Lab 6: The skeleton system - Microscopic & Macroscopic Anatomy
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Bone
Also known as osseous tissue is a hard, dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton.
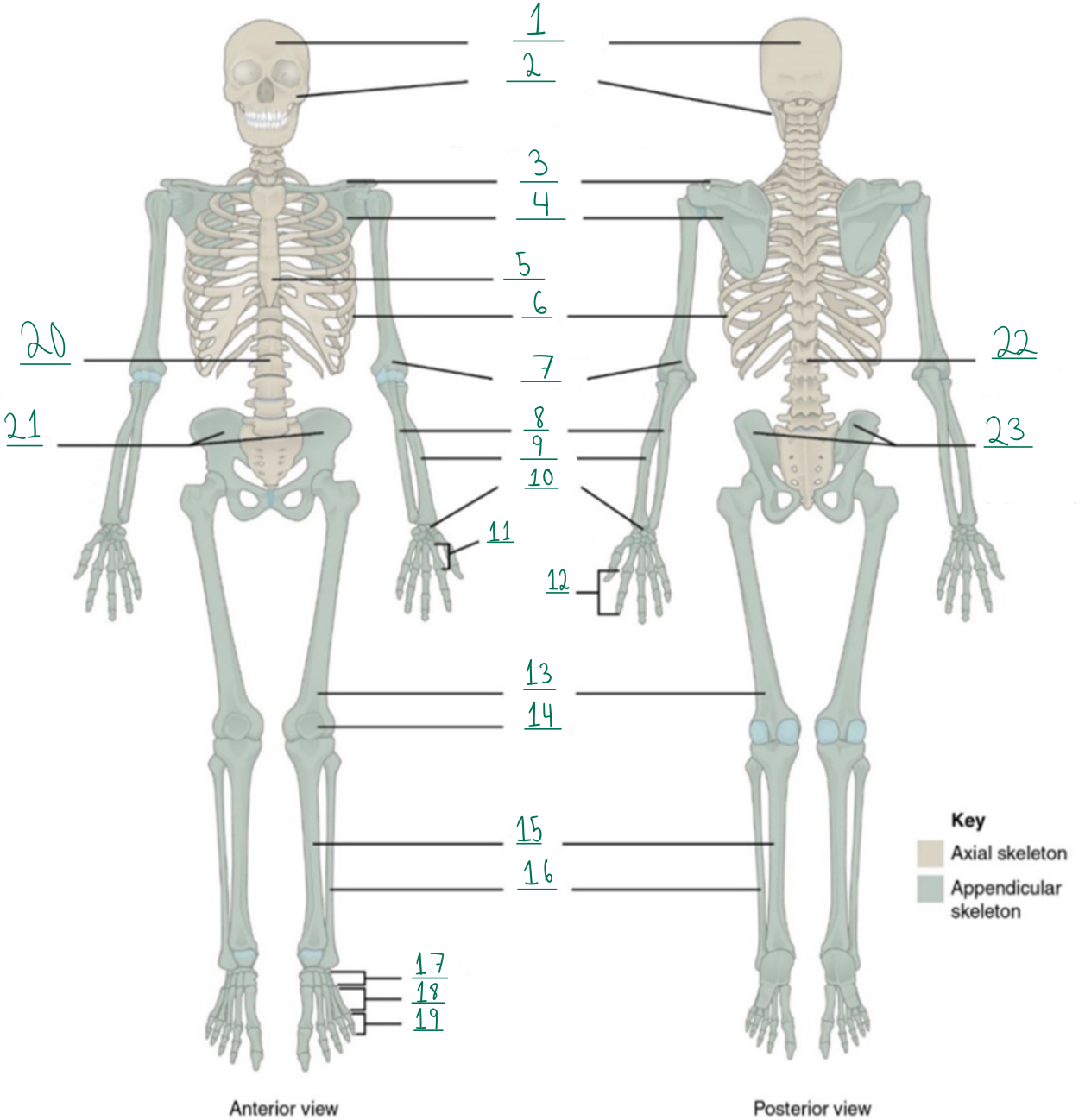
