4. Peptic ulcer
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Peptic ulcer disease
ulcers that occur in the lining of the sotmach, a gastric ulcer and those that develope in the small intestine- duodenal ulcer
PUD Pathophysiology
increased acid production- leads to damage of the mucosal lining
2 damaged mucosal defences- damage to the natural defences that protect the stomach lining from acid
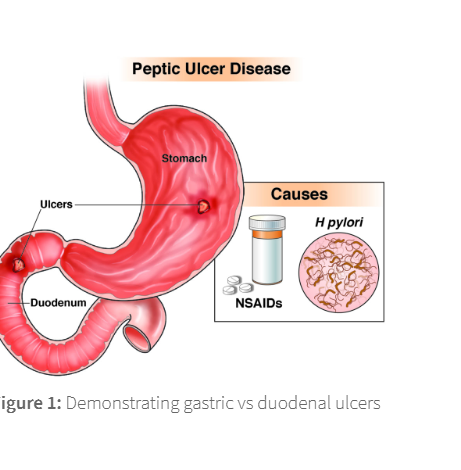
PU primary causes
H pylori infection
NSAIDs
excessive gastric acid rpoduction
smoking
H pylori infection
a bacteria that damages the stomach lining and increases acid production
NSAIDs
medications that inhibit prostaglandins naturally present in thr stomach to protect the stomach lining making the stomach more susceptible to damage from the stomach acid
excessive gastric acid production
if untreated can eventually begin to erode the stomach lining, all GORD risk factors apply
smoking
increases risk of H pylori infection and reduce the baility of the stomach to heal inself from damage
watch video
signs and symptoms
abdominal pain in epigastric region at night (burning sensation)
indigestion
heartburn
nausea + vomiting
bloating
see GP urgently if
pain gets worse
lost appetite
feeling full after small amounts of food
unintentional weightloss
pain when swallowing
go to A&E if
vomitting blood/ vomit looks like ground coffe
blood in stool or its black
severe abdominal pain
admoen tender to touch
sudden chest pain
risk factors
aged over 65
high dose/ prolonged use of NSAIDs
other drugs that increase risk of adverse gastrointestinal events (antiplatlets/antocouagulants/corticosteroids/SSRIs)
heavy smoking
excessive alcohol comsumption
serious co-morbidity (cardiovascular disease, hypertension,diabetes,renal/hepatic impairment)
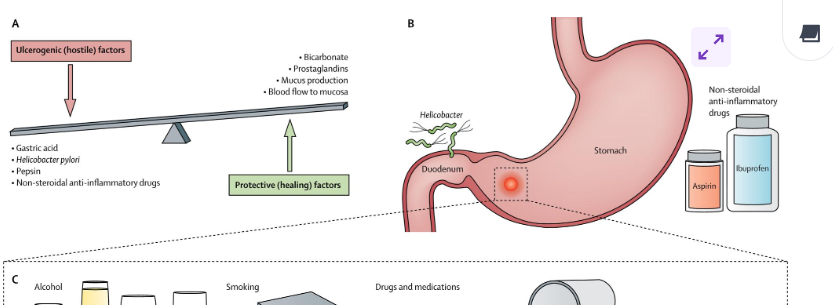
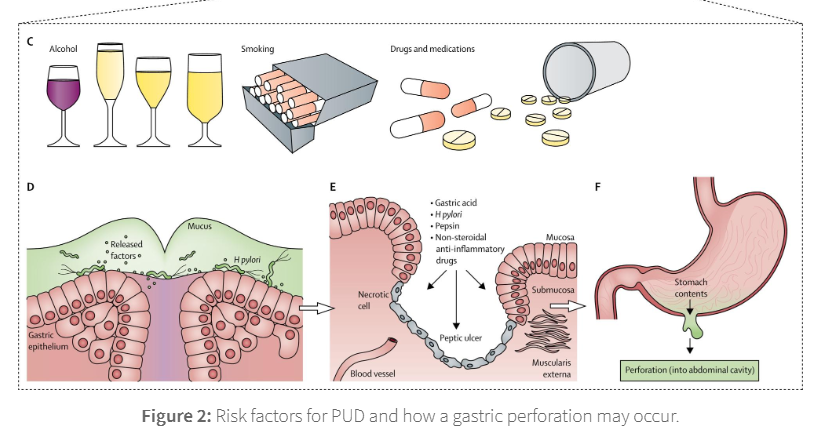
complications of PUs
gastric perforation
haemorrhage
gastric outlet blockage
increased risk of stomach cancer
gastric perforation
can lead to peritonitis, inflammation of the lining of the abdomen
haemorrhage
lead to iron deficieny anaemia, if blood loss is mild and ongoing
if the ulcer perforates the stomach where there is a large blood vessle
this could lead to suffen haemorrhage and hypovolaemic shock, when theres a sudden lack of circulating blood volume causing the body to shut down certain areas to ensure key areas remain perfused, which is life threatening
