DHS IB Biology HL 2025
1/691
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

692 Terms
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE UNIT
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE UNIT
Know how to draw and label a diagram showing the structure of 2 water molecules, including positive and negative charges
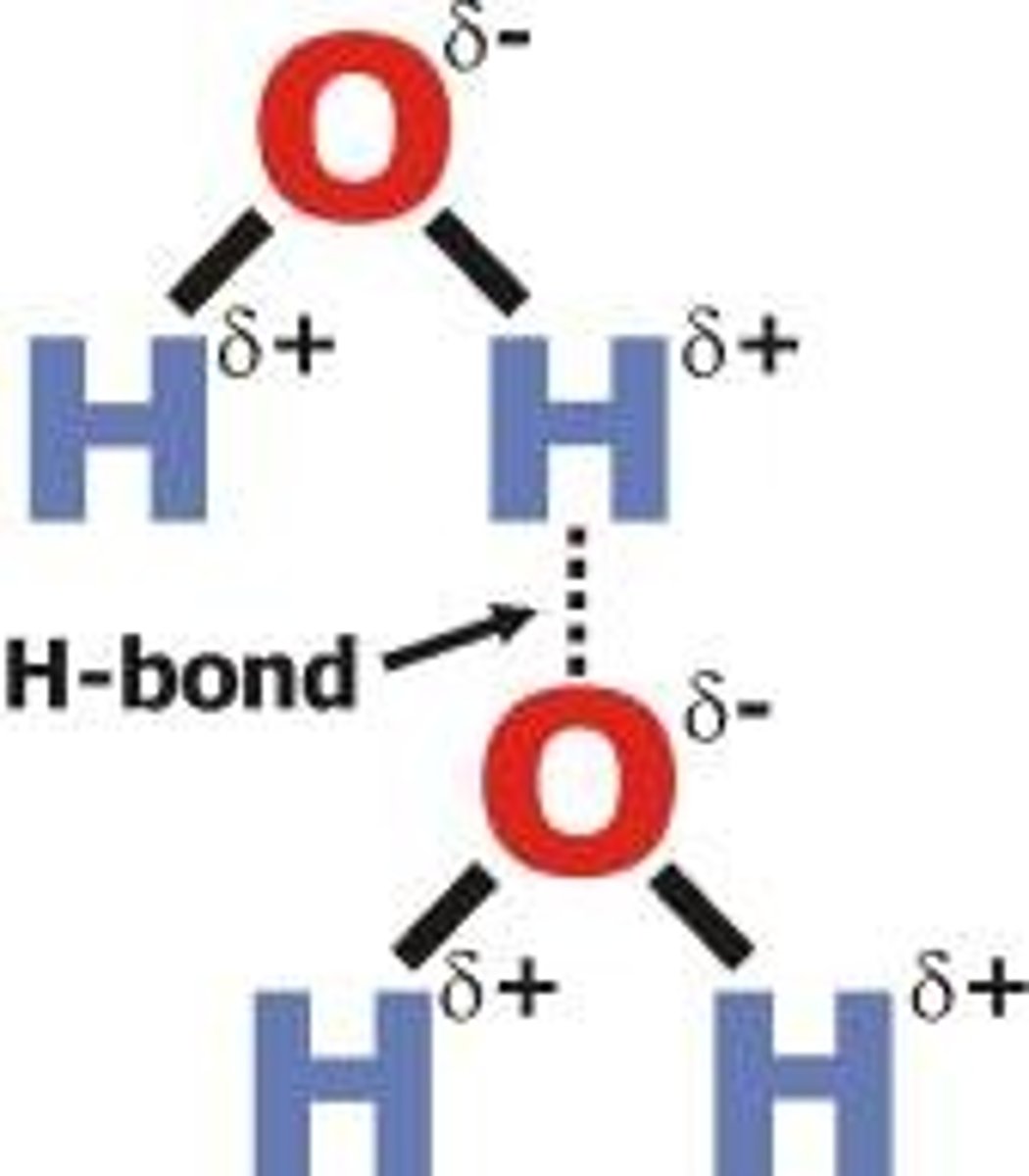
Water has a positive and negative charge, it is _________________
polar
Water binding to water
Cohesive
How is cohesive benefical to living things
surface tension, and helps water move up plants
What is adhesion?
Hydrogen bonds can form between water and other polar molecules
Why is adhesive beneficial to living things
keeps cell walls moist, allowing for substances to pass through
What is high specific heat capacity?
It restricts the motion of water molecules and increases temperature of water in a liquid state. Water doesn't want to boil because it is cohesive, the water sticks together and doesn't want to escape into the air.
How is high specific heat capacity beneficial to living things?
Stable habitat for aquatic organisms, they maintain the same temperature
