Understanding the Periodic Table and Chemical Elements
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What does the Periodic Table of Chemical Elements organize?
All discovered chemical elements in rows (periods) and columns (groups).
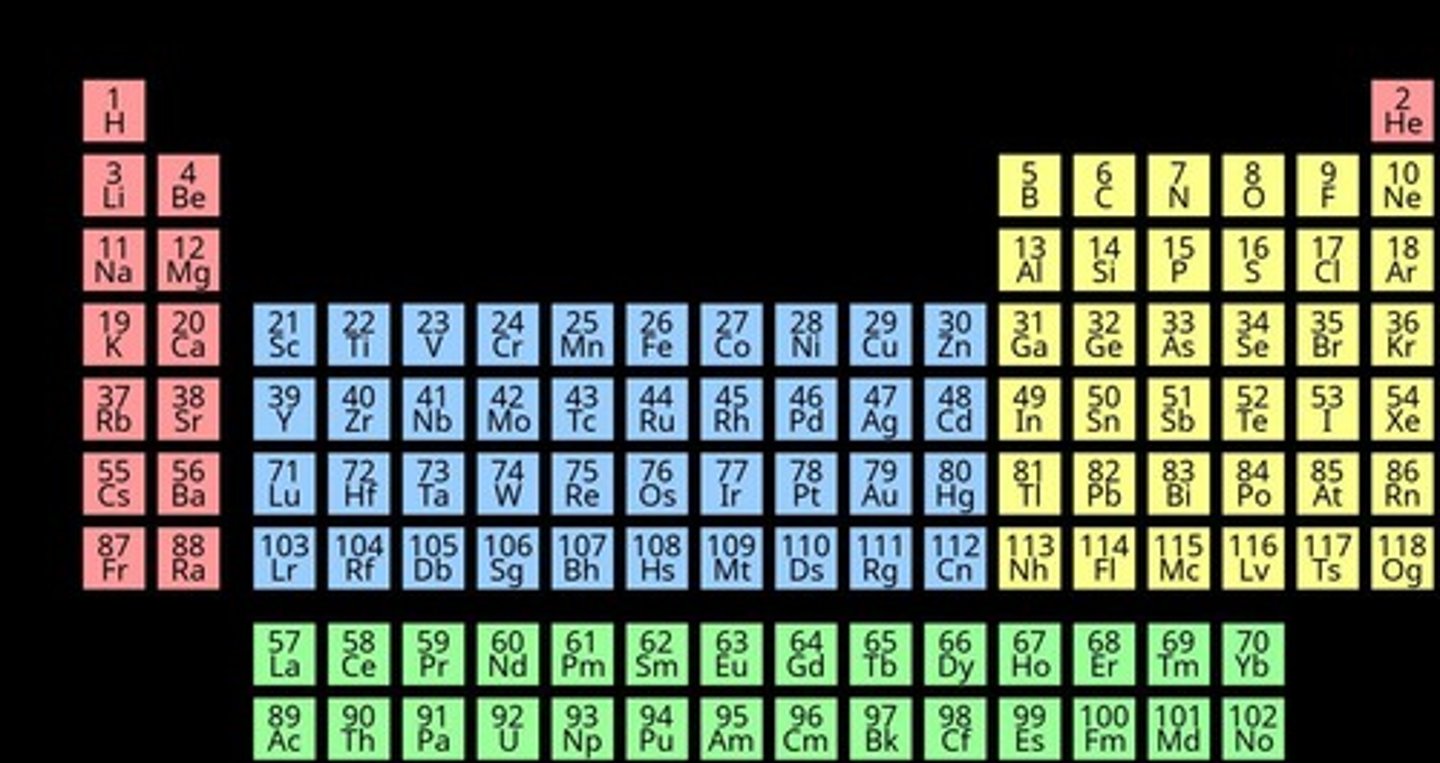
How are elements organized in the Periodic Table?
According to increasing atomic number.
How many known elements were there 2,000 years ago?
Only 10 known elements.
Who arranged the elements by increasing atomic weight in 1864?
British chemist John Newlands.
What significant contribution did Dmitri Mendeleev make to the Periodic Table?
He organized the elements into rows and columns based on their similar properties.
What is the total number of known elements on the Periodic Table as of 2016?
118 elements.
What are the vertical arrangements of elements in the Periodic Table called?
Groups or families.
What is Group 1 on the Periodic Table known as?
The alkali metals.
What is Group 2 on the Periodic Table known as?
The alkaline earth metals.
What are the elements in Group 16 known as?
Chalcogens or the oxygen family.
What are the elements in Group 17 known as?
Halogens.
What are the elements in Group 18 known as?
Noble gases.
What do elements in the same group have in common?
They all have similar properties and the same number of valence electrons.
What does the period number indicate in the Periodic Table?
The number of occupied electron shells.
How many periods are there in the Periodic Table?
7 periods.
What is the atomic number?
The number of protons in an atom.
What is the mass number?
