PSC 041 - UC Davis Unit 2
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
types of variable relationships
positive linear, negative linear, no relationship
how can you tell if a variable is continuous/categorical
continuous predictor variable will be an AVERAGE
categorical predictor variable will be a PERCENT
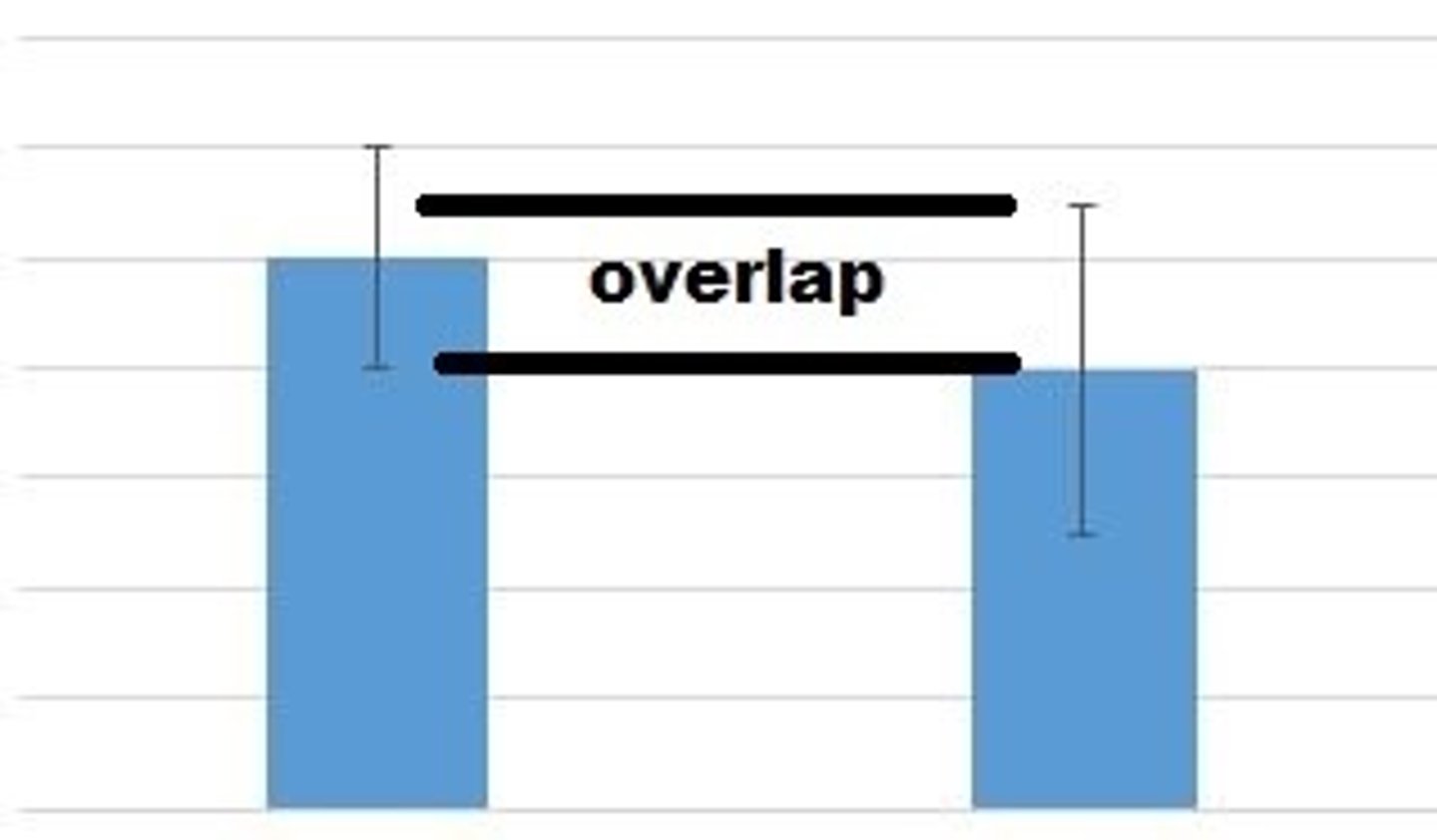
T/F error bars do not overlap means there is a RELATIONSHIP?
