M1| Introduction to Theory of Computation and Related Mathematical Notions
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
It deals with the definitions and properties of
mathematical models of computation
Automata theory
From the Greek word, this means "self-acting, self-willed, self-moving”
Automata theory
Are used in text processing, compilers, and
hardware design
Finite automata
Are used in programming languages and AI
Context-free grammars
It enables both machine/machine and person/machine communication
Languages
True or False:
Both the design and the implementation of modern programming languages rely heavily on the theory of context-free languages that we will study
True
These are used to document the languages' syntax and they form the basis for the parsing techniques that all compilers use
Context-free grammars
True or False:
Systems as diverse as parity checkers, vending machines, communication protocols, and security devices can be described as infinite state machines
False - these are described as finite state machines
True or False:
Many interactive video games are (large and often nondeterministic) finite automata
True
In math and computer science, these consist of words whose letters are taken from an alphabet and are well-formed according to a specific set of rules.
Formal languages
A set of words whose letters come from an alphabet and are well-formed according to specific rules.
Formal language
The set of symbols used in a formal system.
Alphabet
The syntactic rules for constructing sentences in a formal system.
A specific set of rules
A group of objects represented as a unit
Sets
Are called the elements or members in a set
Objects
What does the notation S={7,21,57} represent?
A set named S containing the elements 7, 21, and 57
What symbol denotes membership in a set?
∈
Which expression shows that 7 is an element of the set {7,21,57}?
7 ∈ {7, 21, 57}
Which expression shows that 8 is not an element of the set {7,21,57}?
8 ∉ {7, 21, 57}
A set whose members are all contained in another set.
Subset
How do we denote that set A is a subset of set B?
A ⊆ B
A subset of a set that cannot be equal to the set.
Proper subset
How do we denote that set B is a proper subset of set A?
B ⊂ A
A set that contains an infinite number of elements.
Infinite set
How is the set of integers 𝑍 typically written?
{…,−2,−1,0,1,2,…}
A set with zero members.
Empty set
The set obtained by combining all elements of two sets A and B into a single set.
Union
The set of elements that are in both sets A and B.
Intersection
The set of all elements under consideration that are not in set A.
Complement
Is a widely used diagram style that shows the logical
relation between sets
Venn Diagrams
It represents sets as regions enclosed by circular lines
Venn Diagrams
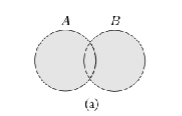
What Venn diagram is this?
A ∪ B
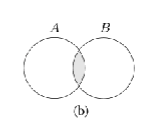
What Venn Diagram is this?
A ∩ B
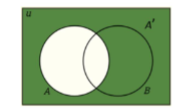
What Venn Diagram is this?
Ā
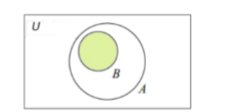
What Venn Diagram is this?
B ⊂ A
A list of objects in a specific order
Sequence
In which type of collection does the order of elements matter?
Sequence
How is the sequence of 7, 21, 57 written?
(7, 21, 57)
In which type of collection does repetition matter?
Sequence
Which of the following shows that sequences (7, 7, 21, 57) and (7, 21, 57) are different?
They are different because sequences care about order and repetition
True or False:
Sets can be finite or infinite, and so can sequences.
True – They are true because sets and sequences can have a limited or unlimited number of elements
True or False:
Sets and sequences cannot appear as elements of other sets and sequences.
False – This is false because sets and sequences can appear as elements of other sets and sequences
A finite sequence is also called a…
Tuple
A 2-tuple, like (0, 1), is also called a…
Pair
The set of all subsets of a set A is called the…
Power set
True or False:
The Cartesian product of two sets A and B, written as A × B, is the set of all ordered pairs where the first element is from A and the second element is from B.
True – This is correct because each pair combines one element from A with one from B
If A = {1,2} and B = {x,y,z}, which of the following is A × B?
{ (1, x), (1, y), (1, z), (2, x), (2, y), (2, z) }
True or False:
In the Cartesian product A × B, the order of elements in each pair does not matter.
False – This is false because the first element must be from A and the second from B
True or False:
A function is an object that sets up an input-output relationship.
True – This is correct because functions pair each input with exactly one output
True or False:
In every function, the same input always produces the same output.
