Biochemistry Exam 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:32 AM on 9/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
Trace Elements Purposes
Many aid as catalyst for biochemical reactions
2
New cards
Carbon
Most stable bonds
Abundant element
Can form bonds with up to 4 other atoms
Abundant element
Can form bonds with up to 4 other atoms
3
New cards
Enthalpy
Making and breaking covalent bonds or ionic interactions
4
New cards
Entropy
Changes in organization, disorganization, chaos
5
New cards
ΔG
Determines the speed at which equilibrium is approached
6
New cards
Thermodynamics
Tells us a reaction should proceed if the products are more stable than the reactants
7
New cards
Kinetics
Tells us how fast the reaction will go, though doesn’t tell us anything about the final state of things
8
New cards
\-ΔH and +ΔS
\-ΔG
Spontaneous at all temperatures
Spontaneous at all temperatures
9
New cards
\+ΔH and -ΔS
\+ΔG
Nonspontaneous at all temperatures
Nonspontaneous at all temperatures
10
New cards
Nucleophile
Attacks molecule for its proton (H)
11
New cards
Electrophile
Gives proton (H) to other molecule
12
New cards
Polarity
Unequal sharing of electrons in covalent bonds
13
New cards
Hydrophobic
Nonpolar molecules
14
New cards
Hydrophilic
Polar molecules
15
New cards
Non-polarity
Equal sharing of electrons in covalent bonds
16
New cards
Amphipathic
Polar and nonpolar parts in the same molecule
17
New cards
Electrostatic Interactions
Charges interacting with each other
Charge can interact with partial or full charges
Decrease in strength when distance increases
Charge can interact with partial or full charges
Decrease in strength when distance increases
18
New cards
Van der Waals
Induces dipole-dipole interaction
Very weak compared to charge or polar forces
Very weak compared to charge or polar forces
19
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
Part electrostatic, part covalent
Donor Hydrogen is the H in polar covalent bond (X-H)
C-H bonds cannot be donor hydrogens because they are nonpolar
Donor Hydrogen is the H in polar covalent bond (X-H)
C-H bonds cannot be donor hydrogens because they are nonpolar
20
New cards
Strongest Bond Angle
180°
21
New cards
Hydrophobic Effect
Strength of hydrophobic effect depends on surface area
Clustered lipids to form bigger clathrate cage is stronger than individual hydrophobic lipids
Entropy is increased with clustered hydrophobic lipids
Clustered lipids to form bigger clathrate cage is stronger than individual hydrophobic lipids
Entropy is increased with clustered hydrophobic lipids
22
New cards
Clathrate Cage
Highly ordered H2O molecules formed around a hydrophobic molecule
23
New cards
Self-Ionization of Water
H2O disassociates and reacts with itself
24
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry Acid
Proton Donors
25
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry Base
Proton Acceptors
26
New cards
pka low and the protons go
pka high and they stand by
27
New cards
When pka = pH
Concentration of acid and base are the same
28
New cards
Buffers
Resists the change in pH when additional acid or base is added
29
New cards
Amino Acid Stereochemistry
Every amino acid is in the L-stereoisomer configuration
30
New cards

Gibbs Free Energy Equation
Finding ΔG from only products and reactants
31
New cards
pH Equation
pH = -log10\[H+\]
32
New cards
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
pH = pKa + log\[A\]/\[HA\]
![pH = pKa + log\[A\]/\[HA\]](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/740d2cedf09c4ac79e31b68d5afef87f.jpeg)
33
New cards
Fischer Projections
Carbon backbone is vertical with most oxidized carbon at the top
Vertical bonds go away from you
Horizontal bonds reach out and hug you
Vertical bonds go away from you
Horizontal bonds reach out and hug you
34
New cards
Hydrolysis
Adding H2O to break a peptide bond
Thermodynamically favorable
Must be catalyzed to break peptide bond
Thermodynamically favorable
Must be catalyzed to break peptide bond
35
New cards
Condensation
Removing H2O to form a peptide bond
36
New cards
Peptide Bond
Using a ribosome to make an NH2 makes the NH2 nucleophilic attack the C to make a peptide bond
Has resonance
Rigid and planar
Trans conformation
Has resonance
Rigid and planar
Trans conformation