What is buoyancy?
floating
What is the effect of buoyancy on living things?
some animals can float
What is viscosity?
a liquid's resistance to flow
What is the effect of viscosity on living things?
animals have to overcome viscosity in the air and water
What is a solvent?
Water forms hydrogen bonds with polar molecules. Water is the universal solvent.
How is a solvent beneficial to living things?
Absorption of complex mixtures and dissolves substances. Helps with digestion
What is hydrophilic?
Chemically attracted to water, water loving
What is an Example of hydrophilic substance?
Cellulose. Sugar. Salt.
What is hydrophobic?
Insoluble in water
What is an example of a hydrophobic substance?
Oil
Carbon atoms can form ____ covalent bonds (which allow a diversity of molecules to be formed)
carbon atoms can form 4 covalent bonds
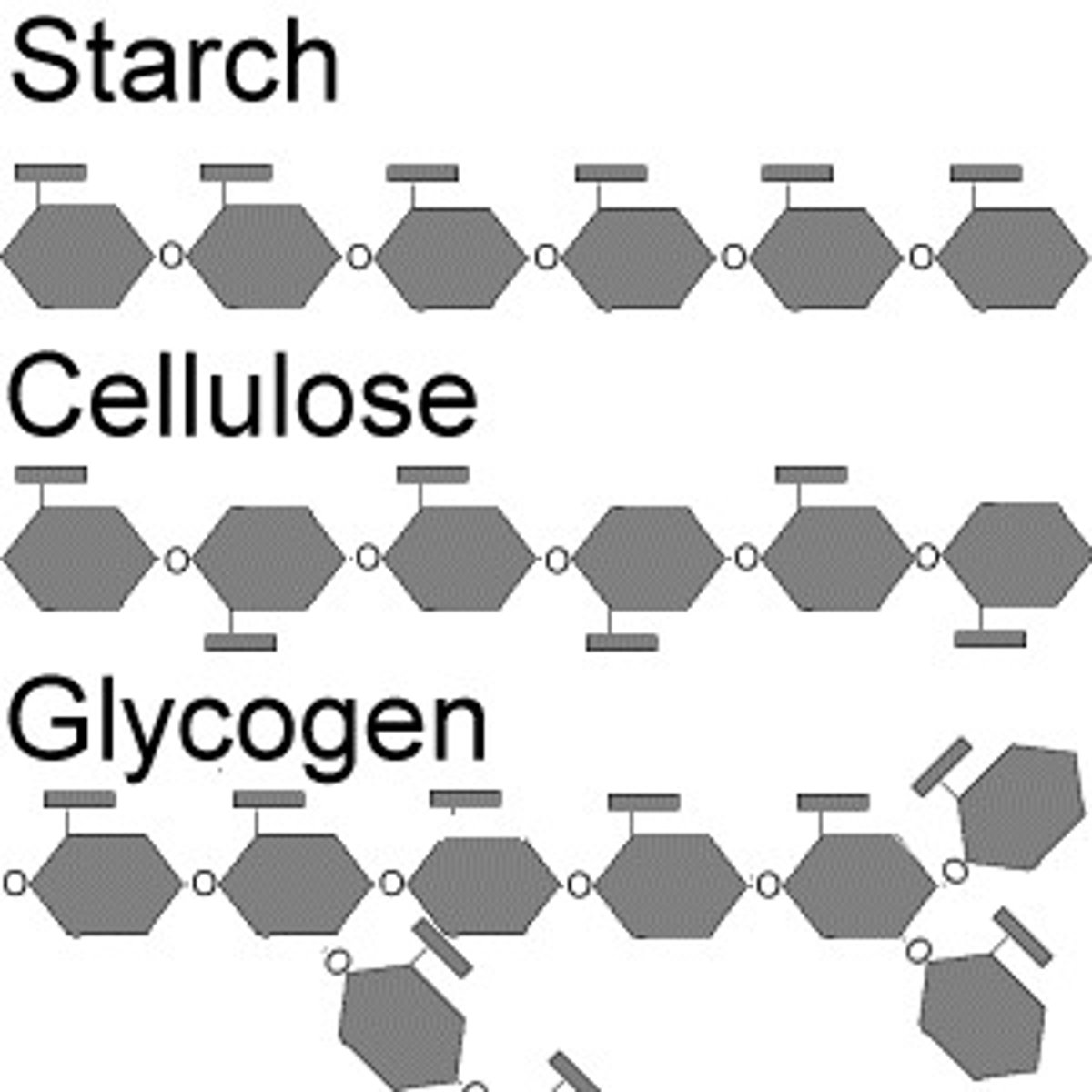
List 3 examples of polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, and cellulose
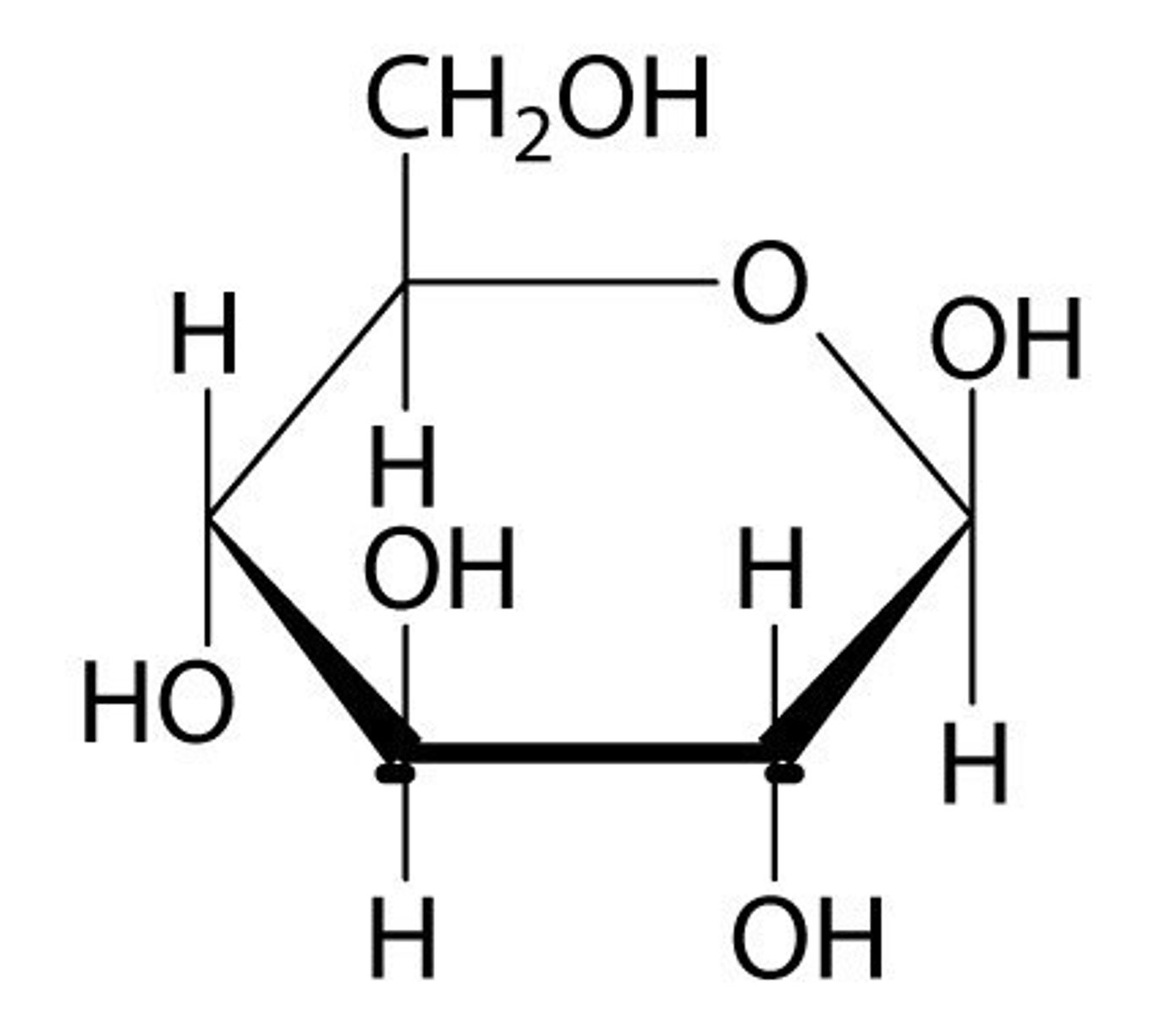
Be able to recognize a molecule of glucose (6 carbon ring, hexagon)
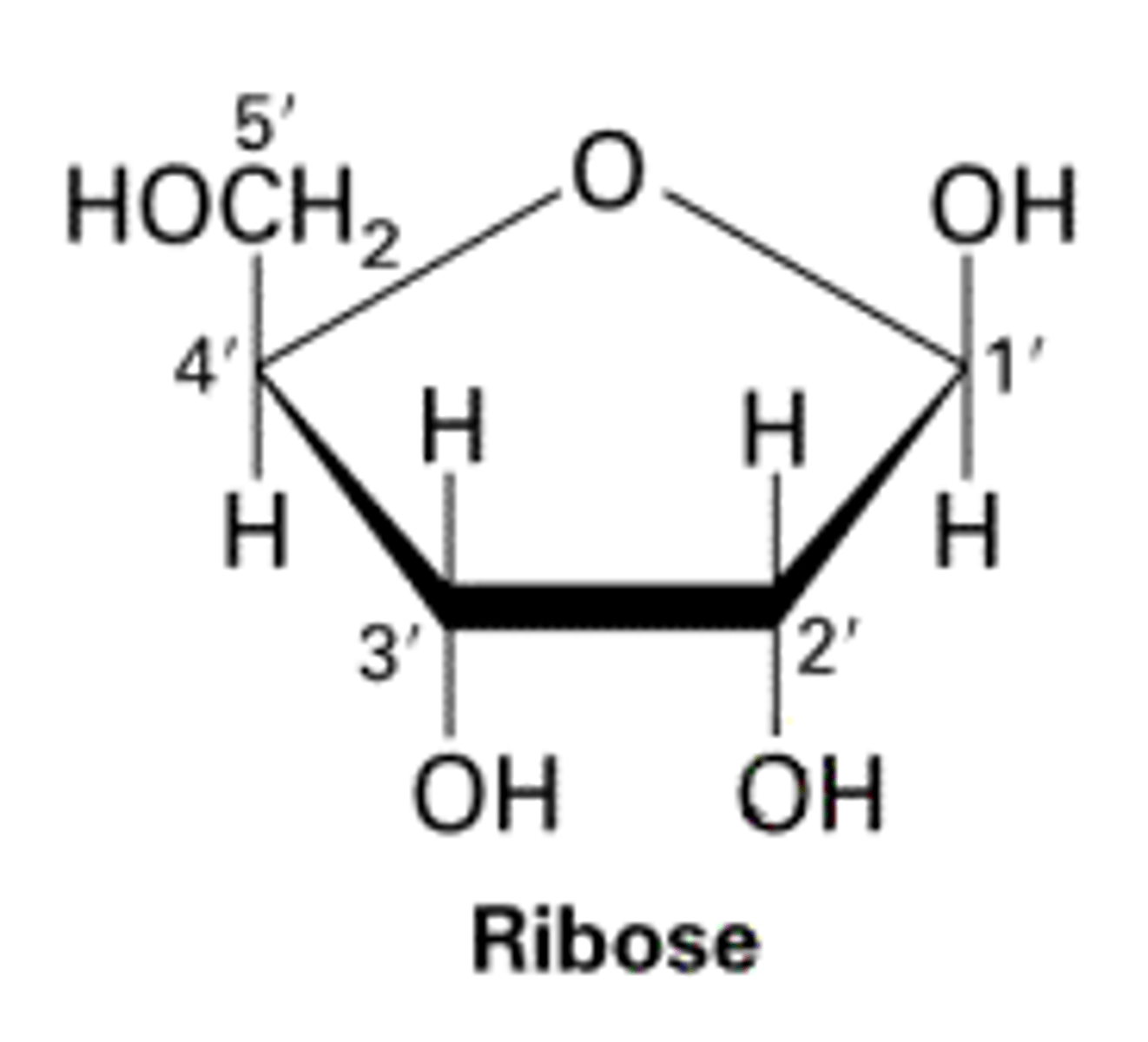