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
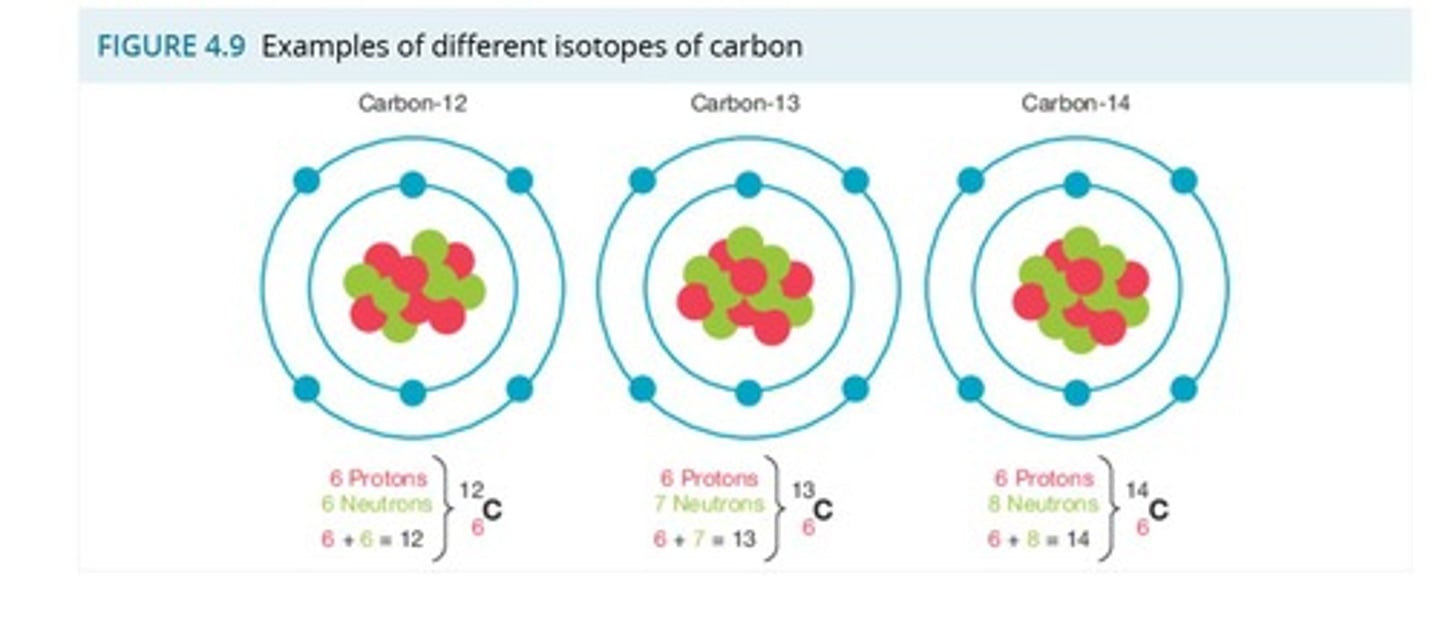
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
What are Group 15 elements known as?
Pnictogens or the nitrogen family.
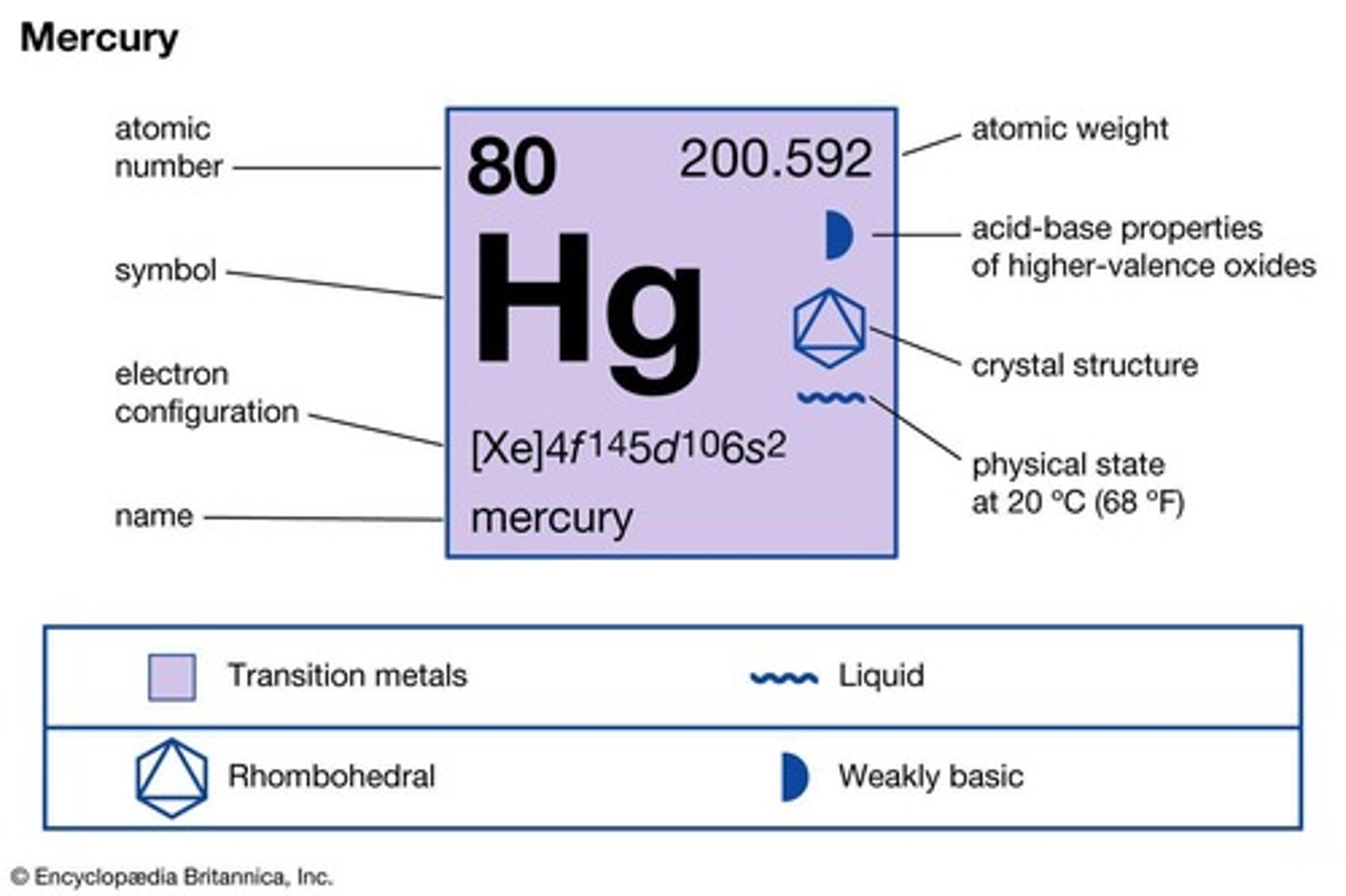
What is the only metal that is a liquid at room temperature?
