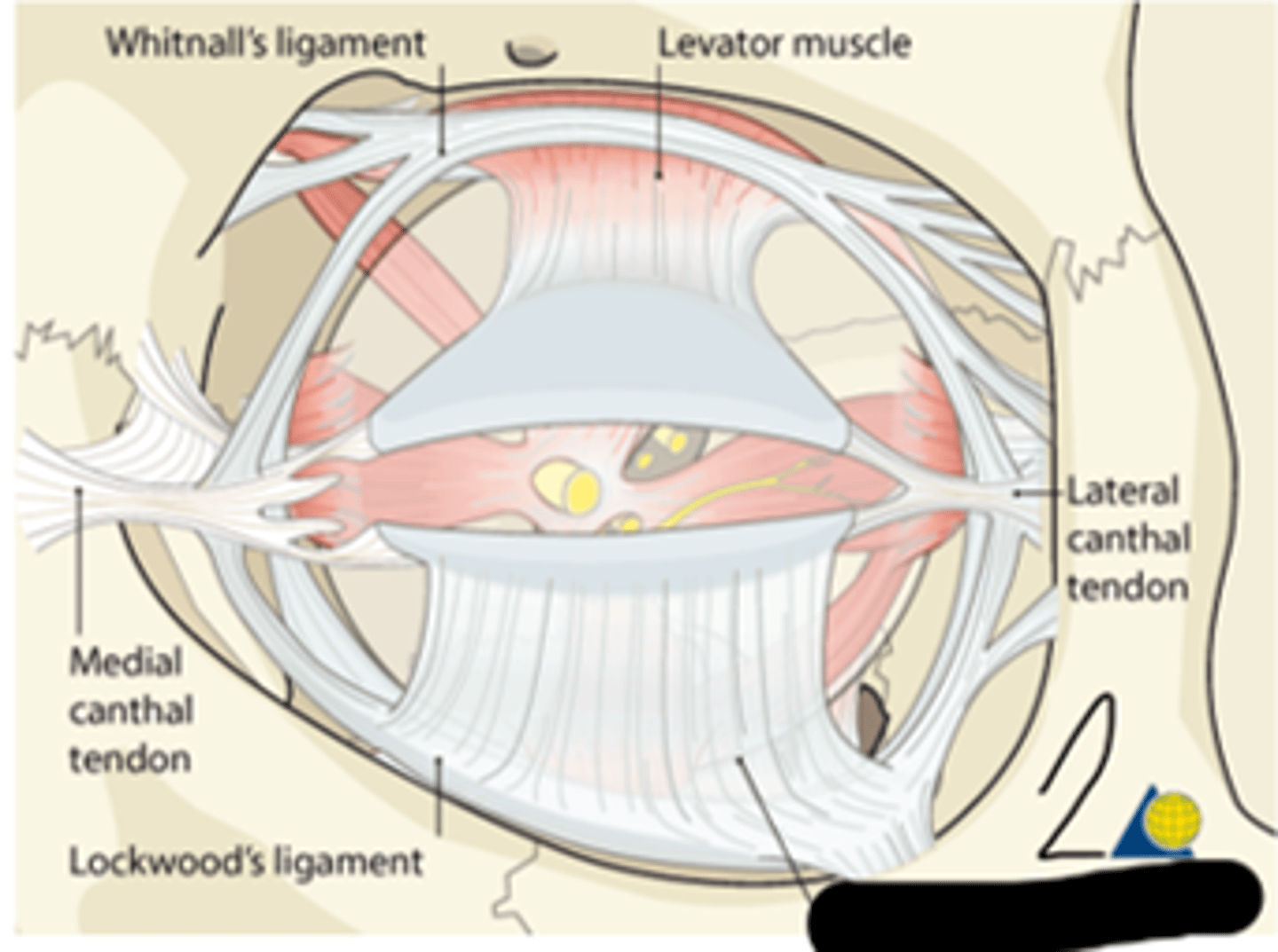
whitnall's ligament
transverse dense connective tissue located in the orbit; courses from lateral orbit wall to medial orbit wall; provides support and maintains spatial relationships between anatomic structures in the superior orbit; formed by the condensation of the levator muscle; where levator muscle fibers end and the levator aponeurosis begins
another name for whitnall's ligament
superior transverse ligament
lockwood's ligament
transverse dense connective tissue located in the inferior orbit; courses from lateral orbital wall to medial orbital wall; provides support and maintains spatial relationships between anatomic structures in the inferior orbit; contributes to the formation of the capsulopalpebral fasica
another name for lockwood's ligament
suspensory ligament
whitnall's ligament; lockwood's ligament
What's "1" and "2", respectfully?
