Exam 2 - Advanced Research Methods
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Define correlational design with at least 1 advantage and at least 1 disadvantage.
Definition: It is used to examine correlation among variables.
Advantage: It can be used when the experiment is impossible to do.
Disadvantage: It is hard to determine whether one variable causes another.
Explain two situations when we cannot use an experimental design, but a correlational design needs to be used, with an example, respectively.
One situation would be when the variable is impossible to manipulate. Another is when it would be unethical to manipulate a variable.
An example of the first situation would be that you cannot manipulate someone’s intelligence or IQ. This is something that is pretty fixed and constant.
An example for the second situation would be if you wanted to expose someone to traumatic events. This would be unethical and you wouldn’t be able to do this experiment.
Explain four factors affecting the results of a correlational design.
Reliability of the measures
This is an issue with the quality of the measure. This is a problem because you need a more reliable measure to ensure that the observed correlation is closer to the true score correlation.
Restriction in range
This is an issue with sampling. It reduces the correlation found in a sample relative to the correlation that exists in the population.
Outliers
This is also an issue with sampling. These are extreme scores compared to other cases in the study. These are an issue because they easily influence the statistics.
Subgroup differences
This is a third factor issue. There might be two or more subgroups included in a study, so the correlation in the combined group will not accurately reflect the subgroup correlations.
Define observational design with at least 1 advantage and at least 1 disadvantage.
Definition: An observational design studies human behavior as it occurs in natural settings in response to natural events.
Advantage: A high level of naturalism and generalization.
Disadvantage: A low level of control and causal inference.
Explain about Full Involvement, Pure Observer, and Researcher Involvement methods.
Full Involvement: The observer becomes a full member of the research setting without the other members of the setting being aware of the observer’s role as researcher.
Pure Observer: The observer avoids taking part in research setting, merely watching what happens and recording to observations without the other members of the setting being ware of the observer’s role as researcher.
Researcher Involvement: Fully informing other people in setting of their role as researcher.
Explain about three possible problems under the Full Involvement observational design.
Cognitive bias/record bias
Can be due to selective attention which would cause the observer to miss important events (important to train observers well to enhance reliability and validity of their behavioral observations)
Can video tape everything to help with this
Influencing events
This is when observers can end up contaminating the naturalism of what they observe by unintentionally influencing the people and events they are observing
Effects on the observer
Acting in the role of the observer can be stressful, especially if they are having to keep their identity as an observer a secret
Explain two possible problems under the Pure Observer observational design.
Superficial observation
This is when the observer cannot understand the underlying situation (because they don’t know the relationship between two people, etc.)
Cognitive bias
Selective attention can be an issue because an observer might miss important details of someone’s behavior
Explain three possible problems under the Researcher Involvement observational design.
Influencing events
This is when observers can end up contaminating the naturalism of what they observe by unintentionally influencing the people and events they are observing.
Reactivity
The person being observed may change their behavior to show themselves in a better light
Record bias
It’s not always possible to record everything (recommended to also video tape the observation)
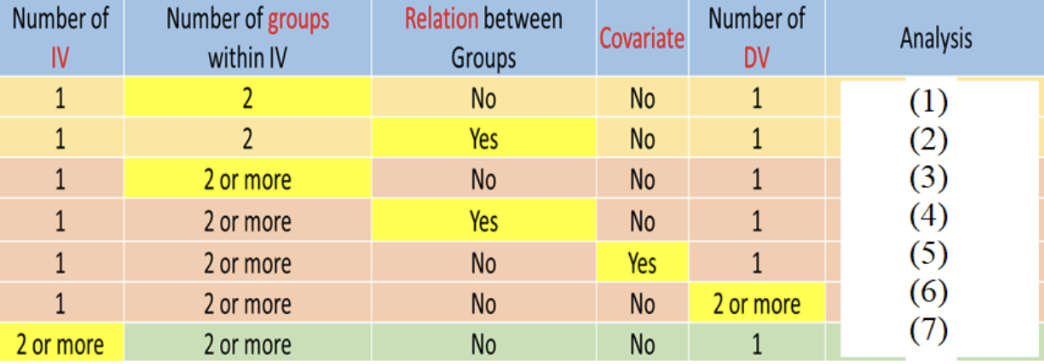
Fill in the blank in the table below.
Independent T-test
Repeated T-test
ANOVA
Repeated ANOVA
ANCOVA
MANOVA
Factorial ANOVA
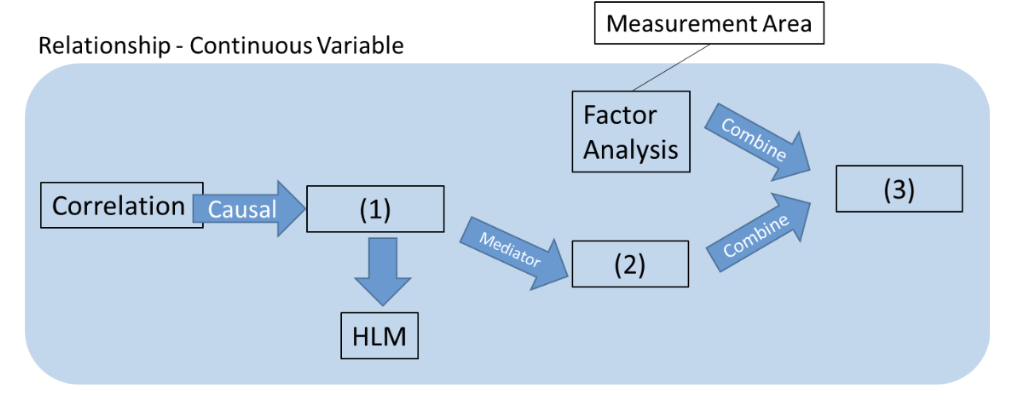
Fill in the blank in the figure below.
Regression
Path Analysis
Structural Equation Modeling
Explain 3 types of qualitative interviews.
Structured interview
All respondents answers the same set of questions in the same specific order (less naturalness in responses)
Semi-structured interview
All respondents answer the same set of questions with additional questions (allows more casual conversation with the interviewee)
Unstructured interview
Can use artifacts to start a conversation with the interviewee on the topic of interest (like using photos and talking about them)
Explain the ideal sample size for a qualitative study.
The ideal sample size can’t be determined before starting a qualitative study. It’s recommended that researchers collect and analyze data until they reach saturation (no new information can be collected). Many studies of this type can be as small as 4-6 participants.
Independent T-test
1 IV
1 DV
2 groups within IV
NO relation between groups
NO covariate
Repeated T-test
1 IV
1 DV
2 groups within IV
YES - relation between groups
NO covariate
ANOVA
1 IV
1 DV
2 or more groups within IV
NO relation between groups
NO covariate
Repeated ANOVA
1 IV
1 DV
2 or more groups within IV
YES - relation between groups
NO covariate
ANCOVA
1 IV
1 DV
2 or more groups between groups
NO relation between groups
YES - covariate
MANOVA
1 IV
2 or more DV
2 or more groups within IV
NO relation between groups
NO covariate
Factorial ANOVA
2 or more IV
1 DV
2 or more groups within IV
NO relation between groups
NO covariate