Be able to recognize a molecule of ribose (5 carbon ring, pentagon)
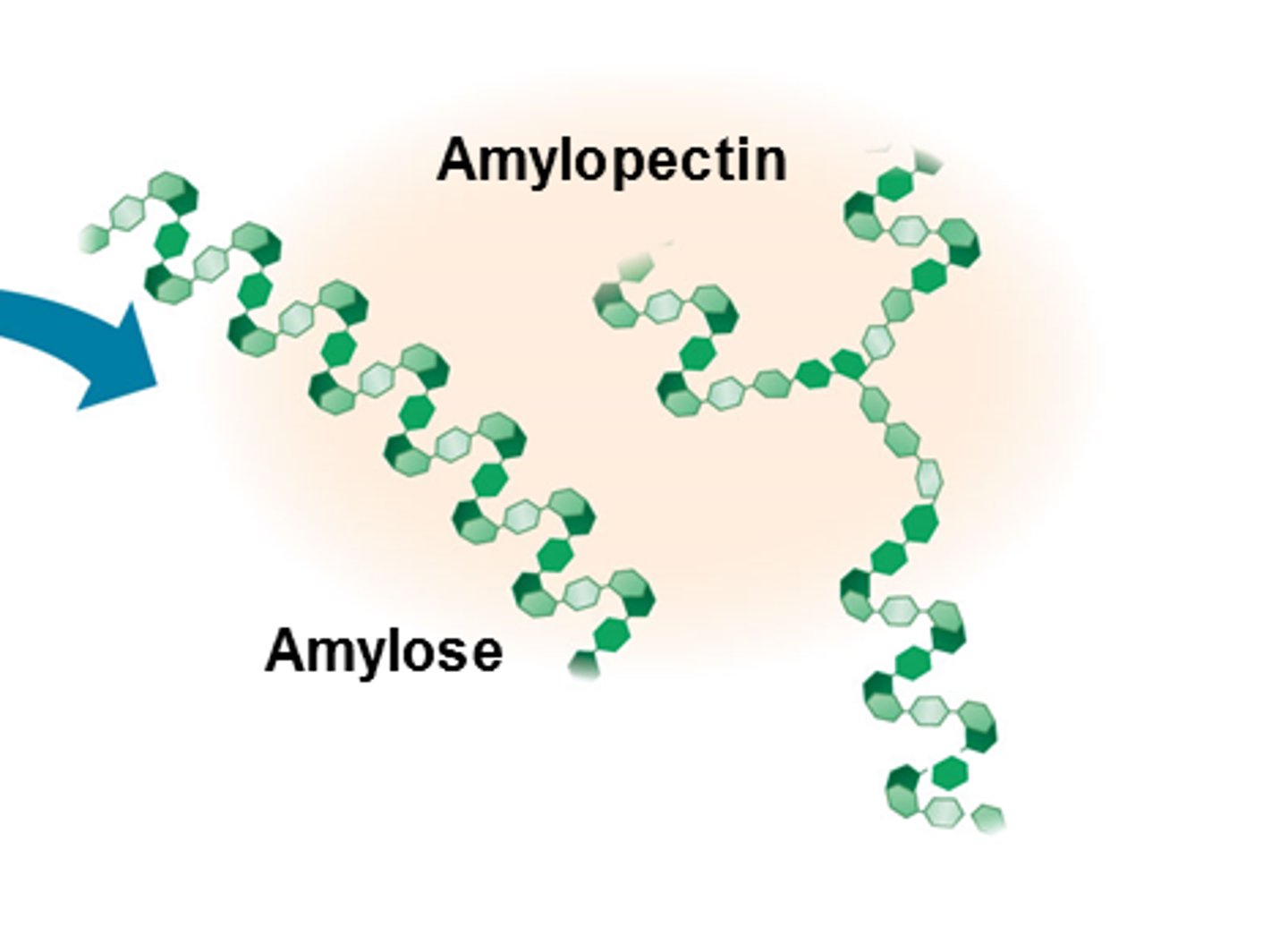
Differentiate between amylose and amylopectin
Amylose is a helix and amylopectin is branched
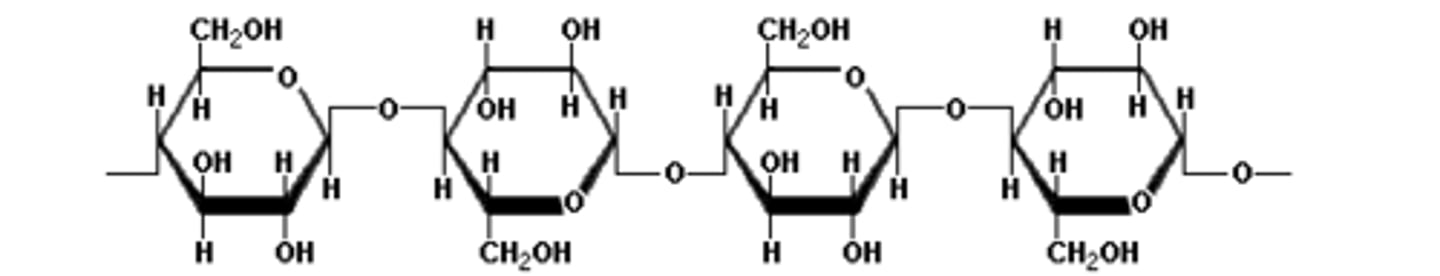
Describe the structure of beta-glucose monomers in cellulose
Glucose alternates up and down making it very strong
Glycoprotein
protein with glucose attached to it
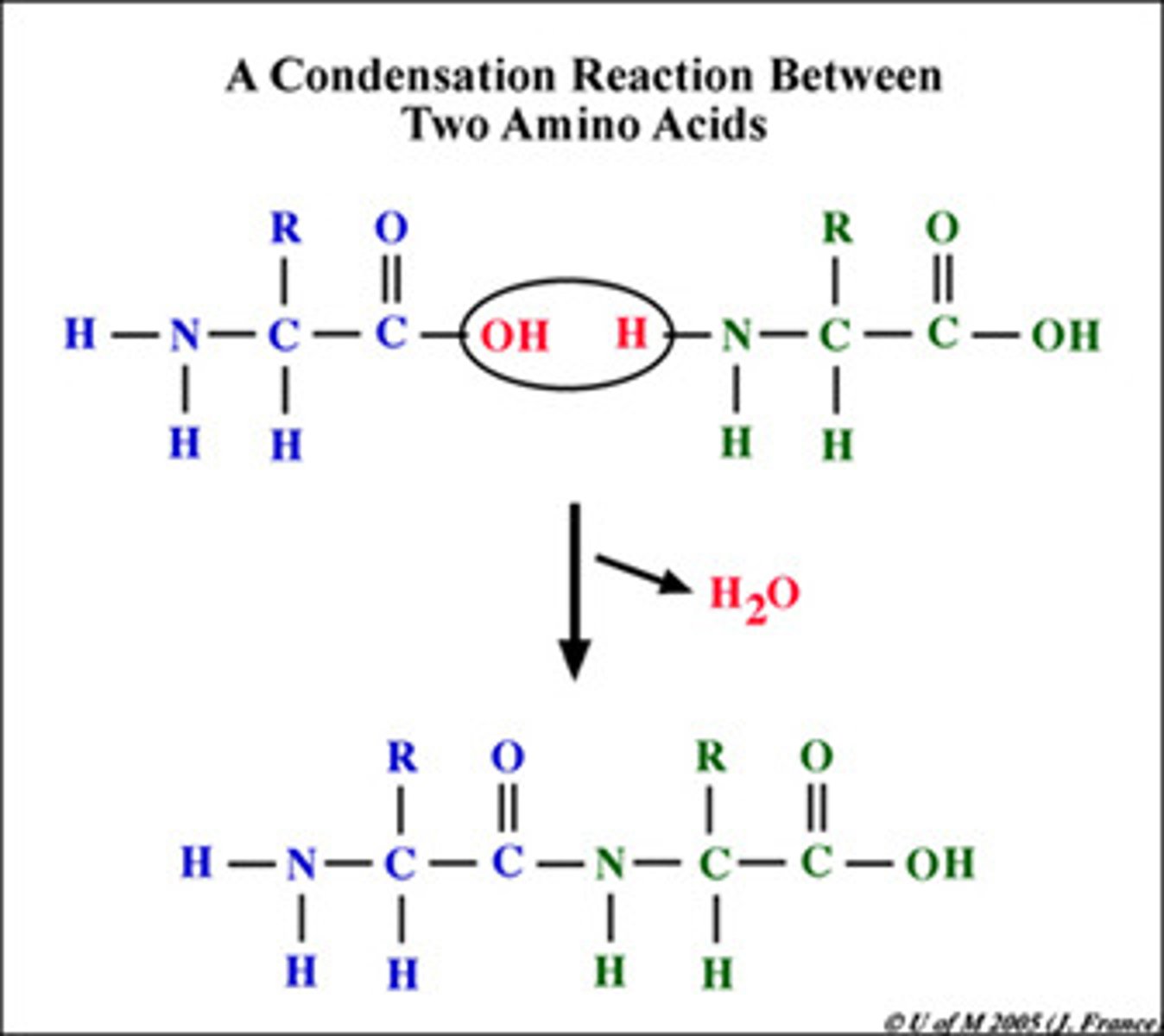
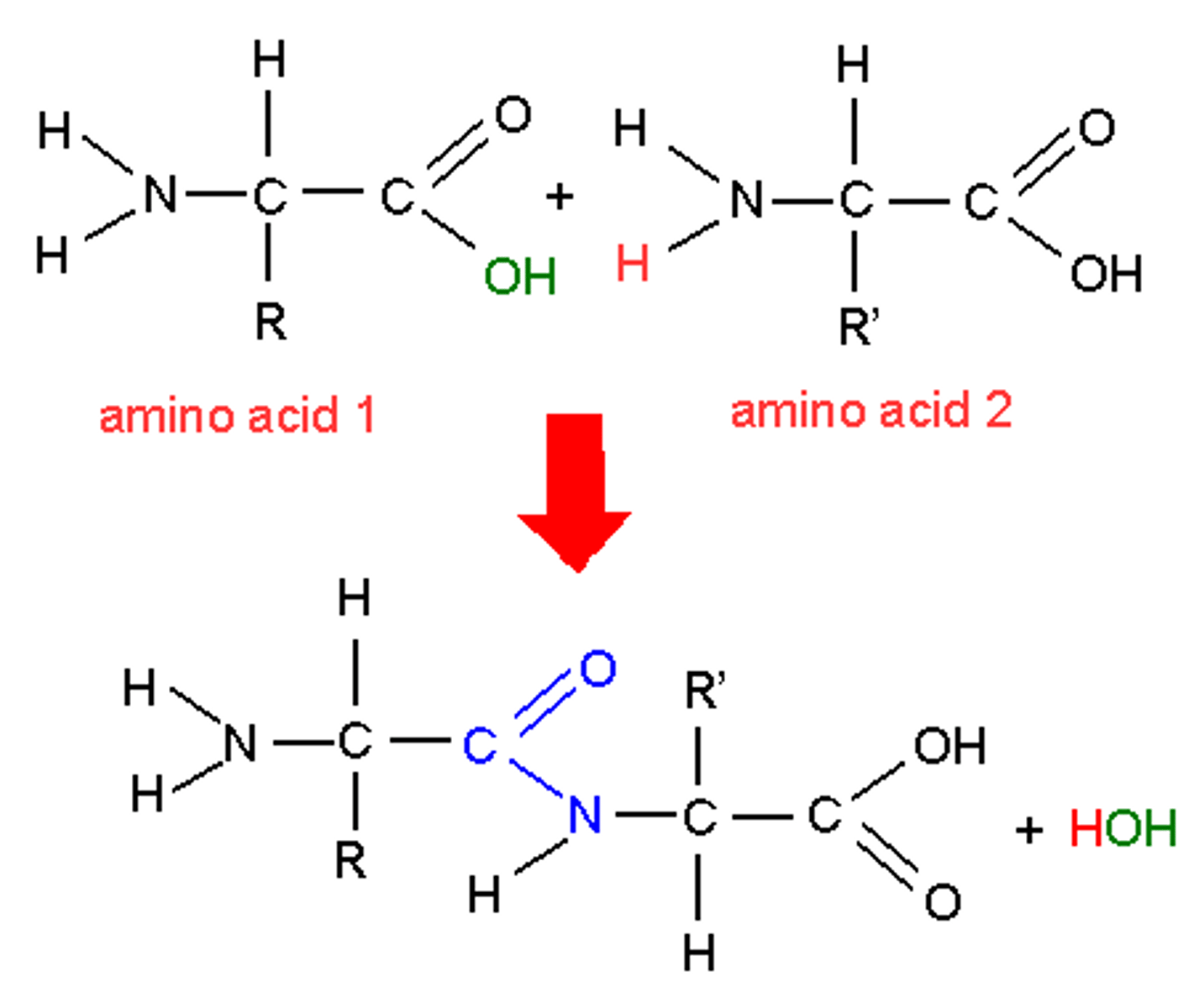
Briefly describe the process of the condensation reaction for amino acids
The forming of a water molecule when 2 amino acids form together
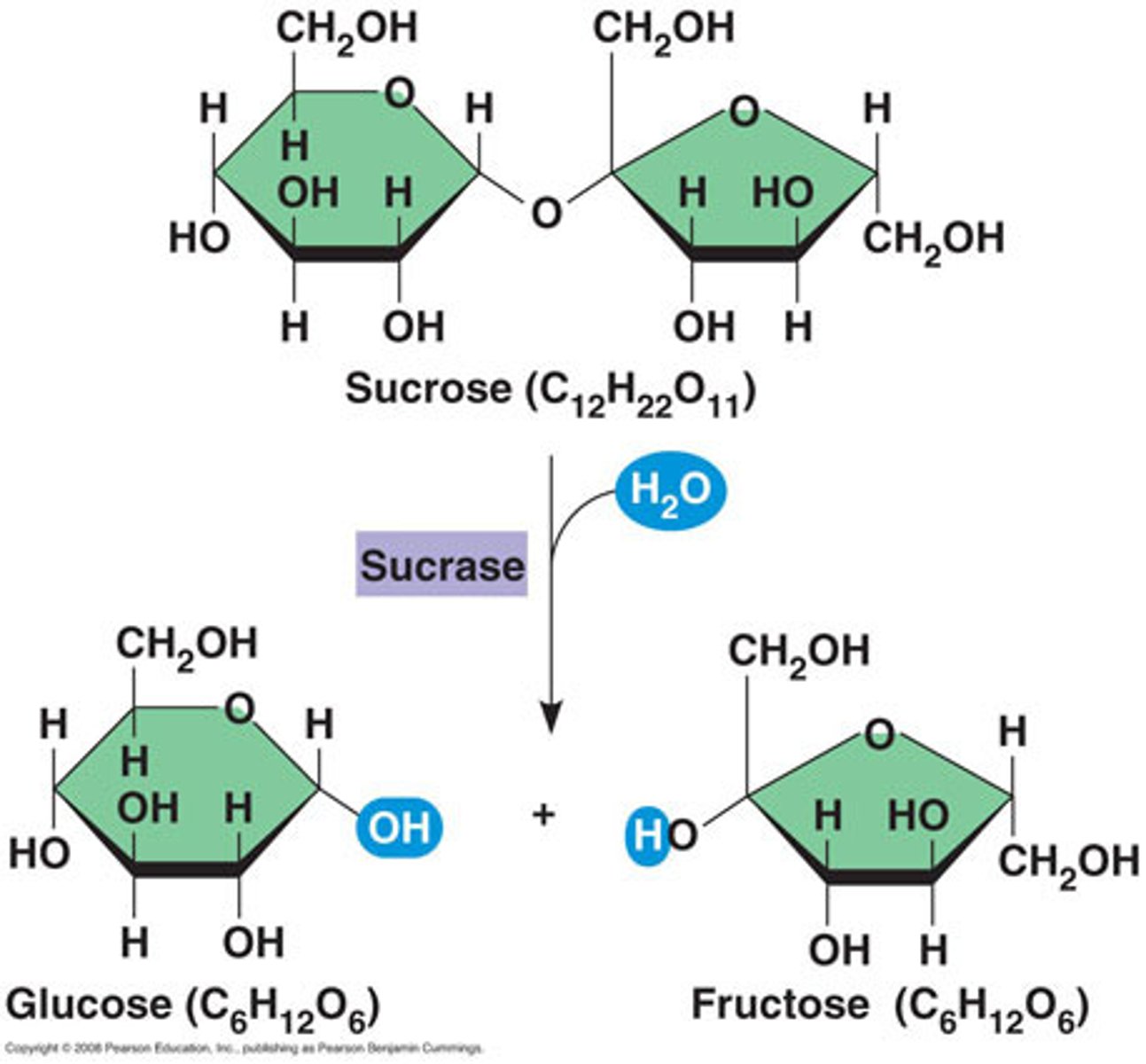
Briefly describe a hydrolysis reaction for amino acids
A water molecule is added to split two amino acids apart. The H joins to one and the OH to the other. The picture here shows hydrolysis of a disaccharide into two monosaccharides
Monounsaturated lipid has how many double bonds?
one double bond
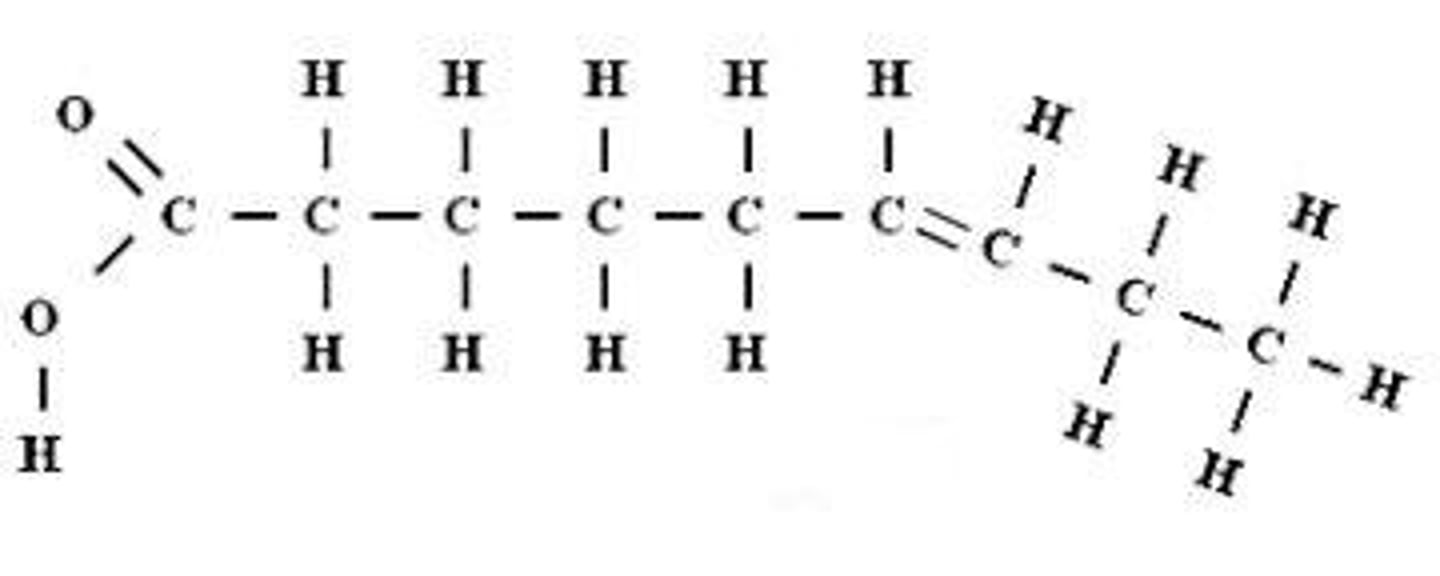
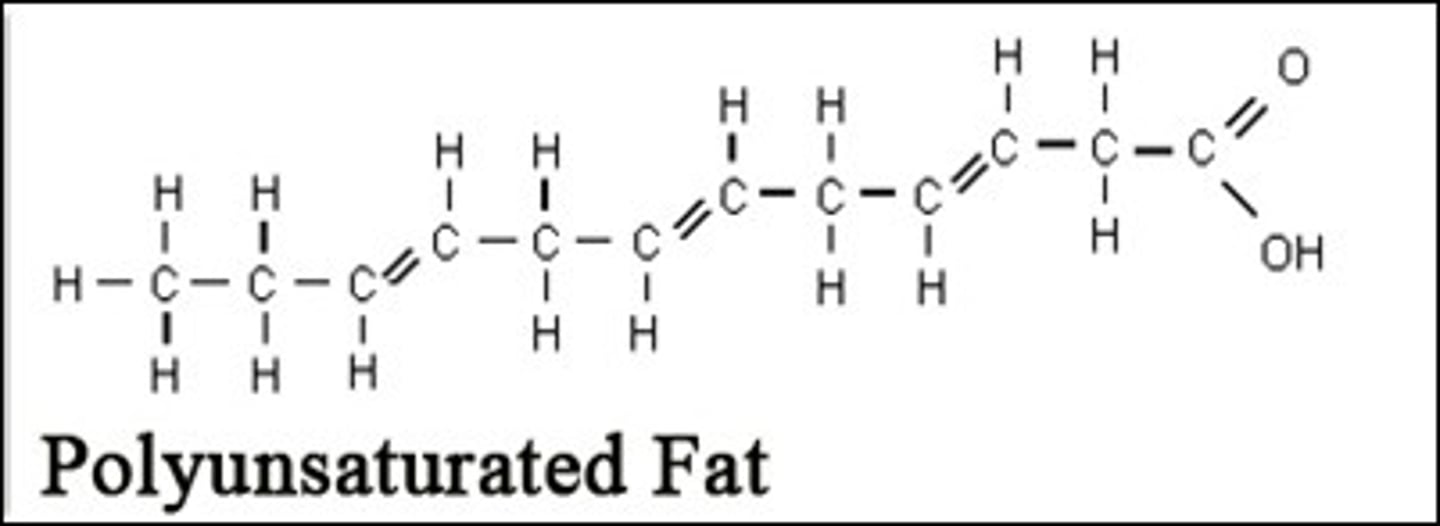
Polyunsaturated of an unsaturated fatty acid has how many double bonds?
