Endocrinology of Pregnancy, Normal Pregnancy, Puerperium, and Lactation
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
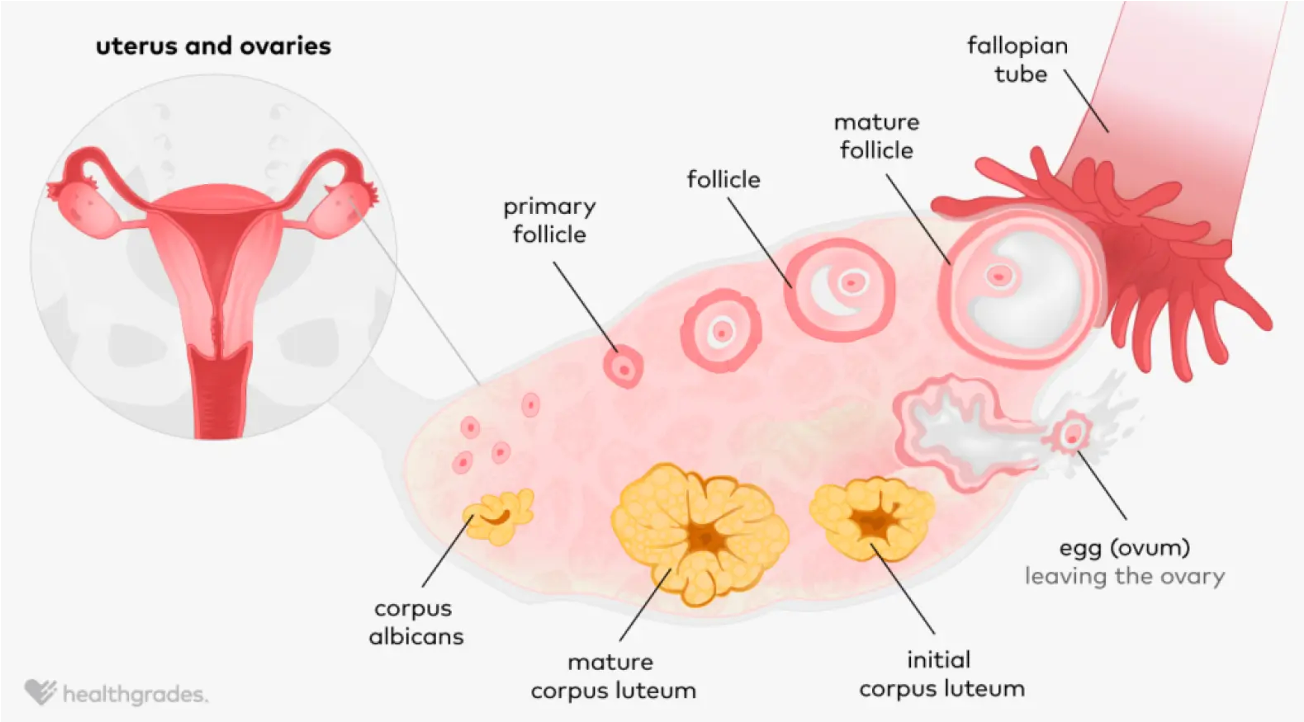
Ovulation Diagram
Have follicles → start to mature but one becomes primary/mature follicle → where egg will be released
Egg meets sperm and embeds in uterine lining
Corpus luteum continues and feeds the pregnancy
No pregnancy → corpus luteum becomes corpus albicans and dies off
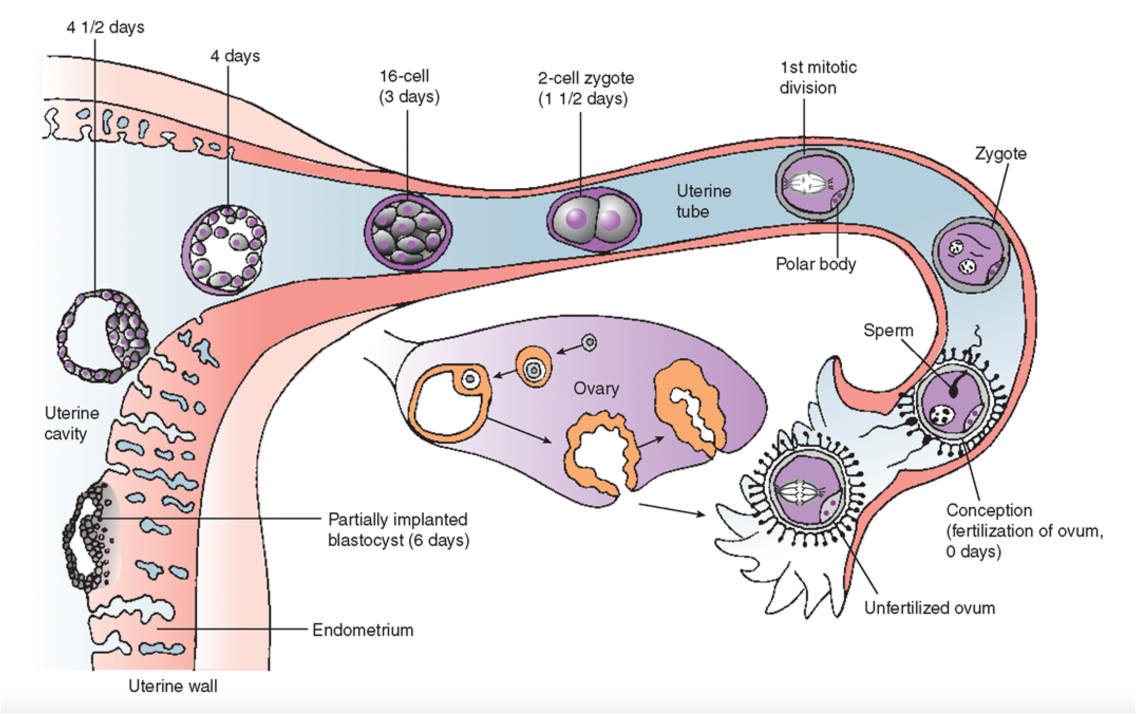
Fertilization and Implantation Diagram
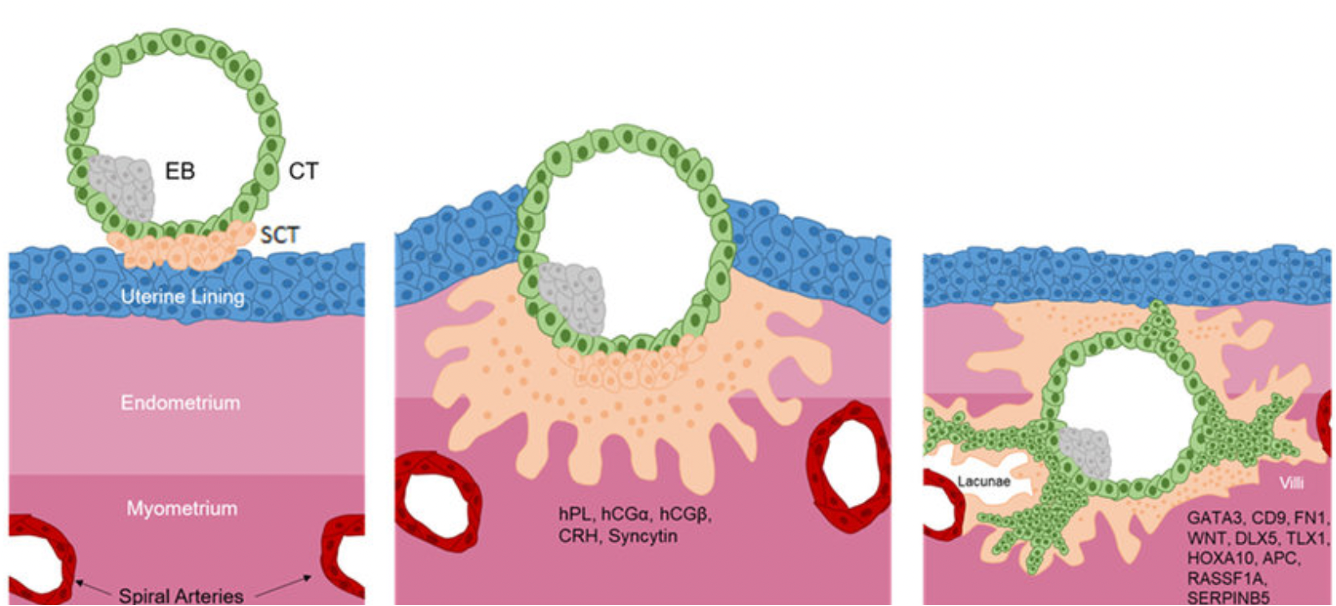
Implantation Diagram
Embryo enters uterine lining: starts to embed
As it embeds there is disruption that can cause implantation spotting
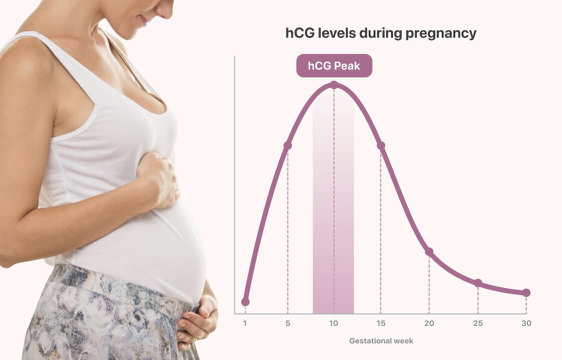
What is the first sign of pregnancy (urine or blood)?
hCG hormone
What is hCG produced by?
The placenta
When does hCG rise during a normal pregnancy?
1st trimester
10-11 days after conception
Doubles every 48-72 hours
Blood hCG test will not be (+) after a certain amount of time (8-11 weeks), but urine hCG will remain (+) throughout the pregnancy and for a little time after
When is hCG elevated with (5) and what is it a marker of (3)?
Elevation of hCG with:
Normal placental tissue
Multiple gestation
Hydatidiform moles
Choriocarcinoma
Ectopic pregnancy
Marker of:
Pregnancy (+ test)
High values: trophoblastic disease, multiple gestation, molar pregnancy
Low values: threatened miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, incomplete miscarriage
What is important to note about hCG?
Number doesn’t matter as much as the change in the number
What is the role of hCG? (1)
Stimulates the corpus luteum to produce progesterone and estrogen to maintain the pregnancy
What is hPL produced by?
