HDFS 4062 Family Finance and Consumer Law Final
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Plauche final for family finance and consumer law. Do not worry about Chapter 2. Mostly multiple choice, but some written. Chapters 8-19.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
Chapter 9: Housing
employment, children, spouse, maintenance costs, loss of mobility, house expenses, stability, space for family members, and wealth building
What impacts a person’s selection of housing?
lose tax advantages, equity growth, and interest on a security deposit
What are the opportunity costs of renting?
time and cost of commuting to work
What are the opportunity costs of living in an area that offers less expensive housing or more space?
time and money spent repairing/improving a lower-priced home, and interest earnings on money for down payment
What are the opportunity costs of buying/owning a house?
time and effort of building
What are the opportunity costs of building a home to your specifications?
ease of mobility, fewer responsibilities for maintenance, minimal financial commitment, lower initial costs, and more amenities
What are the advantages of renting?
few financial benefits, no tax benefits, restricted lifestyle (remodeling, privacy, pets, activities), lease agreements, and security deposits
What are the disadvantages of renting?
protected from rent increases unless stated otherwise, can’t be locked out or evicted without a court hearing, and right to sublet
What protections does a lease offer to a renter?
pride of ownership, tax deductions (mortgage interest and real estate tax), property value increase, borrow against the equity of your home, and lifestyle flexibility
What are the advantages of owning a home?
financial uncertainty, money for down payment, qualifying for mortgage financing, changing property values, limited mobility, and higher living costs
What are the disadvantages of owning a home?
mortgage
What is a long-term loan on a specific piece of property such as a home or other real estate?
decades long
sources include banks, savings and loan associations, credit unions, mortgage companies
home is collateral
how much you can afford (down payment, income, and current living expenses), current mortgage rates, potential future value of property, ability to make monthly payments (mortgage, tax, and insurance), and what you can afford verses what you want
What guidelines might determine the amount to spend for a home?
strengthen property values
A high quality school system can _________, which benefits homeowners in a community who do not have school-age children?
real estate agents
Who provides these services to home buyers?
Showing homes in many areas based on your needs and preapproved mortgage amount
Presenting your offer to the seller based on a market analysis
Negotiating a purchase price
Assisting you in obtaining financing
Representing you at the closing
Recommendations for lawyers, insurance agents, home inspectors, and mortgage companies
personal savings, investments, assets, and assistance from relatives
What are the main sources of money for a down payment?
income, debts, credit score, down payment amount, loan length, and current mortgage rates
What factors affect a person’s ability to qualify for a mortgage?
larger; smaller
When interest rates are lower, banks will allow for ______ mortgages, increasing buying power and lowering payments. As interest rates rise, banks will give out _____ mortgages, increasing monthly payments and decreasing the amount of people who can afford the loan.
when interests rates drop at least 1% less than your current rate
When might refinancing a mortgage be advisable?
benefits occur faster with larger mortgages
want a lower rate and payment
adds several thousand dollars to the upfront cost
How do closing costs affect a person’s ability to afford a home purchase?
Fees for:
loan application
appraisal
home inspection
title insurance
property taxes
attorney fees
prepare home for selling by repairing and staging, determine the selling price, and sell by owner or list with real-estate agent
What actions are recommended when planning to sell your home?
recent selling prices of the surrounding area, current housing market demand, available finance options, mortgage interest rates, economic conditions, the home’s condition, curb appeal, level of maintenance, and housing features
What factors affect the selling price of a home?
selling you own home
What are these advantages and disadvantages of?
saves money on commission
you set price, marketing, advertising, showings, and paperwork
requires more personal effort, time, and negotiation skills
should hire a lawyer or title company for legal aid and closing help
selling your home through a real estate agent
What are these advantages and disadvantages of?
expert help in pricing, marketing, negotiations, and closing
handle open houses, advertising, and coordinating with buyers
access to networks, resources, and experience
comes with commission costs about 6%
saves time and effort
Chapter 10: Home and Auto Insurance
insurance
The purpose of ______ is to provide protection against risk of financial uncertainty and unexpected losses.
give you piece of mind that comes from knowing money will be available to meet the needs of your survivors, pay medical expenses, protect your home and belongings, and cover personal or property damage caused by you when driving.
shares the risk of multiple people
risk
What is uncertainty or lack of predictability, such as the loss that a person or property covered by insurance faces?
peril
What is the cause of a possible loss?
ex. fire, windstorms, explosions, robbery, accidents, and premature death
hazard
What increases the likelihood of a loss?
