Lecture 2: Esophagus
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES)
Internal LES (thickened muscularis propria) + External LES (diaphragm muscle attached by ligaments) anchored together by phrenoesophageal ligament
LES is normally closed (is an antireflux barrier protecting the esophagus from the caustic gastric content)
During swallowing or belching, the LES muscle must relax briefly to allow passage of food or intra-gastric air
Dysphagia
difficulty, discomfort, or sensation of food getting stuck in the throat or chest when swallowing
Odynophagia
pain while swallowing
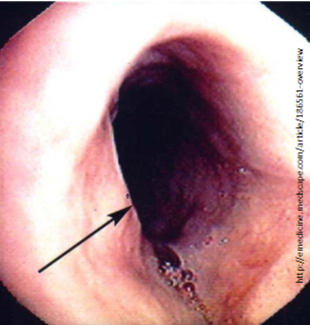
Esophageal Webs
Intraluminal semi-circumferential protrusion of a thin fold of mucosa (mucosa + submucosa)
Women > 40
Usually in upper esophagus
Plummer-Vinson syndrome: Dysphagia due to Esophageal Web & Iron deficiency anemia
PVS considered a risk factor for development of Squamous Carcinoma of Pharynx & Esophagus
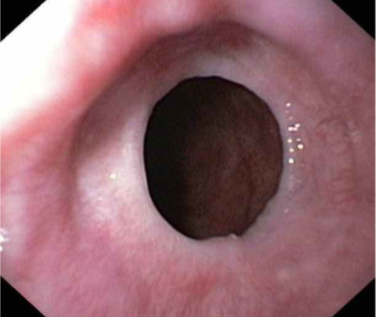
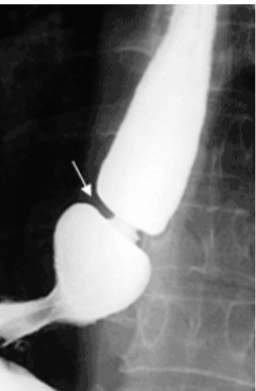
Schatzki Ring
Circumferential & thicker (includes submucosa or muscularis propria)
Usually occur in distal esophagus (immediately above or below the Squamocolumnar junction)
asymptomatic or cause sporadic dysphagia
Obstruction of esophagus by a bolus of food → crushing chest pain
Schatzki Ring
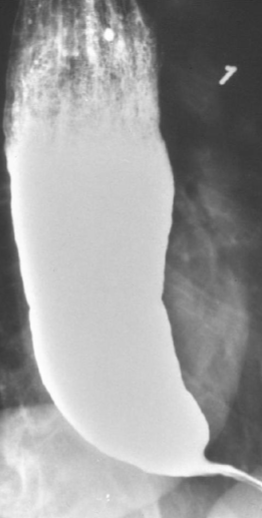
Achalasia
Failure of LES to relax (open) after swallowing + lack of coordinated esophageal peristalsis
Due to selective degeneration or damage to the parasympathetic post-ganglionic neurons that relax the lower sphincter & are responsible for peristalsis
Primary: Idiopathic (most common); incidence ↑ with age
Secondary: Acquired: Chagas Disease (T. Cruzi), Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy, Amyloidosis, Cancer
Triple-A (Achalasia-Addisonianism-Alacrima)/Allgrove syndrome: Achalasia, Adrenal insufficiency & lack of tear production
Dysphagia to solids & liquids, regurgitation of undigested food, chest pain, aspiration pneumonia
Cancer risk for both esophageal Squamous & Adenocarcinoma
Beak sign on Barium swallow with mega-esophagus
Achalasia
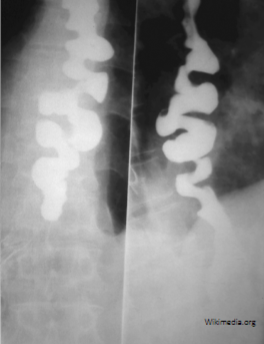
Diffuse/Distal Esophageal Spasm (DES)
Strong, repetitive, simultaneous contractions (non-sequential pressure peaks) of distal esophagus → intermittent dysphagia & atypical chest pain
Nutcracker Esophagus
Increased pressures during peristalsis
Manometry when pressures exceed 180 mmHg
May cause chest pain, dysphagia or be asymptomatic
Hypertensive LES
like Achalasia, but with normal peristalsis (incomplete relaxation confined to sphincter)
Hypotensive LES
GERD
Resting LES pressure <10 mmHg
Esophageal Diverticula
Most are acquired Pseudodiverticula (herniations of mucosa only) associated with dysmotility