The placenta
What are the roles of hPL? (2)
Regulates maternal glucose, fat, and protein metabolism for fetal nutrition
Increases maternal insulin resistance to raise blood glucose levels for the fetus (why we do 1 hour glucose test)
Prepares the breasts for lactation
What is prolactin produced by?
Anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
What is the role of prolactin? (1)
Prepares the mammary glands for lactation: increases as pregnancy progresses and peaks near delivery
What is relaxin produced by?
Corpus luteum
Placenta
Decidua (uterine lining during pregnancy)
What are the roles of relaxin? (3)
It relaxes the ligaments in the pelvis and softens the cervix in preparation for labor (may cause back pain)
It may help prevent uterine contractions in early pregnancy
It contributes to increased flexibility of the pelvis during delivery
What is oxytocin produced by?
Hypothalamus → released from PPG
What are the roles of oxytocin? (3)
Simulates uterine contractions during labor: levels rise significantly during labor
Facilitates bonding between mother and baby
Plays role in milk ejection during breastfeeding
What is progesterone produced by?
Initially produced by corpus luteum
After 10 weeks: placenta
What are the roles of progesterone? (4)
Pregnancy hormone: crucial for maintaining pregnancy
Maintains endometrium for implantation
Inhibits uterine contractions to prevent preterm labor
Prepares breasts for lactation by promoting gland development
Progesterone both inhibits and is needed for pregnancy: depends on the time of the cycle
Second half of cycle: will help with pregnancy
After period: d/c
What are the roles of estrogen (primarily estriol but also some estrone and estradiol)? (5)
Promotes uterine growth to accomodate the fetus
Increases blood flow to the uterus and placenta
Helps develop the placenta
Triggers development of fetal organs
Stimulates development of mammary glands for lactation (alveoli)
hCG, estrogen, and progesterone
The correct balance of these sustains and supports pregnancy
Together, these hormones thicken the uterine lining and tell the body to stop menstruating
Placenta and Uterus
Placenta and uterus should be separate structures but have many blood vessels that temporarily attach them