Mercury (Hg).
What percentage of the elements on the Periodic Table are metals?
91 out of 118 elements are metals.
What are the transition metals?
The block of elements in the middle of the Periodic Table, including Lanthanoids and Actinoids.
What is the charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Protons are positive, neutrons are neutral, and electrons are negative.
What is the relationship between protons and electrons in a neutral atom?
They are equal in number.
What are the common properties of metals?
Metals are shiny when polished, good conductors of heat, electricity, and sound, ductile, malleable, hard, have good tensile strength, high melting and boiling points, and high density.
What are transition metals and where are they found on the periodic table?
Transition metals are found in groups 3 to 12 in periods 4 to 7 of the periodic table.
Name some common transition metals.
Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), Titanium (Ti).
What are some characteristics of transition metals?
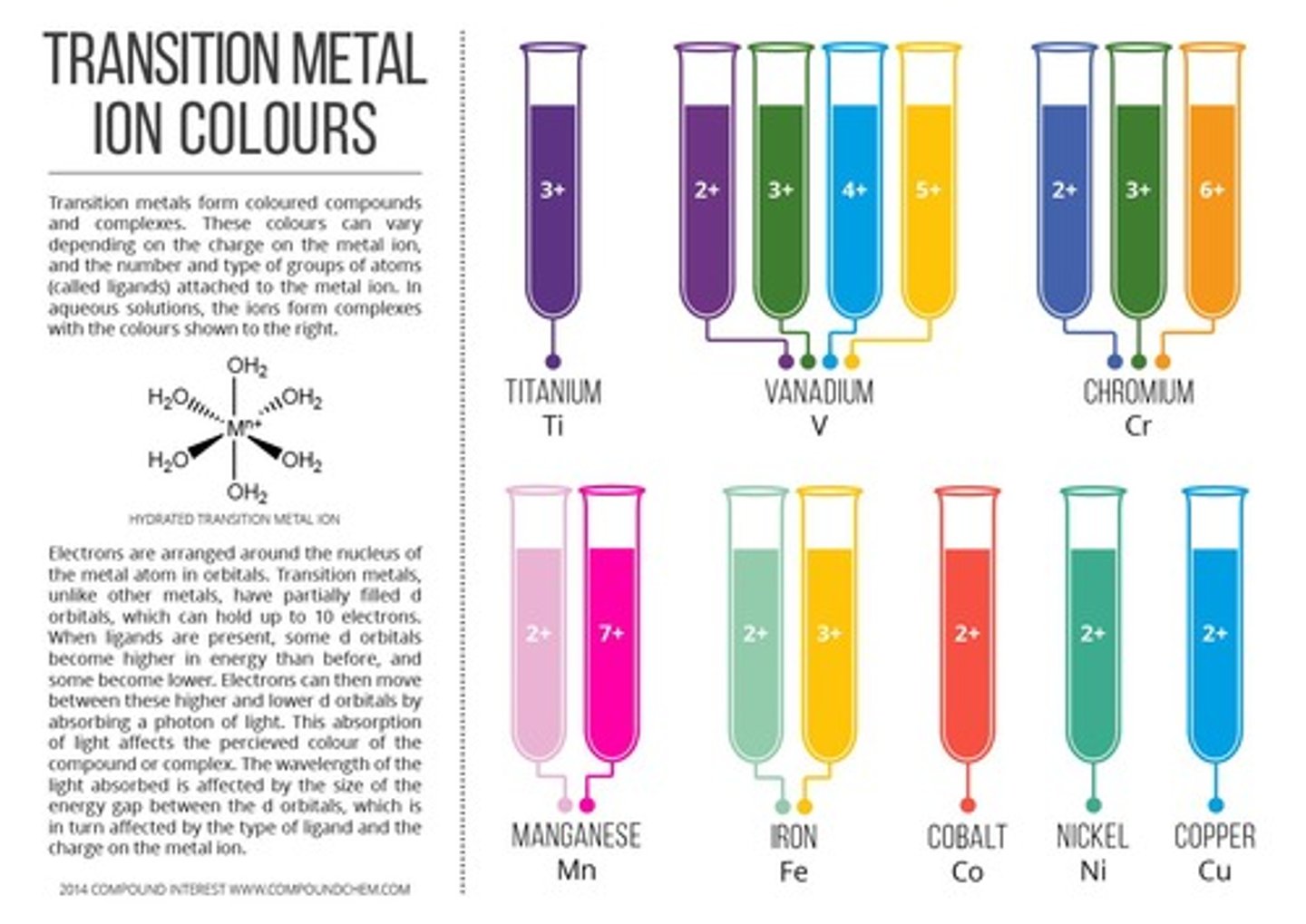
Transition metals are mined in Australia, required in low concentrations in the body, some are magnetic (e.g., Iron, Cobalt, Nickel), and their compounds can have different colors.