TRUE REAL RELATIONSHIP
what is p-value
probability that the null hypothesis is true, evidence is stat significant if p<0.05
when would you use a scatterplot
both predictor and outcome CONTINUOUS
curvilinear relationship means
some areas of predictor and outcome pos and neg
horizontal line of best fit
no relationship
correlation coefficient (r)
A single number, ranging from -1.0 to 1.0, that indicates the strength and direction of an association between two variables.

does r value ever go above -1 or 1
NO
correlational research vs correlation coefficient
correlational research - ASSOCIATIVE, predictor NOT manipulated, variables continuous OR categorical, NO CAUSATION
correlation coefficient - usually both variables continuous, can be correlational OR experimental, CAUSAL OR ASSOCIATIVE
what is a construct
A construct is an unobservable thing (like memory or intelligence) that is useful for explaining or describing behavior.
OFTEN HAVE A HARD TIME MEASURING
what is validity
the degree to which a test measures what it says it measures.
what is reliability
the consistency with which the same event is repeatedly measured (repeat and replicate)
does good reliability = good validity?
NO
how do you calculate reliability
correlation coefficient (r)
tests to check reliability
test and retest (same participants)
parallel forms (new participants)
split half (single test administered, compare odd and even questions)
observation measures
action
self report measures
ideas
monitoring measures
physiological state
self report vs observation
self report - report feelings after the fact
observation - recording feelings while event occurring
qualitative data
subjective response (feelings)
quantitative data
objective response (one right answer) COMPARED TO RUBRIC
open ended question
an interview question that encourages an answer phrased in the respondent's own words
closed ended question (3 types)
multiple choice (forced choice, exhaustive)
rating scale questions (how much agrees)
ranking scale (arrange options in order)
response set
a tendency to respond to questions in a particular way that is unrelated to the content of the questions
nay saying
answering "no" or "strongly disagree" to every item in a questionnaire or interview
yea saying
pattern may be evident in the form of all "yes" or "strongly agree" answers.
reverse wording
changes the direction of the scale by asking the question in a positive (or negative) voice
faking bad
Giving answers on a survey (or other self-report measure) that make one look worse than one really is.
no causation without
manipulation
four types of validity
construct, face, method, procedural
face validity
Measures whether a test looks like it tests what it is supposed to test.
procedural validity
did anything about the procedure add noise or error to the measurement?
is validity formulaic
NO
method validity
did researchers appropriately measure variables in experiment
construct (face validity) is an example of
THINGS WE CANT SEE
procedural/method validity is example of
THINGS WE CAN SEE
method match is only for
measured (not manipulated) variable
values of r (0.50 to 1.00)
strong relationship
values of r (0.30 to 0.50)
moderate relationship
values of r (0.10 to 0.30)
weak relationship
values of r (0.00 to 0.10)
no relationship
r for
relationship!
p for
probability!
direction of relationship (- or +)
(-) negative linear relationship aka inverse
(+) positive linear relationship
does r value ever go above 1?
NO
for calculating reliability what value do you use?
correlation coefficient (r)
r goes with R!
reliability r = +1 to +0.9
reliability excellent
reliability r = +0.9 to +0.8
reliability good
reliability r = +0.8 to +0.7
reliability acceptable
construct validity pro tips
did they actually measure what they said?
make evaluation
use sound reasoning
leave out details, leave out outcome
if a likert scale has 6+ points it is
continuous
do error bars need to be the same height?
no
threats to construct validity
is construct really measured?
is operational definition valid?
is there external factors (observer expectancy, participant expectancy, hawthorne effect, faking bad/social desirability)
line of best fit
A line that is very close to most of the data points in a scatter plot
How to write an operational definition
Identify the characteristic of interest.
Identify the characteristic to be measured or the defect type of concern.
Select the measuring instrument.
The measuring instrument is usually either a physical piece of measuring equipment such as a micrometer, weighing scale, or clock; or alternatively, a visual check. Whenever a visual check is used, it is necessary to state whether normal eyesight is to be used or a visual aid such as a magnifying glass. In the example, normal eyesight is sufficient. In the example, a clear visual indication is given of acceptable and unacceptable, so the observer needs to be in a position where the decision can be made.
Describe the test method.
The test method is the actual procedure used for taking the measurement. When measuring time, the start and finish points of the test need to be specified. When taking any measurement, the degree of accuracy also needs to be stated. For instance, it is important to know whether time will be measured in hours, minutes, or seconds.
State the decision criteria.
The decision criteria represents the conclusion of the test. Does the problem exist? Is the item correct? Whenever a visual check is used, a clear definition of acceptable/unacceptable