many double bonds
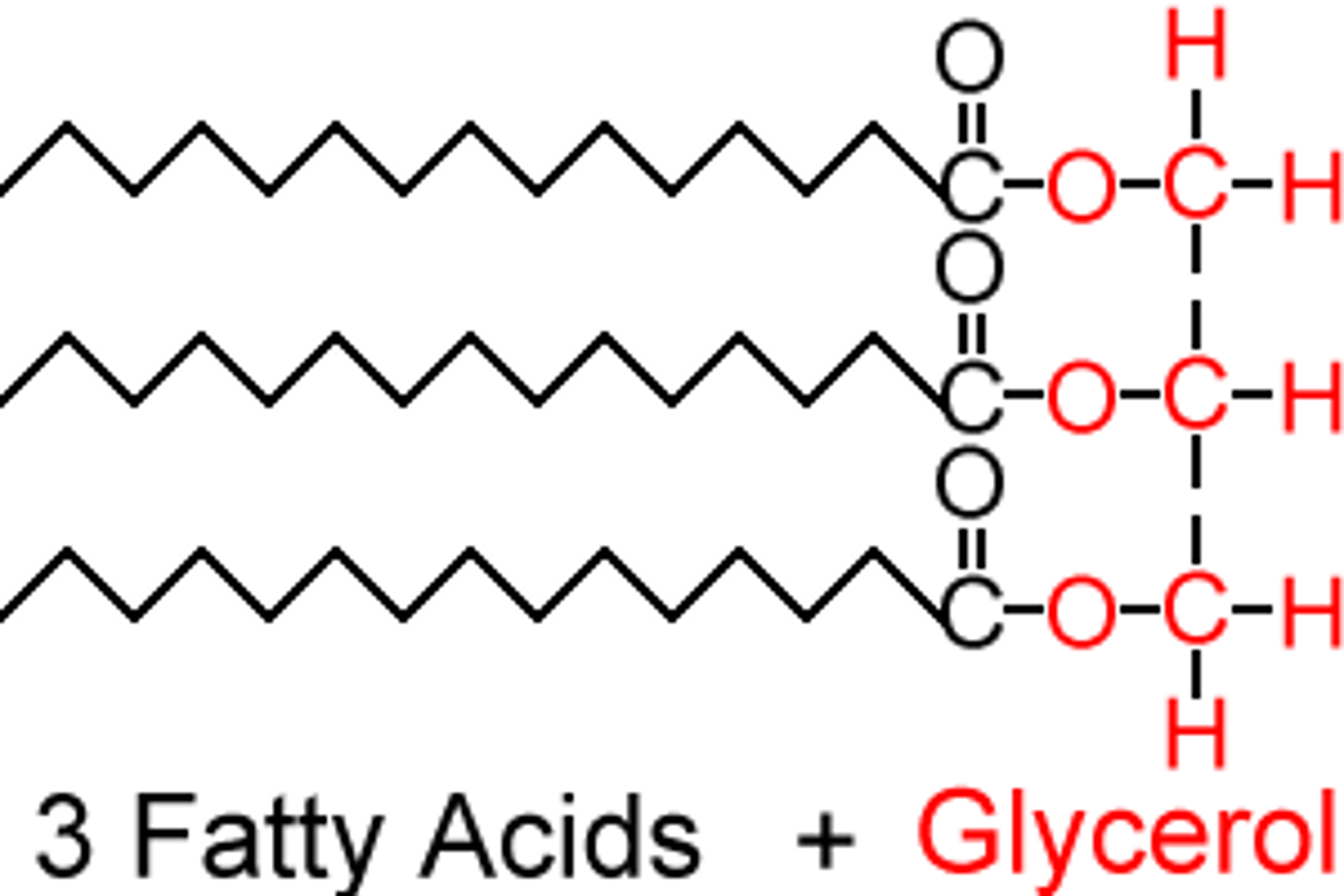
What is a triglyceride?
A triglyceride is 3 fatty acids joined together with glycerol
State three functions of lipids
Long term energy storage, heat insulation, structural component (phospholipid bilayer)
Define Amphipathic
part hydrophilic and part hydrophobic. Phospholipids in the cell membrane are amphipathic. They have a polar head and non-polar lipid tails.
Be able to recognize a steroid molecule
Cholesterol is a steroid molecule, and is technically a lipid
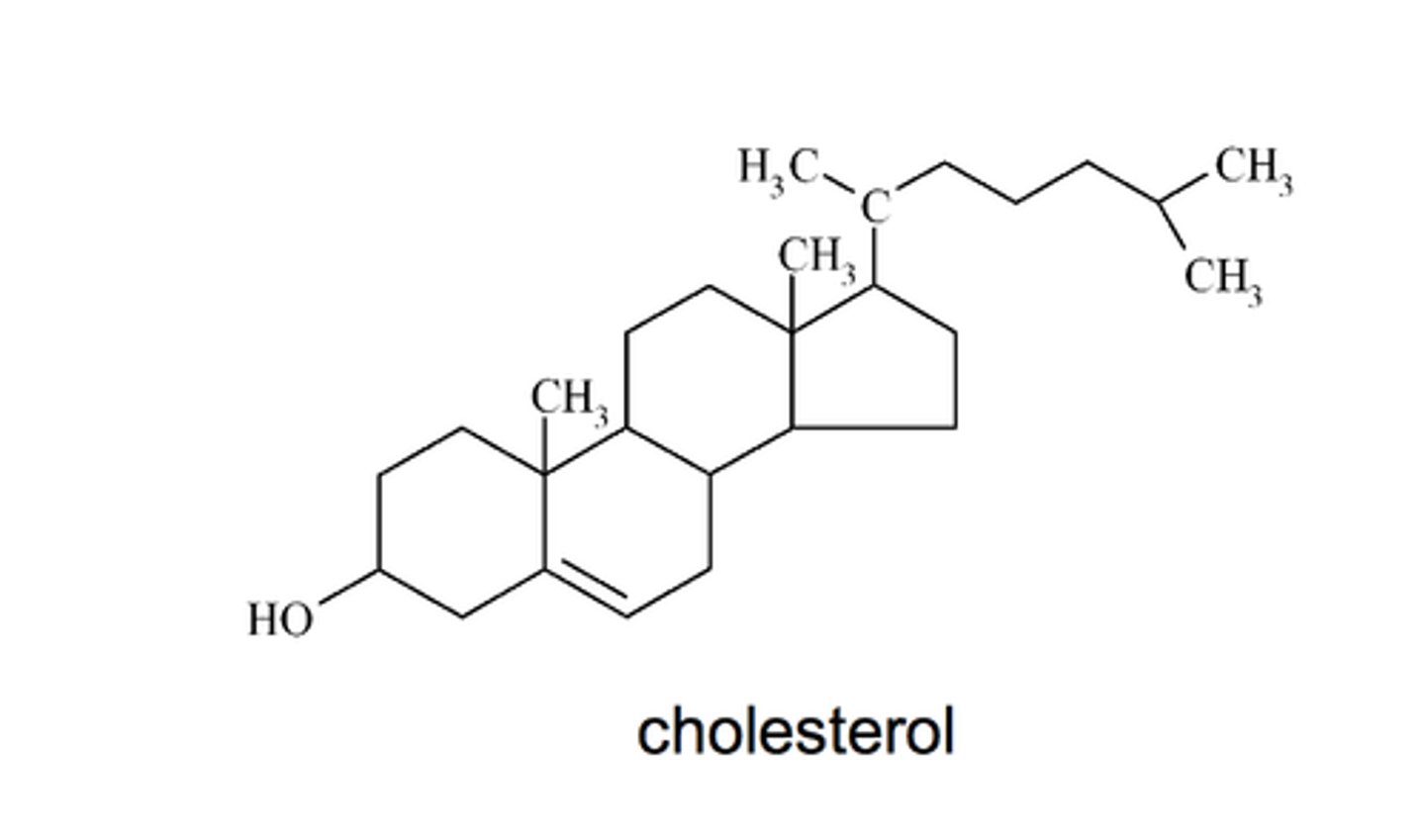
2 Examples of steroid molecules
testosterone and oestradiol and cholesterol
Steroids can pass through the cell membrane because they are H________
Steroids can pass through the cell membrane because they are Hydrophobic
Know how to draw an amino acid
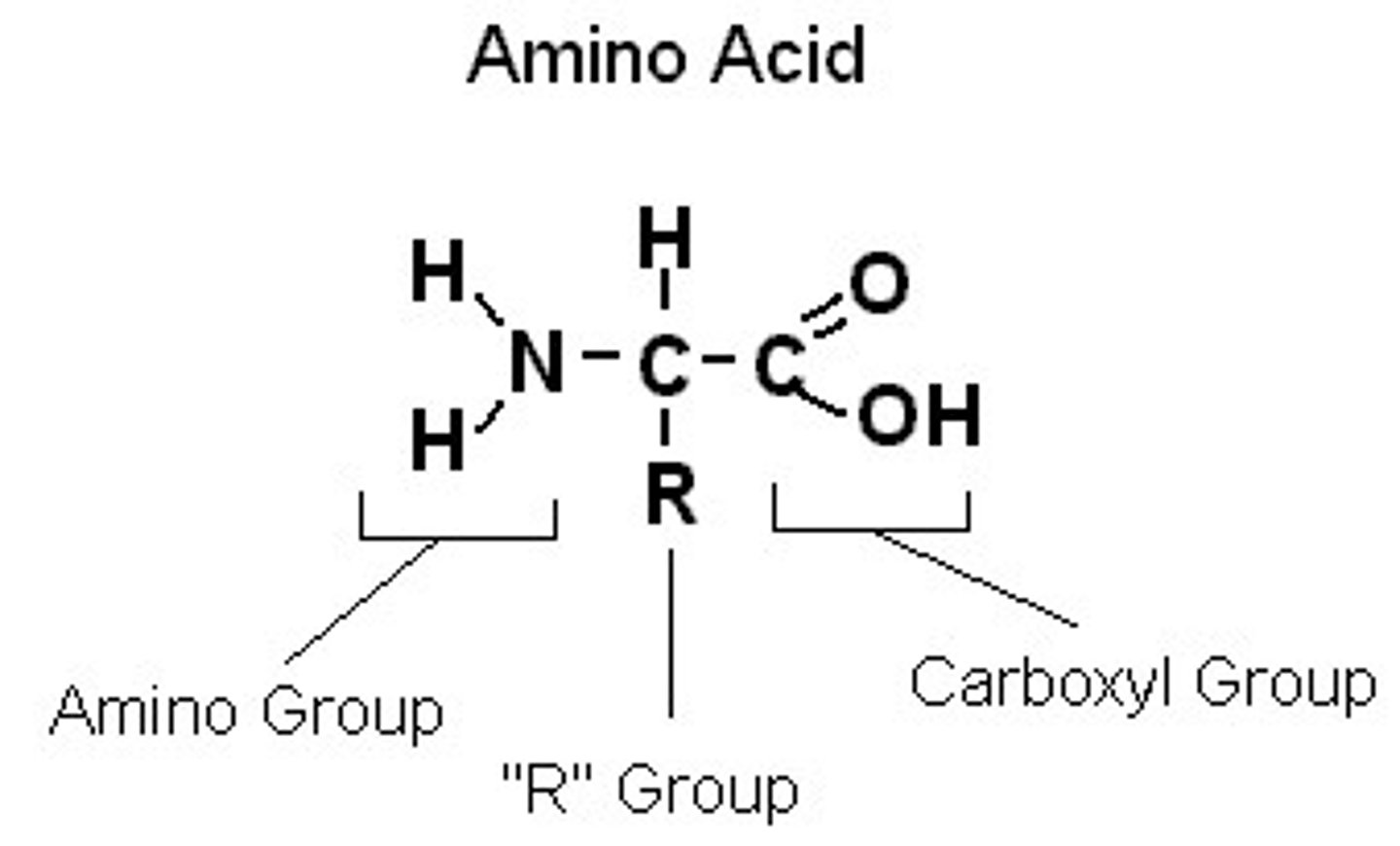
Draw a condensation reaction between 2 amino acids
Explain the difference between essential and non essential amino acids
Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized and must be obtained from food. Non-essential amino acids can be made from other amino acids.
