CH21: GENERATION OF BIOCHEMICAL ENERGY
1/267
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
268 Terms
6 coenzymes functions
Hydrolases: break bonds using water (hydrolysis)
Isomerase: rearrange atoms w/in a molecule (same formula, different structure)
Ligases: join 2 molecules together (bond formation)
Lyases: add or remove groups w/out using H2O or ATP
Oxidoreductases: catalyze oxidation–reduction rxns
Transferase: transfer functional groups
metabolic pathways embedded in the inner mitochondria membrane
ETC (in cristae)
ATP synthase
Cellular energy comes from food:
dietary carbs, fats/lipids, and proteins
_____ can be traced to energy from the sun or solar energy
bioenergy
photosynthesis definition
conversion of solar energy to chemical energy via the bonds of biomolecules w/in plants
what do humans obtain from animal and/or plant food sources?
chemical energy
human energy is utilized for ____ and ____ work or is ____
mechanical
chemical
lost
define mechanical and chemical work (general)
synthesizing molecules and moving them across cell membranes, and muscle contraction
necessity of heat and its loss
necessary to maintain our body temp. w/ some energy,
however,
some heat energy is lost to the environment
too fast of an energy release is _____
bad; heat should be released in a controlled manner
where is energy stored
in the chemical bonds of food molecules
energy must be released _____, allowing the cell to capture it efficiently
gradually rather than all at once
organisms must be able to _____ and in readily _____ to meet immediate metabolic demands
store energy both long term (e.g., as fat or glycogen)
accessible forms (e.g., ATP)
how is a constant body temp maintained?
controlled amount of energy is release as heat, while the remainder is conserved for cellular work
main reason for gradual release of energy as heat from the body
To supply energy for non-spontaneous chemical reactions while preventing excessive heat loss and cellular damage.
food is the source of ___ and of ___ for animals
energy
nutrition
food is usually of ____ origins
plants and/or animals
what generally supplies 100% of our energy?
carbs, proteins, fats
Calories definition
measurement of food energy produced when you consume carbs, fats, and proteins
carbs and protein have ____ Calories per gram, and fats have ____ Calories per gram
4, 9
what are the 3 units of food energy?
calorie, Calorie, and kilojoule
calorie definition
(cal) = energy needed to raise the temp of 1 g of H2O by 1oC
Calorie definition
(Cal) = 1000 calories or 1 kilocalorie (kcal)
energy content described on food labels refers to _____ unit of measure
kilocalories
how do you convert Calories to kilojoules (metric unit)
multiply the number of Calories by 4 (Ex: 10 Cal = 40 KJ)
shows the amount of food listed on a product’s food label
serving size
on a food label this shows the types of carbs in the food, including sugar and fiber
total carbohydrate
what types of food should you choose based upon food label?
foods w/ more fiber, vitamins, and minerals
food w/ less calories, sat. fat, sodium, added sugars, and avoid trans fat
metabolism definition
total of all biochemical rxns in an organism
2 components of metabolism
anabolism
catabolism
catabolism consists of degradative processes that ____, w/ a concomitant release of energy.
breakdown larger molecules into smaller molecules
in catabolism, how is the release of energy primarily captured?
captured in the form of ATP, w/ the breakdown products serving as precursors for biosynthetic pathways
anabolism comprises the biosynthetic processes that construct ____, and these rxns require an input of ____.
larger, more complex molecules from smaller precursor molecules
energy (ATP)
carbs consist of C, H, and O atoms, usually in the ratio of _____
C to H2O
1:1
fats and oils are chemically called ______
triacylglycerols
triacylglycerols are what?
tri-esters of 1 glycerol & 3 (usually) different fatty acids
proteins are polymers of ______ w/ varying composition and may contain N and S.
standard amino acids
what are proteins NOT normally used for
energy storage
ID: C6H12O6
glucose, an aldohexose
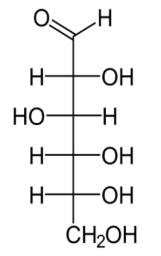
ID this structure:
glucose, an aldohexose
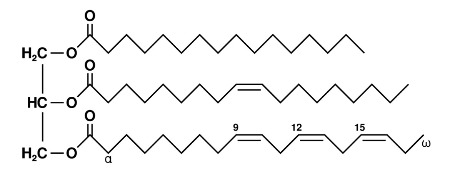
ID this:
triacylglycerol
note location of ester bonds and acyl groups
biomolecules ←→ building blocks + ATP
what is the forward and reverse rxns called?
