Kendrick: Unit 2 Test Review
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mix of units 2 and 3, little of 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Cytology
The structure and function of cells
Light Mircoscope
Based on light passing through a two-lens system. Can view prokaroyitic and eukarotics cells but not virssuse.
Magnification
Ability to enlarge the image
Resoltuion
Ability to provide clarity to the image
Electron Microscope
Uses a beam of e- to provide greater magnification and resolution
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Used to view the internal components of cells (organelles)
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Used to view the surface of cells
Cell Fractionation
The ability to use centrifuges to spin at different high speeds to fractionate (split apart) cells
Prokaryotic Cells (P)
No nucleus. Unicellular bacteria. Contains ribosomes, cytosol, cell wall
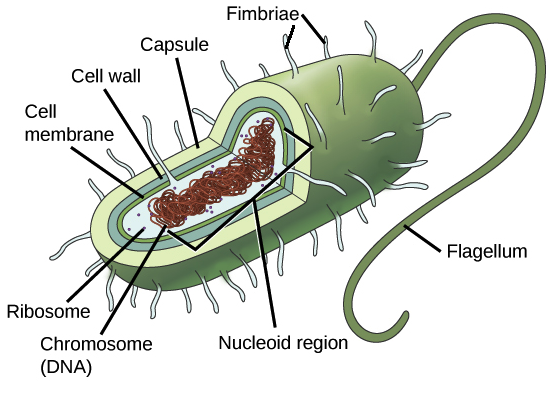
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
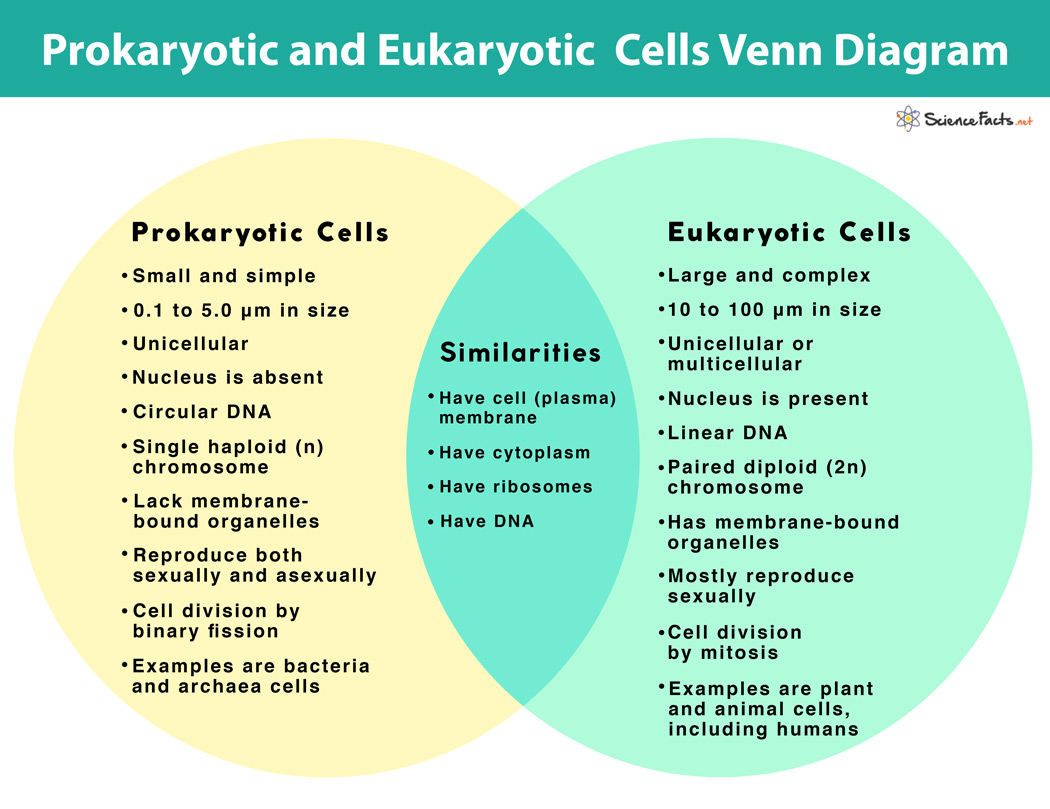
Nucleoid Region
Devoid of a true nucleus, DNA floating in cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
Material and area designating the inside of the cell
Cytosol
Fluid inside the cell (only in prokaryotes)
Ribosomes
Location of Protein synthesis
Capsule
Lies outside the cell wall, is made of carbohydrates and is pathogenic (disease causing)
Eukaryotic cells (E)
Has a nucleus. Animal/Plant cells, all multicellular, some unicellular eukaryotic cells (fungi)
Nuclear envelope (E)
Double memberane made of phospohilpids and proteins.
