3. Finance
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Short- term finance?
Money borrowed for one year or less
Long-term finance
money borrowed for more than one year
Start-up Capital?
Money needed to set up a business
Expansion?
Money needed for a business to grow
Working Capital?
Money needed for daily expenses
Emergency
Money needed for unexpected situations
Internal finance
finance generated by the business from its own means
Retained profit?
Profit kept in the business after paying all costs, expenses.
Advantages of retained profit?
does not have to be repaid
No interest needs to be paid
Readily available
Disadvantages of retained profit?
Profits may be too low
A new business won’t have
Keeping more profits will reduce the return to shareholders
Selling assets?
Selling unwanted assets like property to raise finance
Advantages of selling assets?
Uses capital tied up in the business
Does not become a debt for the business
Disadvantages of selling assets?
Takes time and the expected amount may not be gained
A new business will not have assets to sell.
Personal savings?
Finance the owner invests directly from their savings
Advantages of personal savings?
Will be available fast
No interest has to be paid
Disadvantages of personal savings?
increases risk taken by owners.
Overdraft?
can spend more than whats in their bank accounts
Advantages of overdraft
flexible as it can change
interest is only on amount withdrawn
Disadvantages of overdraft
interest rates can vary
may have to be repaid fast
Trade payable
when a business delays paying their suppliers (30-90) to improve their cash position
advantages of trade payables
Cheap because no interest
Can improve cash flow
disadvantages of trade payables
may damage the relationship with supplier
Credit cards
can borrow money within a limit
bank loan
money borrowed from banks and repaid with an interest
advantages of bank loan
fixed rate of interest
flexible
disadvantages of bank loan
needs to give a bank collateral security
needs to pay interest periodically
Mortgage
a long term goal used for buying land or property
debenture
loans made to business and investors are given a certificate
venture capitalists
investors who provide money to small/medium businesses for a share of the business
advantages of venture capitalists
support with business contracts
can provide expertise and guidance
disadvantages of venture capitalists
share of profitt
may want more control
Share capital
Money raised from the sale of shares
crowd funding
a large number of people who can invest in a business using an online platform
Cash flow forecast?
A financial document that predicts cash inflow and outflow of a business
Importance of cash?
Business cannot survive without cash
to pay suppliers
to pay overheads
to pay employees
Cash flow?
the flow of money in and out of a business
cash inflow
they money coming into a business
cash outflow
money going out of a business
net cash flow
the difference between cash inflow and outflow
Purpose of cash flow?
identifying cash shortages- identifying in advance so a business knows when to borrow cash
Supporting application for funding- to show investors and bankers
Helps when planning the business- helps clarify aims and performance planning
Monitoring cash flow- to see the accuracy of the cash flow forecast
Advantages of cash flow forecast?
Helps businesses plan for times when they might run out of money.
A clear picture of cash coming in and leaving. Decision making.
Easier to get loans or investments, and banks often see forecasts
Disadvantages of cash flow forecast?
based on predictions- can lead to wrong choices
unexpected events may occur
time-consuming and needs to be updated
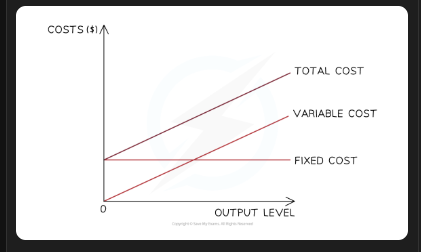
Fixed costs?
costs that don’t change with the level of output (rent, bills, payments)
Variable costs
costs that change based on the level of output (raw materials, wages, fuel)
Total costs formula?
TC= fixed costs + variable costs
Average costs formula?
AC= total costs/quantity produced
Total revenue formula?
TR= quantity sold x price
Profit formula?
P= Total revenue - costs
Break-even point?
when total costs and total revenue are the same
neither a profit or loss is made
profit = 0
Break-even point formula?
BEP = Fixed costs/ (Selling price-Variable cost per unit)
Limitations of the break-even chart?
Costs do not always increase in direct proportion to units sold.
bulk-buying reduces variable costs per unit and increases output
fixed costs might increase due to more staff or equipment
Some output may remain unsold
businesses may keep stock to cope with any changes in demand
some stock could also be sold at a lower price
Data has to be accurate
Wrong cost input could lead to misunderstanding of the break even point
Advantages of the break-even chart?
