Miller & Levine Biology Chapter 17 Darwin's Theory of Evolution
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Charles Darwin
1809-1882 English naturalist and scientist whose theory of evolution through natural selection was first published in 'On The Origin of the Species" in 1859.

Evolution
Change over time
Theory
A well tested explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events.

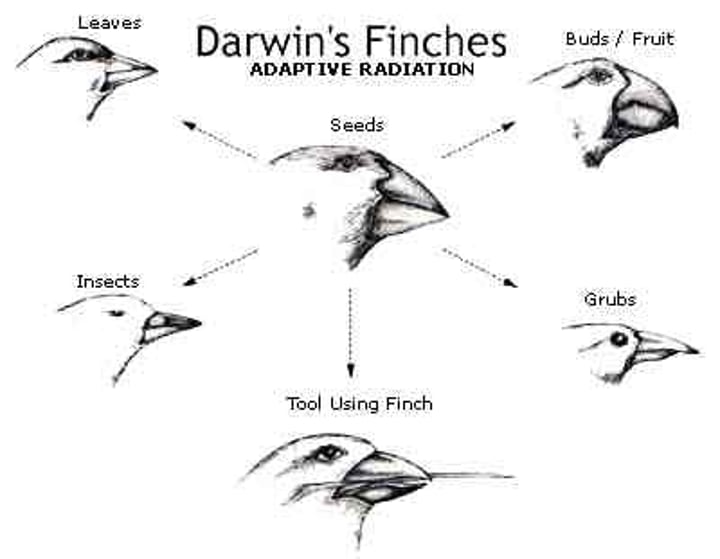
Species Vary Globally
Darwin noticed that different, yet ecologically similar, animal species inhabited separated, but ecologically similar, habitats around the globe.
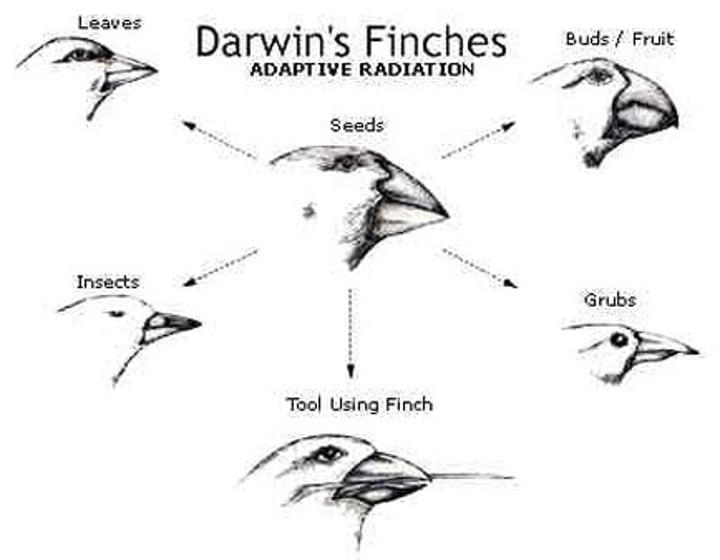
Species Vary Locally
Darwin noticed that different, yet related, animal species often occupied different habitats within a local area

Species Vary Over Time
Darwin noticed that some fossils of extinct animals were similar to living species.

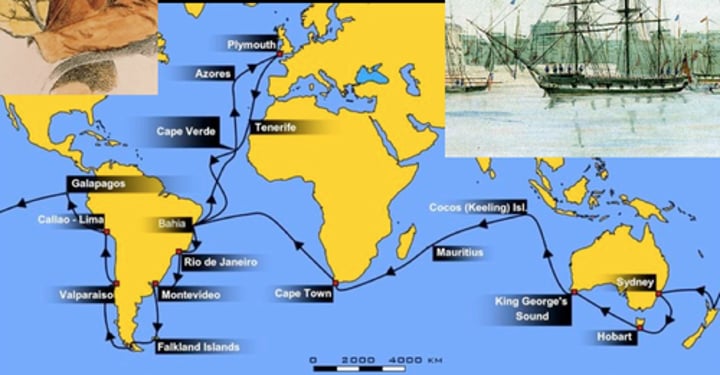
Galapagos Islands
Chain of islands near South America where Darwin developed his theory of natural selection by studying the unique life there.