Nuclear Pores (E)
Holes that allow transportation of materials
Nuclear Lamina (E)
Set of proteins that give the nucleus its structure
Chromosomes (E)
Uncoiled chromatin that contains genes
Chromatin (E)
DNA and proteins combine within the nucleus, coiled DNA
Nucleolus
Inside the nucleus, a location where ribosomes are synthesized
Ribosomes
Found outside the nucleus and where protein synthesis occurs. The only organelle found in BOTH prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Organelles found in ANIMAL cells, not PLANT cells
Centrioles, Flagella, Lysosomes, Intermediate Filaments
Organelles found in PLANT cells, not ANIMAL cells.
Cell Wall, Central Vacuole (anima cells have vacuoles but not a central one), Chloroplast, Plasmodesmata
Cell membrane
Made of phospholipids (have a hydrophobic and hydrophilic region). Are not static, always moving. Semi-permeable: Some molecules can go through. Controls what goes in and out of the cell.
Fluid Mosaic Model of Membranes
The membrane is a mosaic of proteins that float around the phospholipids.
Cholesterol (Membrane)
Found in membranes and assists the membrane to be less fluid
Integral Proteins
Transmembrane proteins with hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions
Peripheral Proteins
Bind to the integral proteins on the outside of the cell membrane
Functions of membrane proteins
Transportation, Enzymatic activity, Signal transduction and cell communication, cell to cell contact and attachment
Membrane Trafficking
Small molecules that are both hydrophobic and nonpolar molecules such as O2 and CO2 can cross the membrane with ease
Large and charged molecules undergo selective permeability with respect to the membrane
Transport Proteins
Proteins that aid is moving molecules across the membrane
Diffusion
Tendency for molecules to move from a higher concentration to a lower concentration. The flow of solute particles through a selectively permeable membrane. NO ENERGY
Passive Transport
Diffusion across a biological membrane
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a membrane. During Osmosis water flows from a hypotonic to a hypertonic soln.
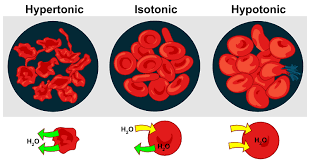
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration of solute compared to the cell. Hypotonic cells will eventually swell and burst. PLANT cells prefer a hypotonic environment.
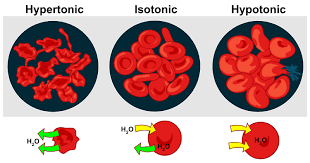
Isotonic
Solutions that contain the same concentration of water and solutes as the cell cytoplasm. Cells placed in an isotonic solution will neither shrink nor swell since there is no net gain or loss of water. ANIMAL cells prefer an Isotonic solution.
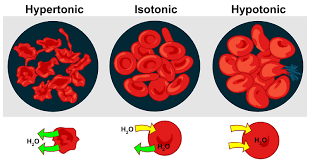
Hypertonic
A hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration compared to the intracellular solute concentration. Neither plant nor animal cells like hypertonic solutions. if a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, it with shrink/shrivel and die.
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of molecules (usually polar) across the membrane with the aid of membrane transport proteins. This is passive transport so no energy (ATP) is required.