There are _________ types of amino acids
There are 20 types of amino acids
What is a polypeptide?
Polypeptide means protein.
List 2 examples of polypeptides (proteins)
insulin regulates glucose, amylase breaks down starch
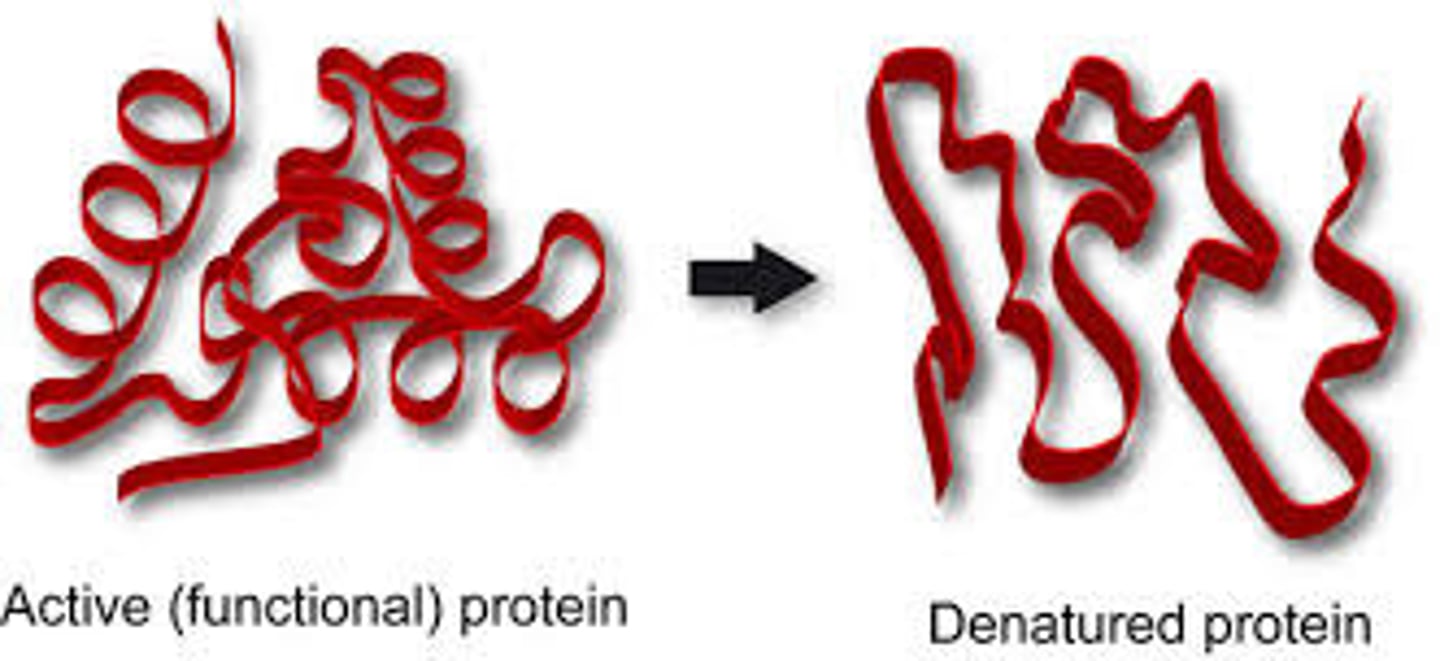
A protein that has been heated until it loses its natural shape has been
denatured (a denatured protein doesn't work any more because it isn't the right shape to fit with the substrate)
ENZYMES UNIT
ENZYMES UNIT
________ is the web of all the enzyme- catalyzed reactions in cell or organism
metabolism
Anabolism
two molecules being joined together
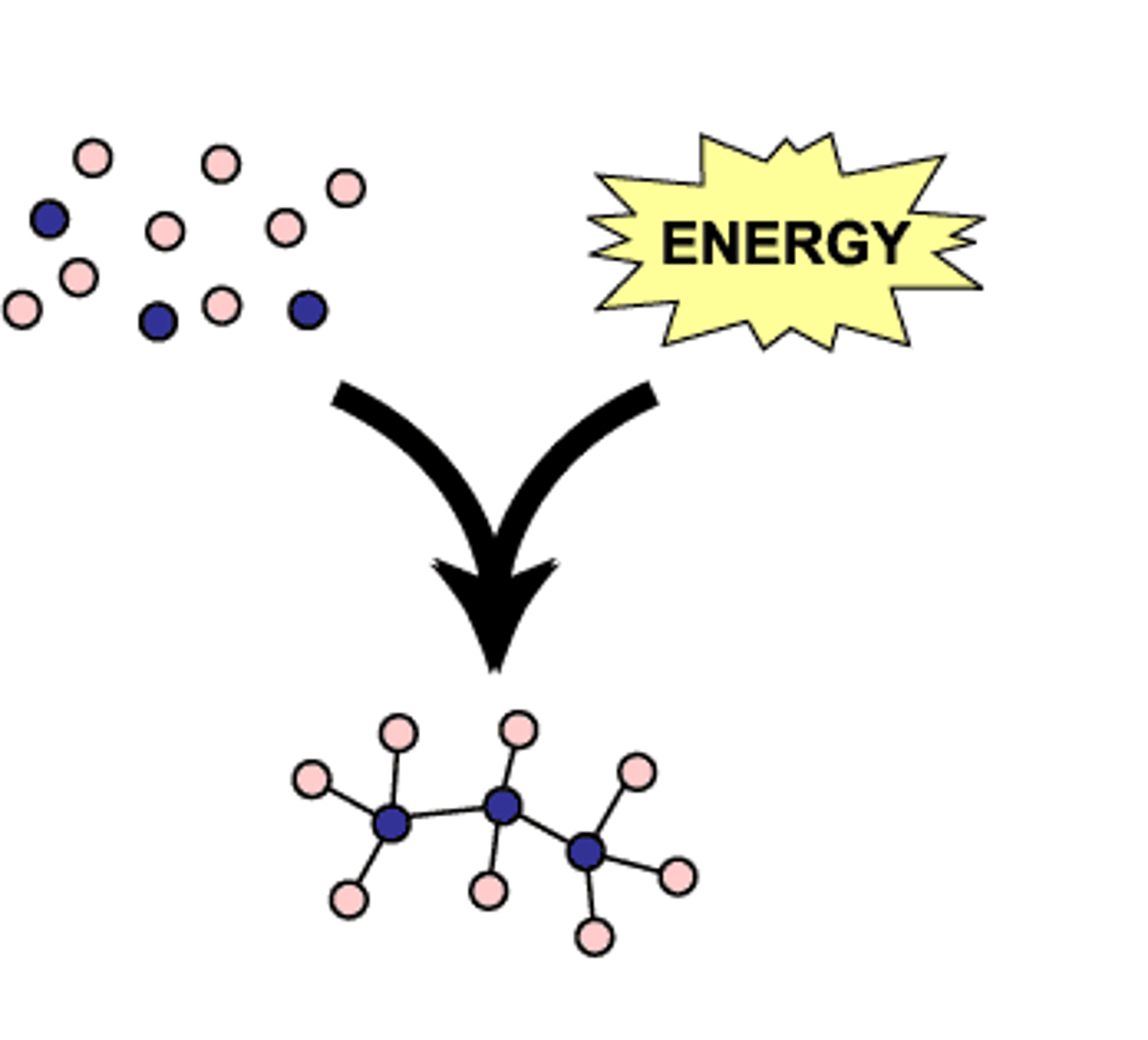