ex. defective house wiring
personal, property, and liability risks
personal risks, property risks, and liability risks
How are the most common risks classified?
liability
What is the legal responsibility for the financial cost of another person’s losses or injuries?
pure risk
What risk guarantees a chance of loss if specified events occur and are insurable?
only you have the potential for loss
insurable loss → chance of loss not gain
accidental and unintentional risks
classified as either personal, property, or liability
nature and financial cost of the loss can be predicted
speculative risk
What type of risk is the chance of either loss or gain?
ex. starting a small business or gambling
uninsurable risk
risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk assumption, and risk shifting
What are the four methods of managing risk?
self-insurance
_______ is a form of risk assumption and is the process of establishing funds to cover the cost of loss.
put away money to cover the losses if you need to
risk shifting
Paying an insurance company to assume your expenses if you cannot is a form of what?
deductible
What is the set amount that the policyholder must pay per loss on an insurance policy?
set insurance goals on what to cover, develop a plan to reach your goals, put your plan into action, and evaluate insurance plan every 2-3 years
What are the steps in planning your personal insurance coverage?
physical damage caused by weather, loss of use, negligence, and vicarious liability of having a child hurt another person
What property and liability risks might some people overlook?
expensive assets need more insurance and higher premiums, insurance for family and children, and ability to afford coverage
How could a person’s life situation influence the need for certain types of property and liability insurance?
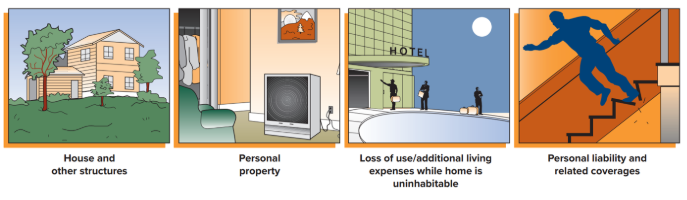
building you live in, any structures on the property, additional living expenses, personal property, personal liability and related coverage, and specialized coverage purchased separately
What main coverage is included in home insurance policies?
liability coverage
The purpose of ___________ is to protect you from financial losses resulting from legal action or claims against you or your family members due to damages to the property of others.
include cost of legal defense
protects your personal property, additional living expenses, personal liability and related coverage, but not buildings or other structures
How does renter’s insurance differ from other home insurance policies?
location of home (weather and place with more claims), type of structure (age, style, and building materials), and coverage amount and type of policy (comprehensive and deductible)
What major factors influence the cost of home insurance?
reduce home insurance costs
These actions help to do what?
gain discounts
smoke detectors or a fire extinguisher
Burglar deterrents (alarm system and dead-bolt locks)
Nonsmoker discounts
“Claim-free” for a few years discount
Insure your car with the same company
company differences
coverage, service
how they settle claims
price differences
check consumer satisfaction index
contact company and independent agents
state insurance commissions, government agencies, and consumer organizations
bodily injury liability, medical payments coverage, uninsured motorist protection, no-fault insurance, property damage liability, collision insurance, comprehensive physical damage
What are the main coverages included in most automobiles insurance policies?
includes bodily injury and property damage coverages, namely wage loss insurance, towing services, accidental death, and care rental while vehicle goes through repairs
no-fault insurance
____________ system says that drivers involved in accidents collect medical expenses, lost wages, and related injury costs from their own insurance companies. This is to provide smooth methods of payment without taking legal action to determine fault.
collision; comprehensive physical damage
__________ coverage pays for damage to your car resulting from an accident with another vehicle or object, regardless of who is a fault. In contrast, ____________________ coverage protects against non-collision-related losses, such as theft, fire, vandalism, natural disasters, or hitting an animal. Essentially, the first covers crash-related incidents, while the second covers other unexpected damage.
type and value of vehicle, selected coverage, where you live, age of driver, gender, marital status, driving record, and credit history
What factors influence how much a person pays for automobile insurance?
reduce cost of automobile insurance
These actions help to do what?