MHS Beagle
Darwin's ship
Earth is
about 4.5 billion years old
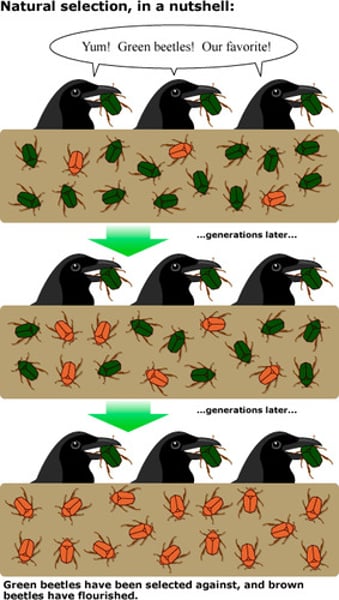
Natural Selection
Individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully
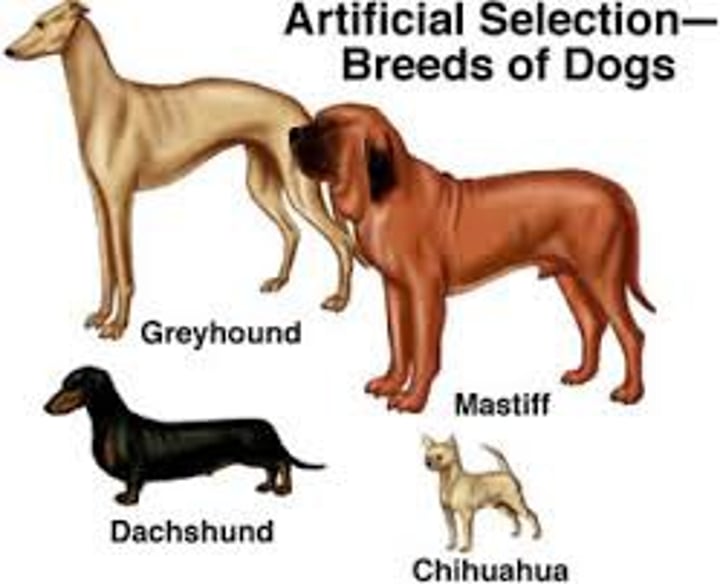
Artificial Selection
Selection by humans for breeding of useful traits from the natural variation among different organisms
The Origin of the Species
Darwin's book explaining how various species evolve over time and only those with advantages can survive and reproduce

Variation and Adaptation
Darwin hypothesized that individuals have natural variations among heritable traits, some are more suitable than others (adaptations)

Survival of the Fittest
Darwin hypothesized that individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce most successfully
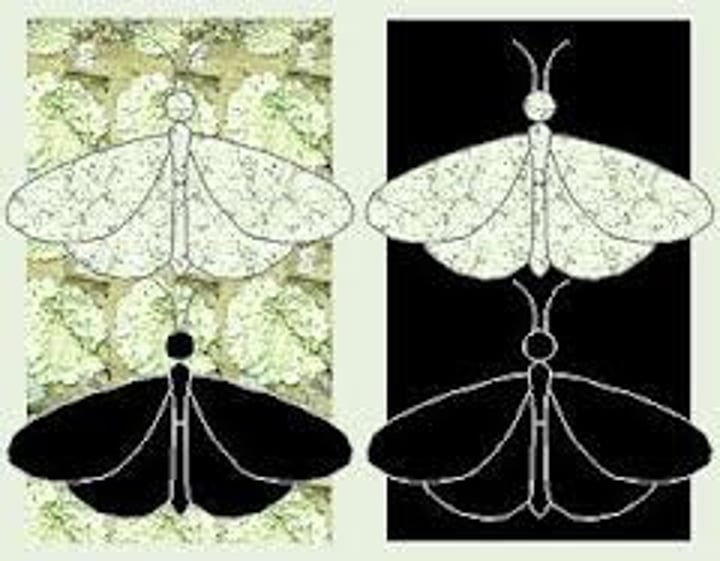
Common Descent
Darwin hypothesized that all living things are derived from common ancestors
Closely related but Different
Closely related species evolve slightly differently in different environments
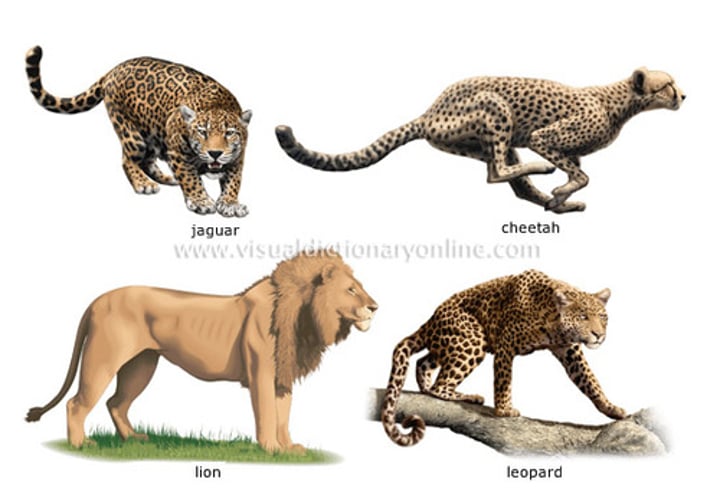
Distantly Related but Similar
Similar environments around the world have organisms that are only distantly related but with similar adaptations