37
New cards
Central Dogma
DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is translated by ribosomes into amino acids that then code into proteins
38
New cards
Amino Terminal End
NH3+ end of peptide chain
Synthesize from amino terminal to carboxyl terminal
Synthesize from amino terminal to carboxyl terminal
39
New cards
\
Carboxyl Terminal End
Carboxyl Terminal End
COO- end of peptide chain
40
New cards
Protein Purification
To understand the properties of individual proteins
41
New cards
Analytical Techniques
Usually takes a small amount of protein that is modified or destroyed in analysis
42
New cards
Preparative Techniques
Produces a large amount of protein and maintains native protein activity
43
New cards
Precipitation
After homogenization of material and removal of insoluble components, differential retention of proteins and other components in a soluble or insoluble phase
44
New cards
Solubility
Affected by pH or ionic strength of solution
pI = 0 when proteins are aggregated (positive charges are equally connected to negative charges)
pI = 0 when proteins are aggregated (positive charges are equally connected to negative charges)
45
New cards
Salting In
Proteins are insoluble at low ionic strength
46
New cards
Salting Out
Proteins are insoluble at high ionic strength
47
New cards
Column Chromatography
Differential retention of proteins and other components of cells using size exclusion, ion exchange, or affinity methods
48
New cards
Size Exclusion Chromatography
Using discs with holes to separate proteins by size
Largest proteins should sink to the bottom
Smallest proteins should stick to the top discs
Largest proteins should sink to the bottom
Smallest proteins should stick to the top discs
49
New cards
Affinity Based Chromatography
Using chemicals to separate proteins of interest
50
New cards
Ion Exchange Chromatography
Using discs that are negatively charged to separate proteins by charge
Negative charges should sink to the bottom
Positive charges should stick to the top discs
Negative charges should sink to the bottom
Positive charges should stick to the top discs
51
New cards
SDS-PAGE Gel Electrophoresis
Denatured proteins are run through an electrically charged gel
Must break disulfide bonds to have a linear polypeptide chain
Smaller, faster proteins will run along the gel further than other proteins
Must break disulfide bonds to have a linear polypeptide chain
Smaller, faster proteins will run along the gel further than other proteins
52
New cards
Two Dimensional Electrophoresis
Columnar tube of decreasing pH
Broken disulfide polypeptides are dropped into tube with decreasing pH
Broken disulfide polypeptides are dropped into tube with decreasing pH
53
New cards
Sanger’s Method
Used to determine identity of N-terminal residue
54
New cards
Edman Degradation
Used to sequence 20-30 N-terminal residues
55
New cards
Mass Spectrometry
Modern method for sequencing proteins and characterizing complex mixtures
56
New cards
Peptide Backbone
C and N make up backbone
Steric constraints on protein backbone angles
Trans conformation, bond angle = 180°
Steric constraints on protein backbone angles
Trans conformation, bond angle = 180°
57
New cards
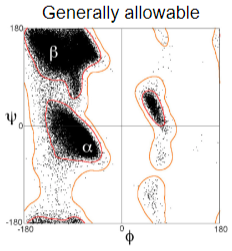
Ramachandran Plot
Map of allowed conformations
Pro and Gly side chains give off different conformations and plots from other amino acids
Pro and Gly side chains give off different conformations and plots from other amino acids
58
New cards
Secondary Structures
Repeating patterns of backbones
Must satisfy all H-bonds
Must satisfy all H-bonds
59
New cards
Alpha Helix
Backbone carbonyl of amino acid forms H-bond to amine
Nearly all are right handed
Nearly all are right handed
60
New cards
Rise Per Turn Equation
p = n \* d
d = 1.5
d = 1.5
61
New cards
Antiparallel Beta Sheet
Side chains are on alternating sides
Interact favorably
H-bonds are 180°
Interact favorably
H-bonds are 180°
62
New cards
Parallel Beta Sheet
Side chains are on same side
Width between H-bonded side chains = 4
Length between R Groups on same side = 7
Width between H-bonded side chains = 4
Length between R Groups on same side = 7
63
New cards
Beta Turns
Gly and Pro chains are in this conformation because they are in cis
64
New cards
Fibrous Protein Structure