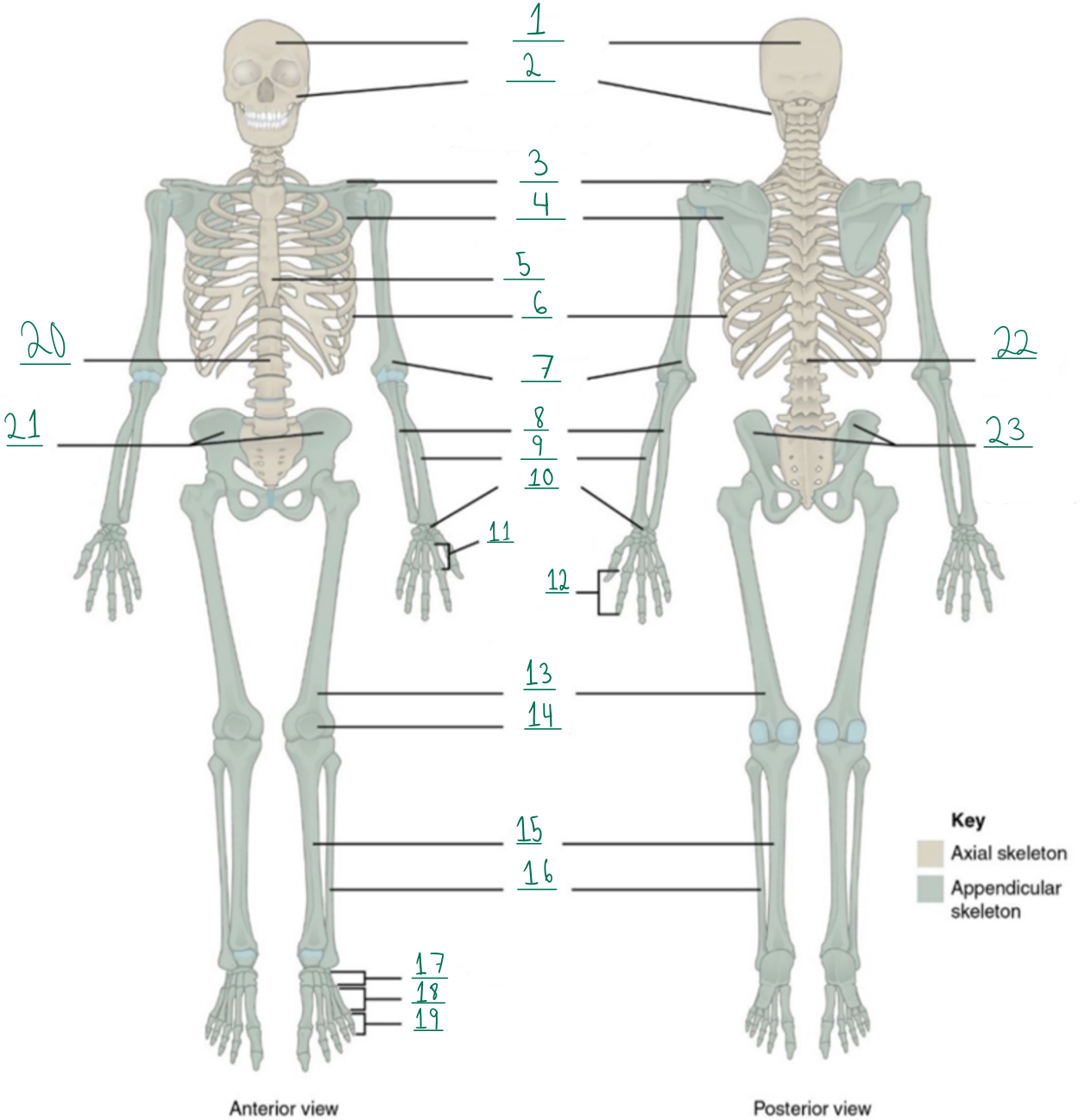
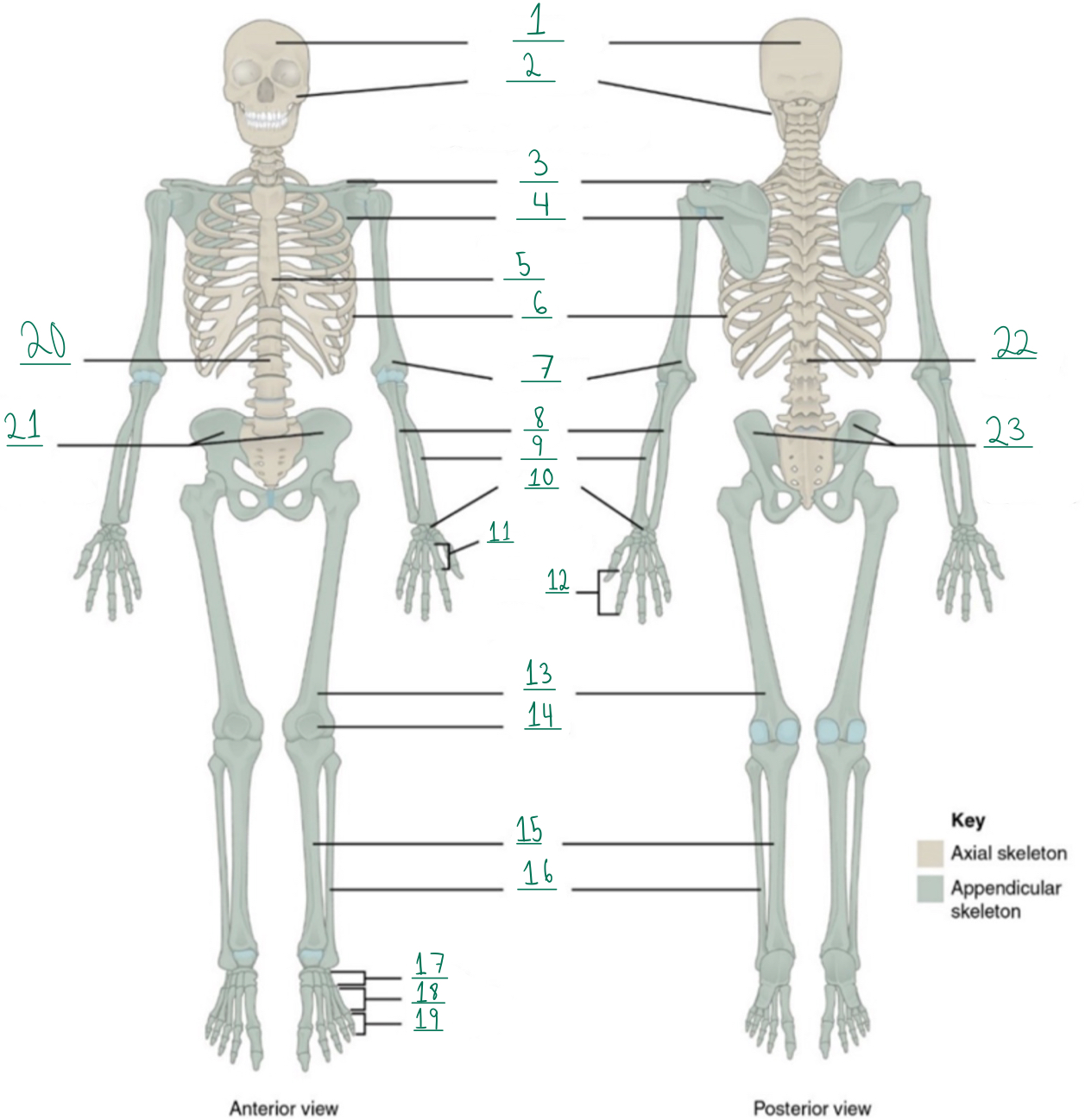
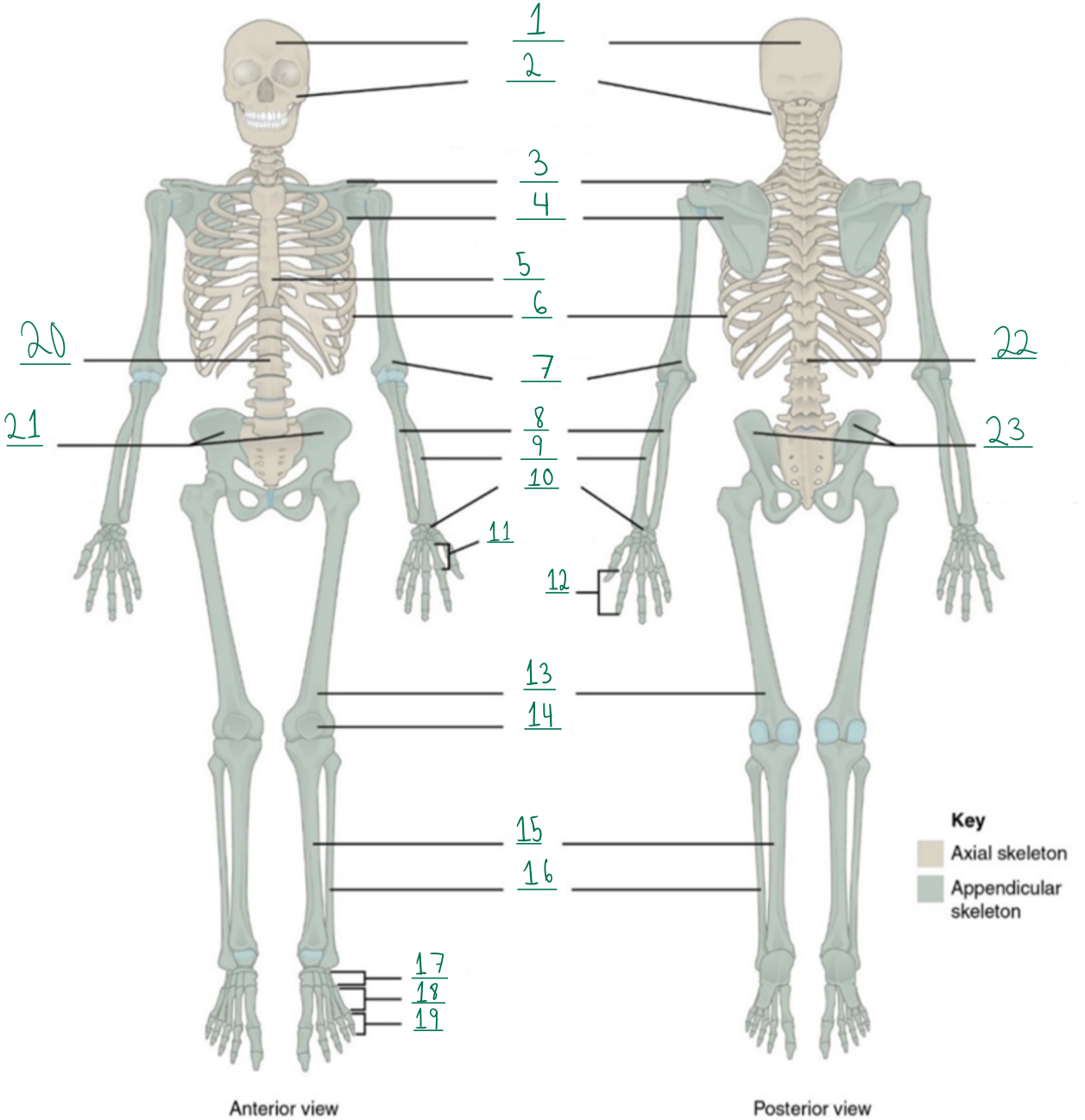
Cranial portion
Identify #1 on this image.
Facial portion
Identify #2 on this image.
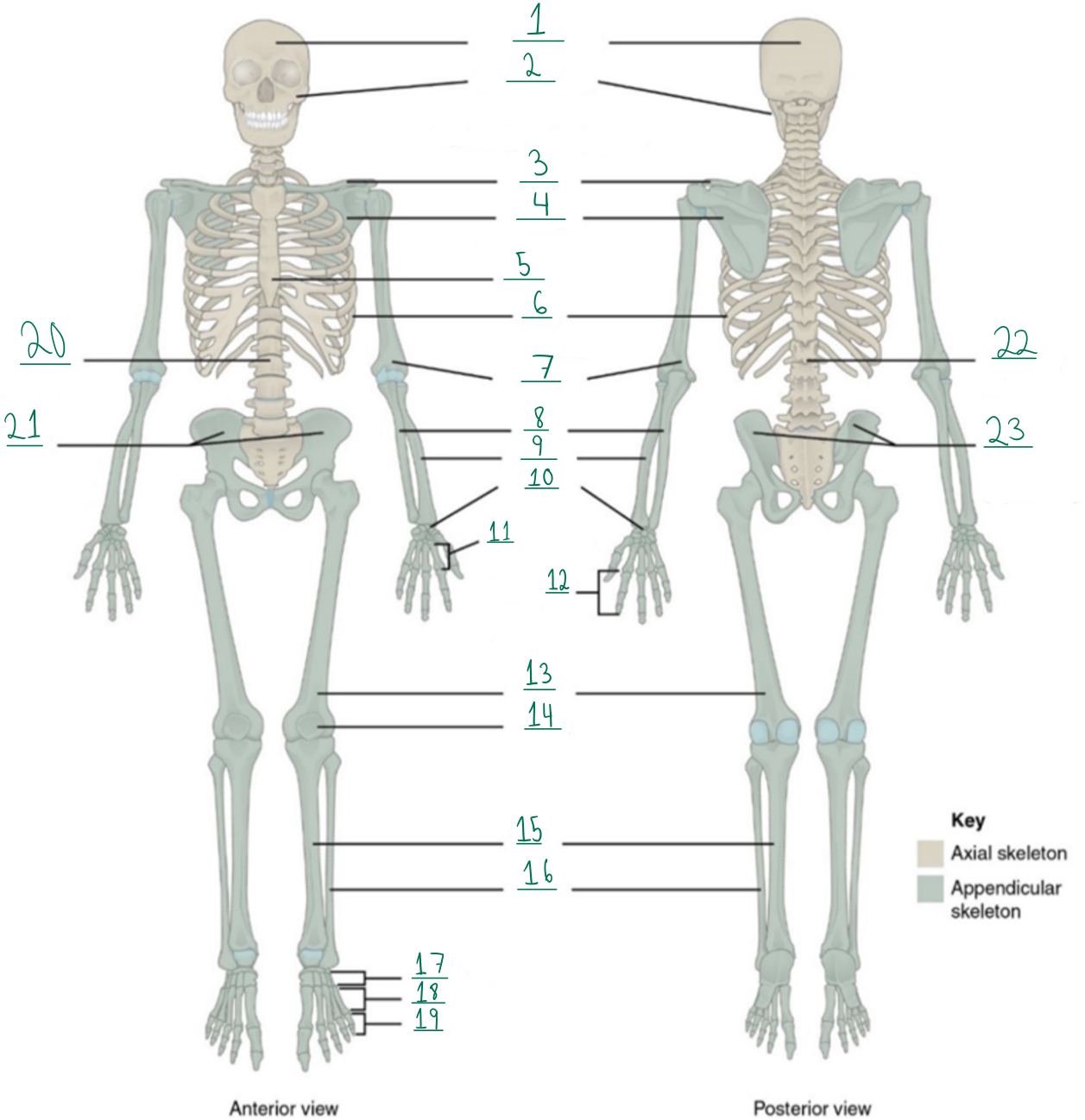
Clavicle
Identify #3 on this image.
