1.Motion, Forces, and Energy (IGCSE Physics)
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
What can be used to measure lengths of tens of centimetres?
A tape measure
What can be used to measure lengths of tens of metres?
A trundle wheel
What can you do to reduce the impact of measurement errors?
Take multiple measurements
What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
Scalar quantities only have a magnitude, vector quantities have magnitude and direction.
What is distance?
a measure of how far an object has travelled.
What is displacement?
a measure of how far it is between two points in space, including the direction.
What does the length of a vector arrow represent?
The magnitude
What does the direction of a vector arrow indicate?
The direction
How do you combine perpendicular vectors?
Draw a right-angle triangle and use Pythagoras to find magnitude; trigonometry for angle.
What does the resultant vector represent?
A single vector producing the same effect as all component vectors combined.
Define speed.
Distance travelled per unit time. Scalar.
Formula for speed?
speed = distance/time
Define velocity.
Speed in a given direction. Vector.
Why can velocity be negative?
Direction opposite to the assigned positive direction.
Define acceleration.
Rate of change of velocity per unit time.
Formula for acceleration?
Change in velocity/change in time
What does a negative acceleration mean?
Constant speed.
What is the SI unit for acceleration?
metres per second squared (m/s²)
What does a horizontal line mean?
Object stationary.
What does slope represent?
Speed. Steeper = faster.
Formula for Average speed
distance travelled/ time taken
What does gradient represent in a speed-time graph?
Acceleration.
What does the area under a speed time graph represent?
Distance travelled.
What do positive and negative gradients mean in a speed time graph?
Positive = speeding up; negative = slowing down.
What is the acceleration of freefall?
9.8 m/s²; all objects fall at same rate without air resistance.
Define a force.
A push or pull caused by an interaction; changes speed, direction, or shape.
What is a resultant force?
Single force equivalent to all forces acting. Determines motion.
What are balanced forces?
Equal magnitude, opposite direction; zero resultant; no change in motion.
What are unbalanced forces?
Do not cancel; produce acceleration.
State Newton's First Law.
Objects stay at rest or constant velocity unless acted on by resultant force.
Why does constant velocity imply zero resultant force?
Because no acceleration is occurring.
State Newton’s Second Law.
An object's acceleration is directly proportional to the net force applied and inversely proportional to its mass
Formula for Newton’s second law?
Force = mass x acceleration
Effect of mass on acceleration?
Higher mass = smaller acceleration for same force.
What is the aim of a force-extension experiment?
Investigate relationship between force and extension of a spring.
How is extension calculated?
Final length - original length.
State Hooke’s Law.
The extension of an elastic object is directly proportional to the force applied, up to the limit of proportionality.
Formula for hooke’s law?
(F = kx) Force = spring constant x extension of a spring
What is spring constant?
Force per unit extension; measure of stiffness (N/m).
What happens beyond limit of proportionality? (Hooke’s law)
Relationship becomes non-linear; spring may not return to original length.
What is friction?
Force opposing motion between surfaces in contact; causes heating and energy loss.
Why does circular motion involve resultant force?
Object continually changes direction → acceleration → requires centripetal force.
What is mass?
The measure of the quantity of matter in the object.
What is weight?
a gravitational force on an object with mass
How does an object’s mass change?
An object’s mass always remains the same, regardless of its location in the Universe
How does an object’s weight change?
The weight force exerted on the object will differ depending on the strength of the gravitational field in its location. The gravitational field strength on the Moon is 1.63 N/kg, meaning an object’s weight will be about 6 times less than on Earth
How can the weight of two objects be compared?
By using a balance.
What is density?
The mass per unit volume of a material.
Why is a gas is less dense than the same substance in liquid or solid form?
because the particles in a gas are more spread out (same mass, over a larger volume).
What is a good sequence to follow when writing about experiments?
Start by giving off an equation if necessary, list the apparatus necessary, state the measurements you need to make, and state that you will repeat each measurement several times and take averages.
What are some safety considerations to take in an experiment?
Ensure that glassware is handled carefully, stand up during the experiment to quickly react to any spills, and liquid should not be poured into the measuring cylinder while it is on the balance, this could lead to electric shock.
When will an object sink?
An object will sink if the object is denser than the fluid.
When will an object float?
An object will float if it is less dense than the fluid.