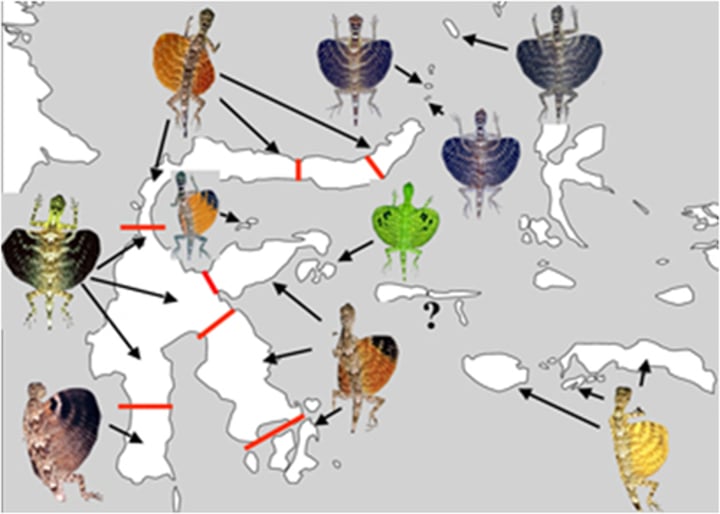
Biogeography
Geographic distribution of species.
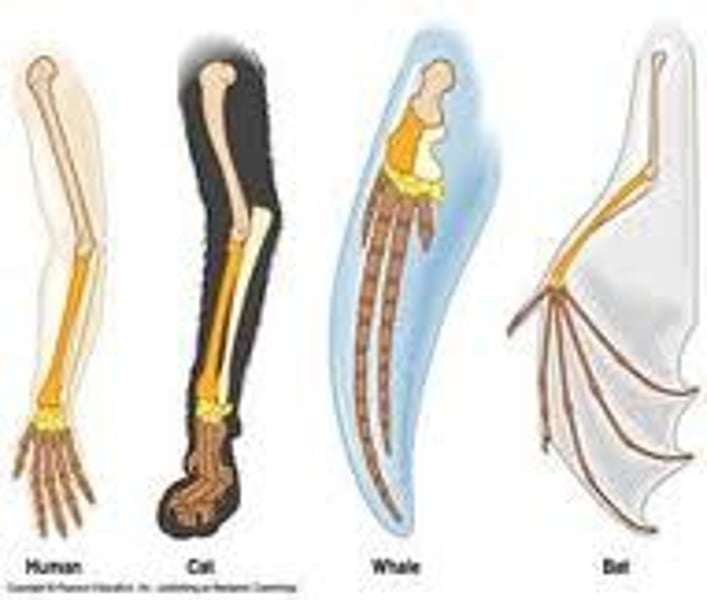
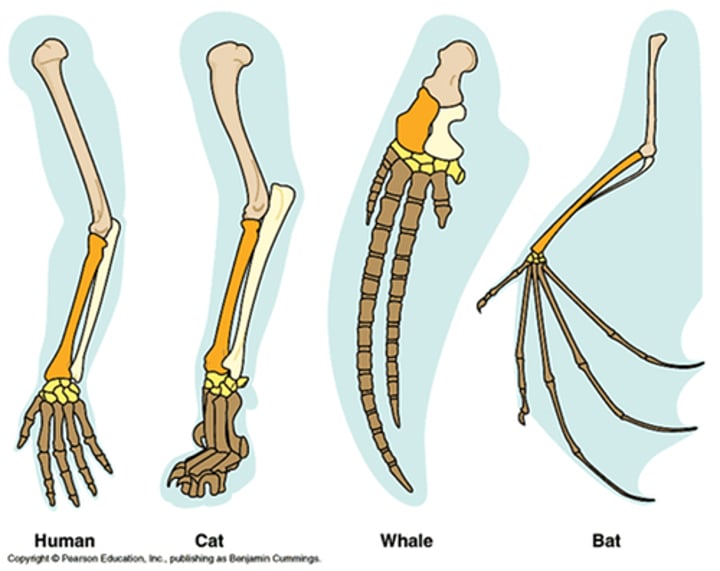
Homologous Structures
Structures that are shared by related species and that have been inherited from a common ancestor.
Same structure, different function
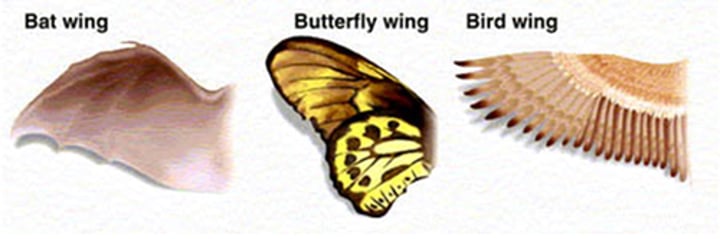
Analogous Structures