Clear visual tool – It’s easy to see when the business will start making a profit.
Helps set targets – Shows how many products need to be sold to avoid a loss.
Supports planning – Useful for making simple business decisions like pricing or budgeting.
Statement of comprehensive income (SOCI)?
A financial document that records all the income generated by the business. (Profit and loss statement)
Cost of sales (direct costs) formula?
Opening inventory of finished goods - closing inventory of finished goods
Gross profit formula?
Sales revenue - cost of sales
it’s the profit made before expenses are taken away.
Net/ operating profit formula?
Gross profit - expenses?
what are expenses?
All INDIRECT costs like rent, wages, bills, marketing.
What does the SOCI include?
Revenue
Cost of Sales
Gross profit
Operating profit
Finance costs
Profit for the year
Profit for the year after tax
Retained profit?
profit that is invested back into the business
Distributed profit?
a portion of the net profit distributed to stakeholders.
How can SOCI be used for decision making?
investment decisions
a rise in profit- more funds for investment
Cost analysis
an increase in cost of sales- reduces COP
Future forecasts
increase in profit- further increase in the future
Statement of Financial position?
A financial document which provides a summary of a firm’s assets, liabilities and capital. (Balance sheet)
Assets?
resources owned by a business (items of value)
Non-current/ fixed assets?
Assets that remain in the business for more than a year (land, vehicles, buildings)
Can also be intangible (copyrights and patents) that add to the value of a business
Current/ Short assets?
Assets that can be changed into cash within a year- liquid assets (inventory, cash ‘in hand’)
Liabilities?
debts owed by the business to its creditors
Non-current liabilites?
Business debts which don’t need to be repaid within a year. (loans, debentures)
Current liabilites?
Business debts that do need to be repaid within a year. (Trade payables, overdrafts)
Net current assets formula?
Current assets - current liabilites
Net assets formula?
Total assets - total liabilities
Interpreting the SOFP
Financing its activities- long-term liabilities are share capital- application for loans may be declined
What a business owes
What a business owns
Advantages of SOFP
Supports comparison – It can be compared with previous years to see how the business is improving or declining.
Helps with decision-making – Managers can decide whether to invest more, cut costs, or take out loans based on the business’s financial position.
Useful for stakeholders – Investors, banks, and owners can use it to make informed decisions (e.g. lending, investing).
Drawbacks of SOFP
Doesn’t show cash flow – It doesn’t reflect how much actual cash the business has or how money is moving in and out.
May be outdated quickly – The information can become irrelevant if the business’s finances change soon after it’s made.
Based on estimates – Some values (like depreciation or inventory) are not exact and may reduce accuracy.
Ratio analysis?
Extracting information from financial accounts to assess business performance. This is compared over time to determine how well financial objectives are being achieved.
Profitability ratios?
Measures the performance of a business and focuses on profit, revenue and amount invested into the business. SOCI is used.
Liquidity ratios?
Measures how easily a business can pay its short-term debts
Gross profit margin?
proportion of a revenue turned into gross profit
Gross profit margin formula?
GPM= (Gross profit/sales revenue) x 100
Operating profit margin?
An accurate reading on how much profit is made.
the higher the number the better
Operating profit margin formula?
OPM= (Operating profit/Sales revenue) x 100
Mark up?
Profit made per item sold.
Mark up formula?
(Profit per item/Cost per item) x 100
Current ratio?
quick way to measure liquidity
answer is shown as a ratio
Current ratio formula?
Current assets/current liabilites
Acid test ratio formula?
ATR= Current assets-Stock/ Current liabilites
stock- inventory ( goods)
How can financial documents be used to assess the performance of a business?
Managers and employees- looking at strategies to improve business performance and job security (wage negotiations)
Owners and shareholders- Profitability or risk.
External stakeholders- Financial history.
Using financial documents for decision making
funding decisions- Sources of finance
Reducing costs- production process
Increasing profitability- can become more competitive
Investment decisions- can attract shareholders to a business by having good financial records.
Advantages of break even analysis
Allows businesses to determine the minimum sales needed to cover costs
Cost Control- By understanding the relationship between fixed and variable costs, businesses can identify areas where they may reduce costs or improve efficiency.