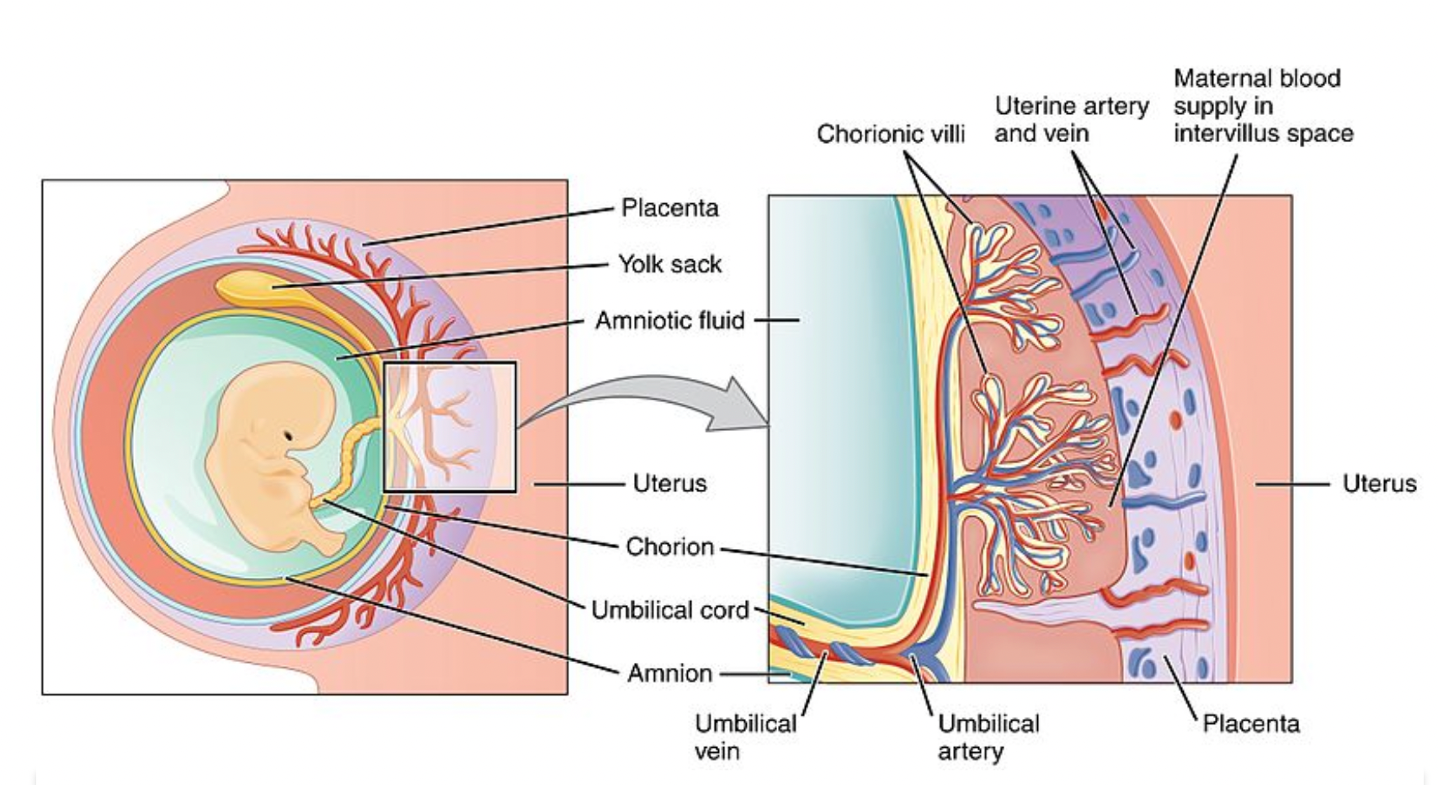
What are the presumptive symptoms to make a diagnosis of pregnancy? (6)
Amenorrhea
Breast changes/tenderness
Frequent urination (from hCG)
Fatigue
Mood changes due to hormones
N/V
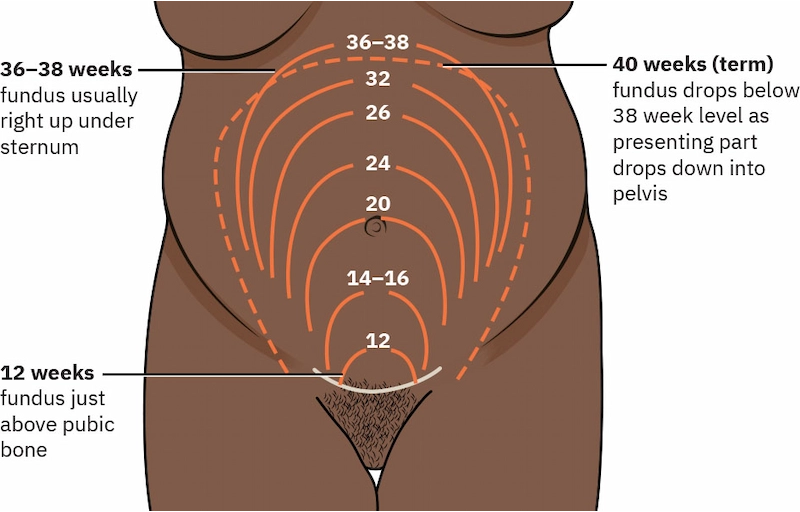
Enlargement of the Abdomen
Week 12: symphysis pubis
Week 20: umbilicus (20 weeks = 20 cm)
Weeks 36-38: right under sternum
Week 40: fundus drops below 38 week level as presenting part drops down into the pelvis
After 20 weeks, the height of the fundus should equal the number of weeks
Uterine and Cervical Changes Associated with Pregnancy
Hegar sign
Softening of the uterus/cervix (relaxin hormone)
Seen around 4th-12th week
Chadwick sign
Blue discoloration of the cervix
30% of CO is going to the pelvis
Seen around 6th-8th week
Leukorrhea
Excess discharge: need to make sure there is no odor/color (need to rule out vaginitis) and if the person is known to be pregnant that they have not broken their water
From hormone stimulation
Braxton-Hicks Contractions
Painless pressure caused by tightening of the uterine muscles
Begins around 28 weeks and varied: resolves with exercise and hydration
Want to make sure that they are resolving
Endocrine Pregnancy Tests
Urine pregnancy test
Quantitative serum hCG: more accurate
Prostaglandins
Not true hormones
PGE2, PGF2, prostacyclin, thromboxane A2: made in endometrium, myometrium, fetal membranes, decidua, and placenta
Concentration of PGE2 and PGF2 in the amniotic fluid rises in pregnancy and in labor
Roles of PGE2 and PGF2
Contraction of uterus: play major role in initiation and control of labor
Prevent significant blood loss in labor
Provokes myometrial ischemia to accelerate labor
Various synthetic prostaglandins are used to terminate pregnancy or to induce labor at term
Misoprostol used for pregnancy termination and labor induction
Identification of Fetal Heart Beat
8-9 weeks by U/S (can be earlier but sometimes early U/S can be frustrating as not everything is seen on U/S)
Should be around 120-160 bpm
U/S Findings
Week 5
Diamond ring sign: embryo and yolk sac (yolk sac feeds the embryo until the placenta takes over in week 12)
Week 6-8
Fetal heart