Active Transport
Movement against the conc. gradient, requiring ATP
Cotransport
Coupling of the movement of molecules into and out of the cell at the same time
Exocytosis
Fusion of vesicles and molecules with the plasma membrane secreting materials to the outside of the cell
Endocytosis
The cell takes in molecules using vesicles
Phagocytosis
Cell engulfs molecules, most commonly involved in immunity
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking, taking in fluids or small molecules
Receptor Meditated endocytosis
Specific sites on the membrane bind to specific molecules on the outside, engulfing them into the cell
Endomembrane System
The different membranes that are within the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Joins the nuclear envelope. Contains the smooth and rough ER.
Smooth ER
The smooth ER lacks ribosomes. Synthesis of lipids and carbohydrates. Detoxification of drugs in the body (why the liver is one of the most important organs in the body). ribosomes
Rough ER
Synthesis of proteins and new membranes. Site of the convergence of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.
Golgi Apparatus
The global shipping and manufacturing area of the cell
Modification of molecules such as proteins takes place
Secretion of proteins to other parts of the cell or other cells
Synthesis of carbohydrates
Lysosome
From Golgi body. Contains hydrolytic enzymes that break down macromolecules. Enzymes in the lysosome work best at low pH range. Aid in phagocytosis and intracellular digestion,
Food vacuoles
Store broken down macromolecules
Contractile vacuoles
Found in protists and releases water allowing contraction and expansion.
Mitochondria
Organelle that produces ATP (energy). Requires oxygen and is enclosed in an envelope of two membranes.
The endosymbiotic theory
The theory is that the mitochondria and chloroplasts were once prokaryotes. As they have their own DNA and divide by binary fusion.