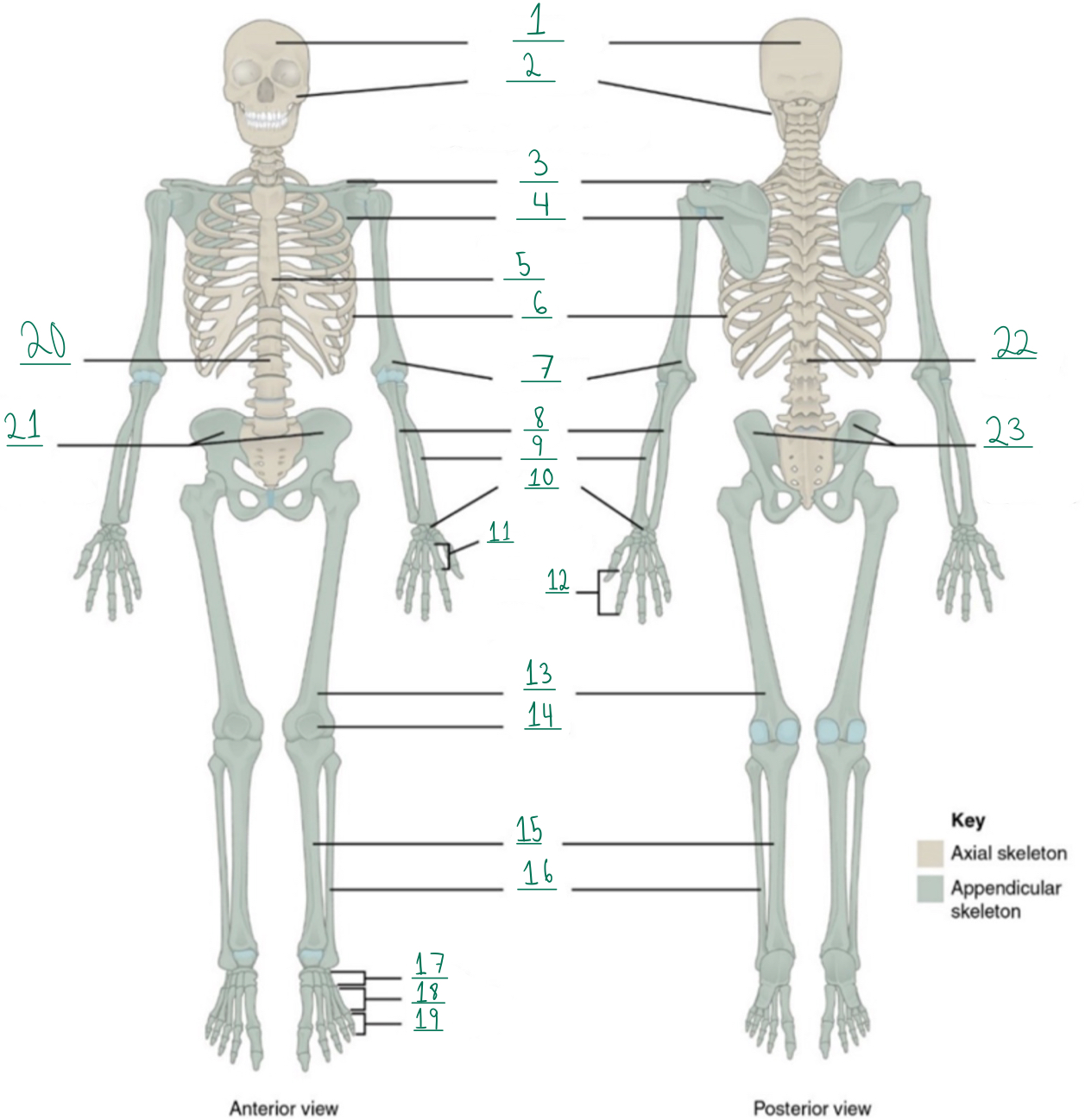
Scapula
Identify #4 on this image.
Sternum
Identify #5 on this image.
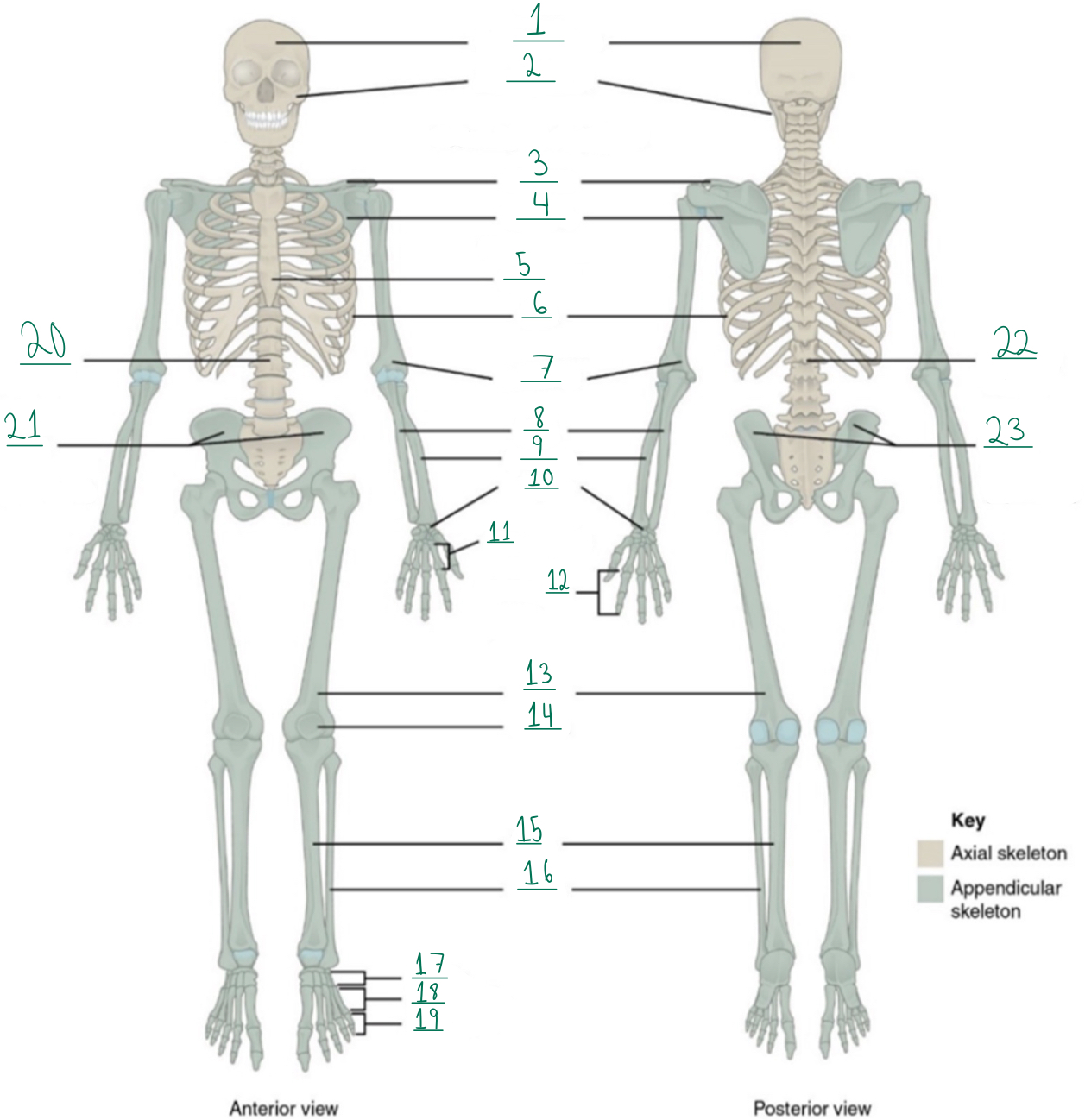
Ribs
Identify #6 on this image.
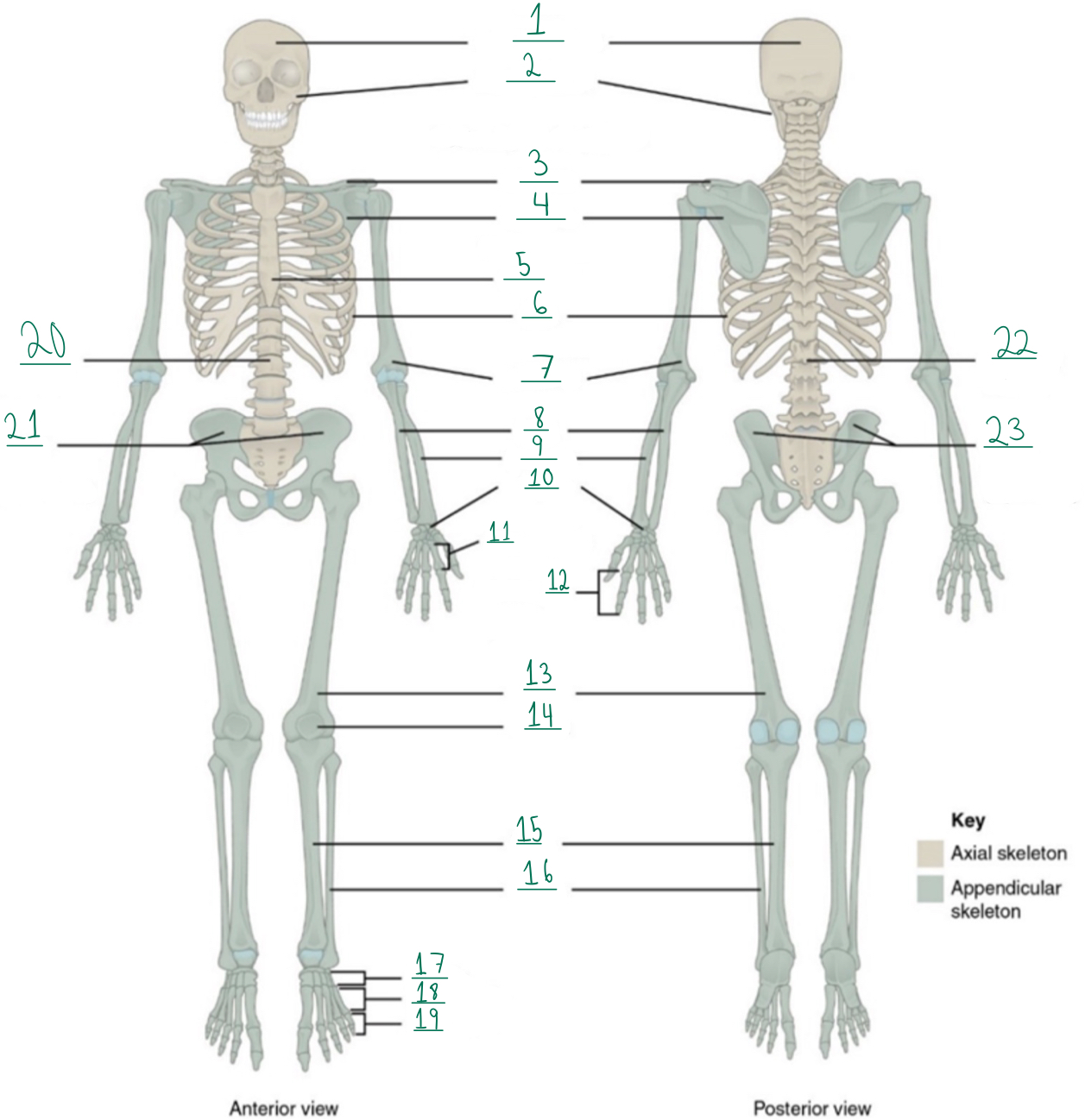
Humerus
Identify #7 on this image.
