Gen Chem II - Chapter 11
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What does IMF stand for?
Intermolecular forces
What are intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are attractions between different molecules.
What do intermolecular forces do?
Intermolecular forces influence the rates at which substances will change states. ei. boiling point and rate of vaporization
What can we assume about the vapor pressure of a molecule with strong IMFs?
A molecule with strong intermolecular forces will have a lower vapor pressure because fewer of the molecules will be able to evaporate, due to strong forces, resulting in a low number of evaporated [gas] molecules. ei. low vapor pressure
![<p>A molecule with strong intermolecular forces will have a lower vapor pressure because fewer of the molecules will be able to evaporate, due to strong forces, resulting in a low number of evaporated [gas] molecules. ei. low vapor pressure</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/aa770436-caca-425e-86bd-5d15f5f4185c.png)
What can we assume about the boiling point of a molecule with strong IMFs?
A molecule with strong intermolecular forces will have a high boiling point. Strong intermolecular forces require more energy [heat] to be broken apart, therefore higher boiling point.
What is the definition of vapor pressure?
Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by vapor at equilibrium. (When the rate of condensation equals the rate of evaporation)
What factors effect vapor pressure?
Vapor pressure is affected by intermolecular forces, surface area, and temperature
How does temperature affect rate of evaporation?
Rate of evaporation increases as temperature increases
What does a stronger IMF indicate in terms of boiling point?
Stronger IMFs indicate higher boiling point
What do stronger IMFs indicate in terms of vapor pressure?
Stronger IMFs indicate lower vapor pressure
What is boiling point?
Boiling point is the point when the vapor pressure of a substance equals the atmospheric pressure
What is normal boiling point?
normal boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure equals 1.0 atm
What is a Phase Diagram?
A phase diagram is a diagram that illustrates the conditions (temperature and pressure) at which a substance reaches different states of matter.
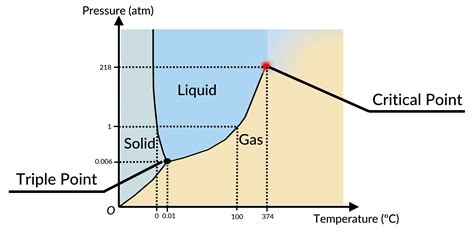
What are the important points on the phase diagram?
The important points on the phase diagram are the triple point and the critical point
What is the triple point on the phase diagram?
The triple point is the point at which a substance has the [temperature and pressure] conditions that allow it to be in either solid, liquid or gas state; All states of matter coexist
![<p>The triple point is the point at which a substance has the [temperature and pressure] conditions that allow it to be in either solid, liquid or gas state; All states of matter coexist</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/13352809-c7ef-4765-ad87-023d7414c56c.jpg)
What is the critical point on phase diagram?
The temperature beyond which gas no longer liquifies.
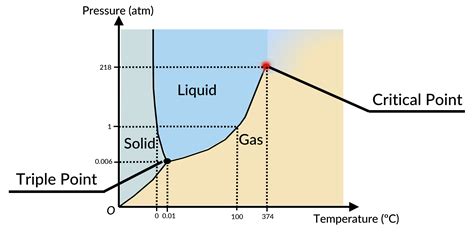
What is supercritical fluid?
Supercritical fluid is a gas-liquid hybrid that occurs when a substance is pressurized beyond the critical point; gas/water hybrid, make good solvents
What are the 3 main properties of liquids?
surface tension
viscosity
capillary action
What is surface tension?
Surface tension is the energy required to increase the surface area
How does IMF relate to surface tension?
Stronger IMF means stronger surface tension
What is viscosity?
The ability to flow; the measure of RESISTANCE to flow. Viscosity increases with temperature
What is capillary action?
Capillary action is the spontaneous rising of liquid in a small tube.
What are the two forces involved in capillary action?
Cohesive force: from IMF
Adhesive force: force with wall of the container
What kind of meniscus is formed when the cohesive forces are stronger than the adhesive force?
