unit 19 bio - Organisms and their Environment
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the principal source of energy input to biological systems?
The Sun
How is energy transferred through living organisms?
Through light energy from the Sun and chemical energy in organisms, eventually transferred to the environment
What is a food chain?
A sequence showing the transfer of energy from one organism to the next, starting with a producer
What is a food web?
A network of interconnected food chains
What is a producer?
An organism that makes its own organic nutrients, usually through photosynthesis
What is a consumer?
An organism that gets its energy by feeding on other organisms
What are the types of consumers?
Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers
What is a herbivore?
An animal that eats plants
What is a carnivore?
An animal that eats other animals
What is a decomposer?
An organism that gets its energy from dead or waste organic material
How do humans impact food chains and webs?
Through overharvesting and introducing foreign species to habitats
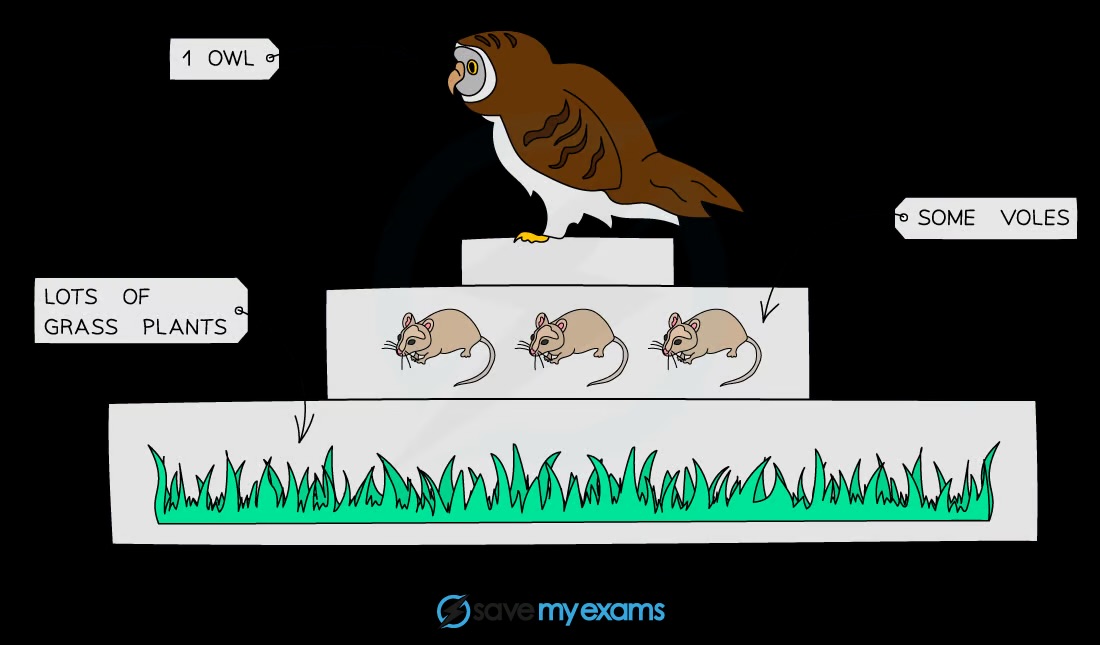
What is a pyramid of numbers?
A graphical representation showing the number of organisms at each trophic level
What is a pyramid of biomass?