Cristae
Components of folded inner membrane in the mitochondria.
Intermembrane space
Mitochondria matrix
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis in plant cells. Has its own DNA and can produce ATP by the light rxn of photosynthesis.
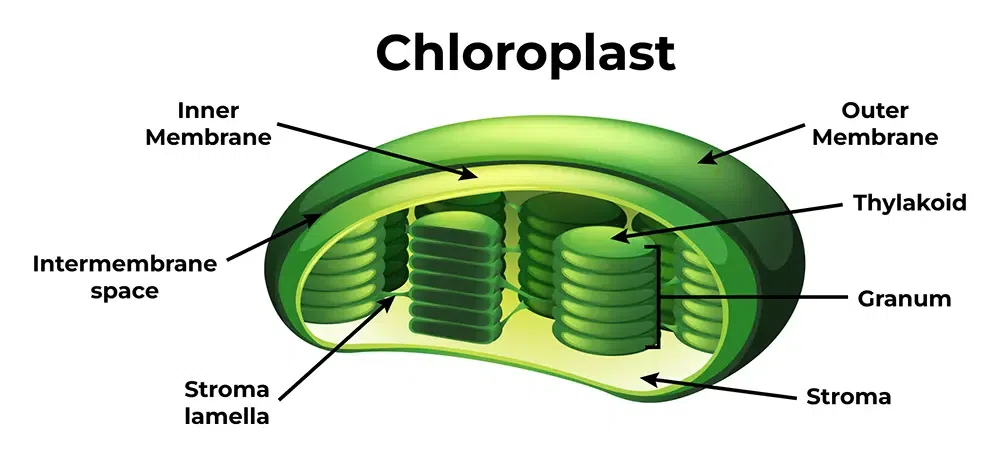
Thylakoids
Membranous sacs inside chloroplasts
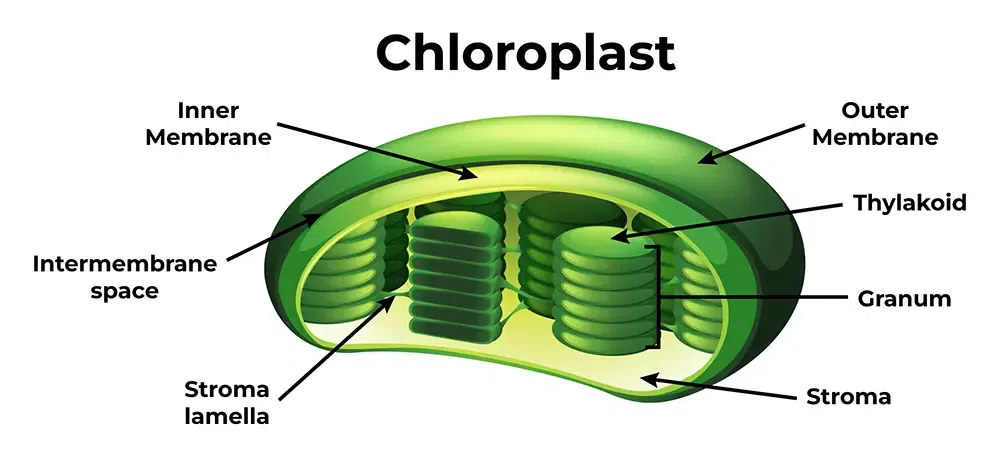
Granum
Stacks of thylakoids
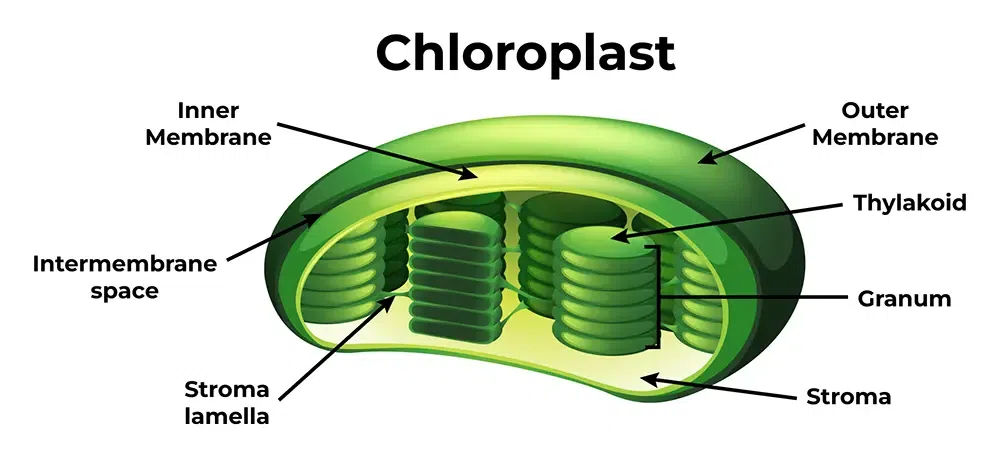
Stroma
Fluid area outside of the grana
Peroxisome
The membrane-bound organelle that transfers hydrogen from compounds to make hydrogen peroxide H2O2
Volume to surface area
As volume gets bigger, surface area gets smaller
Cytoskeleton
A variation of fibers (mostly proteins) that can cover the entire cell. three main types of fibers; Microfilaments, Microtubules, and Intermediate Filaments.
Mircotubles
Made of alpha and tubulin protein, involved in mitosis
Centrosome
Organelle near the nucleus that produces microtubules
Centrioles
Made from the centrosome contains a 9+3 configuration
Cilla
Short and numerous which increase surface tension. Along the surface of the cell and moves stuff along.
Flagella
Long tail propel movement
Microfilaments
These are thin, thread-like structures made of actin protein that play a crucial role in cell shape, movement, and division. They are involved in muscle contraction, support the cell's cytoskeleton, and help in the transport of materials within the cell. Their dynamic nature allows them to grow and shrink rapidly, responding to the needs of the cell.
Intermediate filaments
Made of keratin proteins. Reinforces the cell’s shape and positions organelles in their proper place in the cells.
Extracellular Matrix
Glycoproteins (proteins attached to carbohydrates). Aids in communication of cells and, cell to cell adherence. Positions organelles in the proper place within the cell.
Collagen
Glycoprotein in extracellular matrix