medial check ligament
transverse dense connective tissue that is an expansion of the sheath of the medial rectus; attaches to the lacrimal bone; prevents overaction of the medial rectus
lateral check ligament
transverse dense connective tissue that is an expansion of the sheath of the lateral rectus; attaches to the zygomatic bone; prevents overaction of the lateral rectus
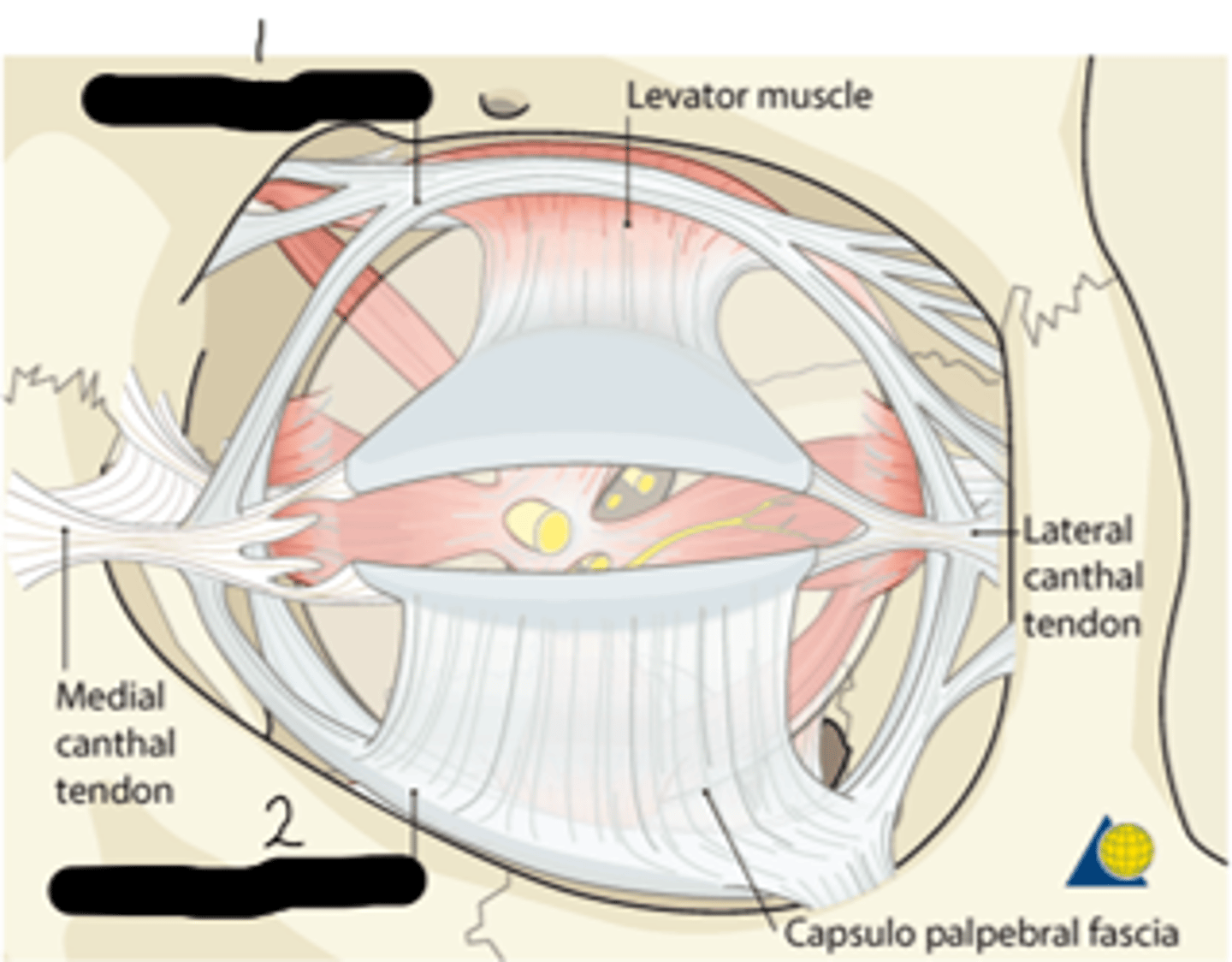
medial check ligament; lateral check ligament
What's "1" and "2", respectfully?