How do transition metals contribute to fireworks?
Different colors in fireworks come from the combustion of different metal salts.

What are lanthanides and where do they fit in the periodic table?
Lanthanides are a set of 15 elements (atomic numbers 58-71) located between groups 1 and 2 and groups 3 to 12.
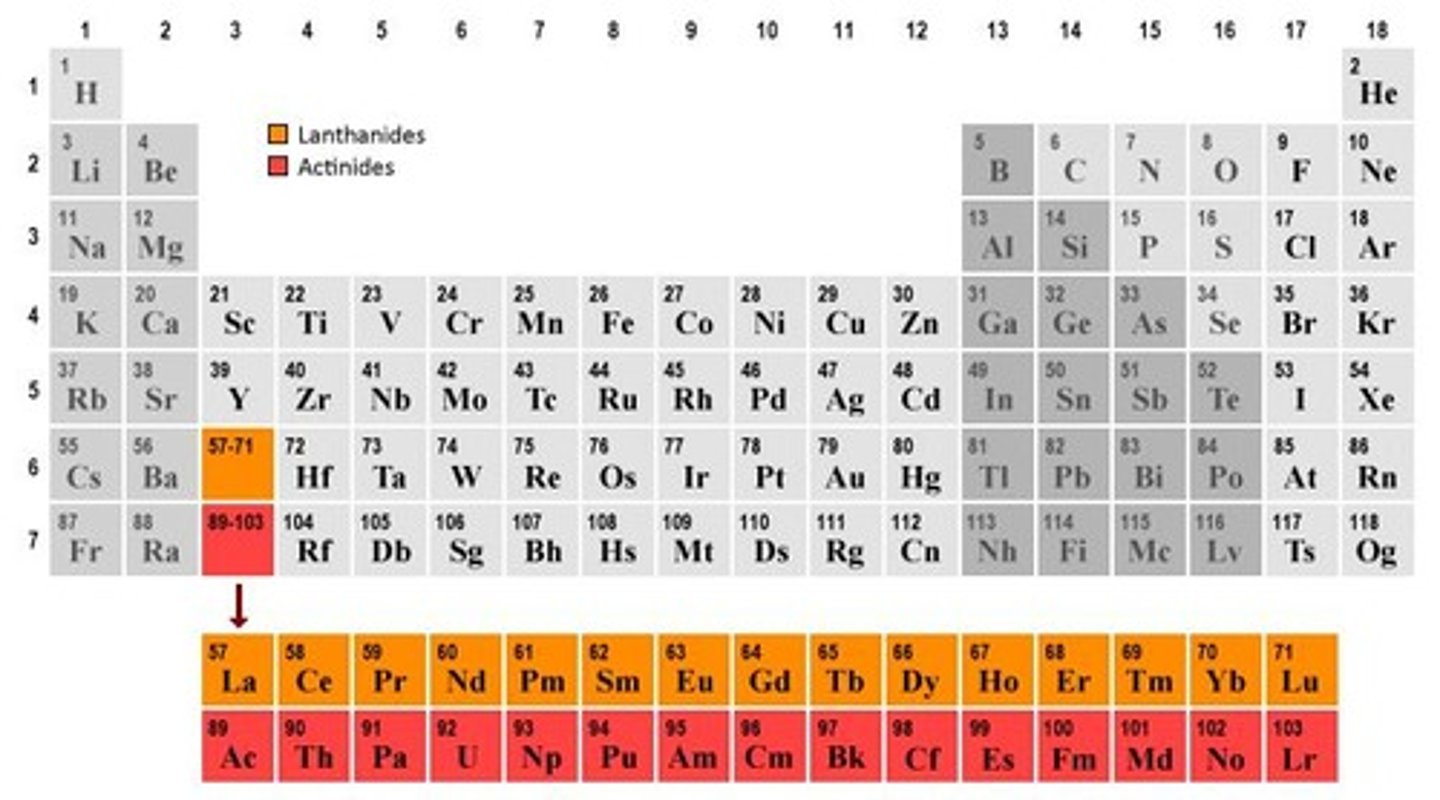
Why are lanthanides called 'rare earth metals'?
They are called 'rare' not because they are hard to find, but because they are difficult to extract.