A graphical representation showing the biomass of organisms at each trophic level
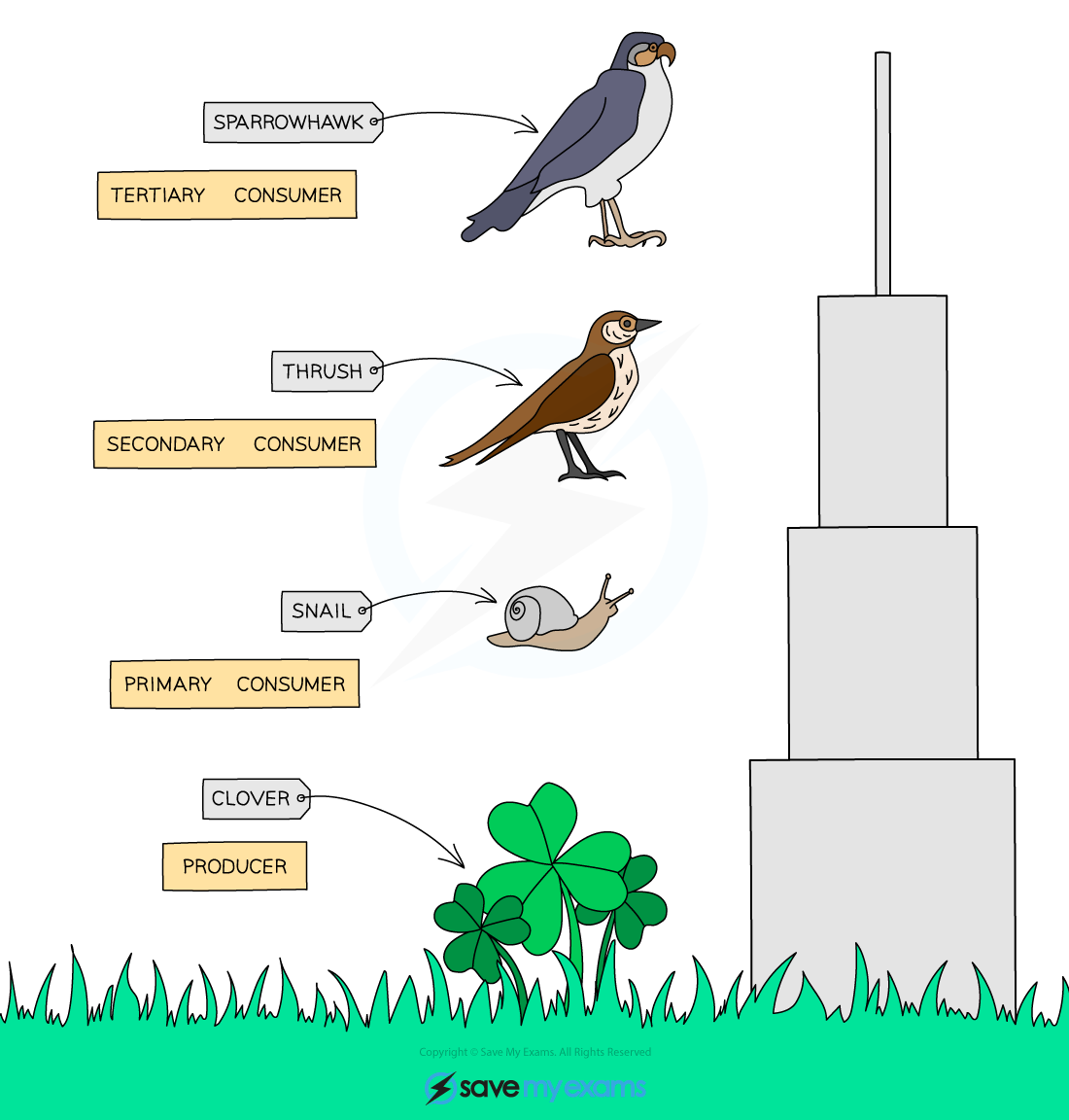
Why is a pyramid of biomass more useful than a pyramid of numbers?
It accounts for the mass of organisms at each trophic level
What is a trophic level?
The position of an organism in a food chain, food web, or ecological pyramid
What is a pyramid of energy?
A graphical representation showing the flow of energy through a food chain
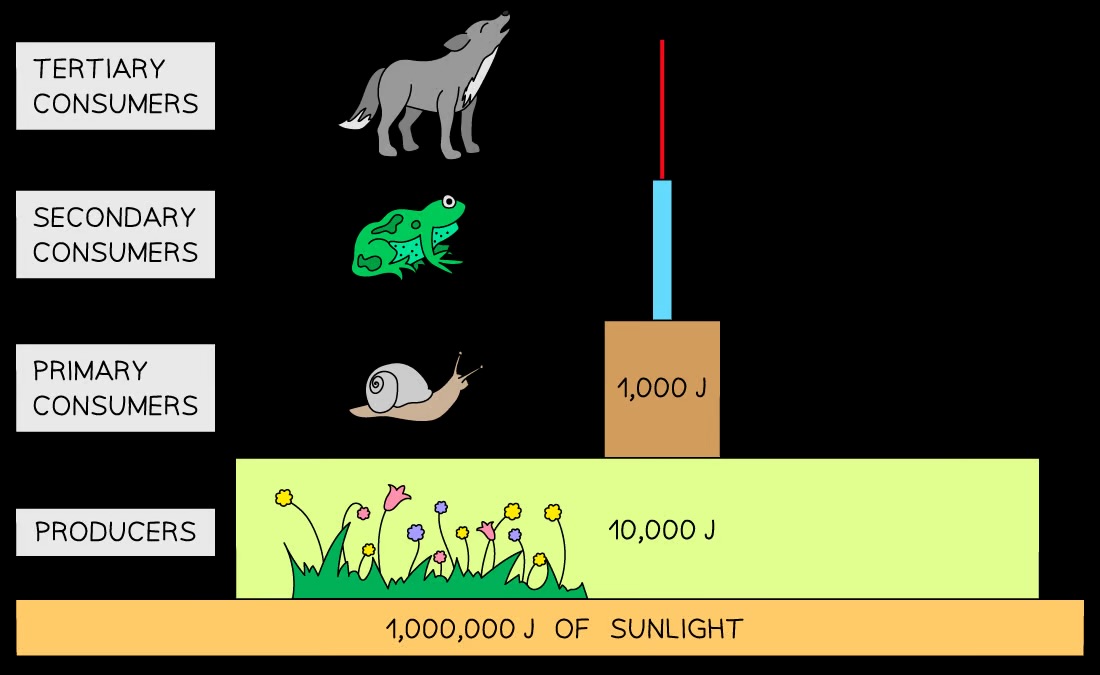
Why is a pyramid of energy more useful than pyramids of numbers or biomass?