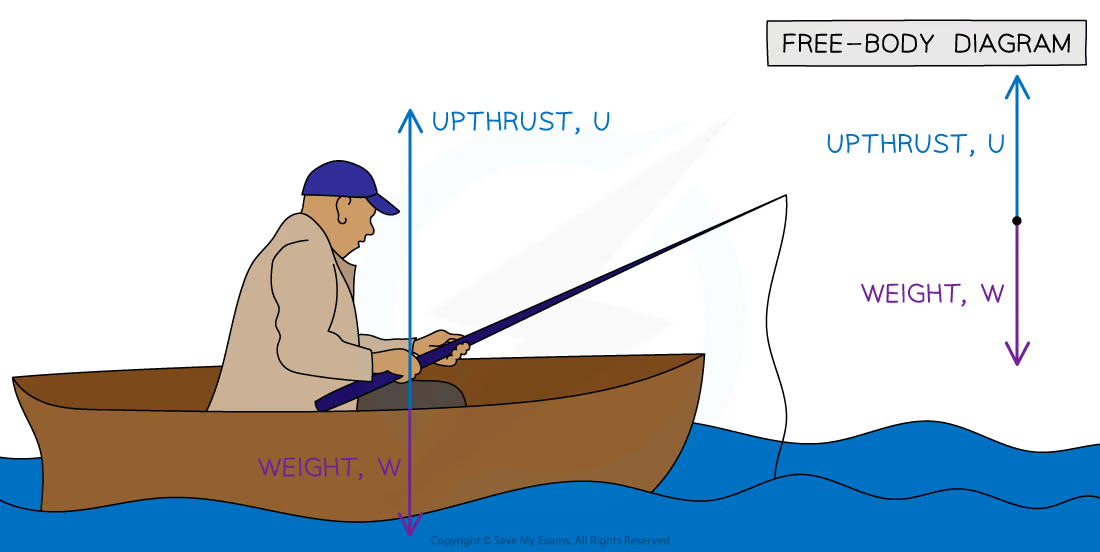
What is upthrust in a fluid?
a force that pushes upwards on an object submerged in a fluid that always acts in the opposite direction to the object's weight force, this is how objects float.
What does the size of upthrust force in a fluid depend on?
The density of the fluid and the volume of the fluid that is displaced.
What factors affect floating and sinking?
Upthrust and density.
How does upthrust affect floating and sinking?
If the force of upthrust on an object is equal to the object’s weight, then the object will float. If the force of upthrust on an object is less than the object’s weight, then the object will sink.
How does density affect floating and sinking?
If the density of the object is greater than the density of the fluid, then the object will sink. If the density of the object is less than the density of the fluid, then the object will float.
What is the moment of a force?
The moment of a force is the turning effect produced when a force is exerted on an object.
What is a moment?
The turning effect of a force about a pivot.
What two factors determine the size of a moment?
The force applied and the perpendicular distance from the pivot.
What is the formula for a moment?
moment = force x Perpendicular distance from pivot
What are the units of a moment?
Newton metres (N m), or Newton centimetres (N cm) if using cm.
What causes an object to rotate clockwise or anticlockwise?
A force applied on one side of a pivot.
How can you determine the direction of rotation?
Imagine a clock hand movement, clockwise or anticlockwise.
Why must forces be perpendicular to create a moment?
Only the perpendicular component of a force causes rotation.
Why is it easier to open a door at the handle than near the hinge?
Because the distance from the pivot is greater, so less force is required.
How do you increase a moment without changing force?
Increase the perpendicular distance from the pivot.
What is the principle of moments?
In equilibrium, total clockwise moments equal total anticlockwise moments.
What does it mean if the moments are not equal?
There is a resultant moment, so the object will rotate.
How do you apply principle of moments with multiple forces?
Sum of clockwise moments = sum of anticlockwise moments.
What is equilibrium?
A state where an object remains stable without change in motion.
What are the conditions for equilibrium?
No resultant force, No resultant moment, and Clockwise moments equal anticlockwise moments
What is centre of gravity?
The point through which an object's weight acts.
Where is CoG in a symmetrical object?
At the point of symmetry.
When is an object stable?
When its centre of gravity is above its base.
What makes an object topple?
When the line of action of weight lies outside the base.
What features improve stability?
Low centre of gravity and Wide base.
What units should be used in moment calculations?
Convert distances to metres unless question states otherwise.
Momentum formula?
momentum = mass x velocity (p = mv)
What is the principle of the conservation of momentum?
In a closed system, the total momentum before an event is equal to the total momentum after the event.
What is impulse?
Impulse is the product of the force applied and the time for which it acts.
What is the formula for impulse?
mv - mu (m = mass, v = final velocity, u = initial velocity)
What are the units for impulse?
Newton seconds (Ns)
What is energy?
Energy is a property that can be stored or transferred, measured in joules (J).
Name the main energy stores.
Kinetic, gravitational, elastic, magnetic, electrostatic, chemical, nuclear, thermal.
What is kinetic store?
Energy stored by a moving object.
What is chemical store?
Energy stored in chemical bonds, released in reactions.
Name the four energy transfer pathways.
Mechanical, electrical, heating, radiation.
What is mechanical transfer?
Energy transfer when a force acts over a distance.
What is electrical transfer?
Energy transfer by moving charges.
What is kinetic energy?
Energy an object has because of its mass and speed.
If mass doubles, what happens to KE?
KE doubles (directly proportional to mass).
If speed doubles, what happens to KE?
KE becomes four times larger (directly proportional to v²).
Kinetic Energy formula?
½ mass x velocity²
What is gravitational potential energy?
Energy an object has due to its height in a gravitational field.
What happens when an object is lifted?
Energy is transferred to its GPE store.
What is the formula for GPE?
mgh (mass x gravity x height)
State the principle of conservation of energy.
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred.
What is the formula for work done (W)?
W = Force x distance = Energy transferred