Chemical elements, compounds and reactions, molecular structure and bonding
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
How quickly can a chemical reaction happen?
Fractions of a second
How slow can a chemical reaction take?
Years
What are reaction rates for a chemical reaction?
Frequency of contact, temperature, and properties of interacting reactants
What accelerates reaction rates?
CatalystsW
What decreases reaction rate?
Inhibitors
What is a combination reaction?
When two or more reactants combine to make a single productW
What are combination reactions also called?
Synthesis Reactions
What side of the arrow is the reactant?
Left
What side of the arrow is the product?
Right
What is a compound?
Substances containing two or more elements
How are compounds formed?
Chemical reactions
Are solutions homogenous or heterogenous?
Homogenous
Solutions contain how many substances?
Two or more
How are mixtures different from solutions?
Substances have combined, but haven’t reacted chemically,
What is a decomposition reaction?
A reactant is broken down into two or more products
What is thermal decomposition caused by?
Heat
How is electrolytic decomposition caused?
Electricity
Most decomposition reactions are
endothermic, energy is absorbed in the process
Byproducts of a decomposition reaction are often
Different from the original
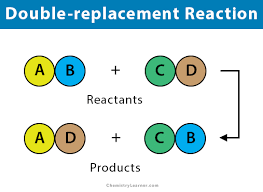
What are double replacement or metathesis reactions?
When two or more bonds are replaced by two compounds to form two different compounds
Organic compounds usually contain
Carbon
What are the two types of classification for organic compounds?
Natural v. Synthetic and Small v. Large
How are natural compounds produced?
Plants and animals
How are synthetic compounds produced?
By humans
Inorganic compounds generally lack
Carbon
How are inorganic compounds usually produced?
Through geological processes
What do Lewis Formulas show?
The bonding or non-bonding of specific valence electron pairs
What do strong acids and bases have in common?
Both completely disassociate in water, with strong electrolytes
What do weak acids and bases have in common?
Do not disassociate completely in water
What is an acid?
A substance that releases hydrogen when dissolved in water
What is a base?
A substance that accepts hydrogen ions and produces hydroxide ions
What is an element?
Matter in its most basic form
What do all elements in a column have in common?
# of Valence Electron shells
What do all elements in a row have in common?
Electron configuration, or same energy level
How many elements in the periodic table are natural
98
How many elements in the periodic table are there in total?
114
What are rows also called?
Periods
What are columns also called?
Groups
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element, with different number of neutrons
Why do isotopes of the same element behave the same chemically?
They all have the same number of valence electrons
What is ionization energy?
The amount of energy that it takes to remove the first valence electron of an atom
As you go from left to right, the ionization energy
Increases
As you go up the periodic table, the ionization energy
Increases