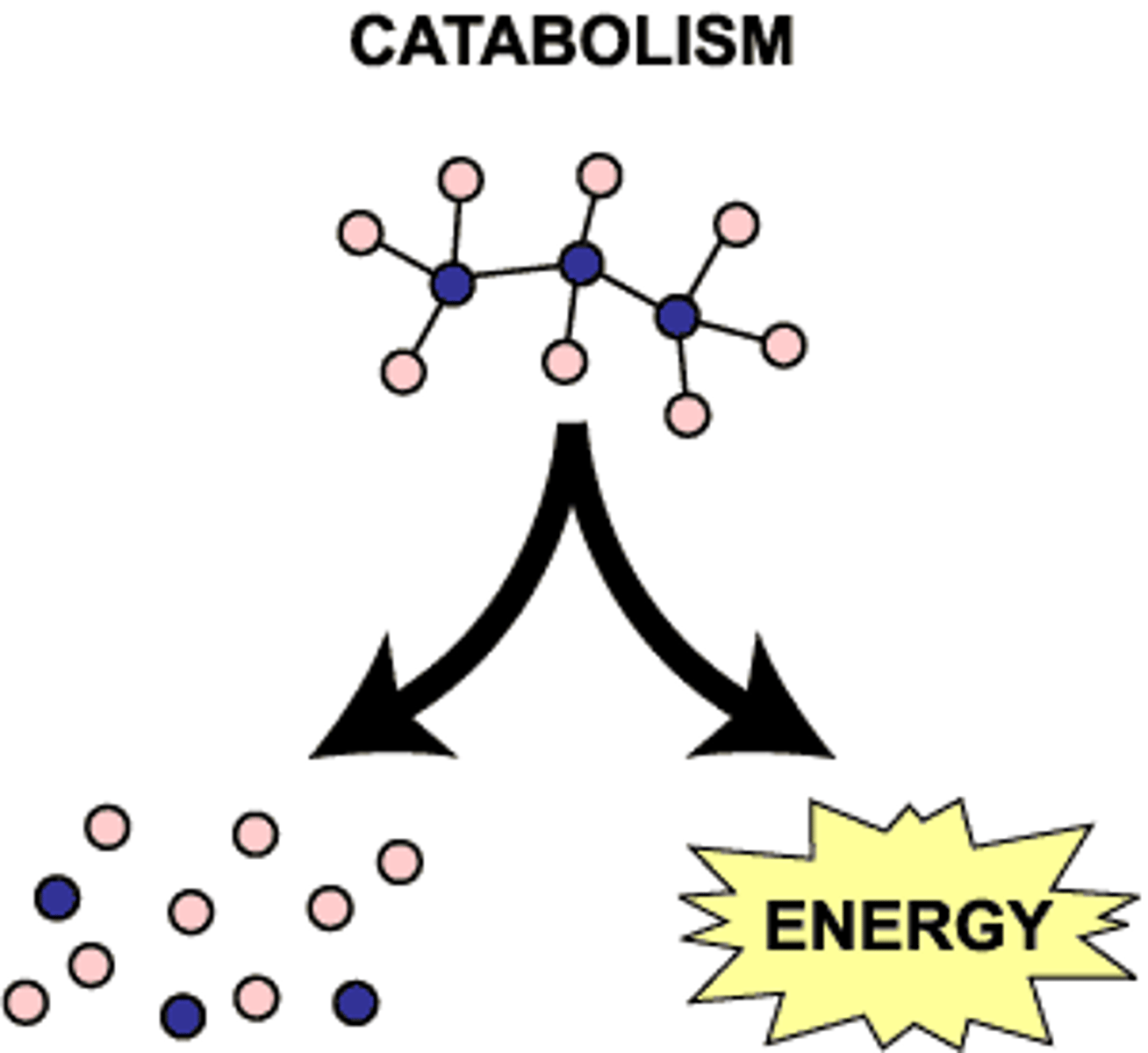
Catabolism
one molecule being split apart into two smaller molecules
Enzyme
A globular protein that performs a function
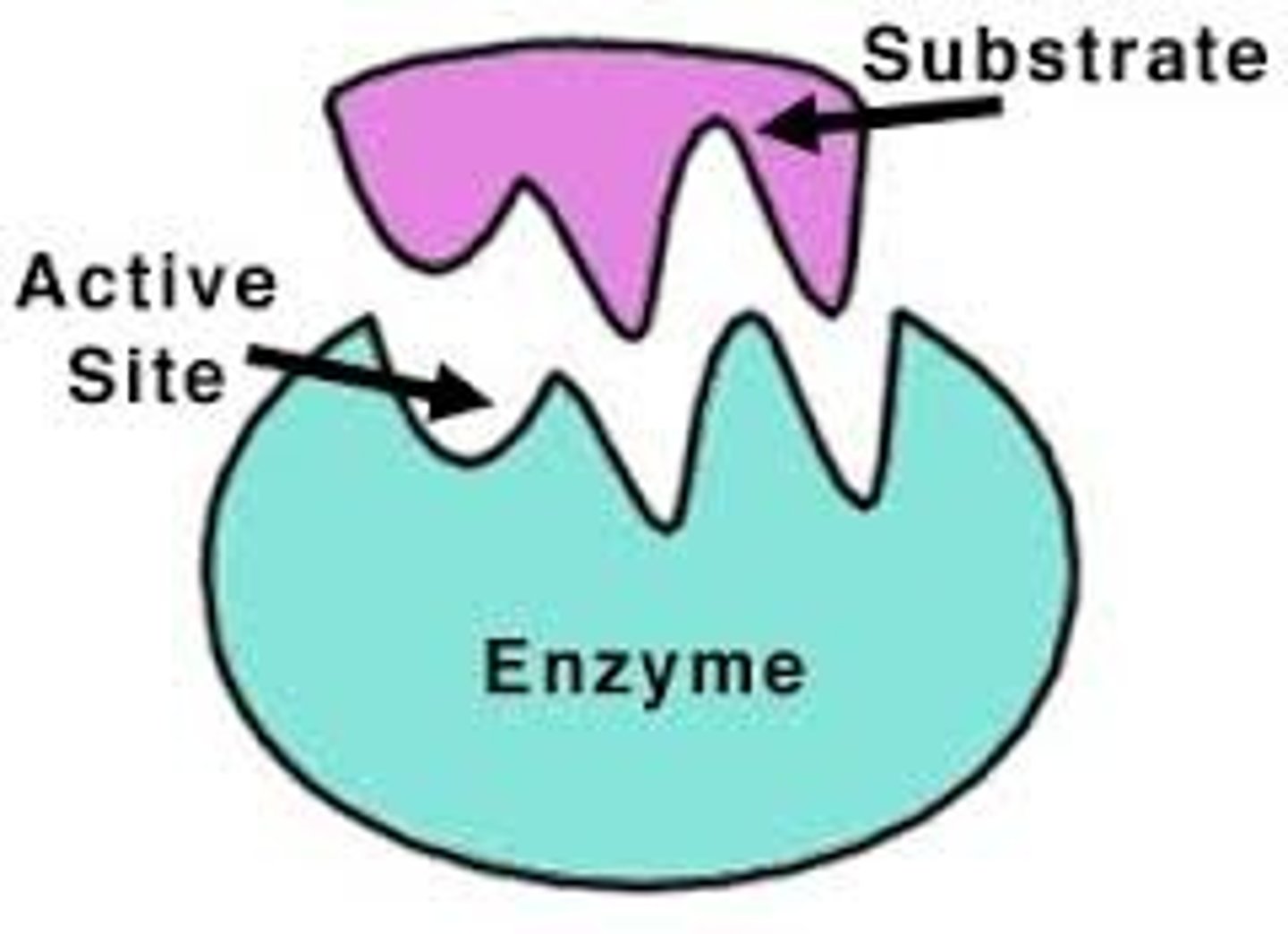
Substrate
The material that is altered by an enzyme
Active Site
The place on an enzyme where the substrate attaches
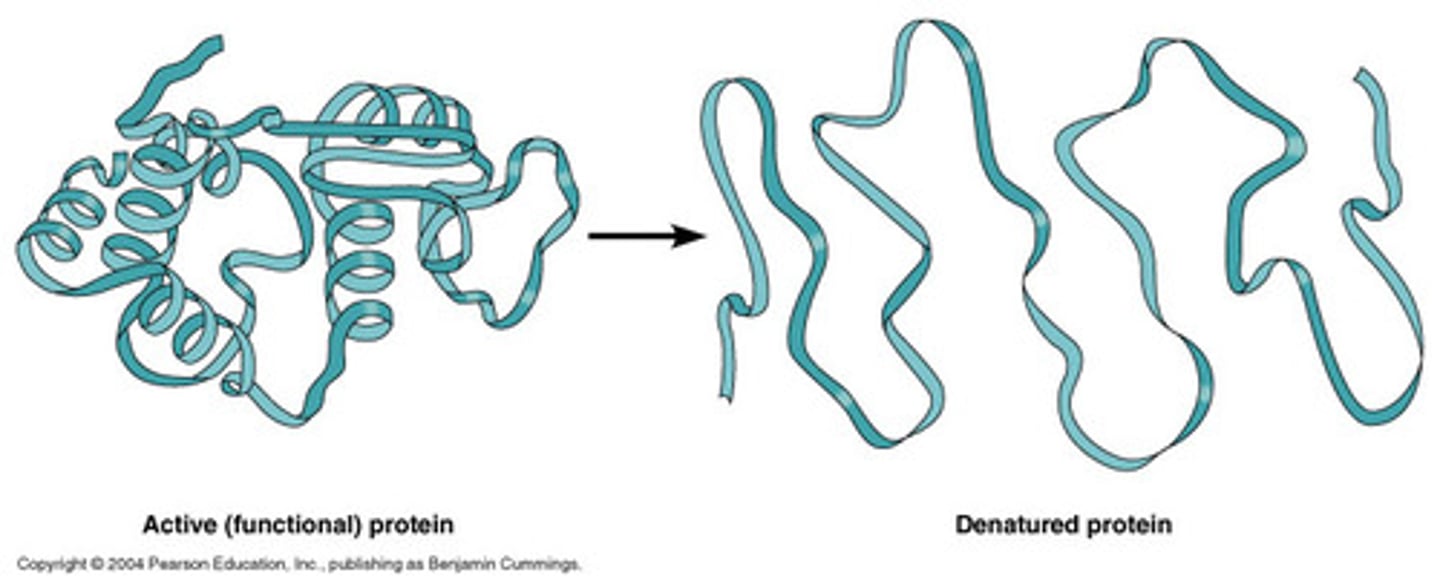
Denaturation
An enzyme's active site is damaged so it can no longer be used
Draw graph showing how enzyme activity is affected by temperature
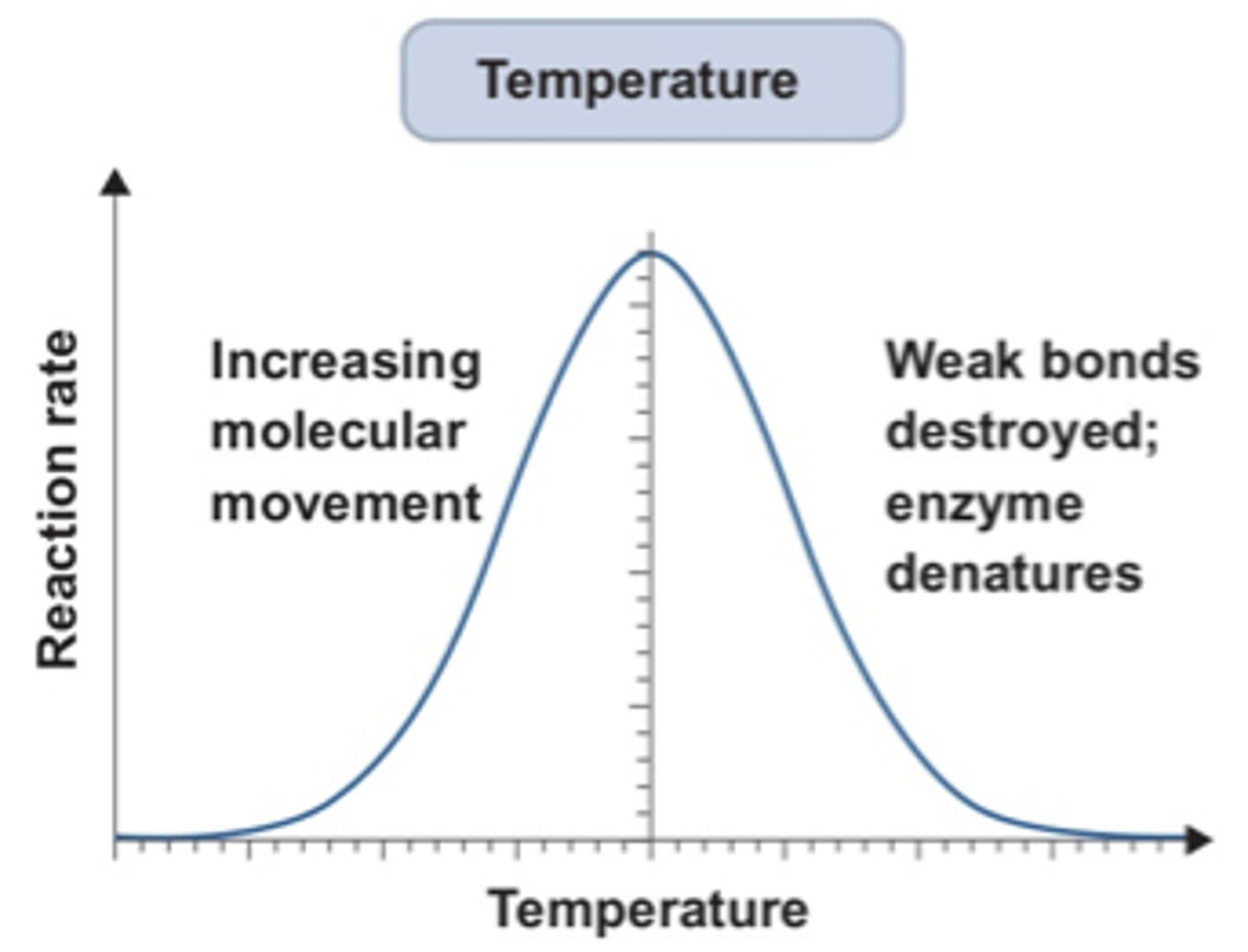
Draw graph showing how enzyme activity is affected by pH

What do extreme temperatures or pH do to proteins?