__________, __________, and ________ form a supporting hammock-like formation for the globe
whitnall's ligament; lockwood's ligament; the check ligaments
orbital septum system
web of interconnecting connective tissue septa; organizes the orbital space surrounding the globe; anchors and supports extraocular muscles, nerves, and blood vessels
orbital septum system
What's "1"?
orbital nerves
optic nerve (II), oculomotor nerve (III), trochlear nerve (IV), ophthalmic nerve (V1), maxillary nerve (V2), abducens nerve (VI)
blood vessels
ophthalmic artery and its branches; superior and inferior ophthalmic vein and its branches
ophthalmic artery
What's the blank?
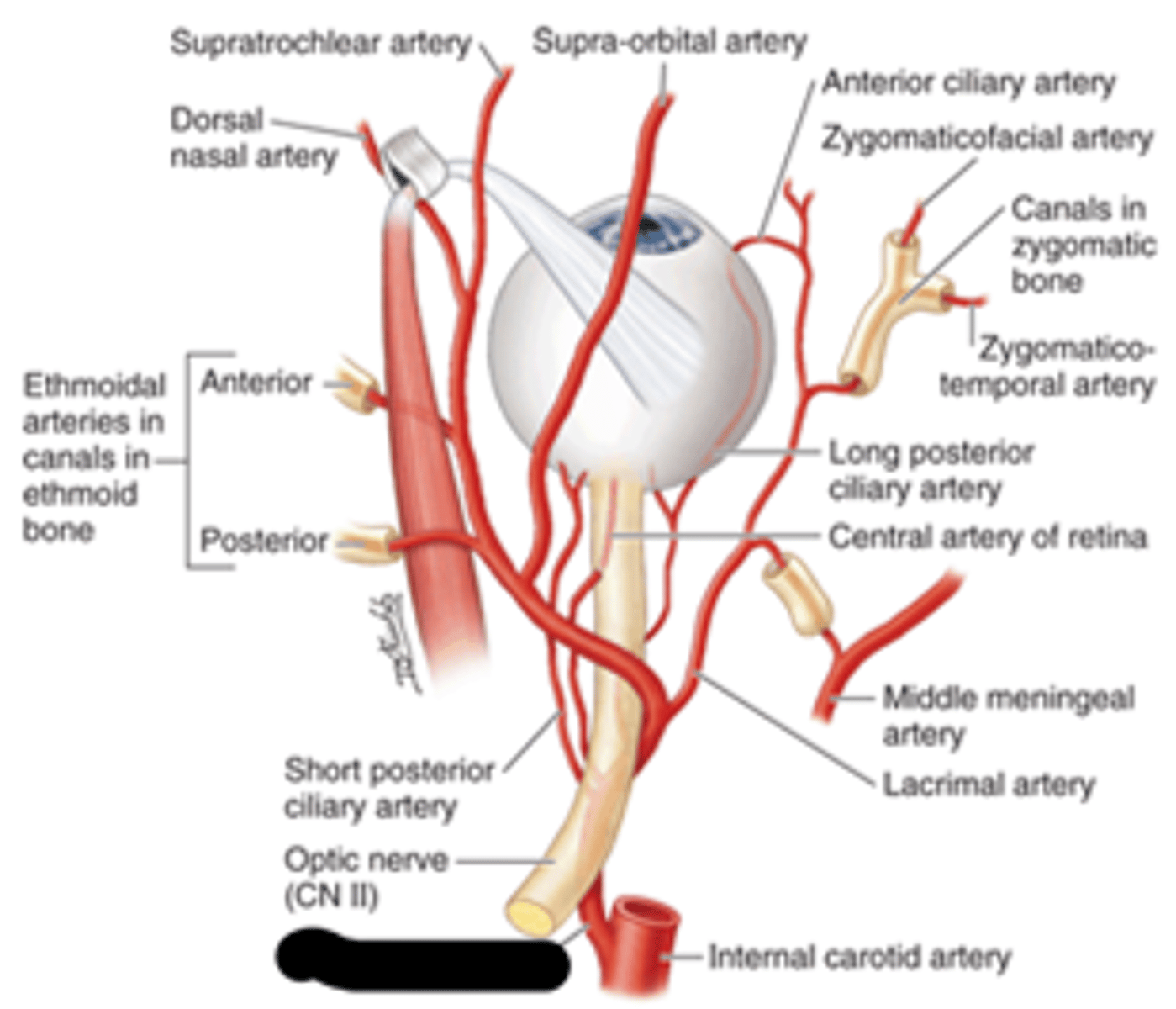
superior ophthalmic vein; inferior ophthalmic vein
What's "1" and "2", respectfully?