Pregnancy Structures Timeline
Do not need to memorize
Pregnancy Dating
EDD/EDC: estimated date of delivery
Nagele’s rule: method to estimate due date
Identify last known menstrual period (start of it) and add one year (unless the date is January to March because the due date falls within the same year), subtract 3 months, and add 7 days
Based on the assumption of normal 28 day menstrual cycle and ovulation on day 14
Abnormal cycles: add number of days beyond 28 day cycle
Not expected to be able to calculate it
Can also use the last ultrasound date as the starting date
First Trimester
Last menstrual period through weeks 12.6
S/S
Nausea
Fatigue
Breast tenderness
Urination
If there is bleeding:
Spontaneous abortion is most common
From implantation
Sub-chorionic hemorrhage/hematoma
Can get cluster of blood from ruptured blood vessel and can sometimes work its way out
Very common
Intercourse/increased activity
Second Trimester
13-27.6 weeks of gestation
S/S
Generally feeling well
Pain/pulling (round ligament pain)
Braxton-Hicks
Bleeding
Most commonly caused by placenta previa (placenta covering the cervix): concerning because patient cannot labor and will need a C-section (may not stick with them the whole pregnancy but need to monitor)
Complications
Incompetent cervix
PPROM
Pre-term labor
Third Trimester
28-40 weeks of gestation
S/S
Braxton-Hicks
Low back/leg pain
Lightening: baby drops lower in the pelvis
Fetus with movements rather then kicks due to increasing size and less room to move
Bleeding: bloody show, placenta previa, abruption (uterus separates from placenta)
Rupture of membranes
Labor contractions → dilation and effacement
Maternal Weight Gain
Depends on:
Pre-pregnancy BMI
Other factors
Benefits
For the baby
Supports proper growth and development
Reduces the risk of low birth weight or pre-term delivery
For the mom
Reduces the risk of complications such as gestational DM, HTN, or C-section
Helps with postpartum recovery and returning to pre-pregnancy weight
Normal BMI and singleton
25-35lbs weight gain recommended
½ lb/week for 28 weeks
1 lb/week after 28 weeks
Calories: 300-500 extra per day
Underweight
BMI < 18.5
28-40 lbs weight gain recommended
Obese
BMI > 30