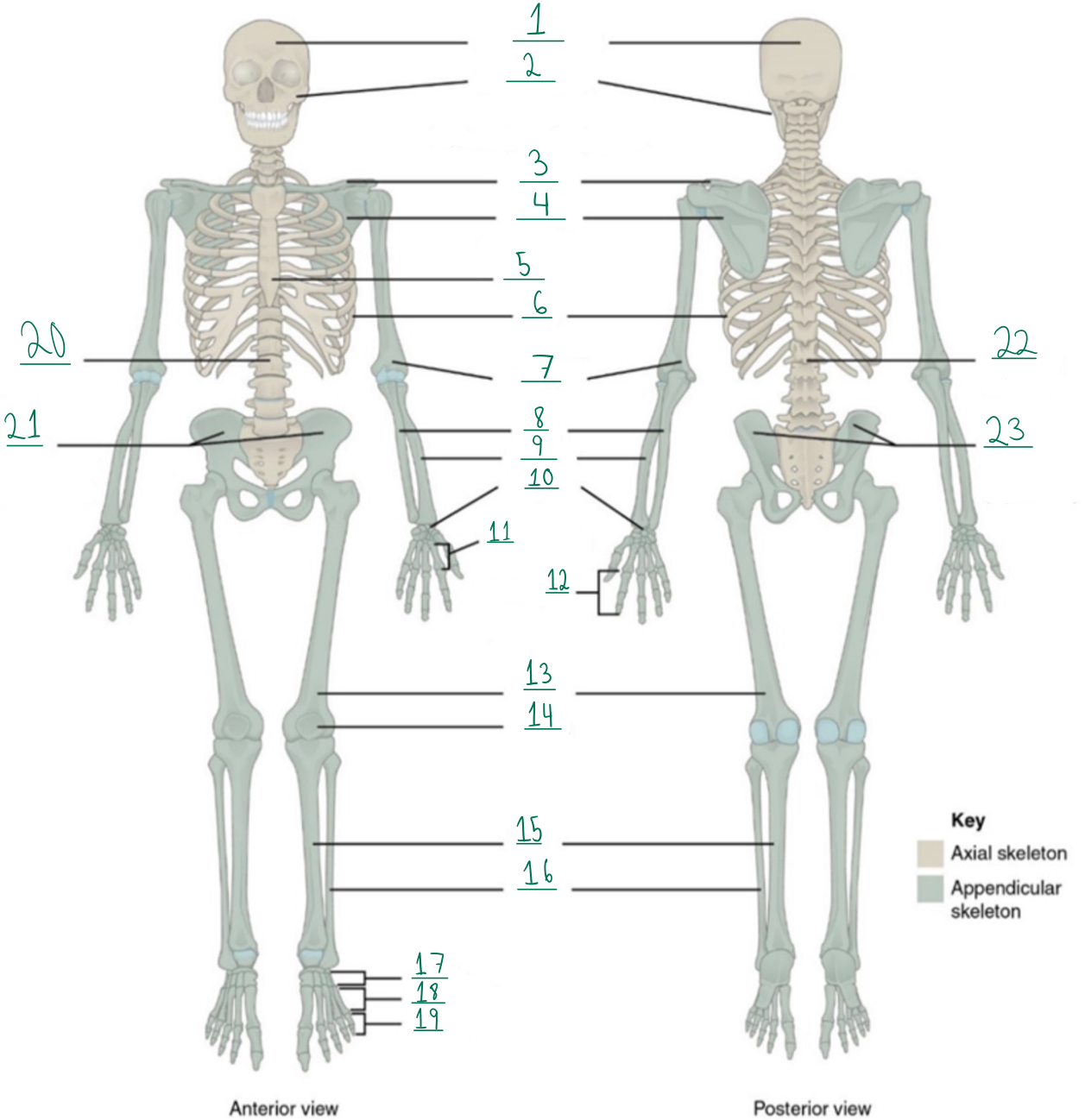
Ulna
Identify #8 on this image.
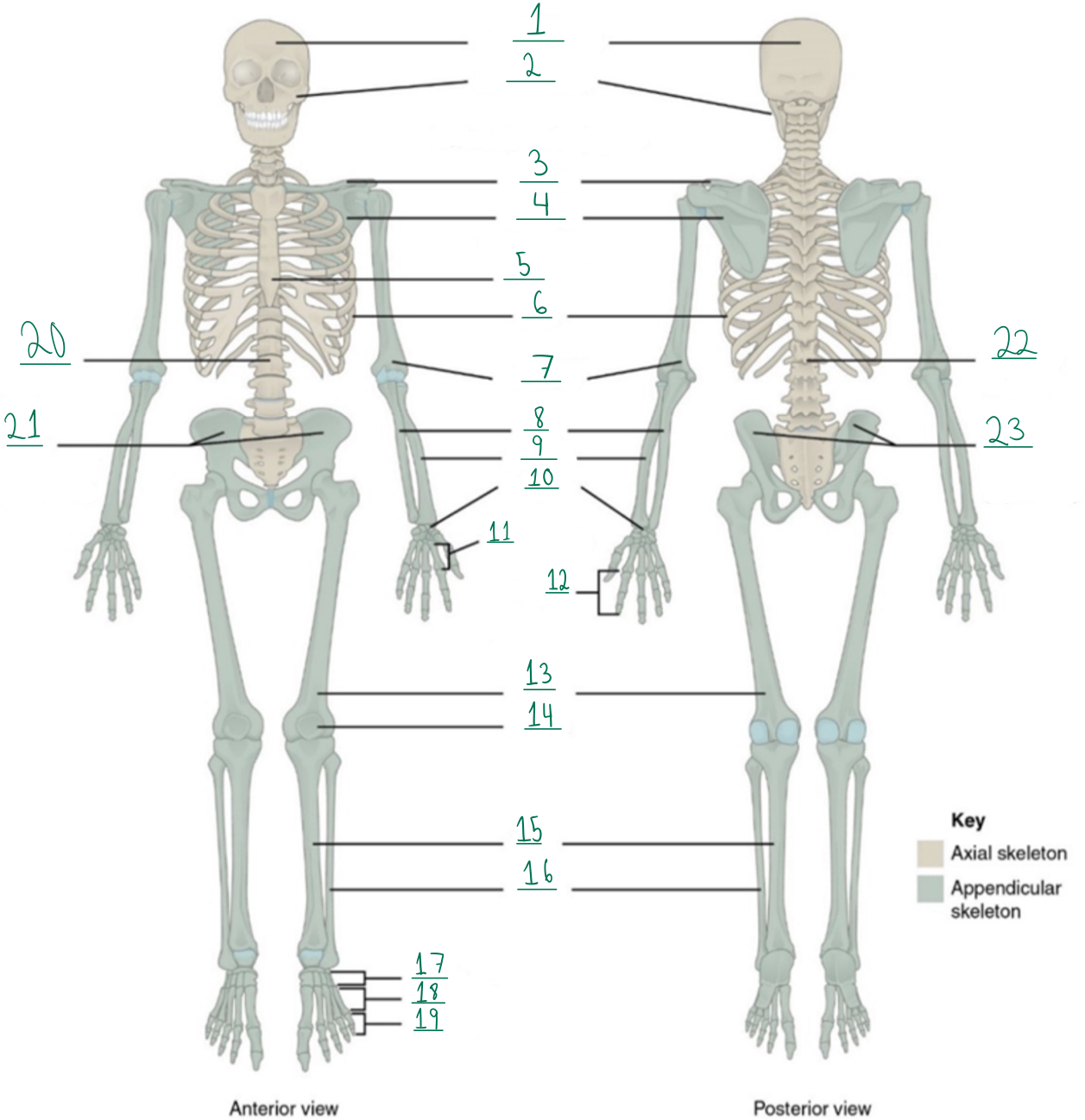
Radius
Identify #9 on this image.
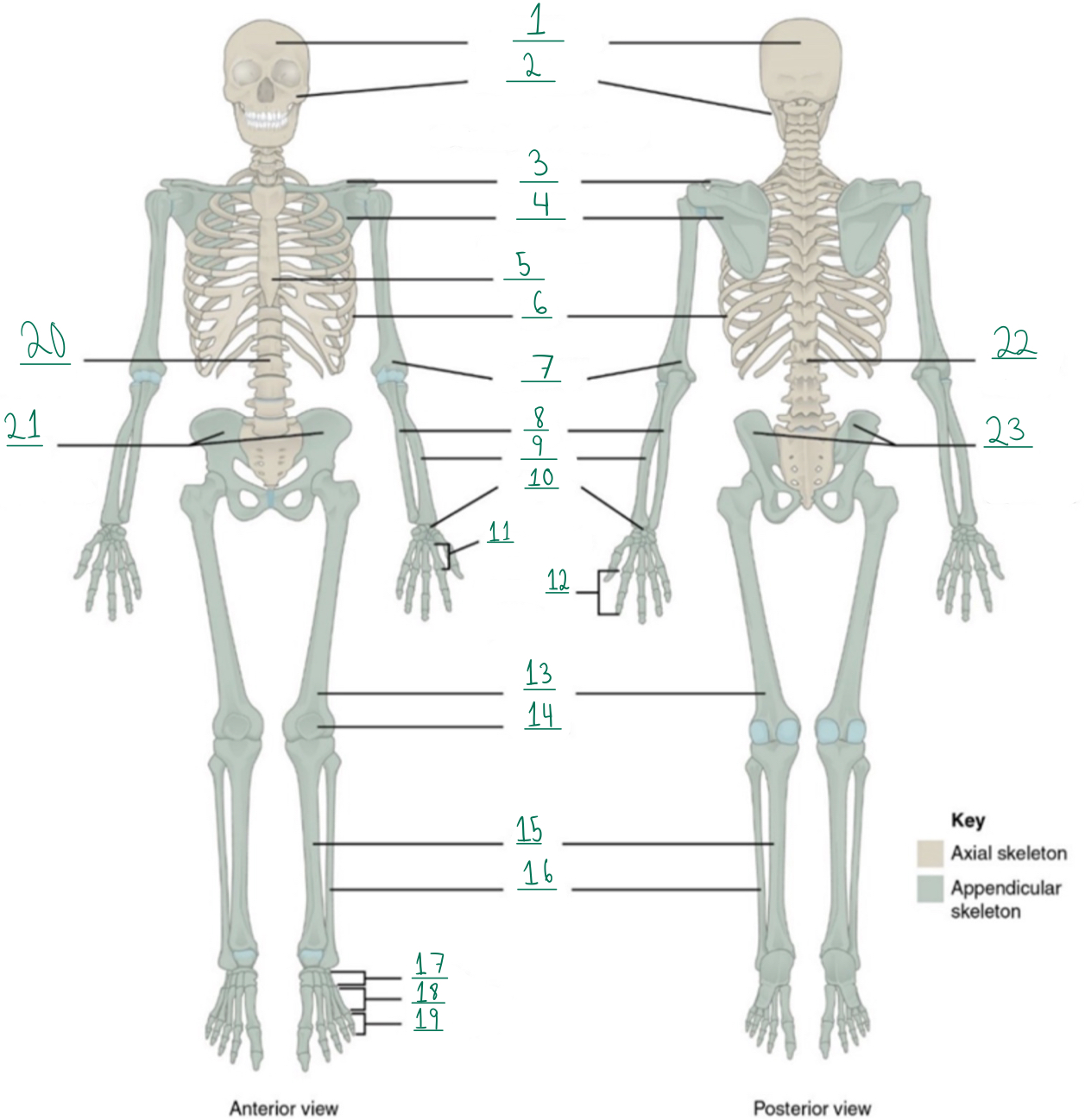
Carpals
Identify #1O on this image.