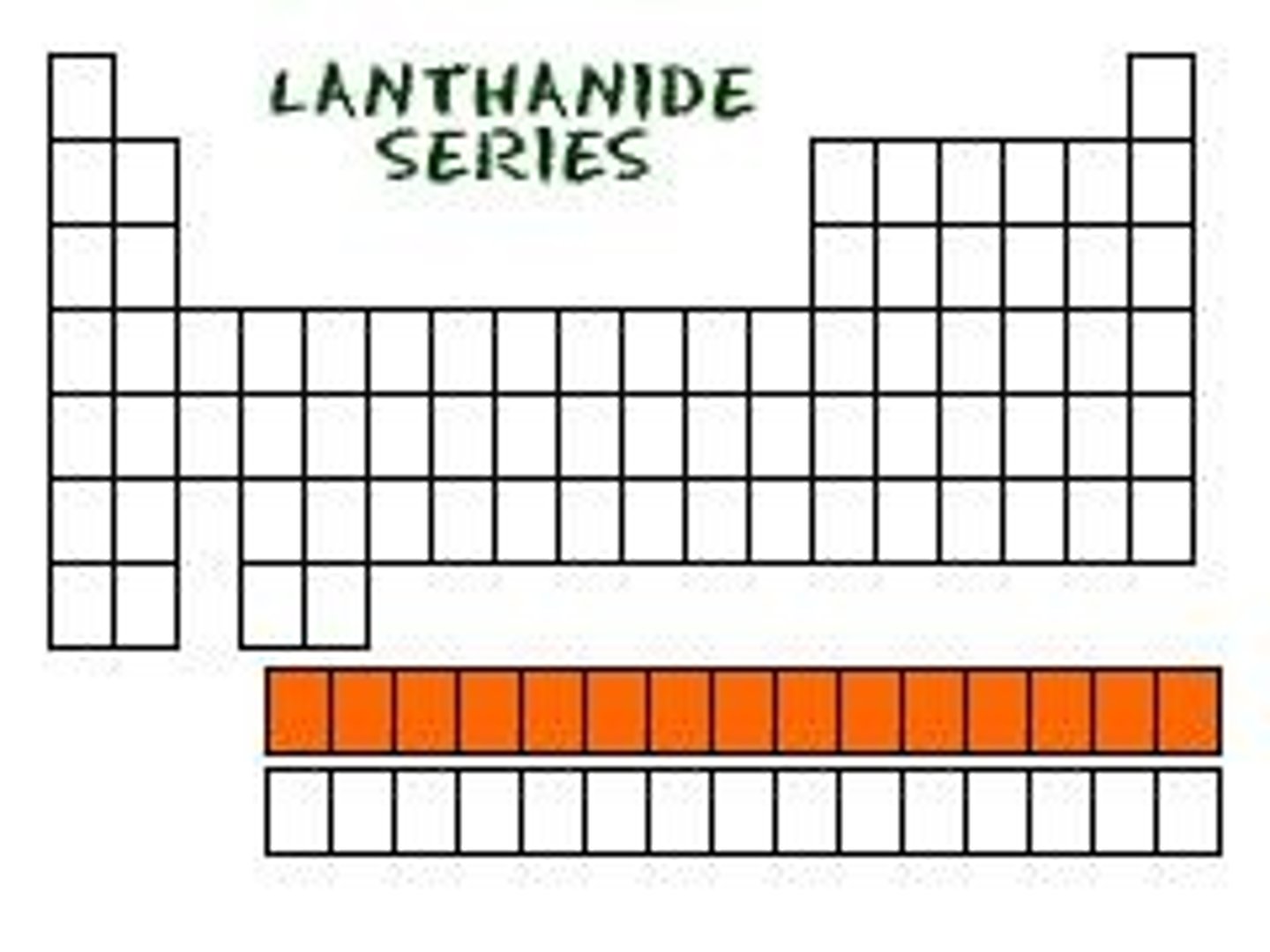
What are actinides and what is a notable characteristic of these elements?
Actinides are a set of 15 elements (atomic numbers 89-103) that are all radioactive and many are synthetic.
What is the largest naturally-occurring element?
Uranium is the largest naturally-occurring element (atomic number 92).
What are the physical states of non-metals at room temperature?
Non-metals can be gas, solid, or liquid at room temperature, with Bromine (Br) being the only liquid non-metal.
What are the general characteristics of non-metals?