11-20 lbs weight gain recommended
Do not need to memorize
Fetal Growth and Development
Fetal weight
8 weeks: 1 gram
28 weeks: 1,000 grams (> 2 lbs)
36 weeks: 2,500 grams (5.5 lbs)
40 weeks (term): 3,400 grams (7.5 lbs)
Surfactant
Critical substance produced in the lungs that enables proper lung function and breathing: plays a key role in fetal lung maturity
Lipid-protein compound produced by type II alveolar cells
Function: lowers surface tension in the alveoli, preventing collapse during exhalation
Babies born < 34 weeks are at higher risk of RDS due to insufficient surfactant production
Do not typically test for fetal lung maturity anymore
Does not reliably predict neonatal outcomes and should not guide delivery timing
Used to be performed when pre-term delivery was anticipated
Usually give them betamethasone to mature lungs and then deliver: do not delay delivering
Fetal Status: Lie
Relation of long axis of fetus to long axis of mother
90%: longitudinal
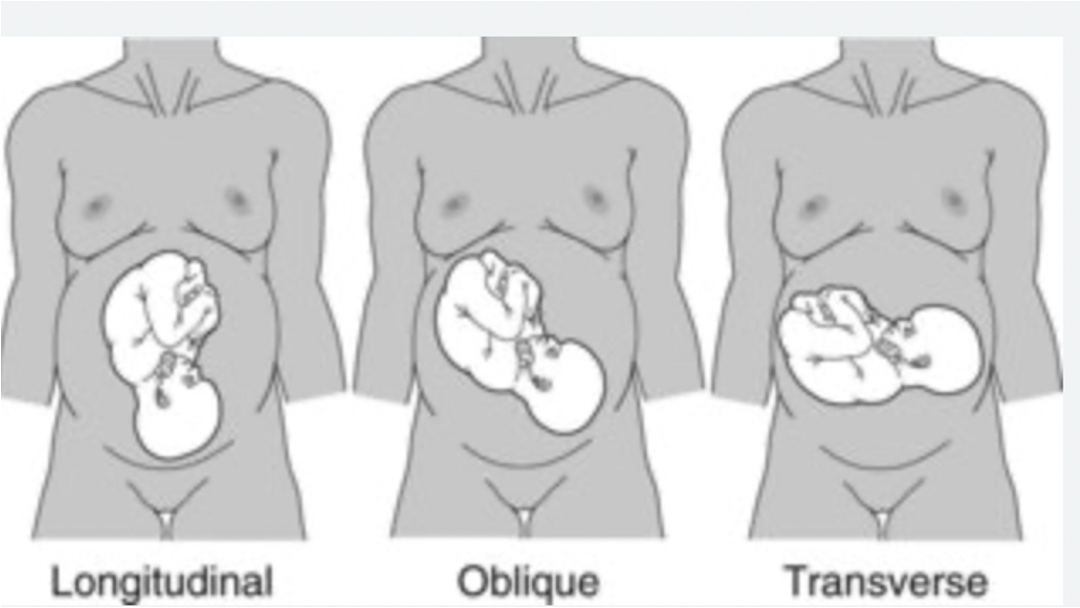
Fetal Status: Presentation
The part of the fetus that first enters the maternal pelvis
Cephalic: vertex, face, brow
Breech: frank, complete, footling
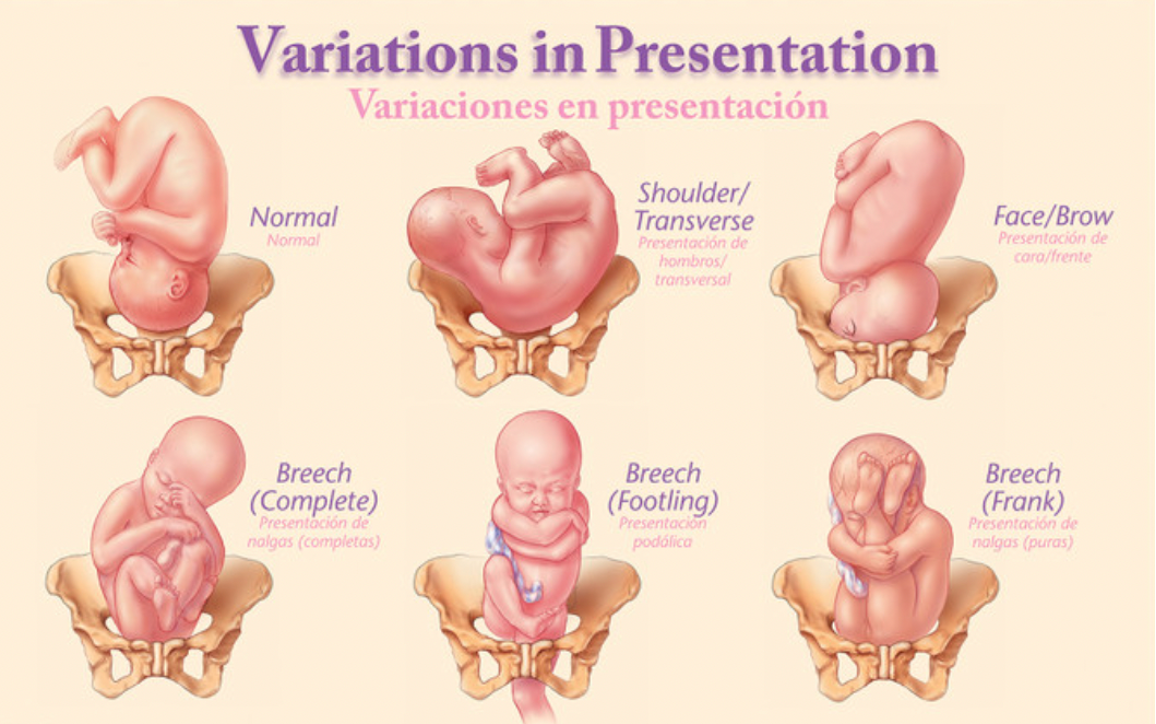
Fetal Status: Attitude/Habits
Positioning of the fetal body parts relative to one another (posture)
Vertex:
Complete flexion
Optimal for labor and delivery
Allows the smallest head diameter to pass through the birth canal
Military
Moderate flexion
May result in longer or more difficult labor as the larger head diameter must pass through the pelvis
Extension:
Increases the likelihood for brow or face (hyper-extended) presentation
Can lead to complications: prolonged labor, assisted delivery, C-section
Fetal Status: Position
Relationship of a designated fetal reference point (usually occiput) to the maternal pelvis
Usually want to see LOA
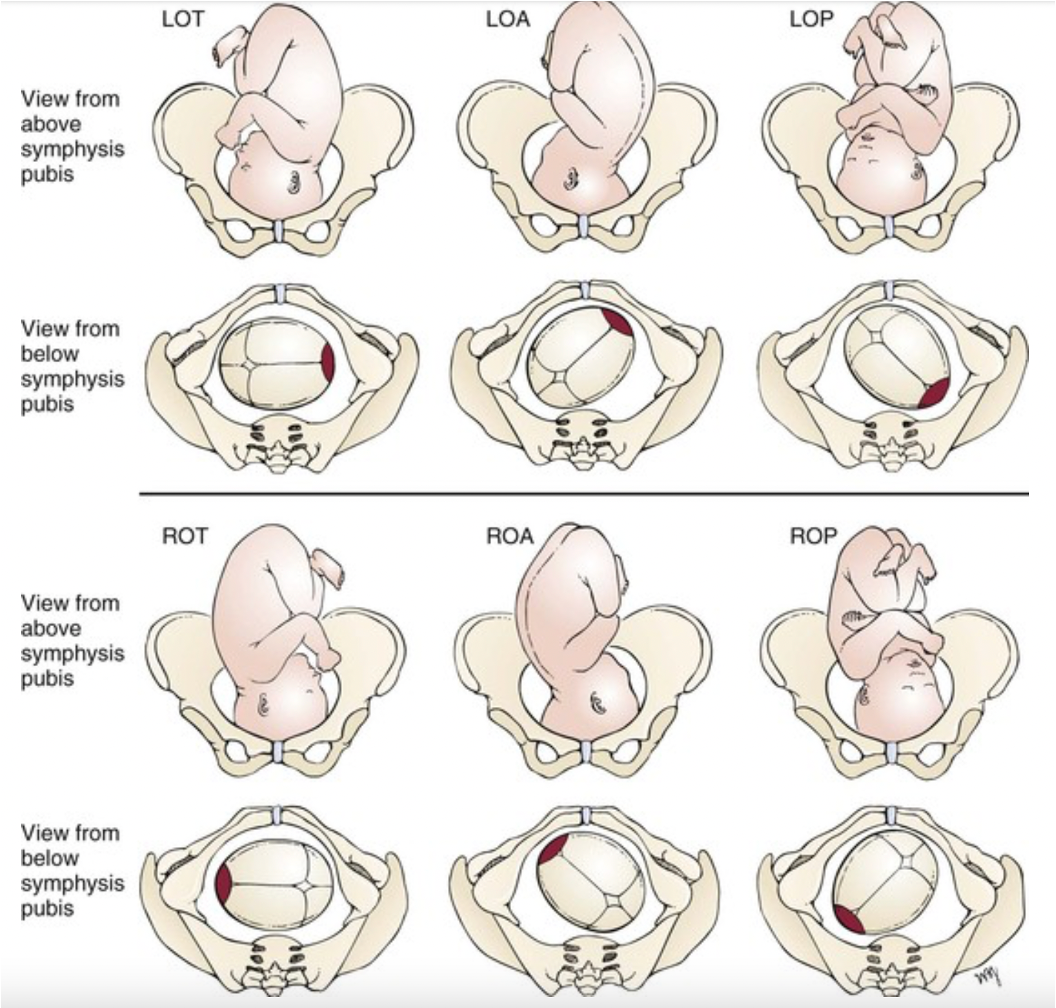
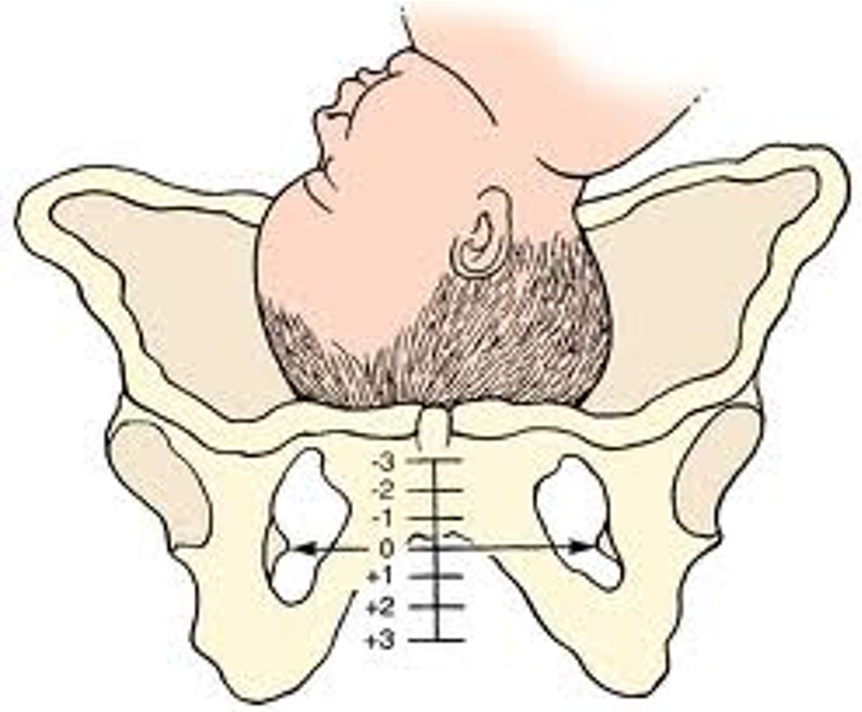
Fetal Status: Station
The level of descent of the presenting part of the fetus above or below the plane of the ischial spines
Ranges from -3 to +3
Puerperium
Period 6 weeks after delivery
See involution of 5-6 weeks
Lochia (vaginal discharge) lasting 3-4 weeks
Rubra: first stage
Dark red in color and around 4 days long