Metacarpals
Identify #11 on this image.
Phalanges
Identify #12 on this image.
Femur
Identify #13 on this image.

Patella
Identify #14 on this image.
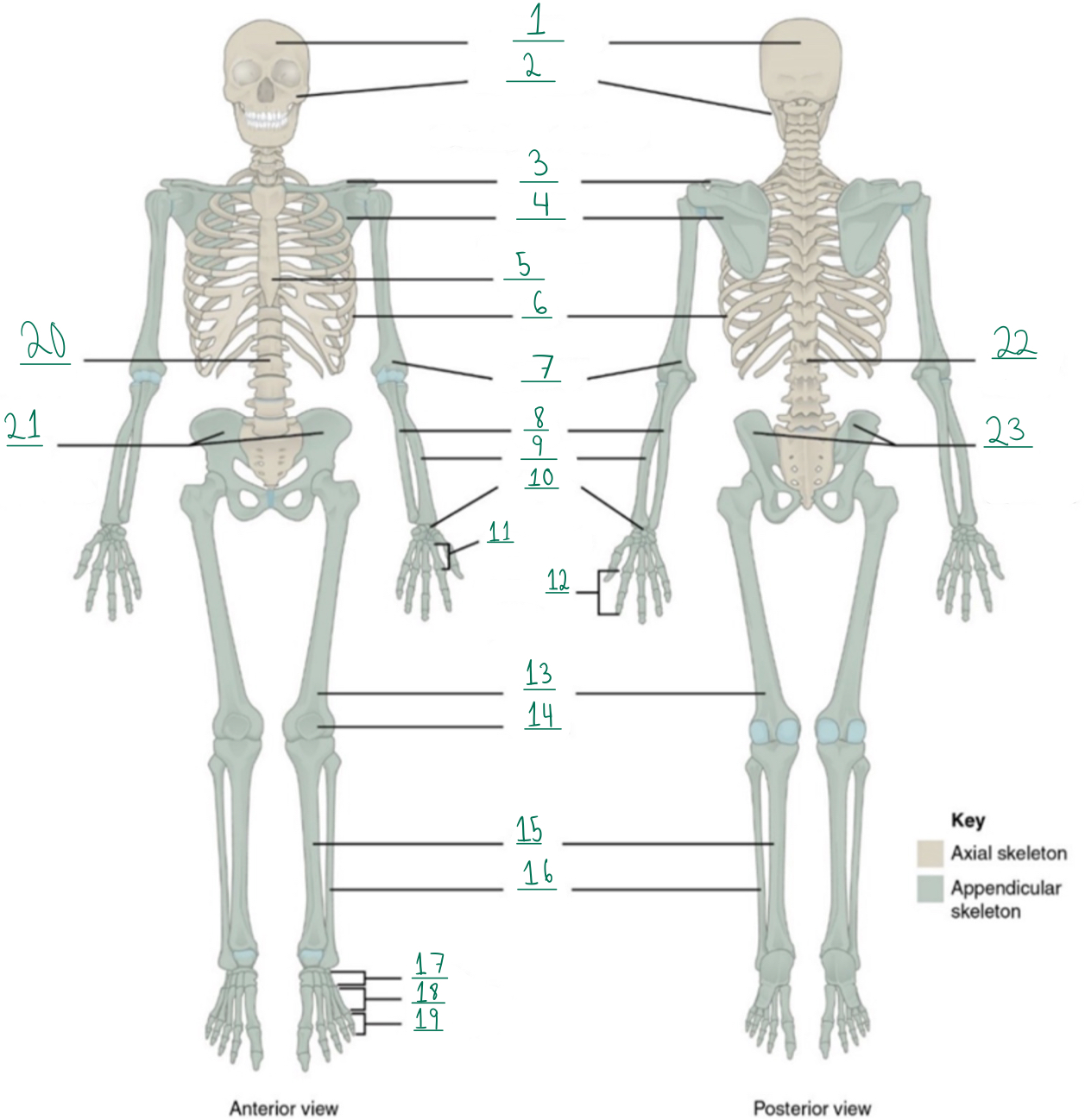
Tibia
Identify #15 on this image.
Fibula
Identity #16 on this image.
Tarsals
Identify #17 on this image.
Metatarsals
Identify #18 on this image.
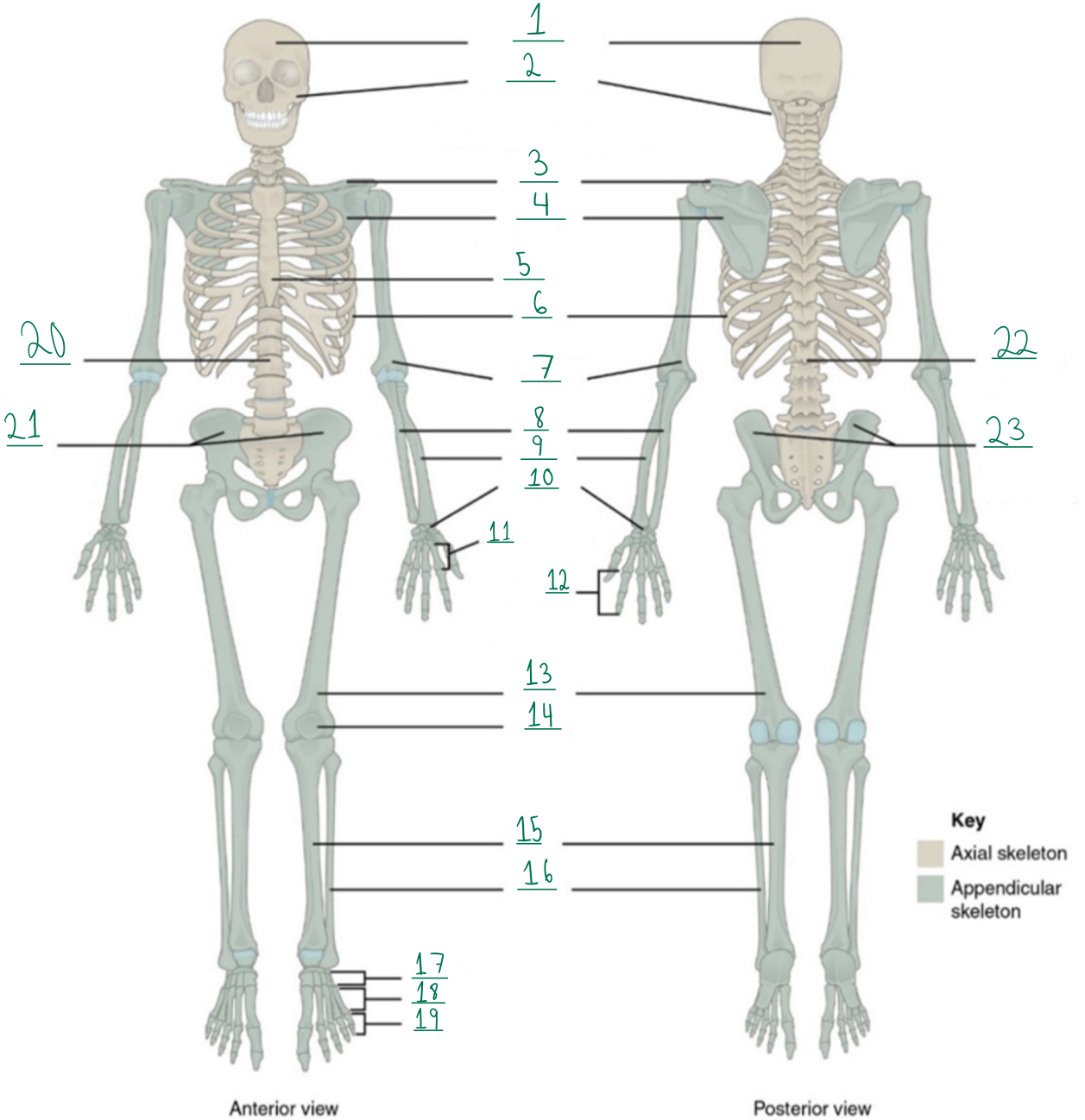
Phalanges
Identify #19 on this image.