It accurately represents the energy transfer between trophic levels
What are the trophic levels in food webs and chains?
Producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers, and quaternary consumers
Why is energy transfer between trophic levels inefficient?
Because energy is lost at each level as heat and waste
Why do food chains usually have fewer than five trophic levels?
Energy loss limits the number of levels
Why is it more energy-efficient for humans to eat crops than livestock?
Because livestock consume more energy in the form of crops than the energy they provide to humans
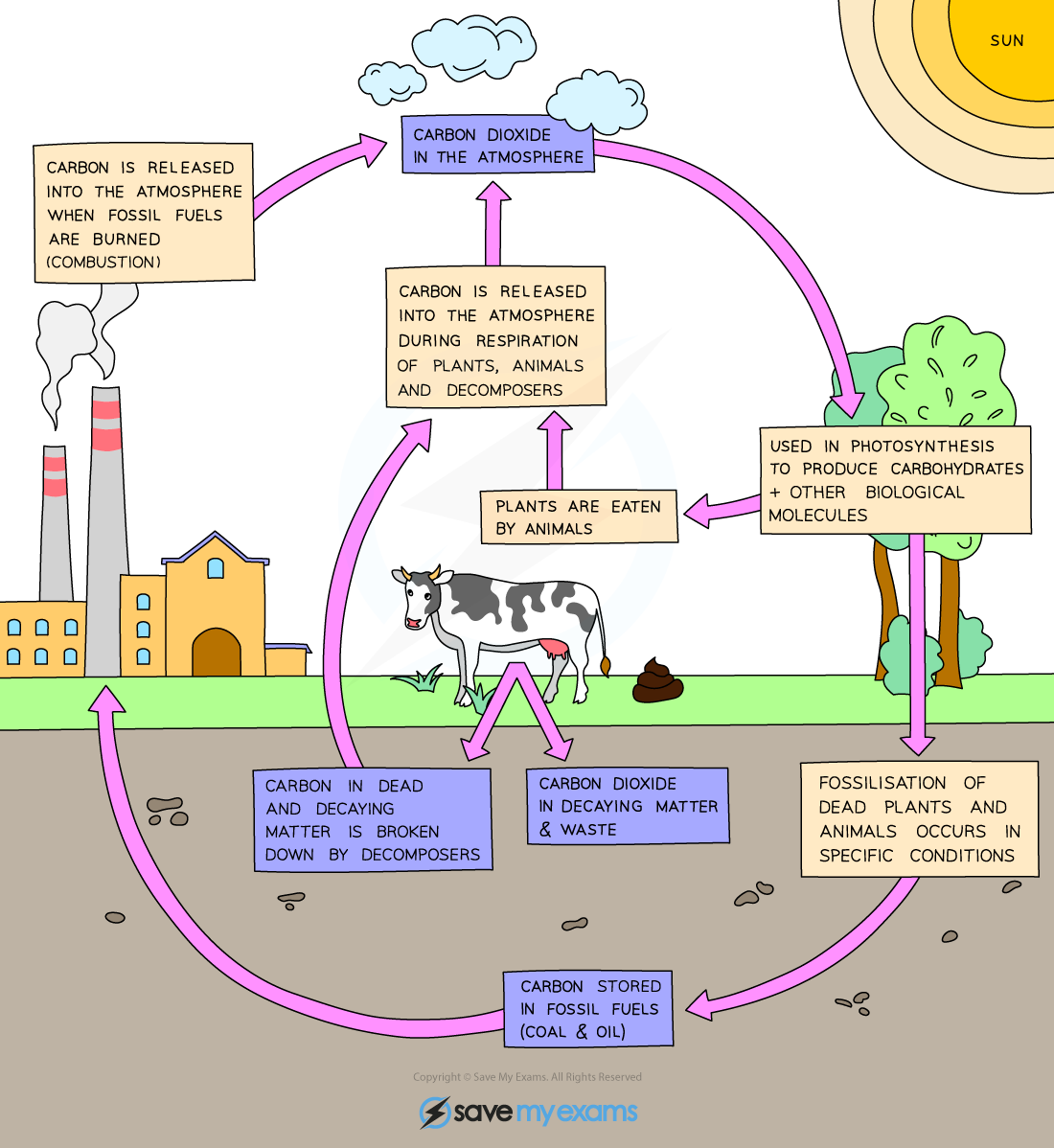
What is the carbon cycle?