Non-metals have low melting and boiling points, are dull, and are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
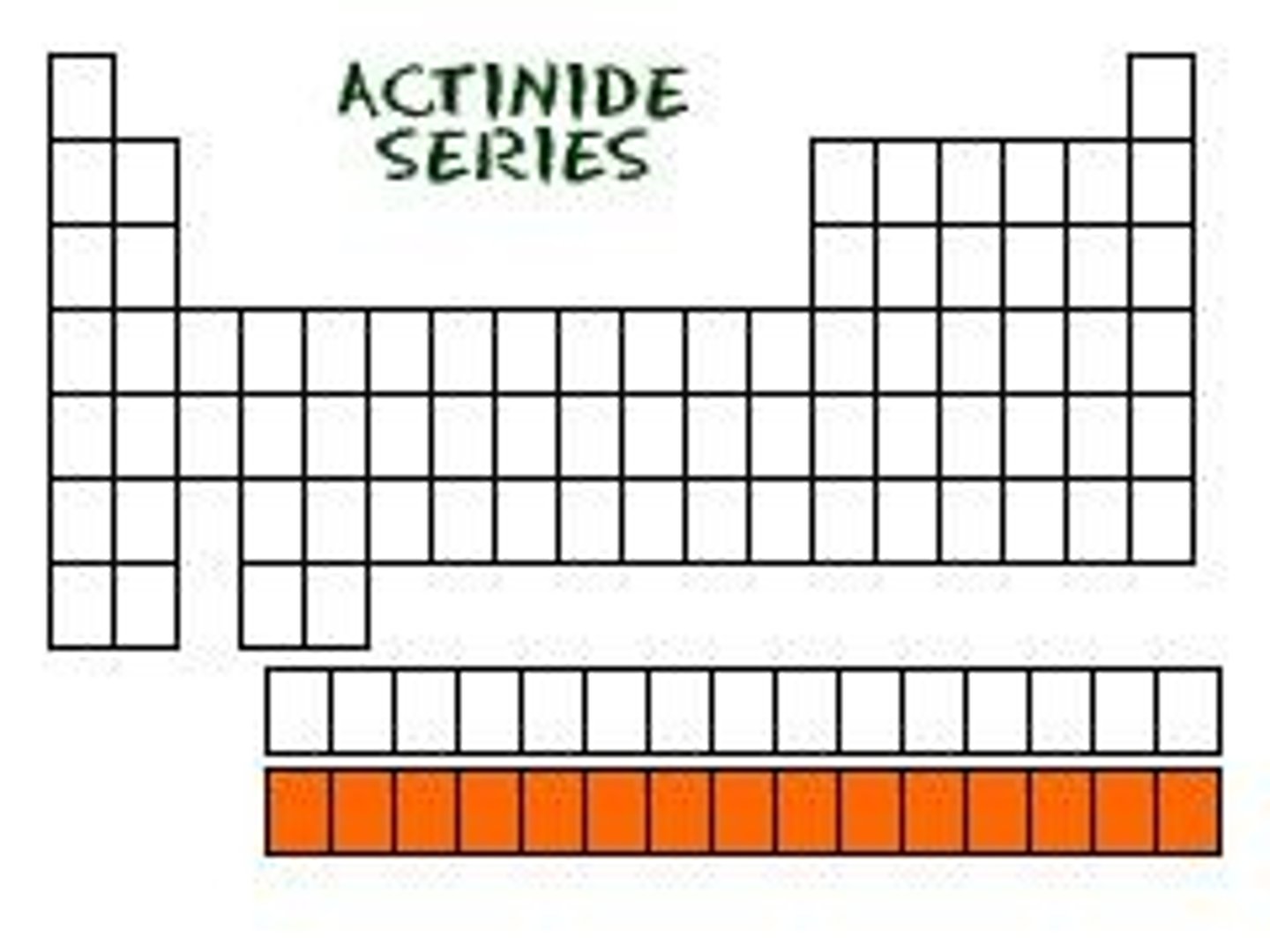
What are metalloids and where are they located on the periodic table?
Metalloids are found between metals and non-metals, creating a zig-zag shape on the periodic table.
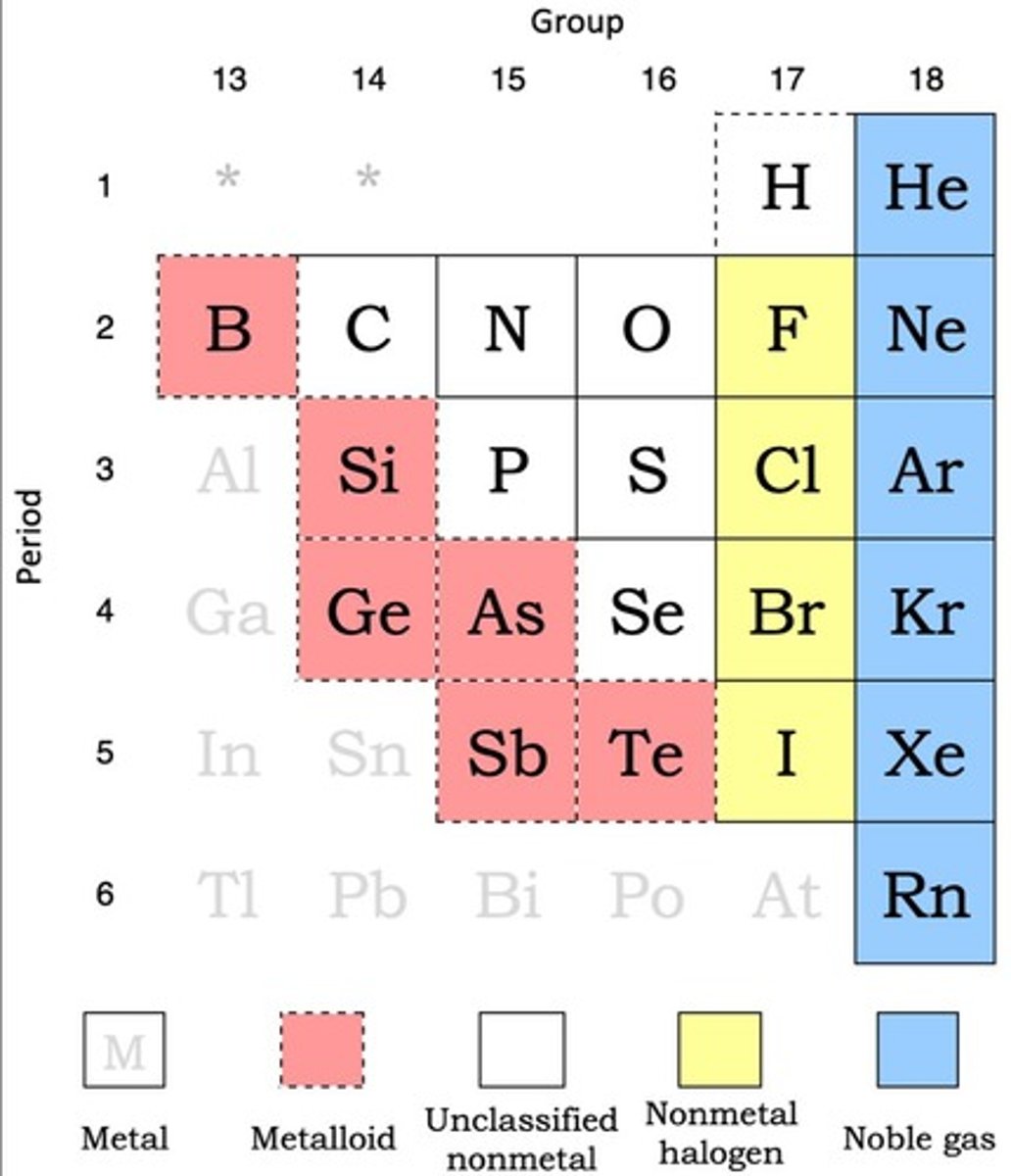
List the six metalloids.
Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te).
What are the characteristics of alkali metals?
Alkali metals are found in Group 1, have 1 valence electron, are very reactive, and must be stored under oil to prevent reaction with water.

