U8 APES Aquatic and terrestrial pollution
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Endocrine Disruptors
chemicals that can interfere with the endocrine (hormone) system in animals and humans.
-These chemicals can mimic, block, or alter hormone signals, which can lead to a variety of health issues, especially during critical periods of development like fetal growth or puberty.
Thermal Pollution
Pollution that occurs when heat released into water produces negative effects to the organisms in that aquatic ecosystem
-Warm water = Less dissolved oxygen
-Less oxygen levels = Supports less aquatic life
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
A group of toxic chemicals used during the industrial boom after World war 2
Purpose: pest and disease control, crop production and industry
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) negative effects
Persist in the environment for a long time,
Bioaccumulate in the food chain, and
Pose risks to human health and the environment.
Bioaccumulation
The process by which toxic substances (pollutants) build up in an organism over time, especially when the organism absorbs a substance faster than it can get rid of it.
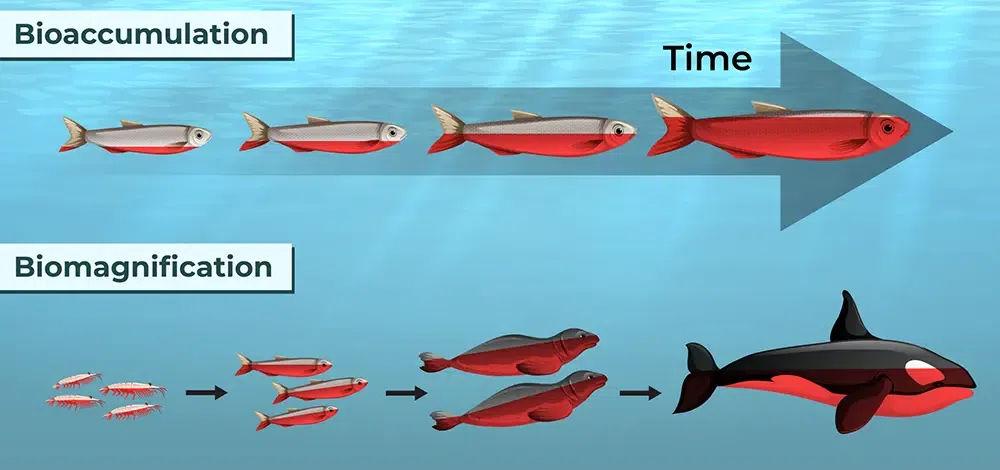
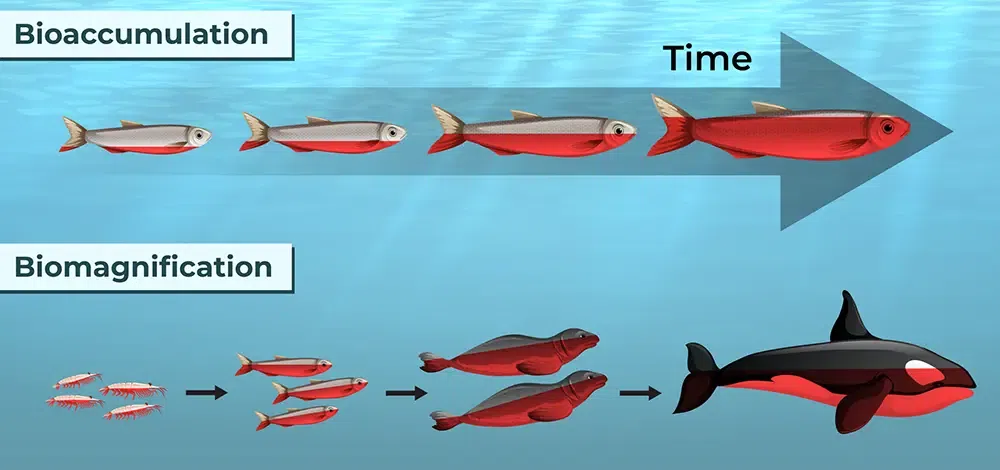
Biomagnification
Biomagnification is the increase in concentration of toxic substances (pollutants) as they move up the food chain.
Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
the amount of free, oxygen gas (O₂) present in water, and it’s essential for aquatic life.
Eutrophication
The process by which a water body becomes overly enriched with nutrients, leading to excessive growth of algae and other aquatic plants.
The excessive growth of algae causes the levels of dissolved oxygen to lower.
Eutrophication Causes
Eutrophication is caused by Agricultural runoff and poorly treated sewage
both carry excess of Phosphorus and nitrogen
Cholera
Spread through Contaminated water (often due to poor sewage treatment)
Malaria
Spreads through Mosquito bites
Tuberculosis (TB)
Spread through: Airborne particles (person-to-person in crowded conditions).
Associated with poor air quality and inadequate housing.
Dysentery
From Contaminated food or water
Hepatitis A
Ingesting contaminated water or food.