maintain a clean driving record
compare rates among different companies
increase deductibles
install security devices
take advantage of discounts for good grades, drivers education courses, or insuring multiple vehicles
choose a care with low insurance costs
maintain a good credit score
update company with changes like marriage and carpooling to reduce premiums
Chapter 11: Health Insurance
rising healthcare expenditures
What are these reasons for? (could be essay question)
Use of sophisticated, expensive technologies
Duplication of tests and technologies
Increases in the variety and frequency of treatments
Increasing number of longevity of elderly people
Regulations that result in cost shifting rather than cost reduction
Increasing number of accidents and crimes that require medical services
Limited competition and restrictive work rules in the health care delivery system
Labor intensiveness and rapid average earnings growth for healthcare professionals
Using more expensive medical care than necessary
Built-in inflation in health care delivery system
Aging baby boomers
Other major factors
Fraud, administrative waste, malpractice insurance, excessive surgical procedures, a wide range of prices for similar services, and double health coverage
Fraud and abuse counted for nearly 10% of all dollars spent on healthcare
15 to 30%
What percent of health care dollars in the US are consumed by high administrative costs, while it only consumes 1% under Canada’s socialized system?
groups, employers, health insurers, healthcare professionals, and consumers
______ can take these actions to reduce healthcare costs.
Employing generative AI to improve the efficiency of patient interactions
Careful review of fees and charges
Establish incentives for preventative care and services provided out of the hospital where medically acceptable
Become involved in community health planning
Encourage prepaid group practices
Offer community health education programs so people take better care of themselves
Encourage patients to pay cash for routine care and lab tests
individuals
______ can do these things to reduce healthcare costs.
Consider participating in a flexible spending account
Consider a high-deductible health plan
Ask for less expensive generic drugs
Use a mail-order or legitimate online pharmacy
Review free or low-cost coverage for uninsured children through state
Review state plans for prescription drug assistance
Follow up with doctor by phone if allowed
Investigate nonurgent procedures recommended by doctor
Review billing statements for errors
Appeal unfair decisions by your health plan
Practice preventative care and stay healthy
Eat balanced diet and control weight
Avoid smoking and drinking in excess
Get rest, relaxation, and exercise
Maintain healthy lifestyle at work and home
Drive carefully and avoid accidents and fire hazards
Get health screenings and manage chronic conditions
Consider care options:
Nurse line
Virtual visits (Telehealth)
Retail clinics
Urgent care
health insurance
The purpose of _________ is to reduce your financial liabilities when you have to receive medical care and safeguards your family’s economic security.
a form of protection to alleviate the financial burdens individuals suffer from illness or injury
You pay premiums or fees to insurer → they pay most medical costs or reimburse your for hospital stays, doctor visits, medication, and sometime vision and dental care
group health insurance
What type of health insurance is typically employer sponsored (they pay most of the cost)?
Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 requires employers with 50+ to provide health insurance to all employees
small businesses also have this opportunity through Association Health Plans
covers you and your immediate family members for most needs
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act 1996 (HIPAA)
Can move from one plan to another without lapses in health insurance and without paying more than other employees
individual health insurance
What type of health insurance is a policy tailored to your particular needs from the company of your choice?
can use as a supplement to other insurances
basic coverage for hospital and doctor bills, 120 days’ hospital room and board in full, pay 80% out-of-hospital expenses, no unreasonable exclusions, and limit out-of-pocket expenses to $9,100 for individual and $18,200 for family
What should a good health insurance plan include?
basic health insurance coverage
What type of coverage is a combination of hospital expense insurance, surgical expense insurance, and physician expense insurance?
Hospital expense insurance: hospital room, board, and other charges
Surgical expense insurance: surgeon’s fee for an operation
Physician expense insurance: pays for physician’s care such as office visits, lab testes, and x-rays
Does not include surgery
major medical expense insurance
What type of coverage covers expenses for a serious injury or long-term illness?
has a deductible, coinsurance, and a stop-loss provision
deductible
What is a provision that requires policy holders to pay a base amount before the policy benefits begin?
coinsurance
What is it called when both the insured and the insurer share the covered losses beyond the deductible amount?
Hospital indemnity policies: pay cash benefit when hospitalized
Critical illness insurance: pays more for certain major health events
Dental expense insurance: covers exams, cleaning, x-rays, fillings, root canals, oral surgery, etc.
Vision insurance: exams, contact lenses, and glasses
Stop-loss (out-of-pocket limit) provision
What requires a policy holder to pay up to a certain amount, after which insurance companies pay 100% of all remaining covered expenses?
long-term care insurance
What type of coverage pays for the cost of daily living for long-term illness or disability?
very expensive
includes nursing home car, assisted living, retirement community, adult day care services, and home health and personal care
annual premiums from under $2,000 to $16,000
eligibility, assigned benefits, internal limits, copayment, service benefits, benefit limits, exclusions and limitations, coordination of benefits, guaranteed renewable, and cancellation and termination
What are the major provisions of a health insurance policy?
private insurance companies, hospital and medical service plans (Blue Cross and Blue Shield), managed care organizations, indemnity insurance companies, home health care agencies, employer self-funded health plans, and health care accounts
What are the major sources of health insurance and health care?