How does reactivity change among alkali metals?
Reactivity increases as you go down the group in alkali metals.
What is the electron structure of alkali metals?
All alkali metals have 1 electron in their outer shell, making it easy for them to achieve a full outer shell by losing that electron.
What are alkaline earth metals and where are they located on the periodic table?
Alkaline earth metals are found in Group 2 of the periodic table and have 2 electrons in their outer shell.
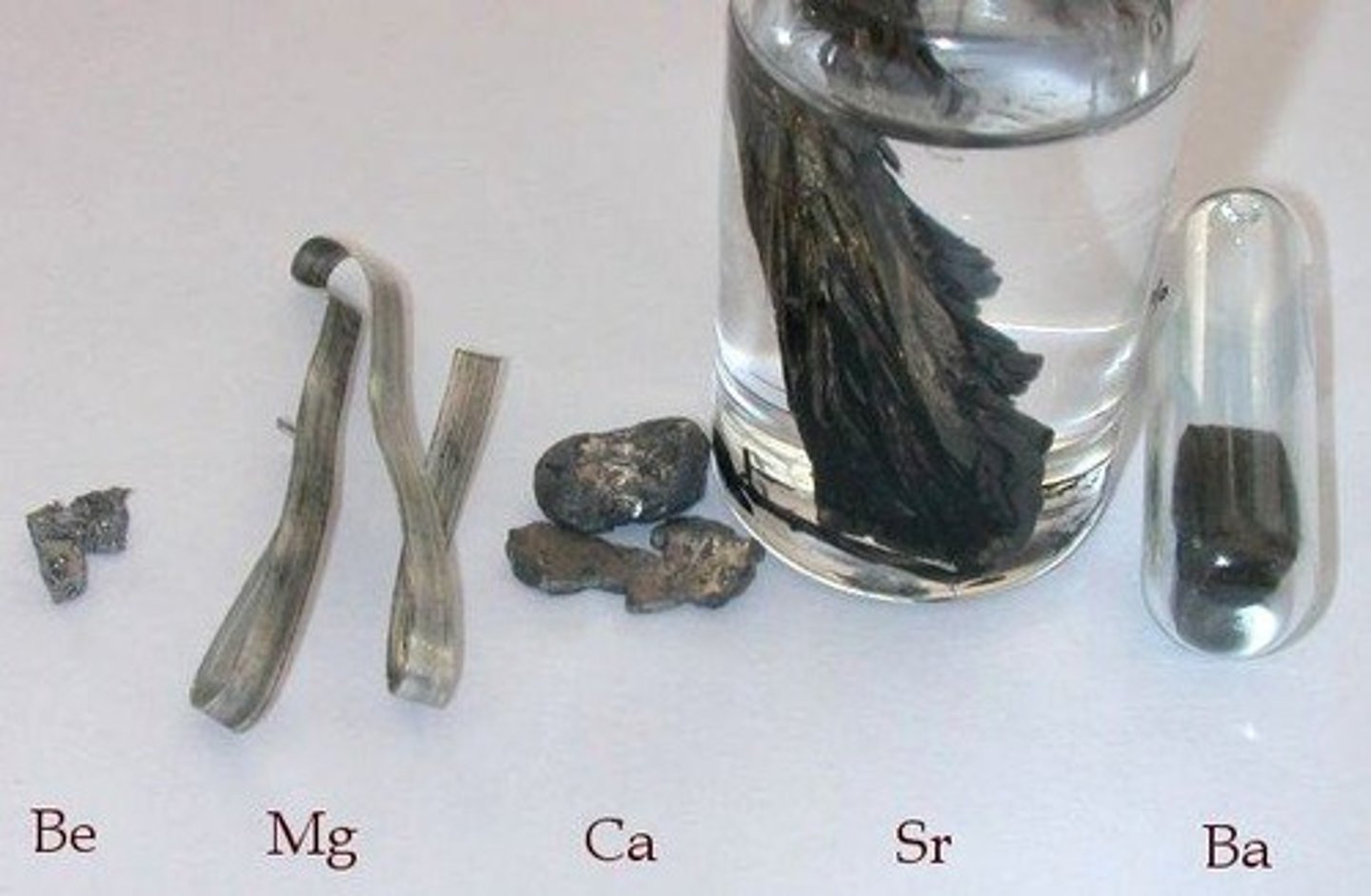

How do alkaline earth metals compare in reactivity to alkali metals?