gastric outlet blockage
if an ulcer is close to the pylorus (exit of the stomach before the duodenum) is could cause inflammation and scarring which blocks the route stomach contets take to the GI tract
increased risk of stomach cancer
due to untreated H pylori infection
pharmacological managment
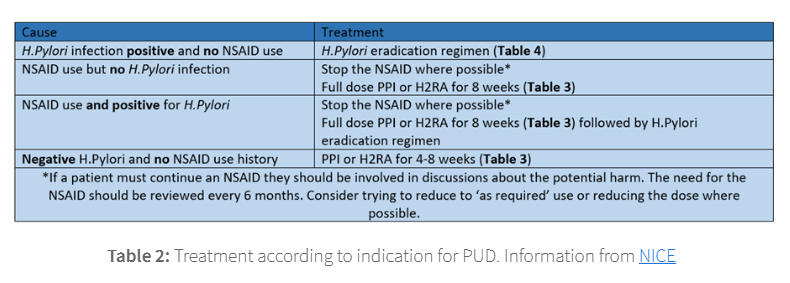
cause: H pylori infection positive and no NSAID use
treatment: h pylori eradication regimen
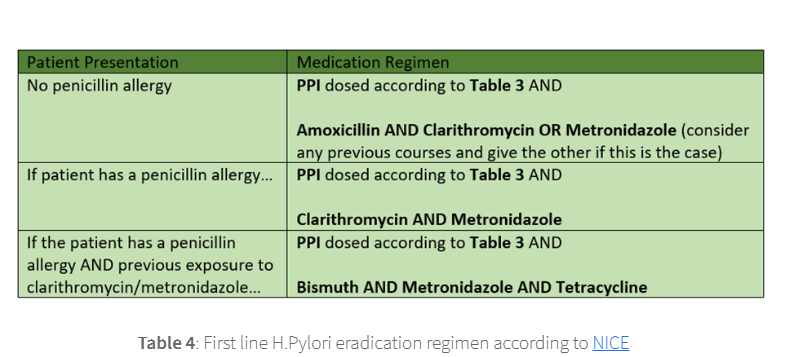
cause: NSAIDs use and no for H pylori infection
treatment: stop the NSAID where possible
full dose PPI or H2RA for 8 weeks
cause:NSAID use and positive for H pylori
treatment stop the NSAID wherer possible
full dose of PPI/H2RA for 8 weeks followed by H pylori eradication regiment
cause: negative for H pylori and no NSAID use history
treatment: PPI/H2RA for 4-8 weeks
mechanism of action
antibodies kill H pylori bacteria which is a primary cause of peptic ulcers
rationale for use
essential for curing ulcers caused by h pylori infections
perscribing information
check product literature for each medication prior to prescribing for dosage contra-indications, interactions etc
amoxicillin clarithomycin metrodonazole tetracycline
all abtibiotics
It is not fully understood how Bismuth exerts its effect, it is thought to be via various mechanisms.
The use of PPIs have been covered previously.
monitoring
monitor for eradication of H pylori and potential alergic reactions
side effects
gastrointestinal upset/ rash/potent9al allergic reactions
patient counselling points
complete the full course of antibiotics
report sever alergic reaction or persistent symptoms
non pharmacological managment
dietary changes
eat small frequent meals
lifestyle modications
limit alcohol comsumption’stress managment
avoid NSAIDs
dietary changes
reduction of caffine alcohol and smoking as they cna exasterbate symptoms
eat small freuent meals
helps avoid excessive stomach acid productio
lifestyle modifications
stomikg can delay ulcer healing and increase acid production
limit alcohom consumption
alcohol can irritate the stomach lining and worsen symptoms
stress managment
stress may exasterbate symptons to techiques like relaxation excersise orstress managment programes can be beneficial
avoid NSAIDs
the use of all NSAIDs should be reviewed for each patient. most will be advised to stop all NSAID use and consider alternative analgesia such as paracetamol