Structures of different species having similar or corresponding function but not from the same evolutionary origin. Different structure, same function
Vestigial Structures
A structure that is present in an organism but no longer serves its original purpose
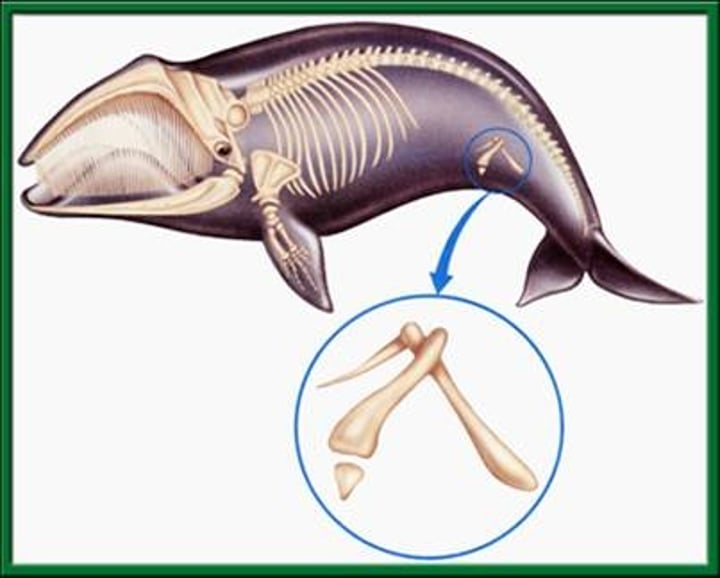
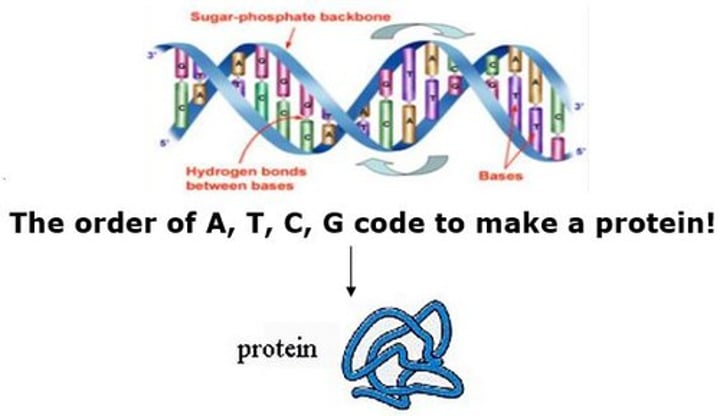
Common Genetic Code
All living organisms share the same 4 bases of DNA (or RNA). This supports that all living organisms come from the same original source