convex- cohesive: the IMFs between molecules
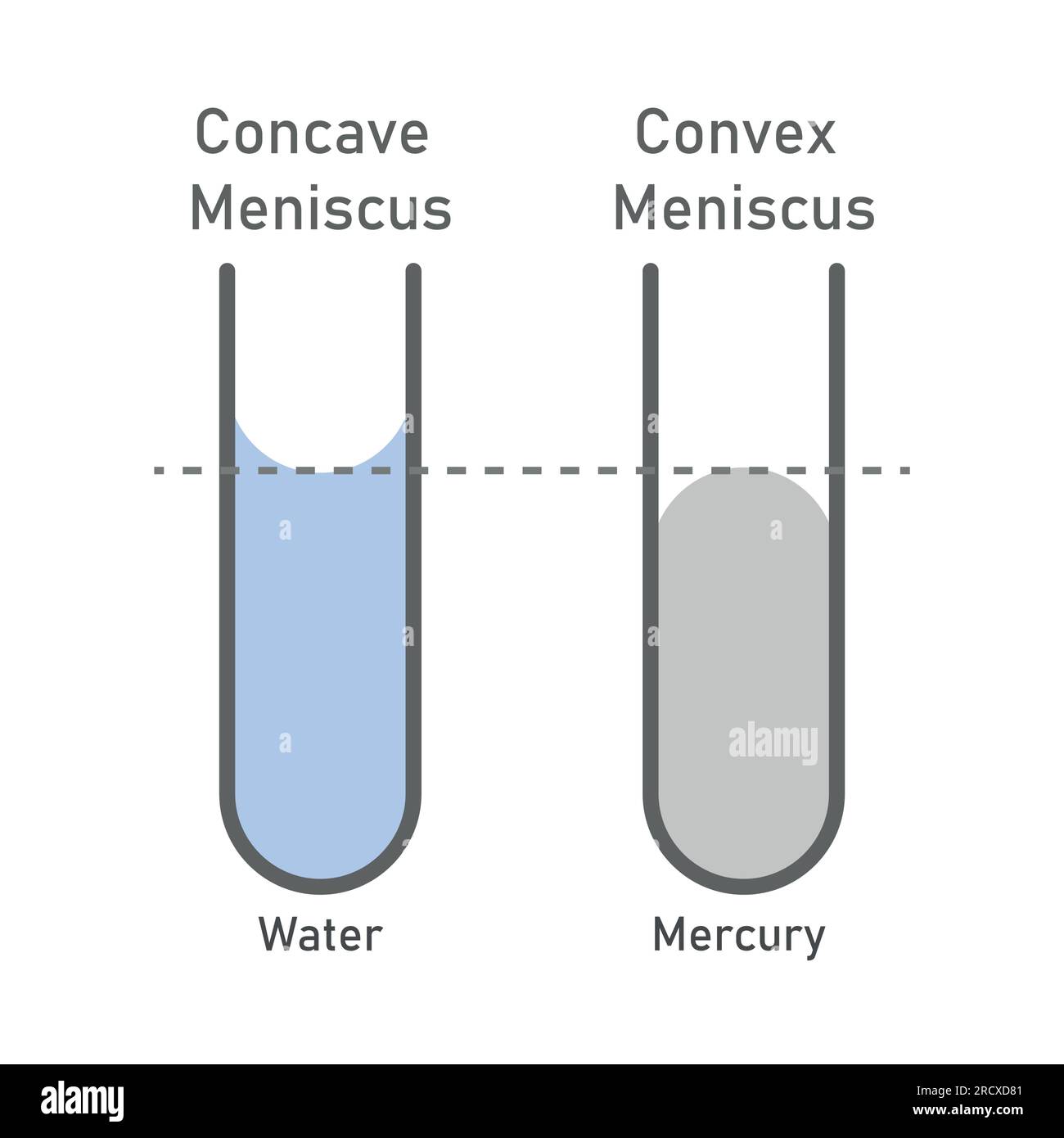
What kind of meniscus is formed when the adhesive forces are stronger than the capillary forces?
Concave- adhesive: binds the fluid the [walls] surroundings
What is a solution?
homogenous mixture of two or more components; an AQUEOUS solution is a solution where the solvent is water
What is a solute?
A solute is the element that gets dissolved
What is a solvent?
A solvent is the substance that is dissolved into
The phase of the solution ALWAYS matches the phase of the ____
solvent
What is solubility (S)?
Solubility (S) is the maximum amount of solute that dissolves in a fixed quantity of solvent at a particular temperature
g solute / 100g solvent
What is a saturated solution?
The solution is in dynamic equilibrium with the undissolved solid
What is an unsaturated solution?
Less solute than required to be saturated is added (not equilibrium)
What is a supersaturated solution?
A supersaturated solution occurs when more than the maximum amount of solute dissolves; semi stable state (coin analogy)
What is miscible?
two liquids that are soluble in all proportions
-ex. ethanol + water
What is immiscible?
Two liquids that do not form a solution
-ex. oil and water
What is solvation?
Clustering of solvent particles around solute particles
occurs as it dissolves
What is hydration?
Hydration is solvation that occurs in water
What is an electrolyte?
an electrolyte is a substance that fully ionizes [forms ions] when it dissolves
What is a non electrolyte?
Non electrolytes do not form ions when dissolved
What is volatile?
Volatile means that a substance easily evaporates.
ei. volatility- the ability to evaporate easily
What is entropy?
disorder/chaos
What are the types of IMFs present in solutions?
d-d
h-bond
london dispersion forces
ion-dipole
ion-induced dipole
dipole- induced dipole
What is an ion-dipole force?
Salt dissolved in water
What is energetics?
Energetics is the energy needed for a solution to form
What kind of [energetics] reaction is endothermic?
breaking bonds between the solvent
breaking bonds between the solute
What kind of [energetics] reaction is exothermic?
forming the bond between the solute and the solvent; exothermic reactions are FAVORABLE. Endothermic reactions do occur, driven by entropy
What is a dilute solution?
Little solute is dissolved
What is a concentrated solution?
lots of solute is dissolved
What are the different units of concentration?
Molarity (M)
Molality (m)
Mass %
Parts per Million (ppm)
Parts per Billion (ppb)
Mole fraction (χ)
Volume %
Molarity (M)
M= mol solute/ L solution
Molality (m)
m= mol solute / kg solvent
Mass %
(mass solute / mass solution) x 100%
Parts per Million (ppm)
ppm = (mass solute/ mass solution) x 10^6
Parts per Billion (ppb)
ppb= (mass solute / mass solution) x 10^9
Mole fraction, χ
does not have a unit
χa = na / nt
Volume %
(Volume solute / Volume solution ) x 100%