Extreme temperatures or pH will denature proteins
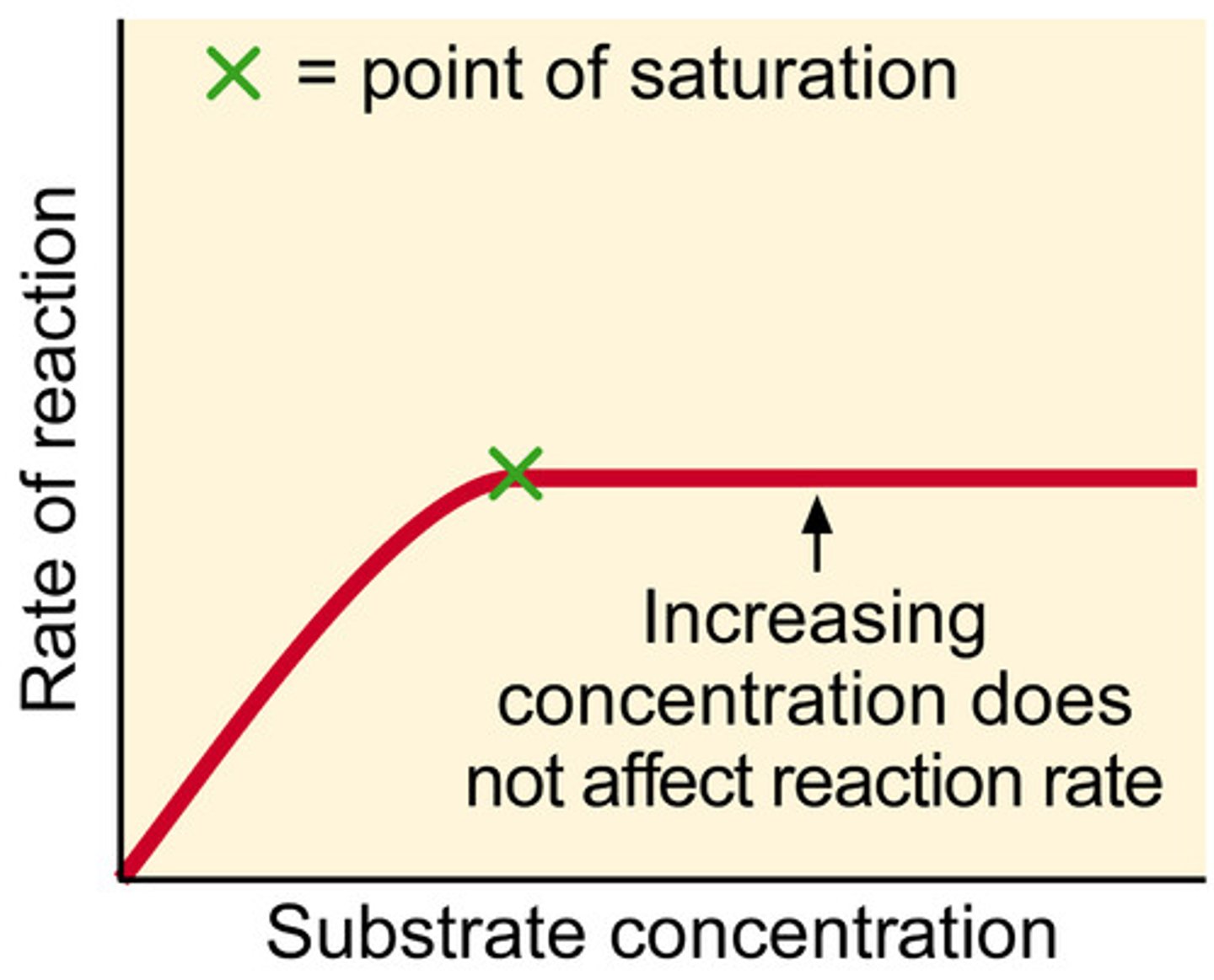
Draw graph showing how enzyme activity is affected by substrate concentration
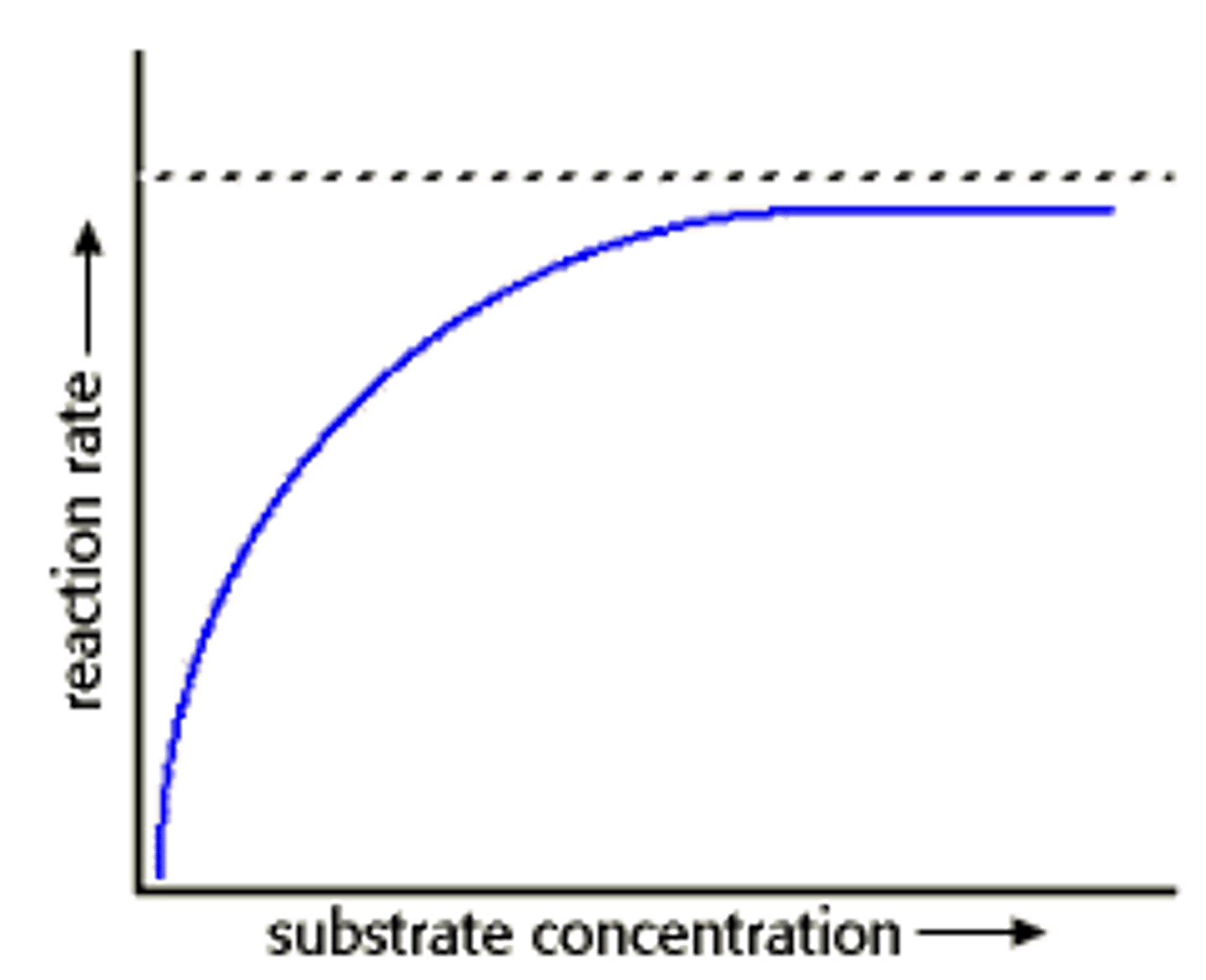
Why does the enzyme graph level off for increasing substrate concentration?
The graph levels off because all the active sites are already preoccupied with substrates and can't do any more
Independent variable
variable the scientist changes (if testing the effect of coca cola on plant growth, the independent variable is the type of liquid given to the plant)
Dependent variable
variable the scientist measures (if testing the effect of coca cola on plant growth, the dependent variable is the height of the plant)
Control group
the normal group (if testing the effect of coca cola on plant growth, the control group is the plant given water)
Be able to draw a graph showing the effect of enzymes on activation energy
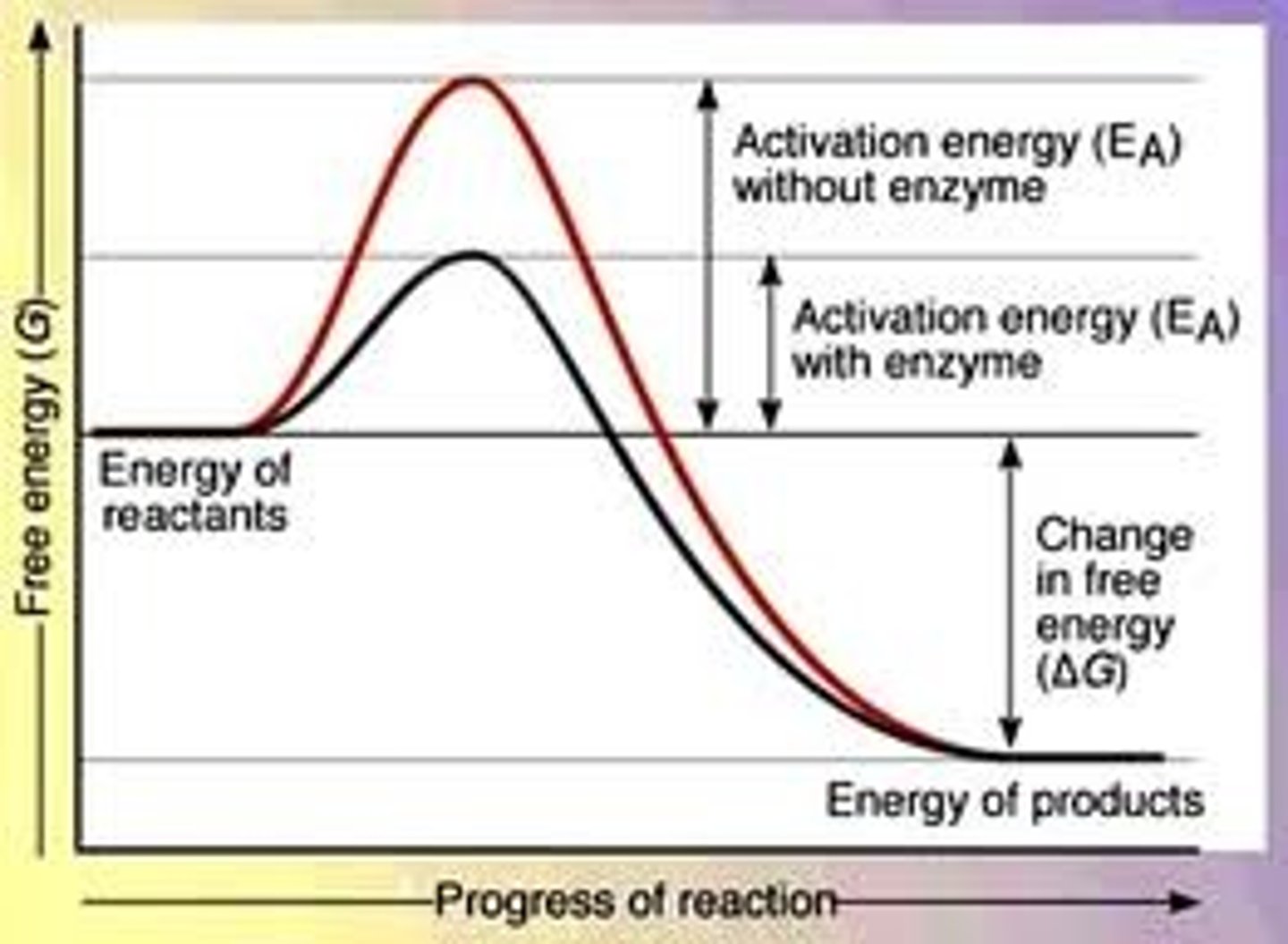
Name one enzyme and one substrate
amylase and starch, protease and amino acids, lipase and fatty acids
CELLS UNIT
CELLS UNIT
Name 3 aspects of cell theory
1. All living things are made of cells
2. The smallest unit of life is the cell
3. All cells come from other cells
be able to calculate magnification
magnification = observed value/labeled value The magnification should be a large number
know how to convert um to a decimal. 5 um = _______
5 um = .000005
What type of microscope has the highest resolution?