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
What provides health care services in exchange for a fixed, prepaid monthly premium?
contracts with selected care providers
focus is on preventative care
basic and supplemental services
requires referrals to see specialists
typically have the lowest premiums
least flexibility
preferred provider organizations (PPOs)
What is a group of doctors and hospitals that agree to provide health care at rates approved by the insurer?
several providers to choose from
premiums slightly higher than HMO
specified services at predetermined fees to members
if you go to a non provider, you pay more
includes Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPO) and Point-of-Service (POS) plans.
no referrals needed
more provider choice
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs)
What only covers care from in-network providers (except emergencies)?
don’t require referrals
don’t reimburse for out-of-network care,
offer moderate flexibility
lower costs than PPOs
Point-of-Service Plans (POS)
What combines features of HMOs and PPs where members choose a PCP for coordinated care and need referrals for specialists, but they can go out-of-network for a higher cost?
offer a balance between flexibility and affordability
home health care agencies
What provides medical and supportive services in a patient’s home under a doctor’s supervision?
includes preventative care, nursing, therapy, and assistance for the elderly or chronically ill
lower cost than hospital care
Medicare and Medicaid
What are two sources of government health insurance?
Part A
Medicare is a federal program for those age 65+ and disabled persons. What part of Medicare is hospital insurance and covers inpatient hospital care, inpatient skilled nursing facility care, home health care, and hospice care?
paid through social security tax
Part B
What part of Medicare is considered medical insurance and helps pay for doctor’s services and a variety of other medical services and supplies not covered by hospital insurance?
pays for 80% of approved charges
voluntary
doctor’s services not covered in hospital insurance
financed by monthly premiums paid by enrollees and general federal revenues
Medigap/MedSup insurance
What supplements Medicare by filling the gap between Medicare payments and medical costs not covered by Medicare like traveling outside of the U.S.?
Does not cover dental/vision, long-term care, hearing aids, eyeglasses, or private-duty nursing
pay for out of pocket
disability income insurance
What provides payments to replace income when an insured person is unable to work; most neglected form of insurance?
provides regular cash income lost as the result of an accident or illness
employer plan, social security, worker’s compensation, payment income insurance program, and other sources
What are the five sources of disability income?
will available benefits meet your disability income needs, how long will you have to wait before benefits begin, and insurers limit benefits to no more than 70-80% of your take home pay
How can you determine the amount of disability income insurance you need?
Chapter 12 Life Insurance
person joins risk sharing group by purchasing a policy, insurance company promises to pay sum of money at the time of policy holder’s death under policy, and company makes promise in return for person to pay premium
What is the basic process of obtaining life insurance?
life insurance
The purpose of ______ is to use to protect someone who depends on the policyholder from financial losses caused by their death.
pay home mortgage or other debts
payments to children
education for children
medical expenses
funeral costs
charitable donations
retirement income
accumulating savings
income for survivors
estate proceeds
tax payments
do you have people you need to protect financially, life stage, and type of household
How do you evaluate the need for life insurance?
determines your life insurance objectives
What do these do?
What you want your life insurance to do for you and your dependents
How much money do you want to leave to your dependents if you were to die today?
Will you require more or less insurance protection to meet their needs as time goes on?
When would you like to be able to retire?
What amount of income do you believe you and your spouse would need in retirement?
How much are you able to pay for your insurance program?
Are the demands on your family budget for other living expenses likely to be greater or lower as time goes on?
multiple of income method, the easy method, DINK method, nonworking spouse method, family need method, and online calculators
What are the six methods of estimating your life insurance requirements?
________________: assumes you are looking for a basic benchmark to determine your insurance needs
Annual income is the sole factor
Identifies insurance needs as a range between 5 and 10 times your income
Most basic but leaves out family size, current assets, living expenses, and expected additional sources of income are excluded from calculation
________________: assumes your family is “typical” (may need more for 4+ children, above-average debt, family member with poor health, or spouse has poor potential employment)
Multiple of income method with slight modification
Insurance agent’s rule of thumb that a “typical family” will need about 70% of your salary for seven years before they adjust to the financial consequences of your death
Smaller family needs less insurance
_________________(dual income, no kids): assumes spouse continue to work after your death
No dependents, similar income levels → simple insurance needs
Ensure your spouse will not be burdened with debts if you die
Insurance needs to cover one-half the family debt + estimated funeral expenses
Reconsider if spouse suffers poor health or uncertain future for occupation
_________________
Insurance experts estimate extra costs of up to $20,000 a year required to replace services of a homemaker in a family with small children
Cost of housekeeper, child care, more meals out, transportation, laundry services, etc.