Increased intraluminal pressures & wall stress from the dysmotility syndromes may cause pulsion type Diverticula
Right above the LES (Epinephric Diverticulum)
Impaired relaxation & spasm of Cricopharyngeal muscle after swallowing → Pharyngoesophageal Diverticulum (Zenker)
Zenker → Dysphagia & sense of a lump in the throat; food trapping leads to regurgitation of food, chronic cough; Halitosis; Infection
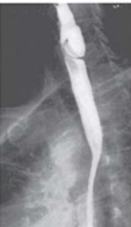
Zenker Diverticulum
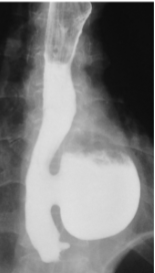
Epinephric Diverticulum
Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
Superficial esophageal tears
Longitudinal mucosal tears, usually near or across GE junction, most often due to retching (dry heaves) or vomiting from acute alcohol intoxication
Painful hematemesis
Boerhaave syndrome
Transmural perforation/Effort rupture
Perforation due to vomiting, but majority of esophageal perforations are Iatrogenic
Rupture of distal esophagus → Mediastinitis
Leakage of esophageal & gastric contents into the mediastinum, produces a chemical burn with superinfection
Untreated, leads to a severe inflammatory response, sepsis & death
Follows repeated episodes of retching & vomiting
Usually no hematemesis; excruciating retrosternal chest & upper abdominal pain
Odynophagia, tachypnea, dyspnea, cyanosis, fever, & shock develop rapidly
May see air in mediastinum and/or subcutaneous emphysema
Esophagitis
erosion, ulceration, bleeding, or scar/fibrosis (stricture) formation with stenosis
Odynophagia
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Reflux Esophagitis
reflux of gastric acid/contents back into the esophagus due to ↓ LES tone or LES incompetence or due to ↑ intra-abdominal pressure
Heartburn (burning sensation rising from the stomach into the chest & neck or regurgitation of sour tasting gastric contents), often worse immediately after eating and/or lying down
Risk factors include alcohol, tobacco, obesity, hiatal hernia, large meals, age >50; bending over or coughing exacerbate
Mild: normal or redness of mucosa due to hyperemia
Severe: Squamous Epithelial hyperplasia + intra-epithelial Eosinophils
Complications of severe long-standing GERD: ulceration with hematemesis or melena, stricture, Barrett’s Esophagus
PPI
Infectious Esophagitis
Immunosuppressed
Herpes, CMV & Candida are AIDS indicators
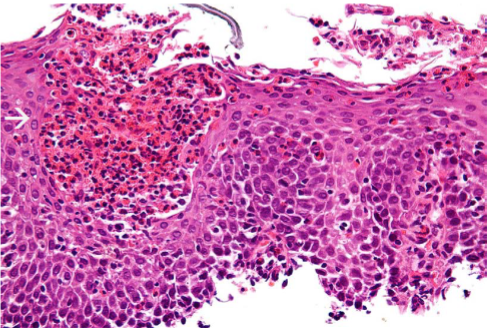
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
eosinophilic microabscesses
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Adults: Dysphagia, odynophagia
Children: feeding intolerance
due to food allergy
most often in Atopic individuals (atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, asthma, eosinophilia)
Concentric rings (trachealization)