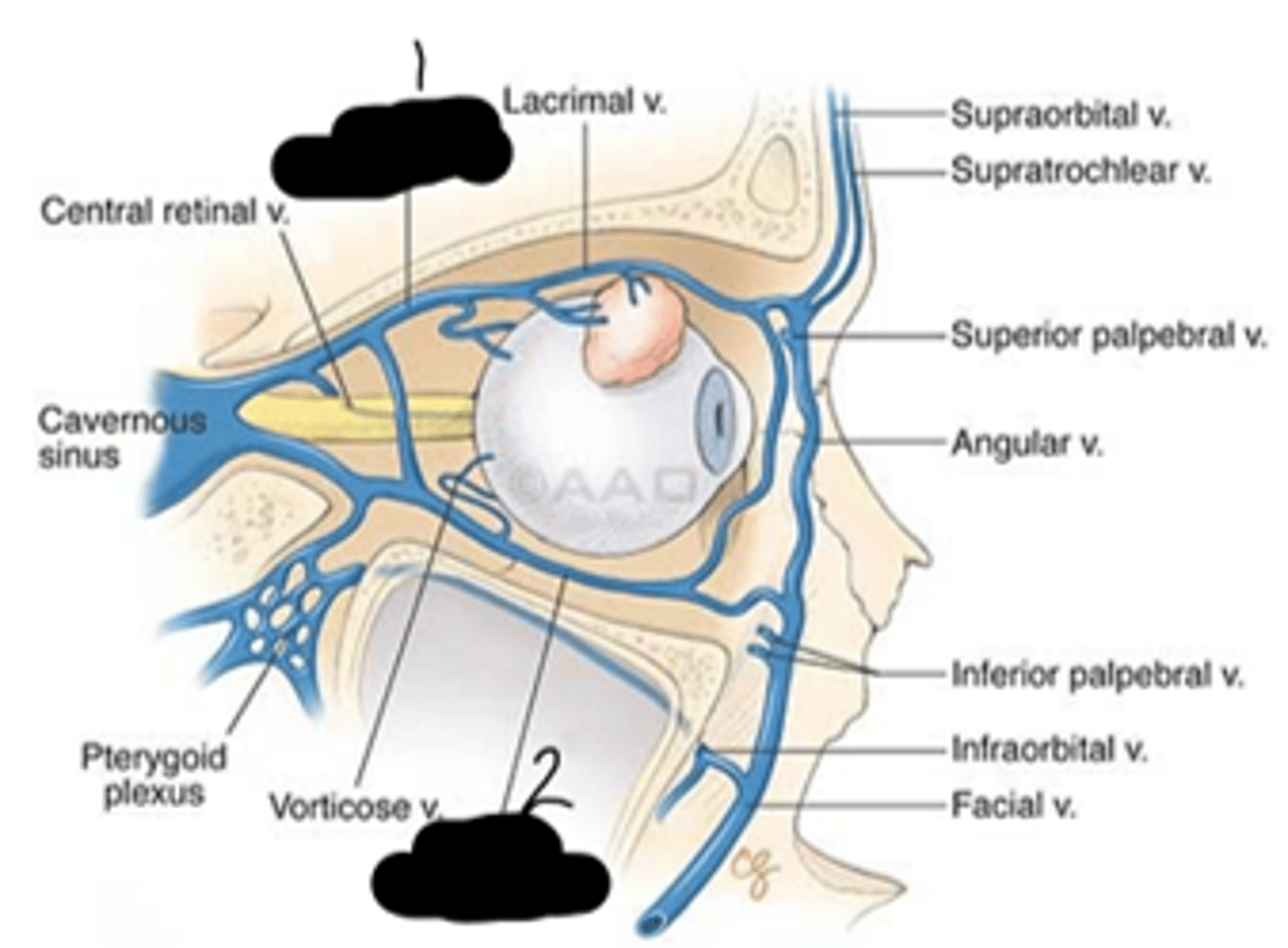
extraocular muscles
control movement of the globe
2 types of extraocular muscles
recti and oblique
recti muscles
superior, inferior, medial, lateral - rectus
oblique muscles
superior and inferior - oblique