Does not include loss of earnings of spouse taking time away to care for family
Multiple the number of years before the youngest child reaches age 18 by $20,000
Teenage children can reduce this number
More than 2 children under 13 then number adjusted up
$20,000 varies based on estimates of duties and proposed wages nearby
_________________
Includes factors such as social security and your liquid assets
What you have now
What your dependents may need
Total of what your dependents may need - total of what you have now = how much estimated life insurance you need
Positive need more life insure
Negative and your estimates are realistic, dependents may be able to manage without additional life insurance
____________
Provide impartial view of your insurance needs versus using an online calculator via an insurance company website
Life insurance estimators on insurance company websites are useful but may provide a higher estimate of insurance needs → higher premium and commission for the agent
There are also apps
stock life insurance companies and mutual life insurance companies
What are the two types of life insurance companies?
stock life insurance companies
What is the most common form of life insurance companies which are owned by shareholders and generally sell nonparticipating (nonpar) policies that don’t pay dividends but also par policies?
Mutual life insurance companies
What type of life insurance company is owned by policyholders, sell participating policies, but have higher premiums?
part of the premium is refunded to the policyholder annually → called the policy dividend
temporary insurance and permanent insurance
What are the major types of life insurance policies?
_________: term, renewable term, convertible term, or decreasing term insurance (premium stays but coverage decreases as you age or debt is repaid)
also includes multiyear term (same premium for life of policy), return of premium (refunds every penny of premiums if you outlive), re-entry term
protection for a specified period of time (you stop paying premiums, coverage stops)
_________: whole life, straight life, ordinary life, or cash value life insurance
you pay specified premium as long as you live
premium depends on your age when you start
provides death benefits and a savings account
includes limited payment, single premium, modified life, variable life, adjustable life, and universal life
group life, endowment life, funeral/burial life, credit life, industrial life
What are the subtypes of life insurance?
Term insurance protects for a specified period of time, whole life insurance covers you till you die, whole life has the same premium the entire time, and term premiums increase with each renewal
What are the main differences between whole life insurance and term life insurance? (could be essay question)
important provisions in a life insurance contract
What are these?
policy reinstatement: Reinstatement of a lapsed policy if it has not been turned in for cash; time limit 1 to 2 years
the grace period: Allows 28-to-31-day late payment without penalty
automatic premium loan: Cash value is used to pay premium if not paid within grace period.
guaranteed insurability option: allows you to buy specified additional amounts of life insurance at stated intervals without proof of insurability; even if not in good health, can increase the amount of insurance as income rises; desirable if you anticipate needing additional life insurance in the future
Nonforfeiture clause- prevents the forfeiture of accrued benefits if you choose to drop the policy
incontestability clause- after the policy has been in force for a specified period of time (about 2 years), the insurance company cannot dispute its validity during the lifetime of the insured for any reason (including fraud)
suicide clause- if the insured dies by suicide during the first two years the policy is in effect, the death benefit will equal the amount of the premium paid; after time elapses, suicide becomes a risk covered by the policy and the beneficiaries receive the same benefits as any other cause of death
beneficiary
What do you call a person who is designated to receive something from the insured?
rider
What is any document that is attached to the policy that modifies its coverage by adding or excluding specified conditions or altering the benefits?
double indemnity
What is a benefit under which the company pays twice the face value of the policy if the insured’s death results from an accident?
underwriting based on characteristics (age, gender, health, occupations, and hobbies), lifestyles choices (smoking), claims history, credit history, and risk profile
How do insurance companies determine your insurability?
before; after
_________ the purchase of a policy, read the contract word for word and as agent for a point-by-point explanation of language in the contract. _______ the purchase, use the 10-day “free look” period and give beneficiaries and lawyer a photocopy of policy.
lump-sum payment, proceeds left with company, limited installment payment, and life income option
What are the 4 most common settlement options?
annuity
What is a financial contract written by an insurance company that provides a regular income to the beneficiary for life?
Chapter 13: Investing Fundamentals