Morphology: large numbers of eosinophils or eosinophilic microabscesses in epithelium
Esophageal Varices
abnormally dilated vein
Portal hypertension is commonly caused by Cirrhosis of the Liver
patients may exsanguinate into their GI tract
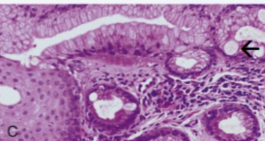
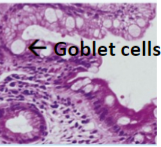
Barrett Esophagus
Metaplasia in the lower esophagus from squamous to intestinal type mucosa with goblet cells
Acid backwash into the esophagus (symptons of GERD) predisposes for Barrett’s
Increased RISK for the development of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
Risk is significant if “pre-cancerous” Dysplasia is present
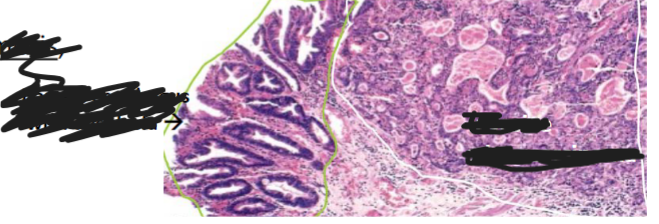
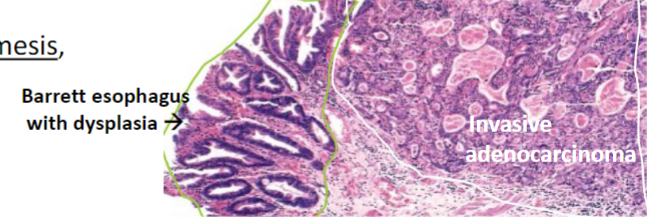
Barrett Esophagus
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
Most are felt to arise from the intestinal metaplastic mucosa of Barrett esophagus
Same risk factors: GERD, male, Caucasian race, obesity, smoking, alcohol
involves Distal 1/3 of esophagus and/or Gastric Cardia/Esophagogastric Junction (if upper edge of the tumor extends to the Esophagus)
Progressive dysphagia (solids → liquids), weight loss, hematemesis, chest pain, vomiting
Squamous Carcinoma
Risk factors: older, male, African-American, alcohol & tobacco, caustic esophageal injury, Achalasia, Plummer-Vinson syndrome, very hot beverages, mediastinum radiation, diet low in fruits & vegetables
Tylosis, familial mutation; hyperkeratosis of palms, soles & oral leukoplakia; high lifetime risk; loss of tumor suppressor gene TEC (Tylosis with Esophageal Cancer)
Half occur in the middle third of the esophagus
Progressive dysphagia, odynophagia, weight loss
Arise from squamous dysplasia
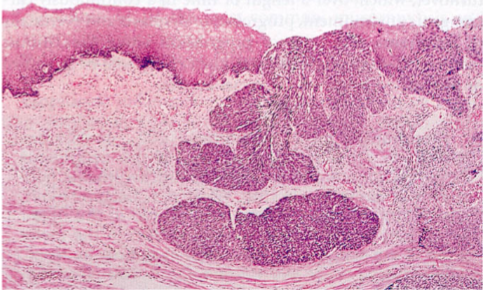
Squamous Carcinoma
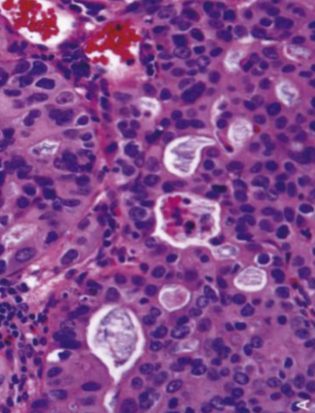
Adenocarcinoma: Abortive Glands with mucin
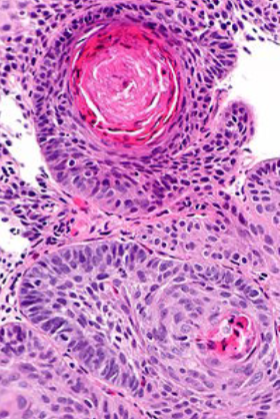
Squamous: squamous pearls
Esophageal Atresia & Tracheoesophageal Fistulae
Atresia or fistula with blind upper segment → regurgitation after feeding
Fistulas → aspiration pneumonia or suffocation by aspirated food
Discovered shortly after birth with first feedings → coughing, choking, vomiting, difficulty breathing, or cyanosis during feeding
Esophageal Obstruction
mechanical cause: stenosis due to tumor, stricture (inflammatory scarring), web
functional cause: disruption of the coordinated waves of contraction (Peristalsis) or failure of LES relaxation that follows swallowing (Achalasia)
Dysphagia, odynophagia, Bringing food back up (regurgitation), coughing or gagging when swallowing or having to cut food into smaller pieces
Mechanical obstruction is more likely to present with Progressive Dysphagia (begins with inability to swallow solids, slowly progressing to difficulty ingesting liquids)