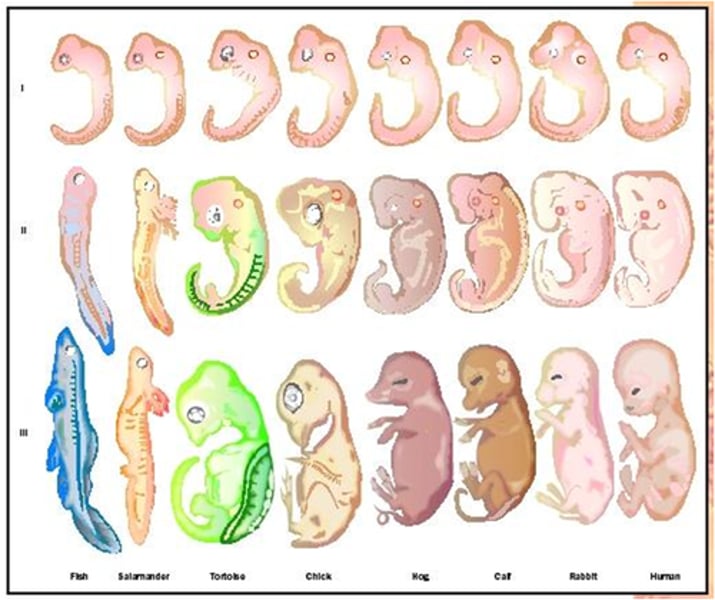
Embryology
The study of the early development of living things - shows that related organisms develop in similar ways.
Descent with Modification
principle that each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time
Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment
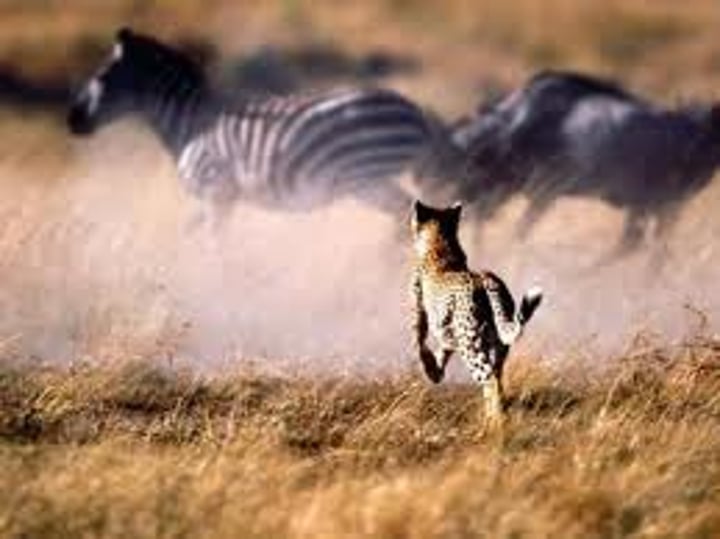