forward: catabolism
reverse: anabolism
building blocks of carbohydrates are
simple sugars and monosaccharides
building blocks of fats and oils
glycerol and fatty acids
building blocks of proteins
20 standard amino acids
carbohydrate form stored in our body
glycogen in the muscles & liver (limited amounts)
fats and oils form stored in our body
fats in adipose tissues (unlimited)
protein form stored in our body
none is specially used as an energy storage
bioenergetics is the branch of biochemistry that focus on _____, often by producing or consuming ____.
how cells transform energy
adenonsine-5’-triphosphate (ATP)
gibbs free energy (G) is the portion of the total chemical energy stored in the chemical bonds that is ________
available to do work (and only the bonds that are available to do work, not all bonds!)
larger molecules are more complex with more ______, and higher ________ than smaller molecules
bonds and energy
G values
sucrose has ____ than glucose and fructose
more energy (due to larger size)
delta G = ?
G products - G reactants
a rxn is generally considered favorable when energy is ____; that is when delta G is ____.
released
negative
free energy content associated with
reactants/substrates
activation complex
activation energy
products
change of energy
activation energy definition
energy required for a rxn to occur
the ± sign of delta G indicates the _____ of a chemical rxn and determines whether a rxn is _______
direction
spontaneous or not
negative delta G
spontaneous in the forward direction
exergonic rxn
delta G = 0 meaning
reactants and products are at equilibrium
positive delta G
reactants are at lower energy than products
non-spontaneous in forward direction
endergonic rxn
glucose is ________ to produce CO2 and H2O
oxidized (oxidation reaction)
glucose is more complex than its breakdown products → the free energy of the reactants > products. The delta G change is _______.
negative
when delta G is negative, the rxn releases energy, is ____, thermodynamically favorable, and can occur spontaneously.
exergonic
____ is a metabolic process that builds up complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring input of energy.
anabolism
glucose is synthesized from CO2 and H2O by _____
photosynthesis
delta G of an anabolic rxn is ____.
positive
when delta G is positive, the rxn is ____, thermodynamically unfavorable, non-spontaneously, and requires an input of energy (i.e., solar energy).
endergonic
in glucose metabolism, photosynthesis is _____
anabolic
endergonic (energy input)
positive delta G value
in glucose metabolism, oxidation is _____
catabolic
exergonic (energy released)
negative delta G value
catabolic and anabolic rxns of glucose have the same delta G value but ______
opposite signs
anabolism utilizes ____ to make macromolecules and biopolymers
ATP
catabolism yields ____ when biopolymers and macromolecules are broken down to small molecules
ATP
ATP plays a central role in coupling ________ and _________ pathways in cellular metabolism
anabolic (energy-consuming)
catabolic (energy-releasing)
ID this rxn:
ATP + H2O → ADP + HOPO32- + H+ + energy
ATP hydrolysis
ATP hydrolysis rxn consists of what?
negative delta G
exergonic (energy release)
spontaneous
ATP hydrolysis is the chemical process by which adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP) is broken down into _____ OR into _______.
adenosine 5’-diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi)
adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and pyrophosphate (PPi)
ATP is often called the ______ or an _______, transporting chemical energy w/in cells for metabolism.
molecular unit of currency of intracellular energy transfer
energy transporter
the energy of ATP is stored in _____ bonds.
two phosphoanhydride
adenosine-p-p-p → adenosine-p-p + Pi
adenosine-p-p → adenosine-p + PPi
chemical energy is transferred from _______ compounds to______ compounds, commonly using ATP as the energy carrier.
higher energy
lower energy
endergonic rxns may occur by ____ to ATP hydrolysis
coupling
_______ the principal molecule for storing and transferring energy
ATP
ATP consists of ____ base attached to a ____ sugar, which is attached to 3 ____ groups.