The process involving photosynthesis, respiration, feeding, decomposition, formation of fossil fuels, and combustion
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The process involving decomposition, nitrification, nitrogen fixation, absorption by plants, protein production, feeding, digestion, deamination, and denitrification
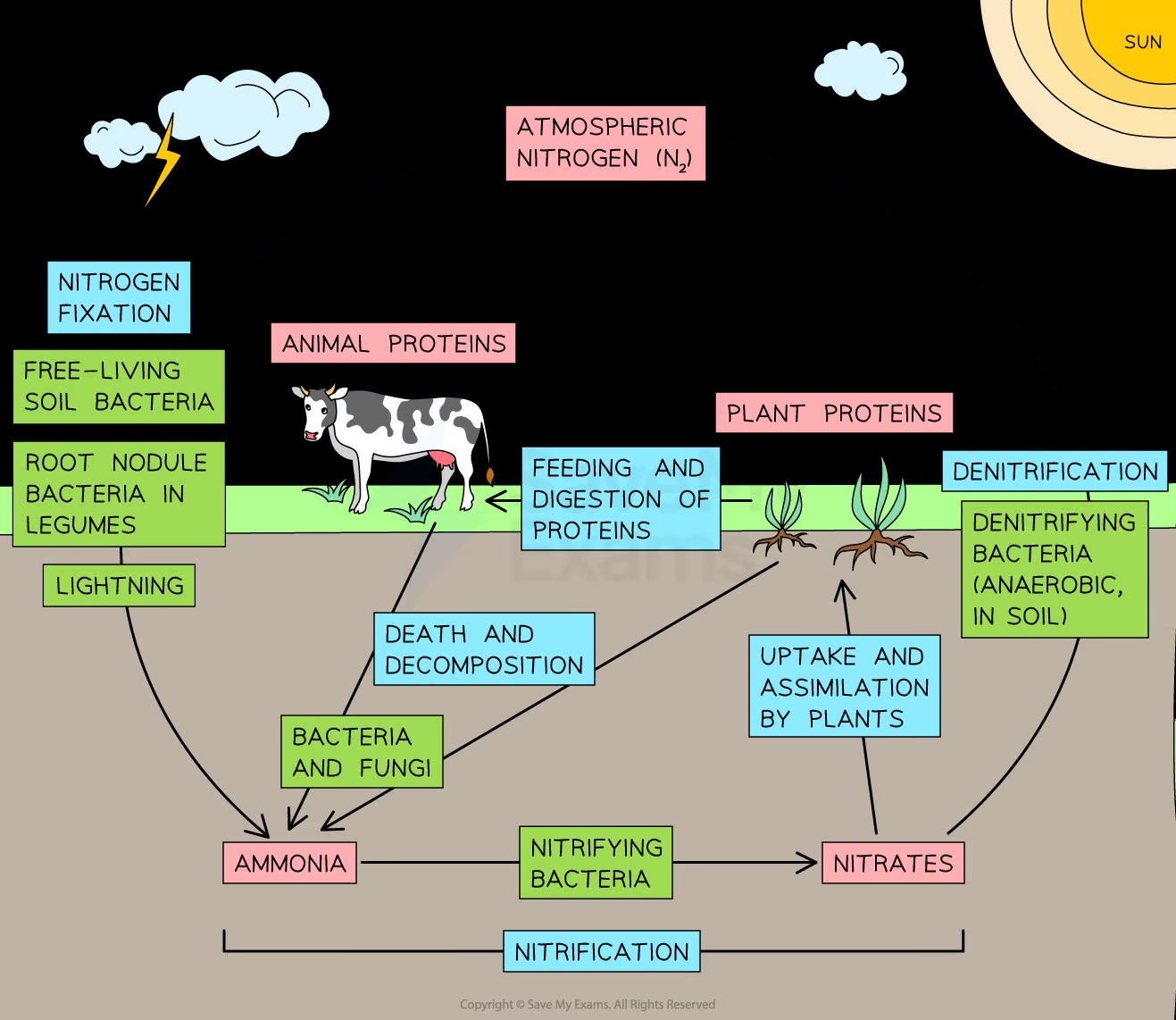
What are the roles of microorganisms in the nitrogen cycle?