Serosa: second stage
Pinkish in color and lasts for 10 days
Alba: third stage
Whitish yellow and lasts for 10-14 days
Diuresis days 2-5
Do have risk of UTI
Blood: leukocytosis at labor
Menstruation: lactating vs non-lactating
Complications
Hemorrhage
Infections

What is a lack of breast feeding associated with in the child?
Obesity
Breast feeding provided protective benefits against obesity later on in life
Longer duration of breastfeeding associated with greater reduction in obesity risk
Reasons
Better appetite regulation: formula fed infants may be encouraged to finish bottles, overriding satiety clues
Hormonal composition: breast milk contains hormones that regulate energy balance and fat storage
Microbiome development: fosters growth of healthy gut microbiome
Breastfeeding and Maternal HTN
Longer durations of breastfeeding associated with greater benefit in blood pressure
Women who breastfed are less likely to develop HTN during menopause
Mom’s with pre-existing HTN may not experience the benefit
Reasons
Hormonal effects: breastfeeding promotes the release of oxytocin, which lowers BP by relaxing blood vessels and reducing stress levels
Cardiovascular: lowers cholesterol and triglyceride levels and enhances glucose regulation
Weight regulation: faster postpartum weight loss
Hormones Involved in Lactation
Prolactin: milk production
Oxytocin: milk let-down
Milk Components
Carbs and fat: energy
The mom makes milk that has exactly what the baby needs (stimulated from latching)
Immunity/antibodies
Colostrum
Started food: babies stomach is so small that they have this in smaller doses and more frequently for 2-3 days postpartum
Yellow
High protein, Vitamin A, sodium, chloride, immunoglobulin
Low carbs and low fat
Breastfeeding Recommendations
Exclusive breastfeeding for first 6 months of life
Continued breastfeeding for at least 12 months while gradually introducing complementary foods beginning around 6 months
By 12 months: breastfeeding can continue for as long as mutually desired by mom and baby for 2 years or beyond
Breastfeeding Benefits for Baby (8)
Provides nutrition
Digestible
Available at right temperature
Free from bacterial contamination
Reduces risk of infections