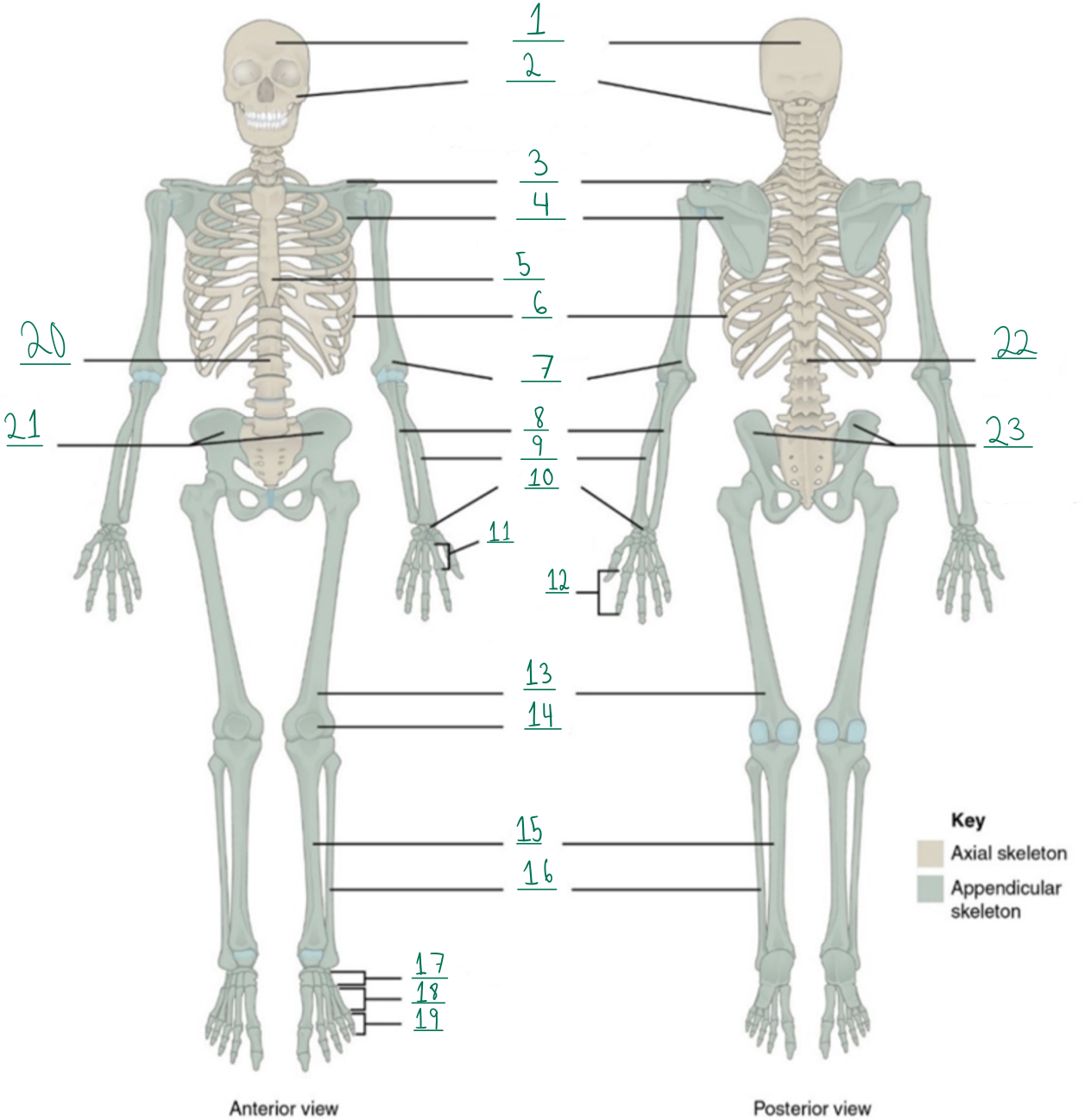
Vertebral column
Identify #20 on this image.
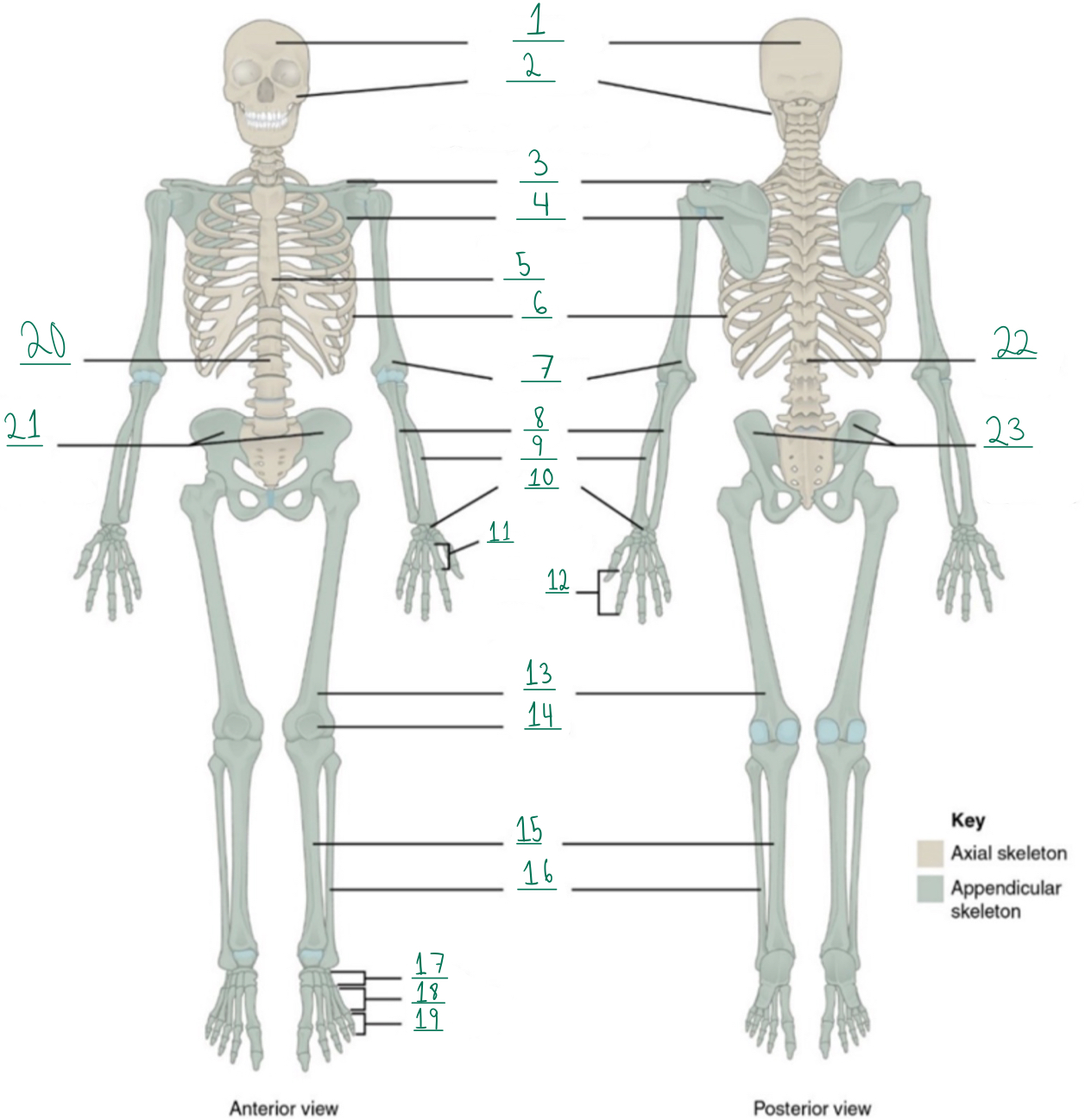
Pelvic girdle
Identify #21 on this image.
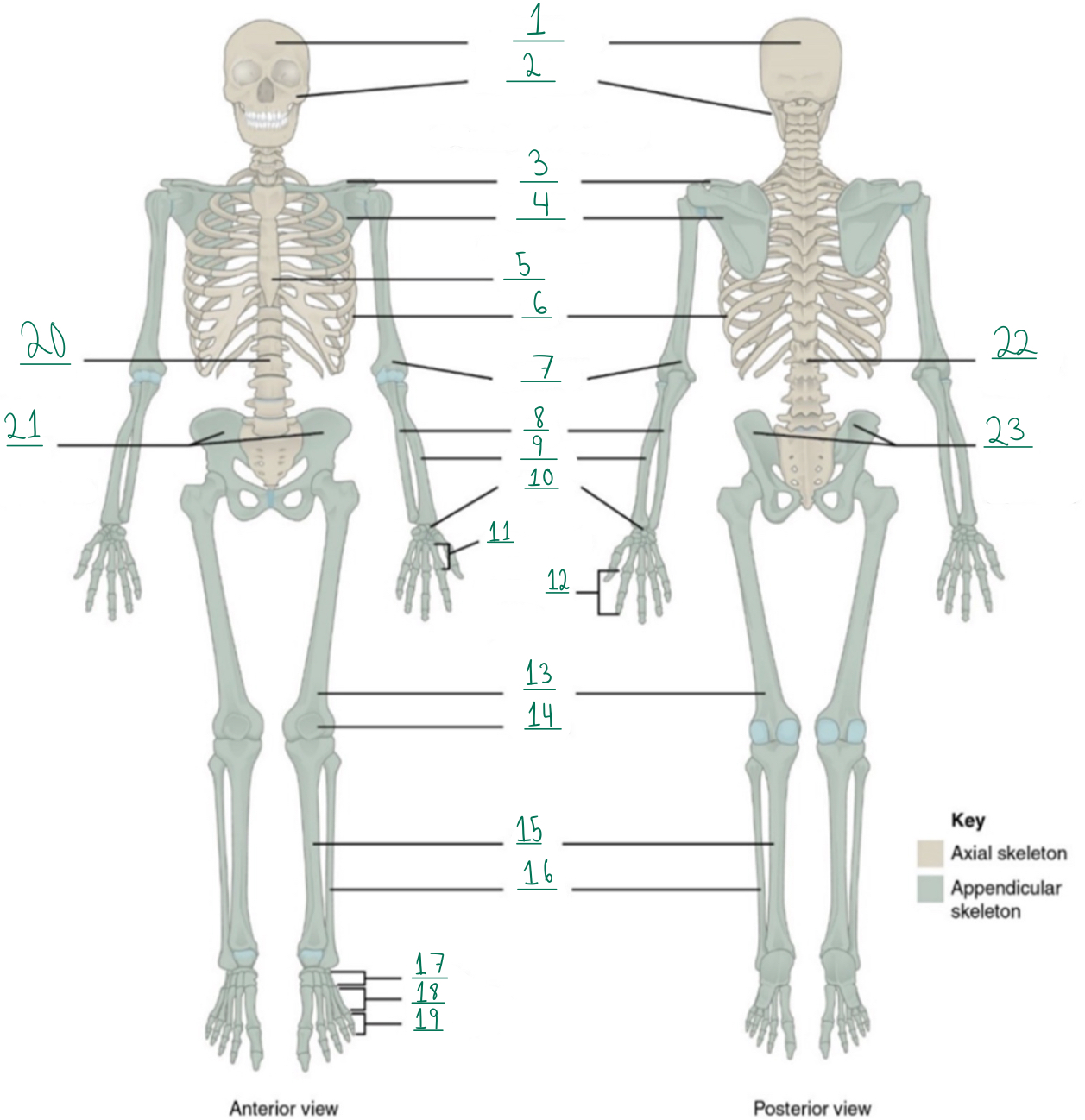
Vertebral column
Identify #22 on this image.
Pelvic girdle
Identify #23 on this image.
Skull
Cranial portion and Facial portion are part of the _____.
Pectoral girdle
The Clavicle and the Scapula are part of the _______.
Thoracic cage
The Sternum and Ribs are part of the ______.
Upper limb
The Humerus, Ulna, Radius, Carpals, Metacarpals, and Phalanges are all part of the ______.