Repeating protein structures
All secondary structures
All secondary structures
65
New cards
Keratin
Fibrous
Rich in AVLIMF
Nonpolar and hydrophobic
Coiled coil
Right handed
Rich in AVLIMF
Nonpolar and hydrophobic
Coiled coil
Right handed
66
New cards
Coiled Coil
Left handed
Reduces overall turns in each alpha helix to 3.5 (originally 3.6) residues per turn
Leads to a repeating pattern of hydrophobic side chains
Reduces overall turns in each alpha helix to 3.5 (originally 3.6) residues per turn
Leads to a repeating pattern of hydrophobic side chains
67
New cards
Collagen
Triple helical cable
Repeats of Gly and Pro
Repeats of Gly and Pro
68
New cards
Fibroin Protein
Aligned, stacked, packed antiparallel beta sheets
Gly and Ala
Knobs and holes of Gly and Ala align
Gly and Ala
Knobs and holes of Gly and Ala align
69
New cards
Energetics of Protein Folding
Disfavorable entropy (-ΔS) change due to many possible conformations (+ΔG)
Favorable entropy (+ΔS) change due to hydrophobic effect (-ΔG)
Favorable enthalpy (+ΔH) change due to stronger H-bonds (-ΔG)
Favorable entropy (+ΔS) change due to hydrophobic effect (-ΔG)
Favorable enthalpy (+ΔH) change due to stronger H-bonds (-ΔG)
70
New cards
Hydrophobic Core
Most proteins have hydrophobic, nonpolar R Groups LIVMF
Optimizes density and packing
Large negative effects for hydrophobicity on surface
Optimizes density and packing
Large negative effects for hydrophobicity on surface
71
New cards
Hydrophilic Surface
Most proteins have hydrophilic, polar R Groups RHKDE
Large negative effects for hydrophilicity in core
Large negative effects for hydrophilicity in core
72
New cards
Side Chain Hydrogen and Salt Bridge Bonding
When hydrophilic surface is in the core
Buried H-bonds don’t give full benefits because they were already partially satisfied by water in unfolded state
Buried salt bridges are stronger, more likely to bond to each other than to H2O
Buried H-bonds don’t give full benefits because they were already partially satisfied by water in unfolded state
Buried salt bridges are stronger, more likely to bond to each other than to H2O
73
New cards
Domain Tertiary Pattern
Independently folding segment of protein sequence
74
New cards
Motif Tertiary Pattern
Commonly recurring structural element found in domains with different overall folds
75
New cards
Quaternary Structure
Interactions between separately folded protein subunits to form an overall complex
Stabilized by non-covalent interactions or disulfide bonds
May include one or several polypeptides
Stabilized by non-covalent interactions or disulfide bonds
May include one or several polypeptides
76
New cards
Levinthal’s Paradox
10^143 conformations for a 100 amino acid protein
There is not enough history in the universe to randomly sample every combo of amino acids to find a native
There is not enough history in the universe to randomly sample every combo of amino acids to find a native
77
New cards
Denature a Protein
Heat
Chemical Denaturants
Chemical Denaturants
78
New cards
Pathway Dependent Folding
Steps must be taken before protein refolds to native state
Heat and chemical denaturation could interrupt beginning steps of protein folding
Heat and chemical denaturation could interrupt beginning steps of protein folding
79
New cards
Energy Landscapes
Proteins follow favorable paths in conformation space that funnel them towards a native state
Ideally, protein only has a few errors and step backs to get to native state
In reality, protein takes many steps and errors to get to native state, may not reach it at all
Ideally, protein only has a few errors and step backs to get to native state
In reality, protein takes many steps and errors to get to native state, may not reach it at all
80
New cards
Disulfide Isomerases
Speed up exchange of incorrect with correct disulfide bonds to get to native state
81
New cards
Prolyl Cis-Trans Isomerases
Flip proline between cis and trans isomers to affect backbone to get protein to native state
82
New cards
Molecular Chaperones
Uses ATP to bind misfolded and partially unfolded proteins
83
New cards
Misfolding Diseases
Ultra stable fibers and aggregates are formed that are more stable than native state
Form amyloid plaques that cause neurodegeneration
Form amyloid plaques that cause neurodegeneration