Lowers risk of chronic conditions
Promotes cognitive development
Proper development of jaw/teeth/brain
Breastfeeding Benefits for Mom (5)
Reduces risk for postpartum hemorrhage (contracts the uterus)
Lowers risk of breast and ovarian cancer
Reduced risk of hypotension and DMI II
Promotes bonding
Economical
Challenges to breastfeeding (7)
Separation of newborn and mom in hospital
Not enough uninterrupted time in hospital
Breastfeeding is not easy: both need to learn
Moms need support: babies can be fussy
Pumping milk takes time
Need space and support at work
U.S. culture not fully supportive
Absolute Contraindications to breastfeeding
Maternal
HIV infection
Human T-cell lymphotrophic virus infection
Untreated brucellosis
Suspected or confirmed Ebola
Active chemotherapy: may resume after 3 week safety window following last dose
Infant
Classic galactosemia
Temporary Contraindications to breastfeeding
Active TB
Varicella disease
Active herpetic breast lesions
Illicit substance use
Moms on stable methadone or buprenorphine maintenance therapy are encouraged to breastfeed
Pasteurized Donor Human Milk (PDHM)
PDHM specifically recommended while baby is in NICU for low birth weight (< 1500 grams)
Recommends this from established milk banks when mother’s own milk is unavailable, insufficient, or contraindicated
Discouraged informal milk sharing and purchasing milk from internet based sources
Informal milk sharing may be associated with infectious risks and contaminants
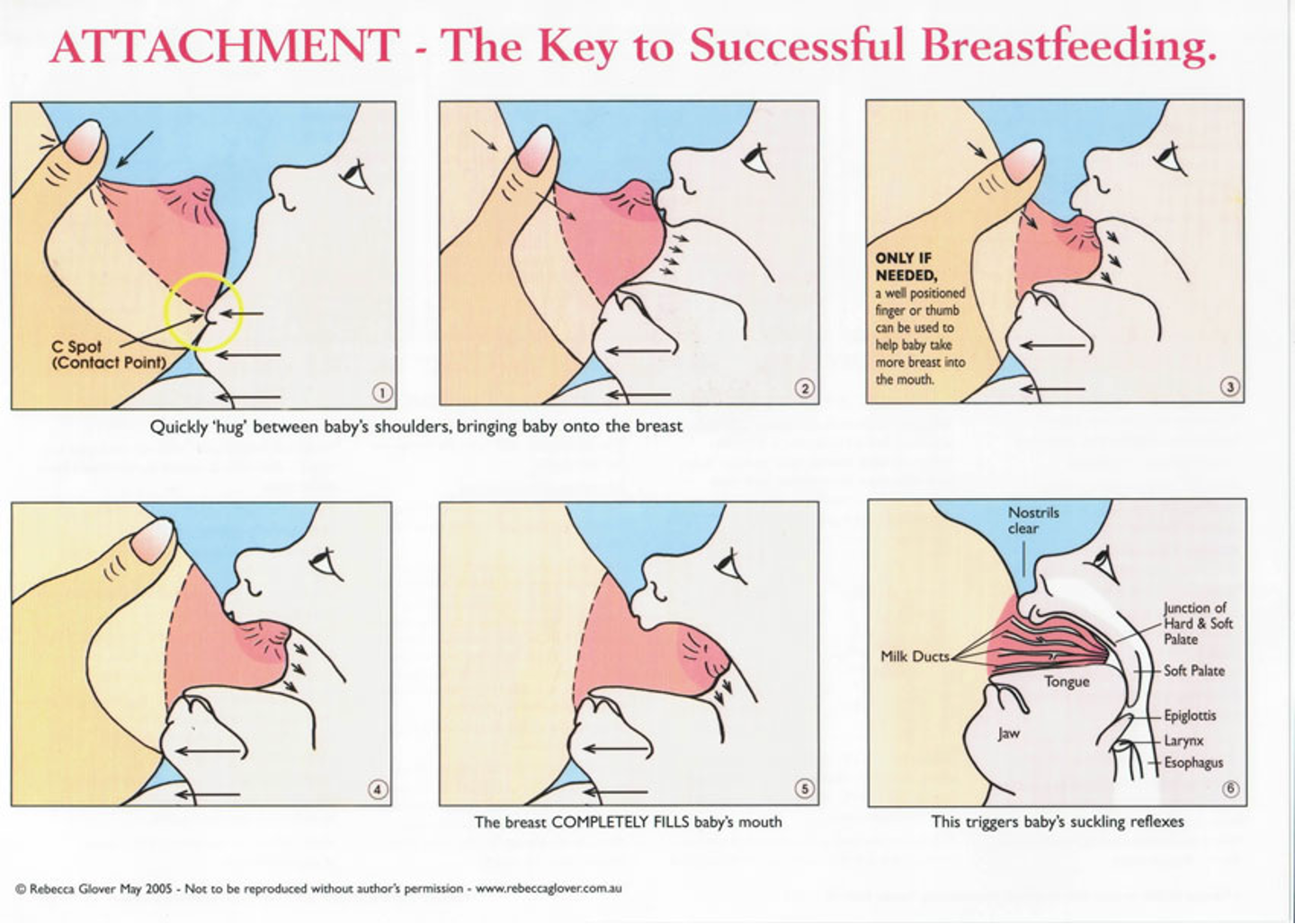
Techniques of breastfeeding
Rooting
Detaching infant
Avoid bottle (until breastfeeding is well established → 4-6 weeks)
Feed on demand
Newborns can take 20-45 minutes per feeding every 2-3 hours
Signs of adequate milk production
Baby gaining weight appropriately
Appears satisfied after feedings
Breasts soft after feeding
Wet diapers produced

Suppression of Lactation
Gradually wean off nursing
Cold compresses
Supportive and well-fitting bra
Avoid breast stimulation
Hydrate (not too much)
Avoid lactogenic foods
Pain relief: ibuprofen/Tylenol
Herbal remedies: sage or peppermint
Medications: reserved for medical reasons
Dopamine agonists (cabergoline or bromocriptine): inhibit prolactin