Lower limb
The Femur, Patella, Tibia, Fibula, Tarsals, Metatarsals, and phalanges are all part of the _______.
Axial skeleton
The Skull, Thoracic cage, and Vertebral column all part of the _______.
Appendicular Skeleton
The Pectoral girdle, Upper limb, Lower limb, and Pelvic girdle are part of the ______.
Long bones
Bones that are cylindrical and are longer than wide. (Move when muscles contract).
Short bones
Cube-like shape bones, equal in length, width, and thickness. (Provide stability and support as well as some limited motion).
Flat bones
Bones that are typically thin, but can also be curved. (Serve as point of attachment for muscles and often protect internal organs).
Irregular bones
Bones that do not have any characterized shape and don't fit in any other bone classification.
Compact bone
Hard part of bone, is not as flexible and not a lot of space for cellular activity and movement.
Spongy bone
Less hard part of bone, has some flexibility and has room for cellular activity and movement.
Osteogenic cells
Bone stem cells (blank cells). Are undifferentiated with mitotic activity; they are the only bone cells that divide.
Osteoblast cells
Immature bone cells that produce bone matrix. Are responsible for forming new bone matrix and are found in the growing portion of bone, including the periosteum and endosteum.
Osteocyte cells
Mature bone calls that maintain the bone matrix. Maintain the mineral concentration of the bone matrix via the secretion of enzymes.
Osteoclasts cells
Bone destroying Cells. Are cells responsible for bone resorption or breakdown.
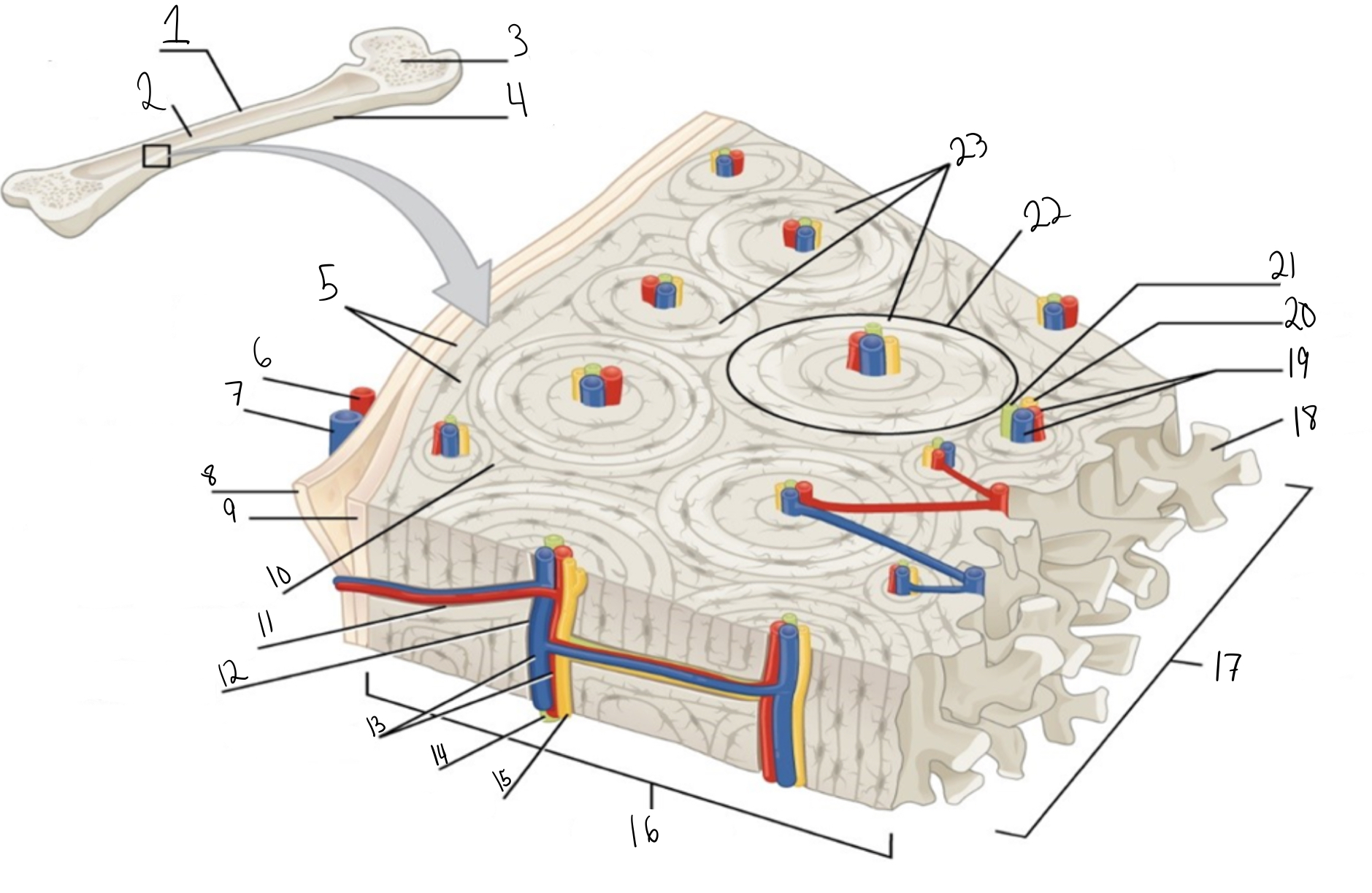
Compact bone
Identify #1 on this image
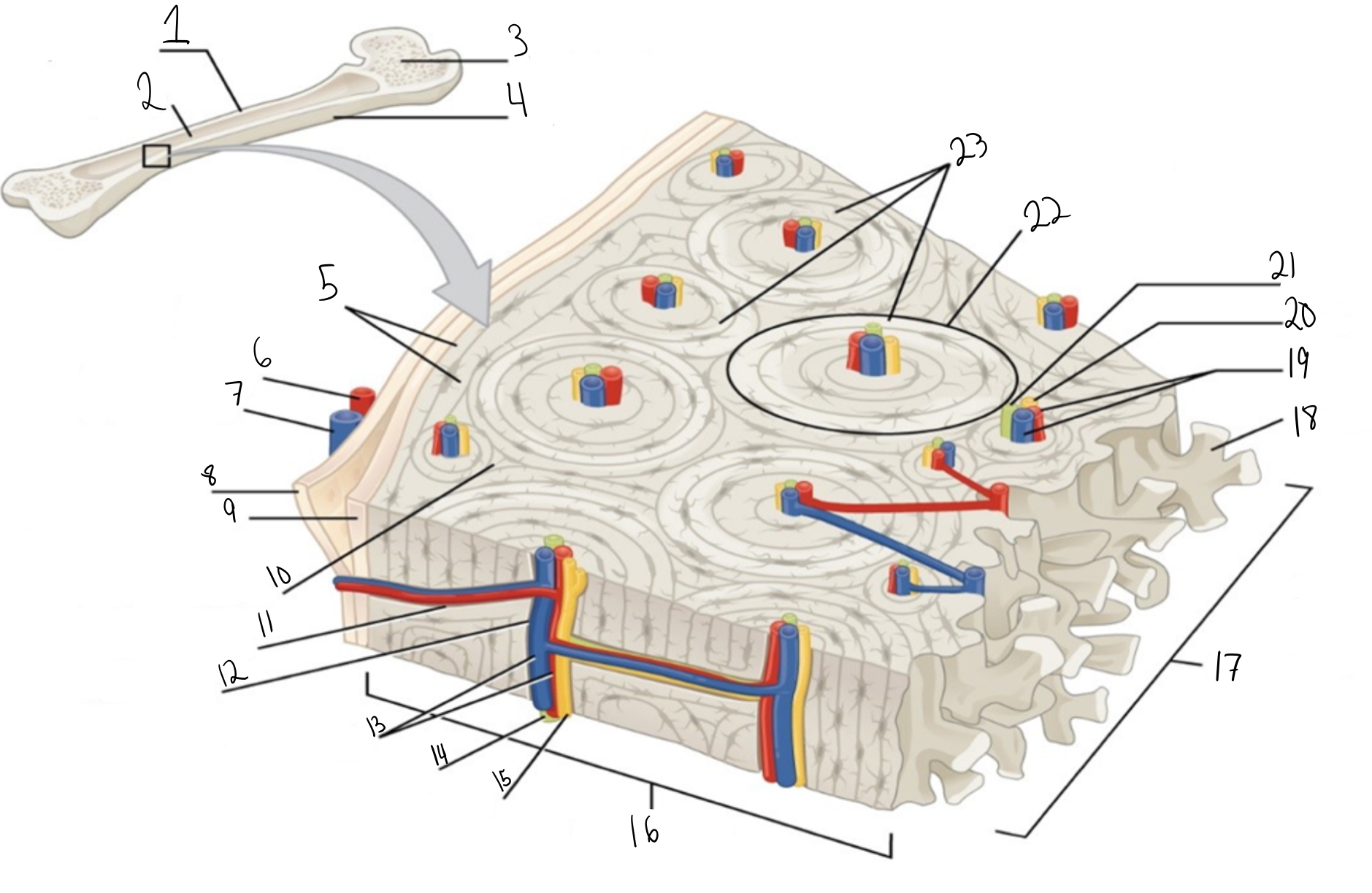
Medullary cavity
Identify #2 on this image.
