Year 1 Physics Key Flashcards
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/75
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
1
New cards
What are SI units?
Base unit of all physical quantities
2
New cards
What is the SI Unit Acronym
SMACK A MOLE KELVIN
(second)(meter)(ampere)(candela)(kilogram) (Moles)
(Kelvin)
3
New cards
What is the SI Unit for Length
Metres
4
New cards
Whats is Electrical Current Measured In?
Amps
5
New cards
What is the SI unit used for Light intensity?
Candela
6
New cards
What is the SI Units for Mass?
Kilogram
7
New cards
What Quantity is Measured In Kelvin?
Temperature
8
New cards
what is Moles used to quantify
Amount of Substance
9
New cards
whats the SI unit of Force
Kg m s-2 since F = M x A
10
New cards
SI Units of Energy
Kg m2s-2
KE = ½ x Mass x Velocity
11
New cards
which power of 10 is Tera
1012
12
New cards
which power of 10 is Giga
109
13
New cards
which power of 10 is Mega
106
14
New cards
which power of 10 is Kilo
103
15
New cards
which power of 10 is Centi
10-2
16
New cards
which power of 10 is Milli
10-3
17
New cards
which power of 10 is Micro
10-6
18
New cards
which power of 10 is Nano
10-9
19
New cards
which power of 10 is Pico
10-12
20
New cards
which power of 10 is Femto
10-15
21
New cards
What is a Anomaly?
Anomaly is a data point or value in a set of results which does not fit the trend of the data.
22
New cards
Whats is a systematic error
An error which occurs due to faulty equipment or experimental method. systematic error causes the results to differ by the same amount each time making it predictable.
23
New cards
What are 2 ways of reducing random errors
take atleast 3 repeats and calculate a mean (this decreases anamolies)
use higher resolution equipment
24
New cards
How can a systematic error be reduced?
By calibrating the apparatus before use.
25
New cards
What is precision
precision is is how consistant/close together data is, in a data set.
26
New cards
what is repeatable experiment?
Repeatable - If the original experimenter can redo the experiment wit the same equipment and method and get the same results
27
New cards
What is a reproducible experiment
Reproducible - if the experiment can be redone by a different person or different technique and same results are found
28
New cards
What is resolution?
Resolution is the smallest change in the quantity being measured like for e.g on a ruler 1mm
29
New cards
What is absolute uncertainty?
Absolute uncertainty is a uncertainty given as a fixed quantity
30
New cards
How to calculate absolute uncertainty on analog?
Analog + half the smallest division for a single reading (e.g 0.5mm for ruler)
31
New cards
How to calculate absolute uncertainty on digital?
digital + the smallest increment (e.g smallest increment being 0.1 then it has + 0.1 uncertainty)
32
New cards
How to calculate precentage uncertainty?
(Absolute uncertainty ÷ measured value) x 100 = % Uncertainty
33
New cards
How can fractional and percentage uncertainty be reduced
by measuring larger quantities.
(for e.g a longer rope will have smaller percentage uncertainty )
34
New cards
Difference between reading and measurements.
Reading - is one value found
Measurement - difference between two readings found.
35
New cards
whats the rule of uncertainty with a range of values
to find uncertainty with a range of values you do ( Max - min ) / 2
result = Mean of range + uncertainty
36
New cards
What is the order of magnitude?
Powers of ten which are used to measure how big an object is.
37
New cards
What is a scalar quantity
A quantity which only has magnitude.
38
New cards
What is a vector Quantity?
Vector quantity has Magnitude and Direction
39
New cards
How is speed calculated
Speed = Distance / time
ms-1 = m / s
40
New cards
Define displacement
displacement of an object is the distance it has travelled in a certain direction.
41
New cards
What is velocity and what is the equation used to calculate velocity
Velocity is rate of change of displacement, or speed (Vector)
42
New cards
What is acceleration and how do you calculate it?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity (vector)
Acceleration(ms-2) = change in velocity / time
43
New cards
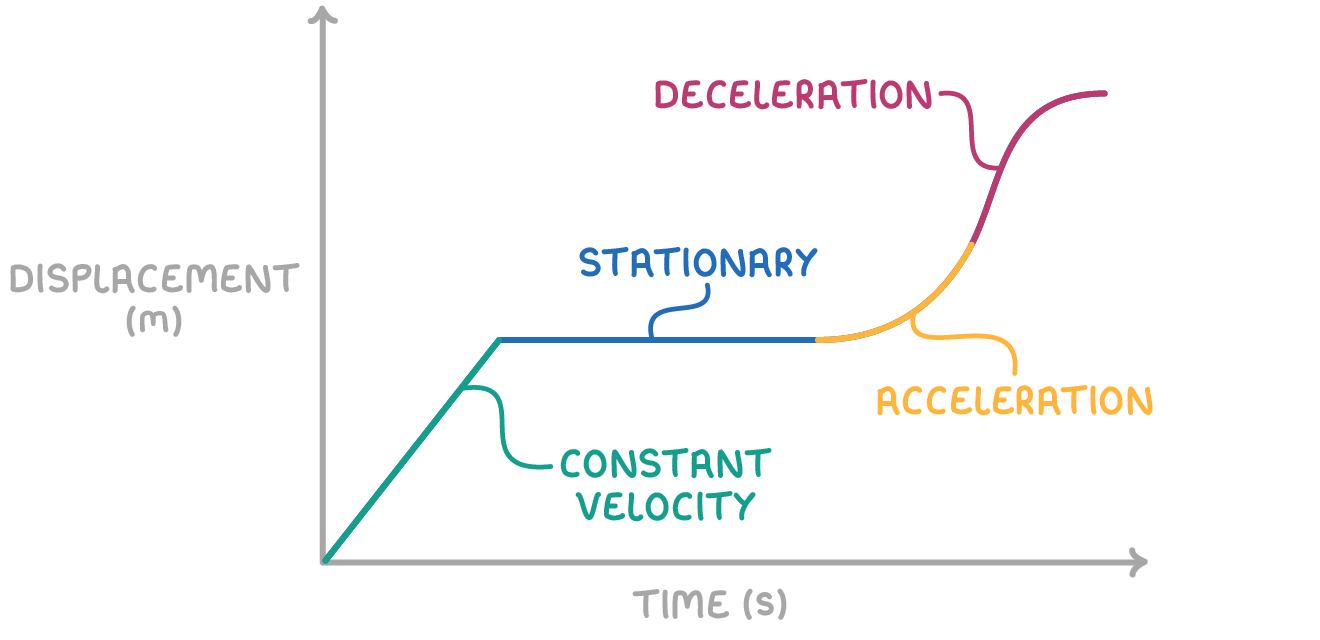
understand this graph
yeah
44
New cards
What does the area under a velocity-time graph represent?