Decomposition, nitrification, nitrogen fixation, and denitrification
What is a population?
A group of organisms of one species, living in the same area, at the same time
What is a community?
All the populations of different species in an ecosystem
What is an ecosystem?
A unit containing the community of organisms and their environment, interacting together
What factors affect population growth?
Food supply, competition, predation, and disease
What are the phases of population growth in a sigmoid curve?
Lag, exponential (log), stationary, and death phases
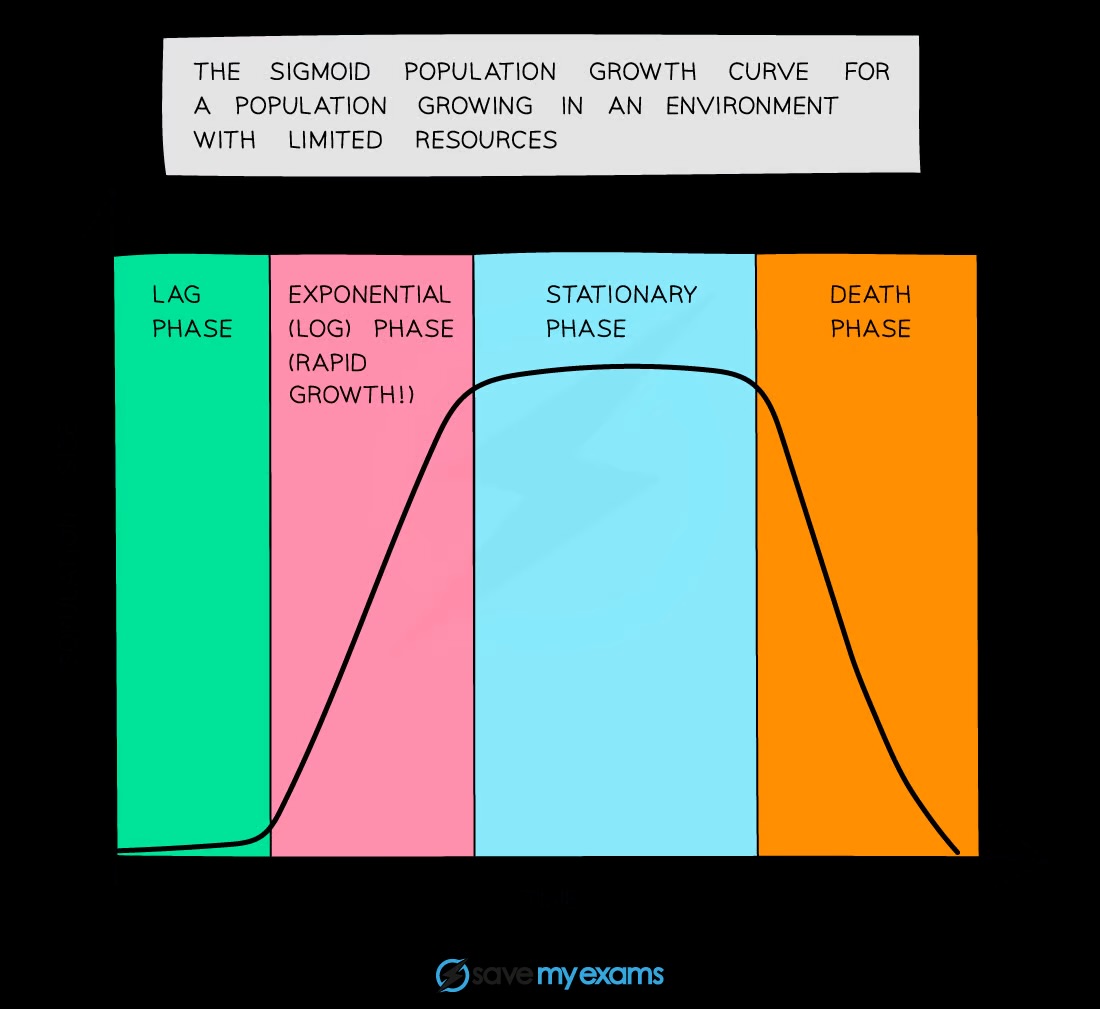
How can population growth be interpreted in graphs?
By analyzing the shape of the sigmoid curve
What factors lead to each phase in the sigmoid curve?
Limiting factors, such as food availability and competition, influence each phase