Electron microscope
Describe fluorescent stains in microscopy
Stains that glow and make it easier to see cell structures
Describe immunofluorescence in microscopy
antibody proteins stick to interesting molecules (antigens) and fluorescent stains then stick to the antibodies
Describe Freeze fracture electron microscopy
A cell is frozen, then split in two, and metal vapor makes an impression of it
Describe cryogenic electron microscopy
proteins are frozen under an electron microscope
Name three structures prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share
DNA, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm
Are bacteria prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Bacteria are prokaryotes (YOU are a eukaryote)
Draw a diagram of the ultrastucture of E. coli as an example of a prokaryote
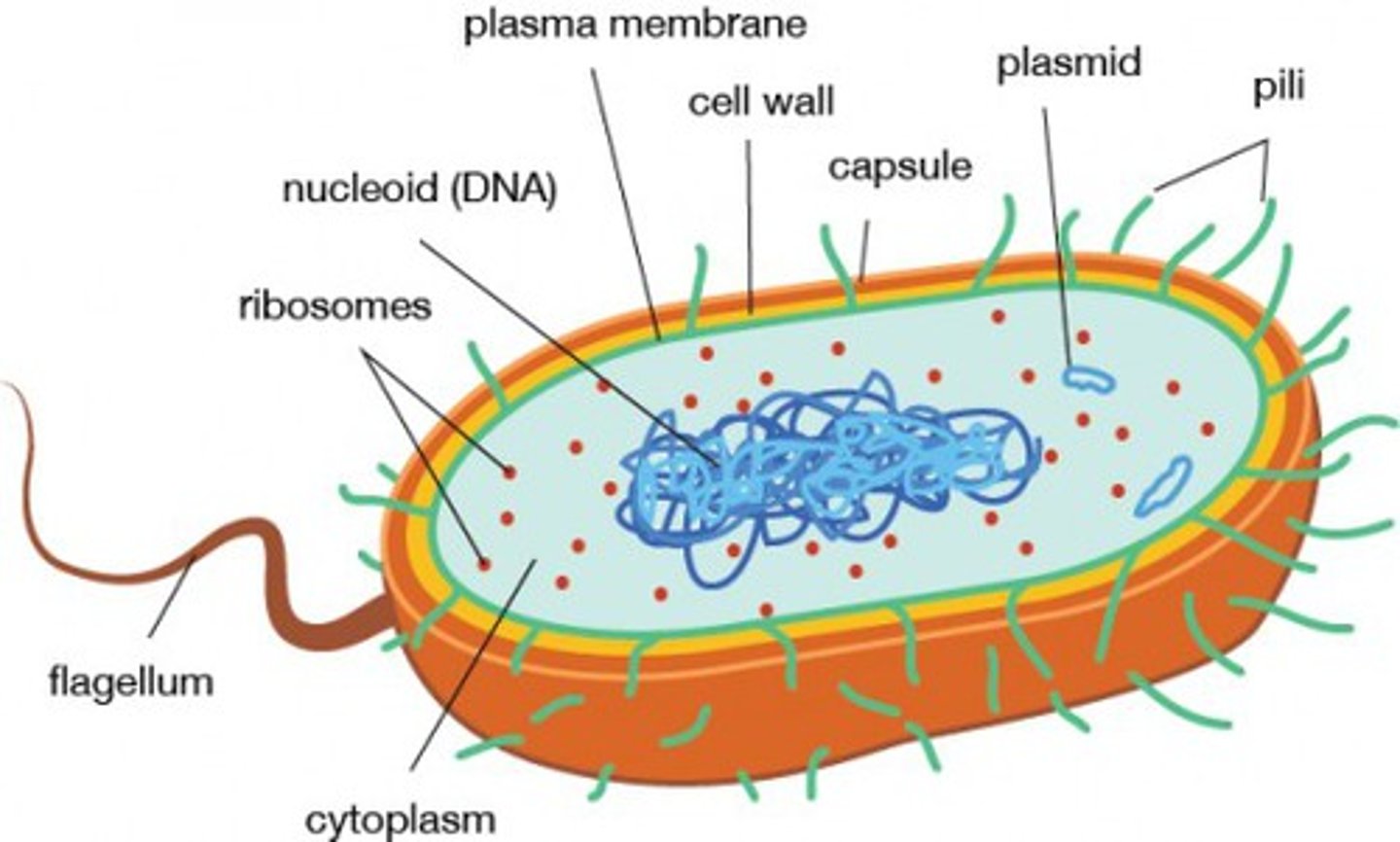
Cell membrane
controls what goes in and out of the cell
Nucleus
Contains DNA
Chromosomes
DNA
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
transport of proteins within the cell (has ribosomes on it that make it look rough)
Golgi
modify, sort, and ship proteins and lipids outside the cell
Lysosome
break down food/organelles
Mitochondrion
ATP formation, krebs and the ETC occur here
80s Ribosomes
location of protein synthesis
Chloroplast
capture solar energy for photosynthesis. Contains thylakoids and stroma
Vacuole and Vesicles
absorb/digest food, expel excess water. Storage
What is a vesicle and what does it do?
A vesicle is a small vacuole/bubble that is used to transport things within a cell. Vesicles leave the E.R. and go within the cell, and they leave the golgi to go out of the cell
Microtubules and centrioles
move chromosomes in cell division, centrioles are organelles that make the microtubles (tubes that form the cytoskeleton)
Cilia and Flagella
used for cell locomotion, cilia are hairlike, flagella are larger corkscrew shaped
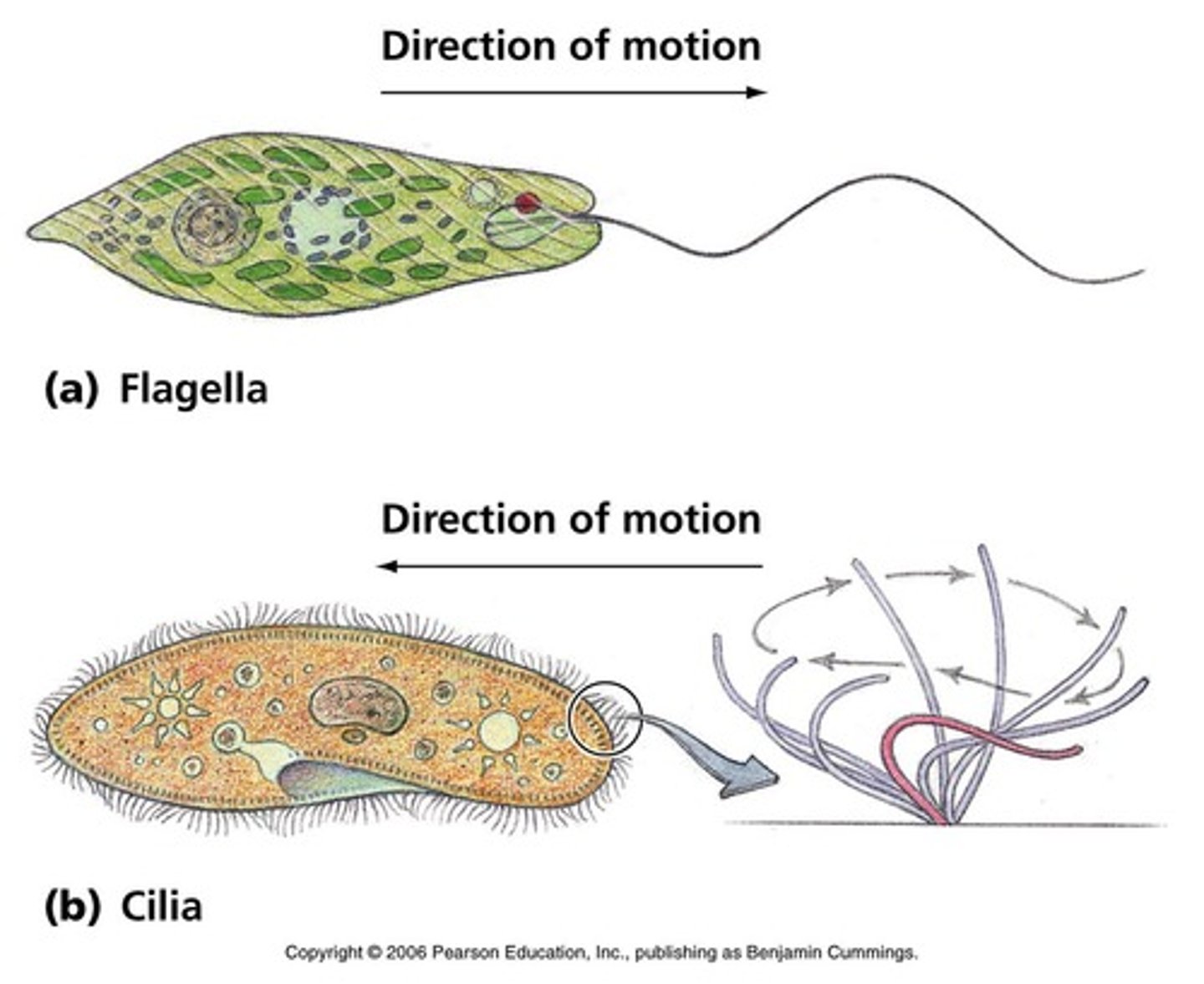
Name 3 things prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common
dna, ribosomes, cell membrane
Define Homeostasis
keeping condition inside the organism within tolerable limits
Give an example of homeostasis
maintaining the correct temperature by shivering or sweating
Define Metabolism
chemical reactions inside the cell
Define Nutrition
obtaining food to provide energy for growth
Define Excretion
getting rid of waste products of metabolism
Define Growth
an irreversible increase in size
Define Response
the ability to react to changes in environment
Define Reproduction
producing offspring either sexually or asexually
Name two things plant cells have which animal cells do not
Cell wall, chloroplasts
Give one example of a cell that goes against cell theory
muscle cell with multiple nuclei
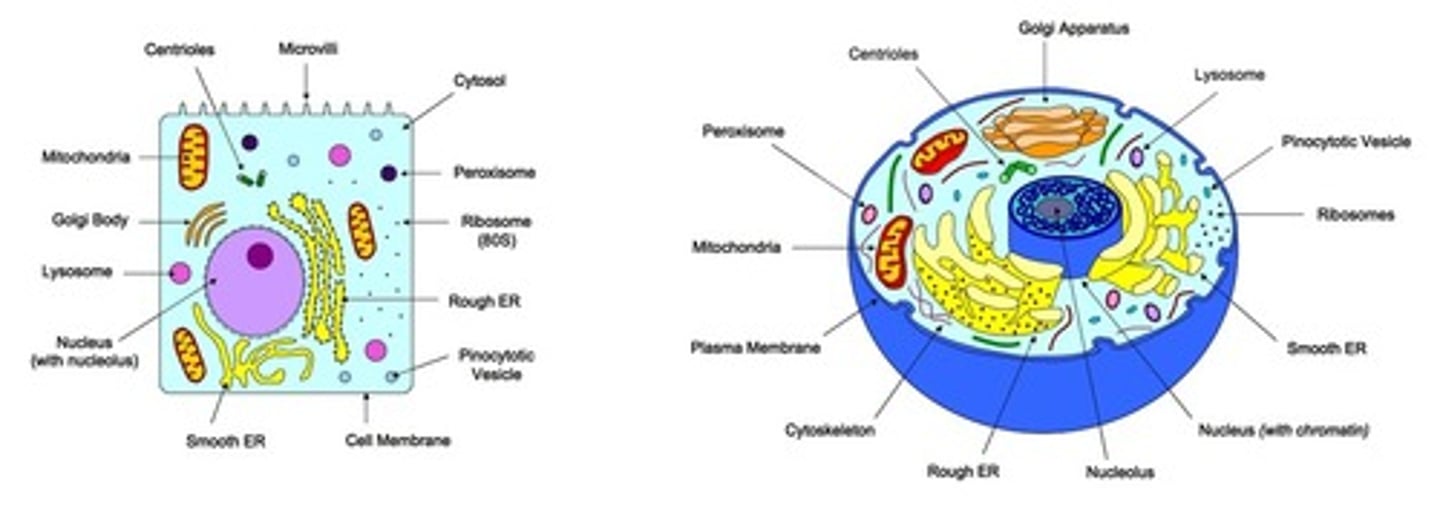
Draw a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell
Define Amphipathic
part hydrophilic and part hydrophobic. Phospholipids in the cell membrane are amphipathic. They have a polar head and non-polar lipid tails.
Define Hydrophilic
Attracted to water