eyelid retractors
control movement of the eyelids
eyelid retractors examples
levator palpebrae, superior & inferior tarsal muscles, capsulopalpebral fascia
another name for superior tarsal muscle
Muller's muscle (an eyelid retractor)
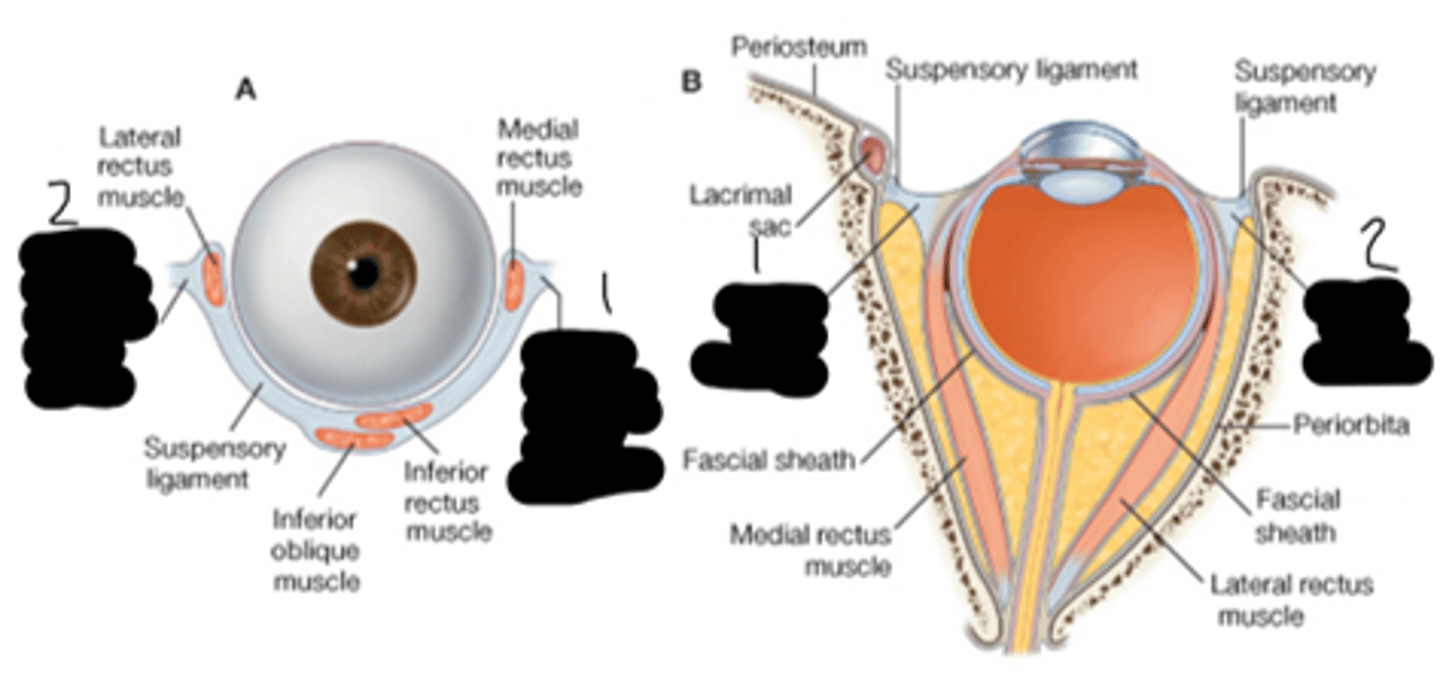
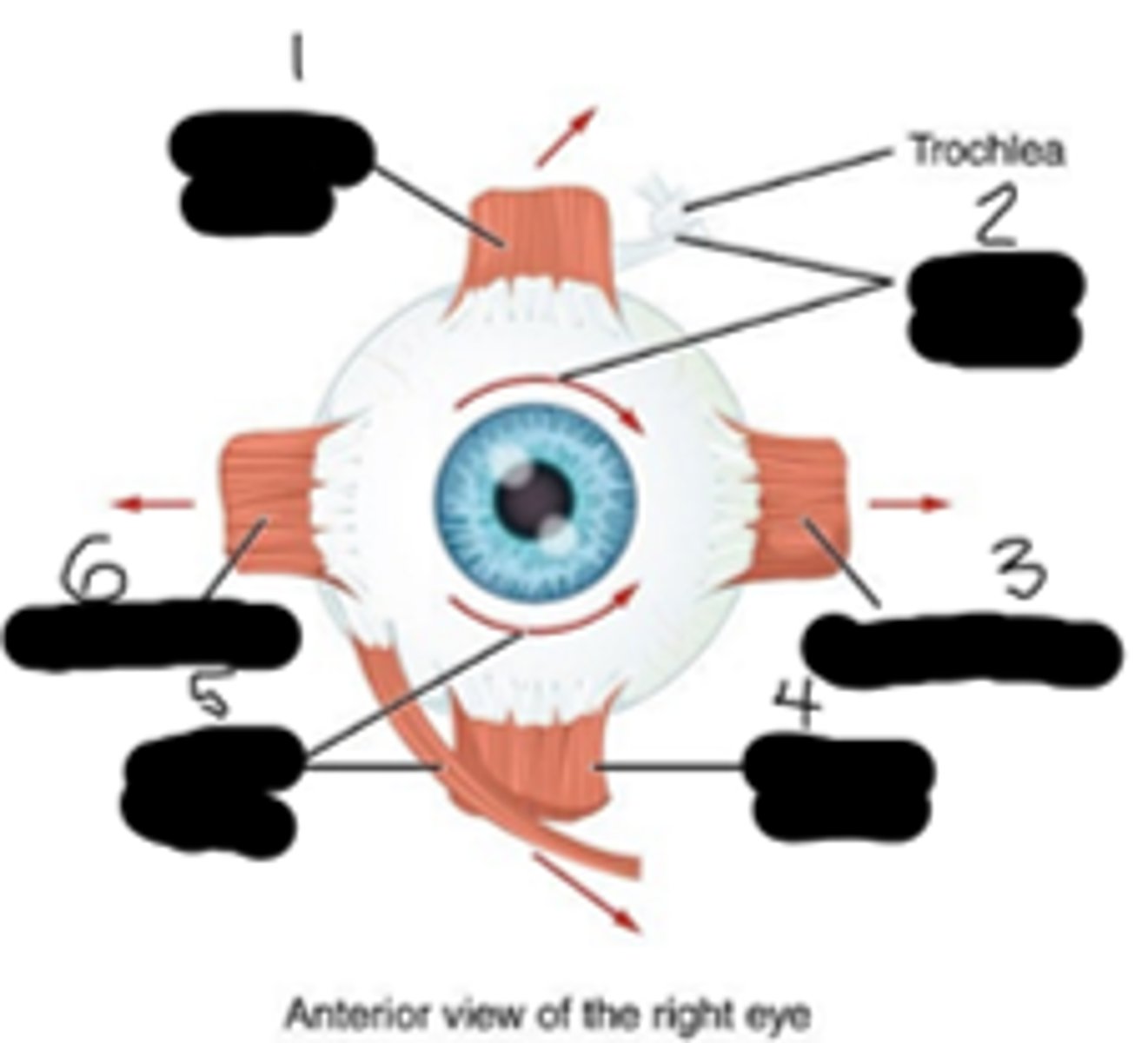
superior rectus; superior oblique; medial rectus; inferior rectus; inferior oblique; lateral rectus
What's "1","2","3","4","5", and "6" respectfully?