Mutation
A change in DNA that can aid the organism in survival or limit the organism's survival.
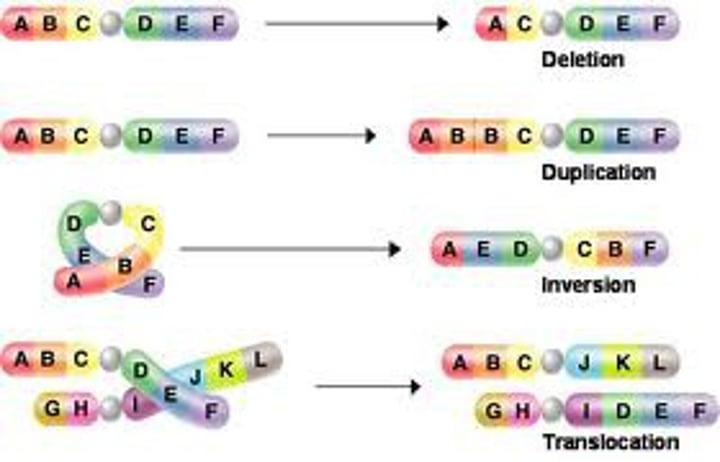
Adaptation
A characteristic that improves an individual's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment.
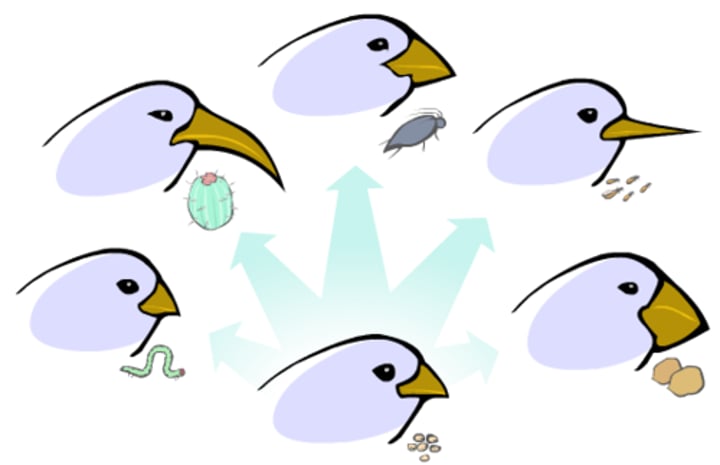
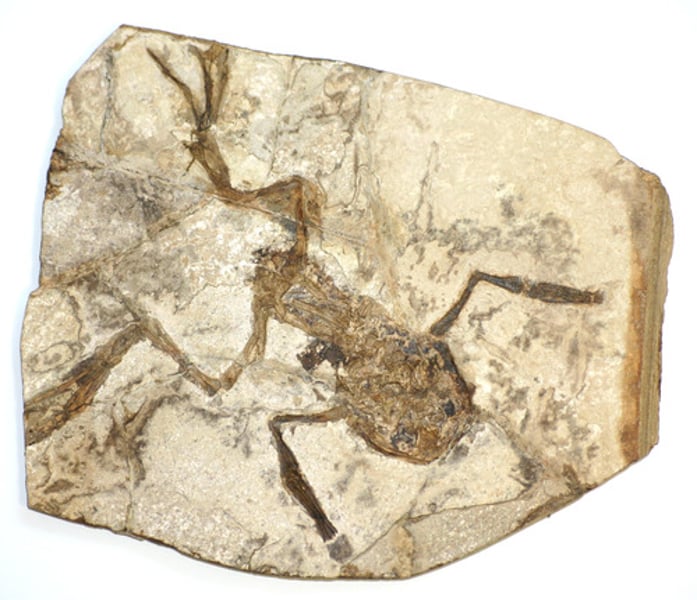
Fossil
The preserved remains of a once living organism; used for geological study and biological comparisons
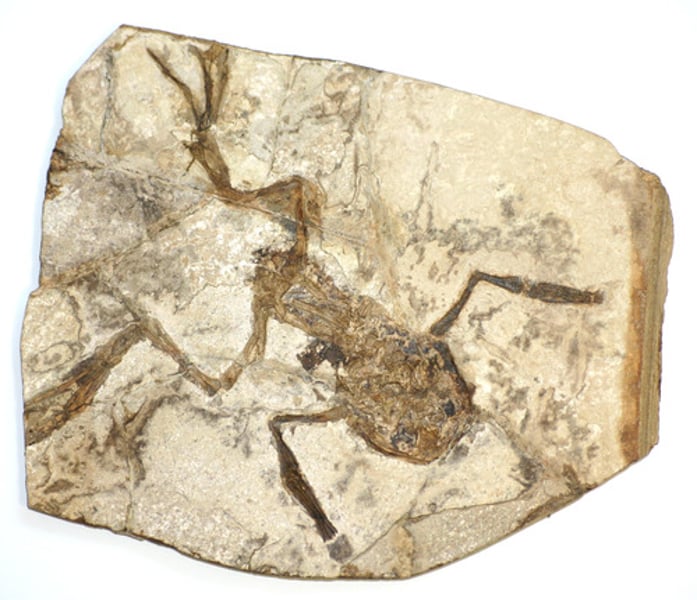

Evidence of Evolution
Fossil record
Common genetic code
Embryology
Anatomy
Biogeography.

Struggle for Existance
Organisms compete for food, space, and other resources

Hutton and Lyell
Geologists that said the earth was very old and had changed over time
Lamarck's Evolution Hypothesis
If an organism changes during life in order to adapt to its environment, those changes are passed on to its offspring.
Malthus, Thomas
Was one of the first to argue that the worlds rate of population increase was far outrunning the development of food population. This is important because he brought up the point that we may be outrunning our supplies because of our exponentially growing population.
common ancestry of life
a fundamental conclusion of natural selection
fossil record
information about past life, including the structure of organisms, what they ate, what ate them, in what environment they lived, and the order in which they lived