Alkaline earth metals are less reactive than alkali metals because they need to lose 2 electrons to achieve a full outer shell.
What is a fun fact about Beryllium?
Beryllium is found in emeralds.
Where are halogens found on the periodic table?
Halogens are found in Group 17 (VII) of the periodic table.
What group of the Periodic Table do Halogens belong to?
Group 17 (VII)
How many valence electrons do Halogens have?
7 valence electrons
What charge do Halogens typically acquire when they become anions?
-1 charge
What type of molecules do Halogens form?
Diatomic molecules (e.g., F2)
How do the melting and boiling points of Halogens change as you go down the group?
They increase as you go down the group.
How does the reactivity of Halogens change as you go down the group?
Reactivity decreases as you go down the group.
Which Halogen is more reactive, Fluorine (F) or Astatine (At)?
Fluorine (F) is more reactive.
What group of the Periodic Table do Noble Gases belong to?
Group 18 (VIII)
How many electrons do Noble Gases have in their outer shell?
8 electrons (full outer shell)
Why are Noble Gases considered stable and non-reactive?
They have a full outer shell of electrons.
What is a historical term used for Noble Gases?
Inert gases.
What happens to the weight of Noble Gases as you go down the group?
They get heavier.
What is the maximum number of electrons that can fit into the first shell?
2 electrons.
What is the formula to calculate the maximum number of electrons in a shell?
Maximum electrons = 2n² (where n is the shell number).
What is the maximum number of electrons that can fit into the outermost shell?
Up to 8 electrons.
What is the electron configuration for Calcium?
2, 8, 8, 2.
What determines the type of bonding an element will undergo?
The number of valence electrons.
What occurs when enough energy is supplied to an atom?
Electrons can move from one energy level (shell) to another.
What is released when electrons return to a lower energy level?
Energy in the form of light.
What causes different colors in flames when elements are burned?
The release of energy as light when electrons return to lower energy levels.
What is the significance of valence electrons in ionic bonding?
They determine how atoms gain or lose electrons to attain a full outer shell.
What is the electron configuration for an element with 5 valence electrons?
2, 5.
What is the electron configuration for an element with 8 valence electrons?
2, 8, 8.
What is the electron configuration for an element with 2 valence electrons?
2, 8, 8, 2.
What do atoms gain or lose electrons for?
To attain a full outer shell.
What is formed when an atom loses or gains electrons?
An ion, which is a charged atom.
What are positive ions formed by metals called?
Cations.
What are negative ions formed by non-metals called?
Anions.
What is the formula to determine the total charge of an atom?
Total charge = number of protons - number of electrons.
What is the total charge of a lithium ion with 3 protons and 2 electrons?
1 positive charge (1+ or +).
What happens to a lithium atom when it becomes a lithium ion?
It loses one electron to form Li+.
What happens to a calcium atom when it becomes a calcium ion?
It loses two electrons to form Ca2+.
What charge does an oxide ion have?
A charge of -2 (O2-).
What charge does a fluoride ion have?
A charge of -1 (F-).
What is formed when a cation is attracted to an anion?
An ionic bond.
What are the properties of ionic compounds?
They are made of positive and negative ions, typically solid at room temperature, have high melting points, and usually dissolve in water.
What is the process of forming sodium chloride?
A sodium atom transfers one electron to a chlorine atom, forming Na+ and Cl-.
How are ionic compounds named?
By listing the cation first and the anion last, changing the suffix of the anion to -ide if it is a single element.
What is electrovalency?
The size of the positive or negative charge on an ion.
What charge does a sodium ion have?
+1 (Na+).
What charge does a calcium ion have?
+2 (Ca2+).
What charge does a chloride ion have?
−1 (Cl-).
What is a covalent bond?
A bond formed when a non-metal atom is attracted to another non-metal atom, involving shared pairs of electrons.
What do electron dot diagrams represent?
They show how elements share their electrons to create covalent bonds.
What is the difference between single, double, and triple covalent bonds?
Single bonds share one electron pair, double bonds share two, and triple bonds share three.
What does the activity series of metals indicate?
It ranks metals from most reactive to least reactive.
What happens in metal displacement reactions?
A metal will displace any metal ion that is below it on the activity series.
Give an example of a metal displacement reaction.
Fe(s) + SnSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Sn(s).