adenine
ribose
phosphate
ATP phosphate groups are linked together via ______
phosphoanhydride bonds (2 high-energy bonds)
adenine and ribose together is called ______
adenosine
2 phosphoranhydride bonds when hydrolyzed, release sufficient energy to power _____
endergonic reactions
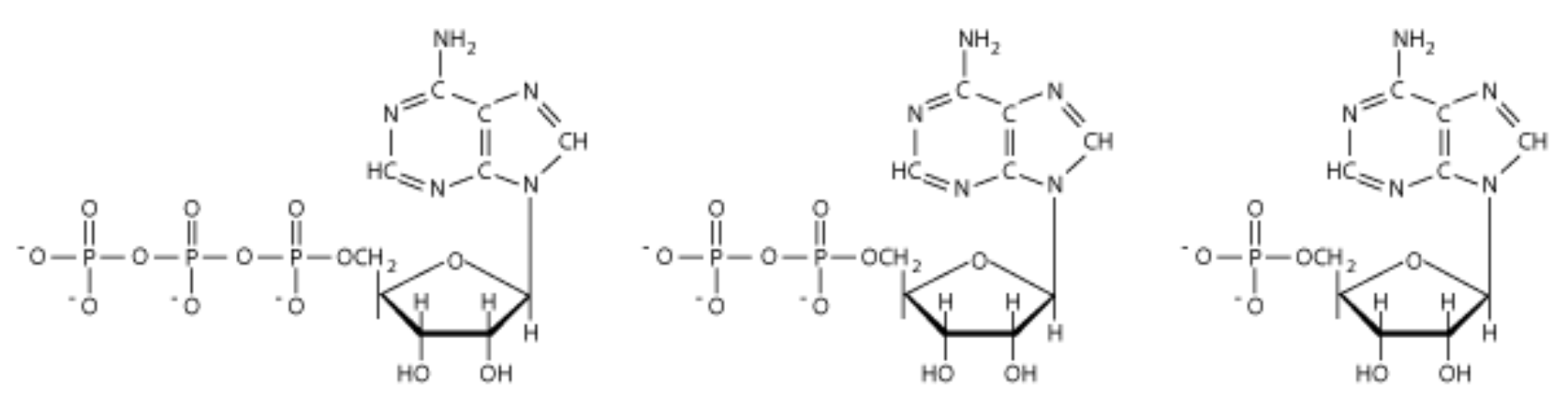
ID these structures
L to R
ATP
ADP
AMP
ATP contains 2 high energy phosphoanhydride bonds. Hydrolysis of each bond yields __________
the same amount of energy
ATP and ADP are high-energy phosphate compounds that are often ______ through cellular processes
interconverted
ATP-ADP cycle refers the continuous process by which __________ to supply energy for cellular work and _________ using energy derived from food metabolism.
ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP
ADP is rephosphorylated back to ATP
the total cellular________ is small but is recycled thousands of times per day to provide energy for biological processes
ATP pool
Organophosphates are organic compounds containing a _______ that can release energy upon hydrolysis of the ____________ bond.
phosphate group (R–O–PO₃²⁻)
phosphate ester
examples of high energy phosphate containing organic molecules
Most to least free energy:
phosphoenol pyruvate
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
creatine phosphate
ATP (→ ADP)
glucose 1-phosphate
glucose 6-phosphate
fructose 6-phosphate
ID this rxn:
substrate—P + ADP → substrate + ATP
substrate-level phosphorylation
although essential, ATP is _____.
rapidly consumed and regenerated
During exercise, a common way our body regenerates ATP from ADP is to use _______ as a phosphate group donor
creatine phosphate
_______ is stored in the muscle as a reservoir to form ATP readily from ADP every time we need energy, such as exercise strenuously.
Creatine phosphate
Why must ATP be continuously regenerated?
ATP stores are limited (~100 g) and can be depleted in ~10–12 seconds during intense activity.
How much ATP does the body use during activity?
Up to ~500 g/min during intense exertion; ~60 kg over a 2-hour run.
How is ATP regenerated and what determines the fuel source?
Regenerated from ADP via nutrient catabolism—mainly carbohydrates and fats; fuel use depends on activity level and physiological state.
How does ATP supply change during exercise?
ATP → creatine phosphate → ATP regenerated from glycogen or fats based on intensity and duration.