Displacement
45
New cards
What does the area under an acceleration-time graph represent?
Velocity
46
New cards
How to determine g practical
1. Have an electro magnet hold steel ball suspended over 2 light gates, when
2.the ball is electronically released
3 ball passes through the first light gate it will start timer and when it passes the 2nd gate it stops the timer
4. and data logger will display time taken to pass through the gate.
5.repeat step 1-3 but with different amount of light gate distances.
we use the equation s = ut + ½ at2 (and you calculate a which is g)
47
New cards
a ball is projected off a castle at 6ms-1 how does its horizontal velocity change from it’s launch until it hits the ground?
Horizontal velocity will remain the same as there is no acceleration in horizontal direction
48
New cards
In projectile motion what is vertical acceleration?
The vertical acceleration is equal to the gravitational field strength(g)
49
New cards
give 3 examples of common forces and what they do?
1. Friction is the force that arises when 2 surfaces rub against each other
2. Drag the resistive force on an object travelling through a fluid (e.g water or air)
3. Upthrust - the upward buoyancy force acting on an object when an object is in fluid
50
New cards
What is terminal velocity?
When forces acting on falling object become balanced so resultant force is 0
51
New cards
What is the principle of moments?
for an object in equilibrium, the sum of the clockwise moment is the sum of anti clockwise movements
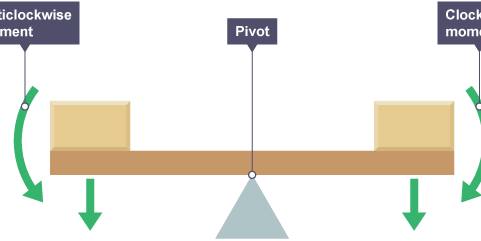
52
New cards
What is a moment?
a turning force:
force x perpendicular
(perpendicular distance from the point to the line of action of the force)
53
New cards
What is a couple?
A pair of equal and opposite forces which have same magnitude but opposite direction.
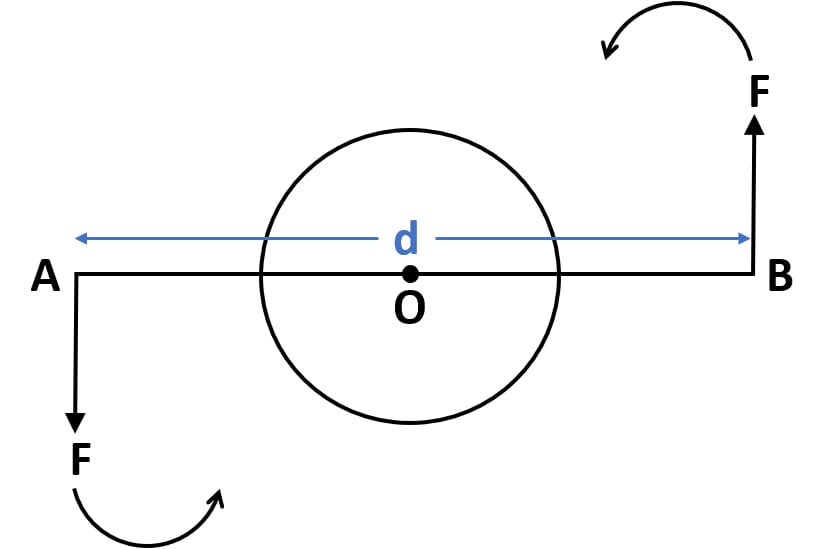
54
New cards
55
New cards
56
New cards
57
New cards
58
New cards
59
New cards
60
New cards
61
New cards
62
New cards
63
New cards
64
New cards
65
New cards
66
New cards
67
New cards
68
New cards
69
New cards
70
New cards
71
New cards
72
New cards
73
New cards
74
New cards
75
New cards
76
New cards