True – This is correct because functions are deterministic
How do we write that a function f outputs b when the input is a?
f(a) = b
A function is also called a…
Mapping
Which of the following is an example of a function?
An addition function where the input is an ordered pair of numbers and the output is their sum
Is an object that setups up an input - output relationship
Function
True or False:
A graph is a set of points with lines connecting some of the points.
True – This is correct because graphs consist of vertices connected by edges
The points in a graph are called…
Nodes or vertices
The lines connecting nodes in a graph are called…
Edges
For a graph G with nodes i and j, the pair (i, j) represents…
The edge connecting i and j
If V is the set of nodes and E is the set of edges of a graph G, then we write…
G = (V, E)
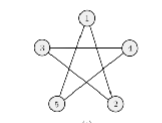
A formal description of the graph is:
G = ( {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4), (4, 5), (5, 1)} )
True or False:
A path in a graph is a sequence of nodes connected by edges.
True – This is correct because a path links nodes through edges
A simple path is…
A path that doesn’t repeat any nodes
A graph is connected if…
Every two nodes have a path between them
A path is a cycle if…
It starts and ends at the same node
A simple cycle is…
A cycle that contains at least three nodes and repeats only the first and last nodes
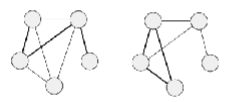
These are example of what?
Simple path and simple cycle
True or False:
A graph is a tree if it is connected and has no simple cycles.
True – This is correct because trees are connected graphs without cycles
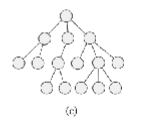
This graph is an example of what?
Tree
True or False:
A directed graph has arrows instead of lines.
True – This is correct because edges have a direction in directed graphs
The number of arrows pointing from a particular node is called…
Outdegree
The number of arrows pointing to a particular node is called…
Indegree
In a directed graph, an edge from node i to node j is represented as…
(i, j)
The formal description of a directed graph G is…
G = (V, E)
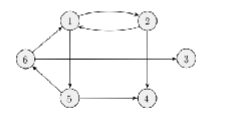
A formal description of the graph is:
G = ( {1,2,3,4,5,6}, {(1,2), (1,5), (2,1), (2,4), (5,4), (5,6), (6,1), (6,3)} )
True or False:
Strings of characters are fundamental building blocks in computer science.
True – This is correct because strings are used to represent data and text
An alphabet is defined as…
Any non-empty finite set
The members of an alphabet are also called…
Symbols
Which symbol is commonly used to designate alphabets?
Σ
The alphabet over which strings are defined…
May vary depending on the application
True or False:
A string over an alphabet is a finite sequence of symbols from that alphabet.
True – This is correct because strings are made by sequencing symbols from the alphabet
True or False:
If Σ1 = {0,1}, then 01001 is a string over Σ1.
True – This is correct because all symbols in 01001 are from Σ1
True or False:
The string of length zero is called the empty string.
True – This is correct because the empty string is denoted ε
What do you call a set of strings?
A language
True or False:
If Σ2 = {a,b,c,...,z}, then abracadabra is a string over Σ2.
True – Every character is from Σ2
True or False:
Boolean logic is a mathematical system built around the two values TRUE and FALSE.
True – Boolean logic only uses TRUE and FALSE.
True or False:
Boolean logic is the foundation of digital electronics and computer design.
True – Boolean logic underlies digital circuits and computing.
True or False:
The values TRUE and FALSE are called Boolean values.
True – TRUE and FALSE represent Boolean values.
Boolean values are often represented by the numbers…
0 and 1
Which symbol represents the NOT operation in Boolean logic?
¬
What is the result of ¬0 in Boolean logic?
1
The AND operation produces 1 only if both inputs are…
1
Which symbol represents the OR operation in Boolean logic?
∨
If P represents “the sun is shining” and Q represents “today is Monday,” what does P ∧ Q represent?
The sun is shining and today is Monday
In the expression P ∨ Q, the symbol ∨ represents…
OR
True or False:
The values P and Q in a Boolean operation are called operands.
True – Operands are the input values for Boolean operations.
True or False:
P ∧ Q will be true if either P or Q is true.
False – AND only outputs 1 when both operands are true.