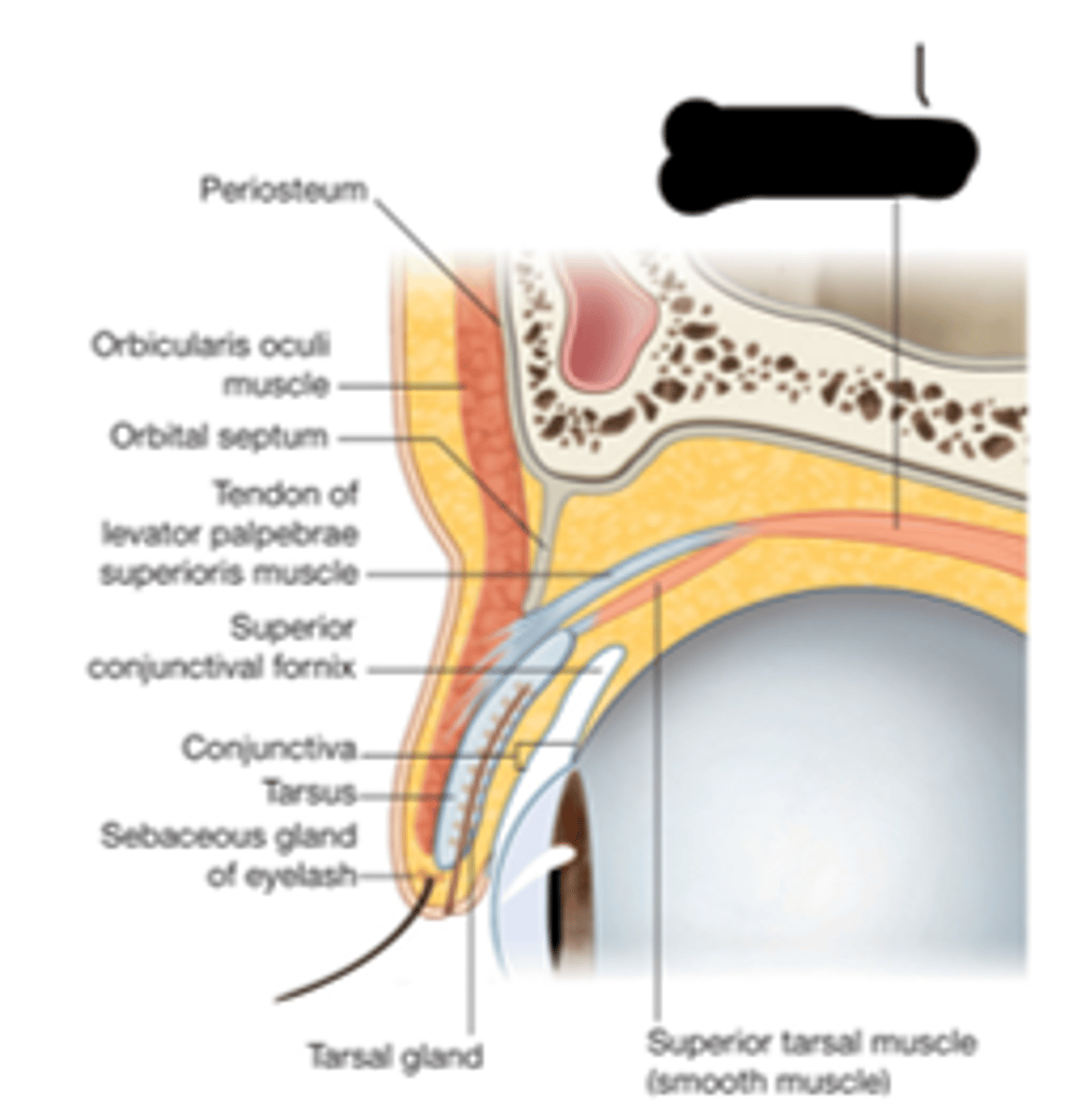
levator palpebrae superioris muscle
What's "1"?
capsulopalpebral fascia
What's "2"?
orbital fat
space not occupied by orbital structures becomes filled with adipose tissue; predominant tissue in orbital apex; surrounds the optic nerve, separating it from the extraocular muscles; separates the muscles in the orbit from the orbital walls
In the anterosuperior orbit, __ fat pads are anterior to the levator aponeurosis. They are _____ and _____.
2; nasal; central
Anteriorly and inferiorly, ___ fat pads are posterior to the orbital septum and anterior to the capsulopalpebral fascia. They are _______, ________, and ______.
3; nasal; central; temporal
The fat pads are held in place by the _________ __________.
orbital septum
preaponeurotic fat pads
2 fat pads in the anterosuperior orbit
preaponeurotic fat pad, nasal fat pad, central fat pad, temporal fat pad
What's "1", "2", "3", and "4", respectfully?