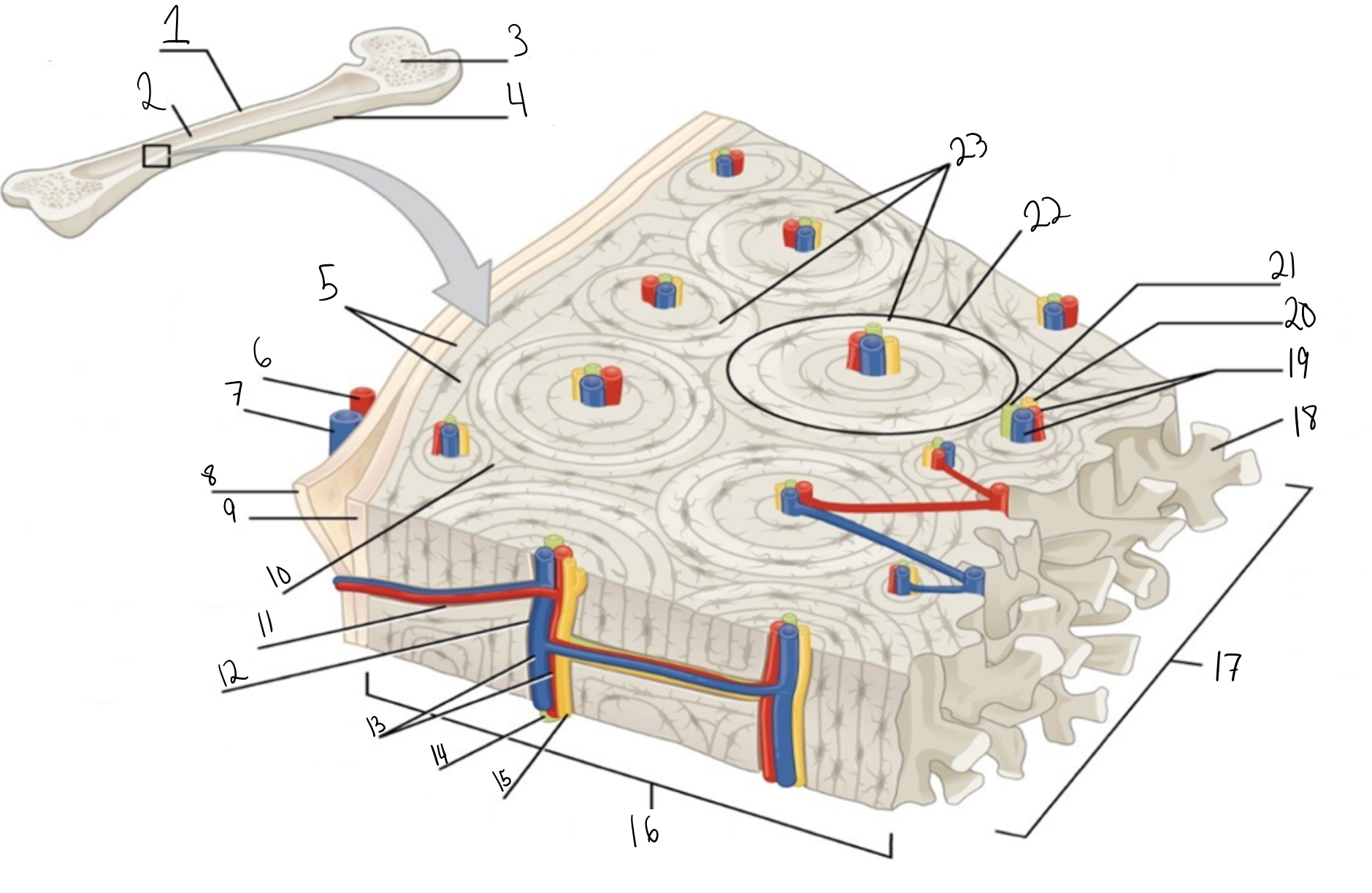
Spongy bone
Identify #3 on this image.
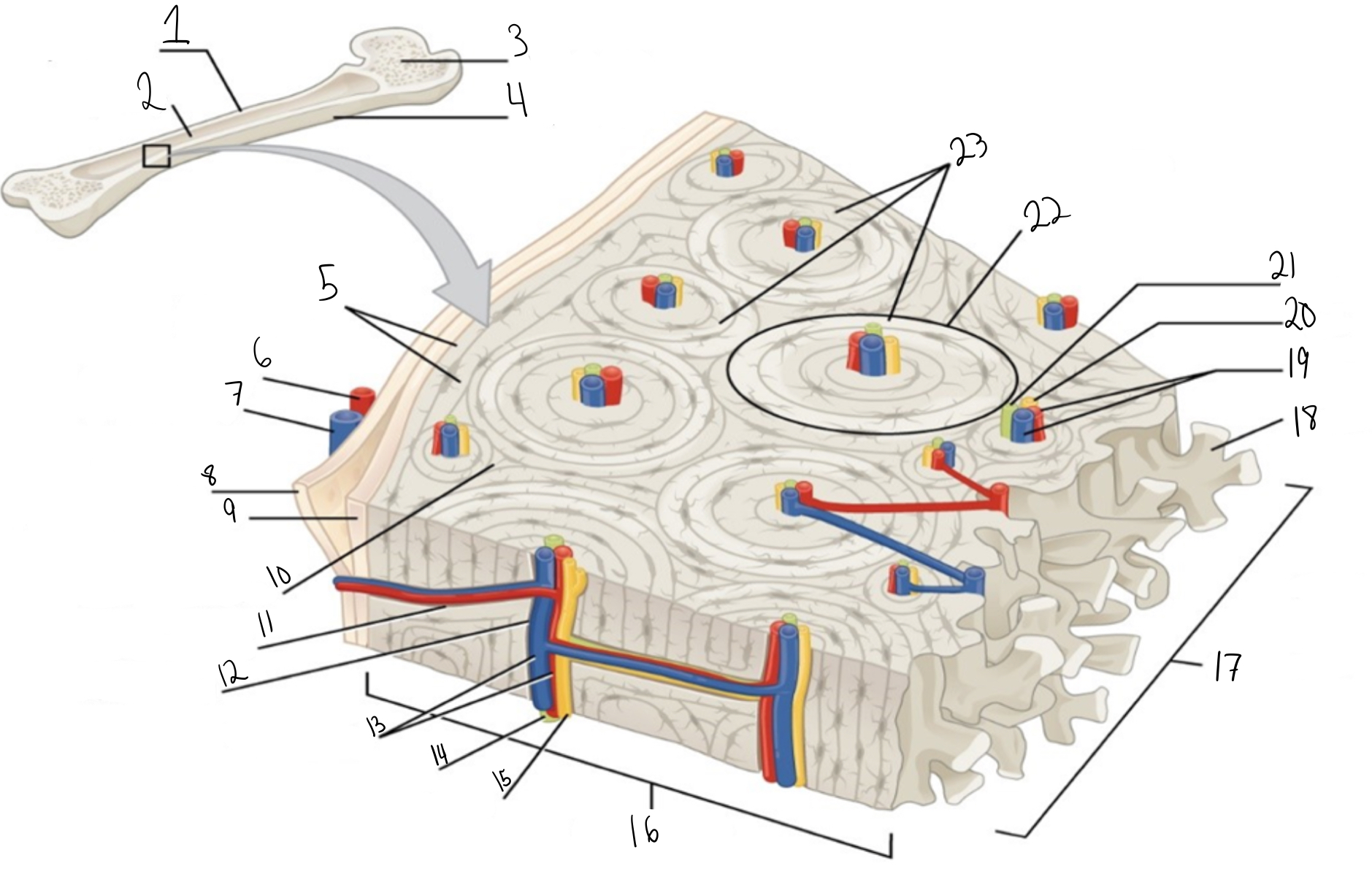
Periosteum
Identify #4 on this image.
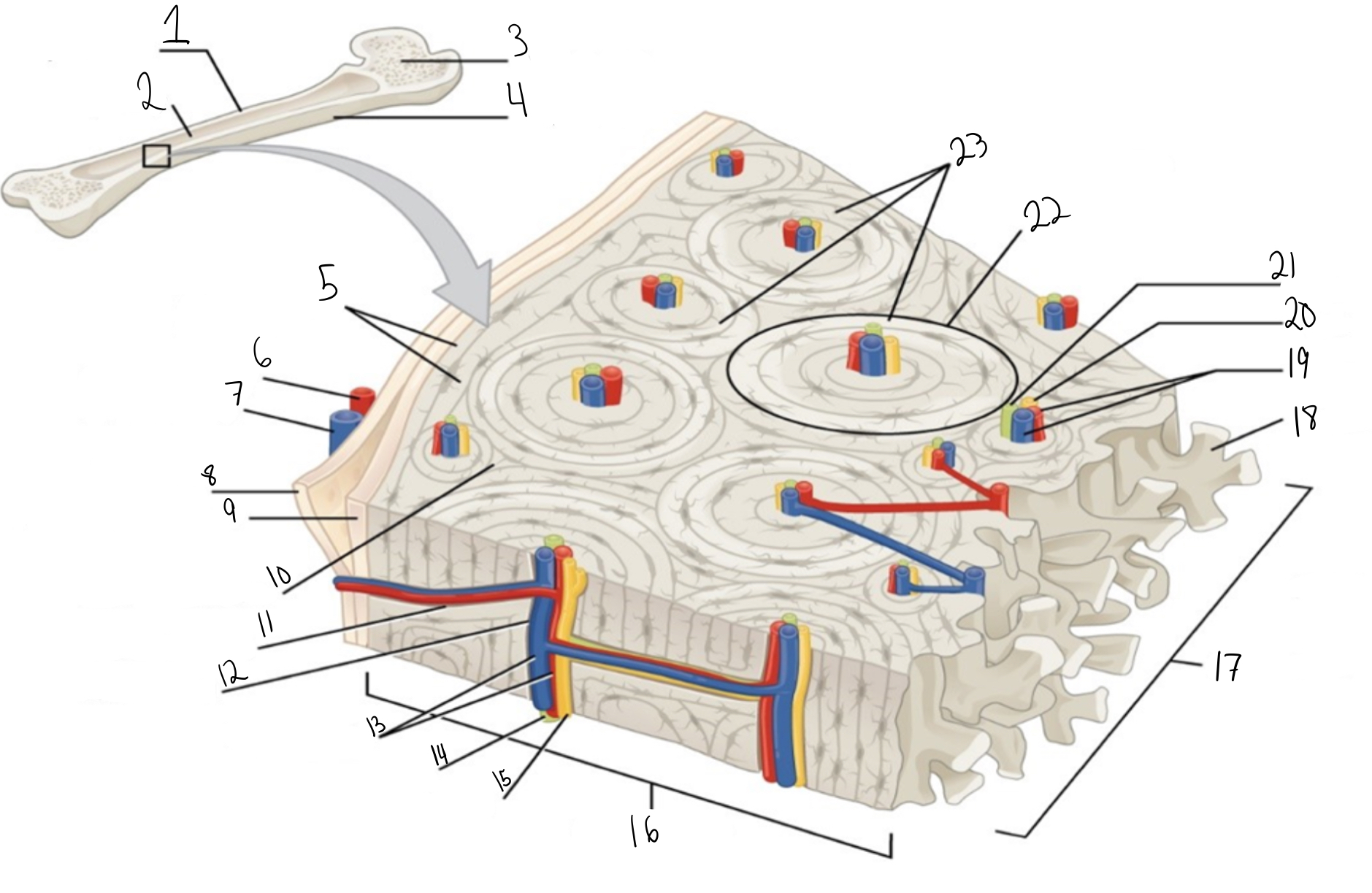
Circumferential lamellae
Identity #5 on this image.
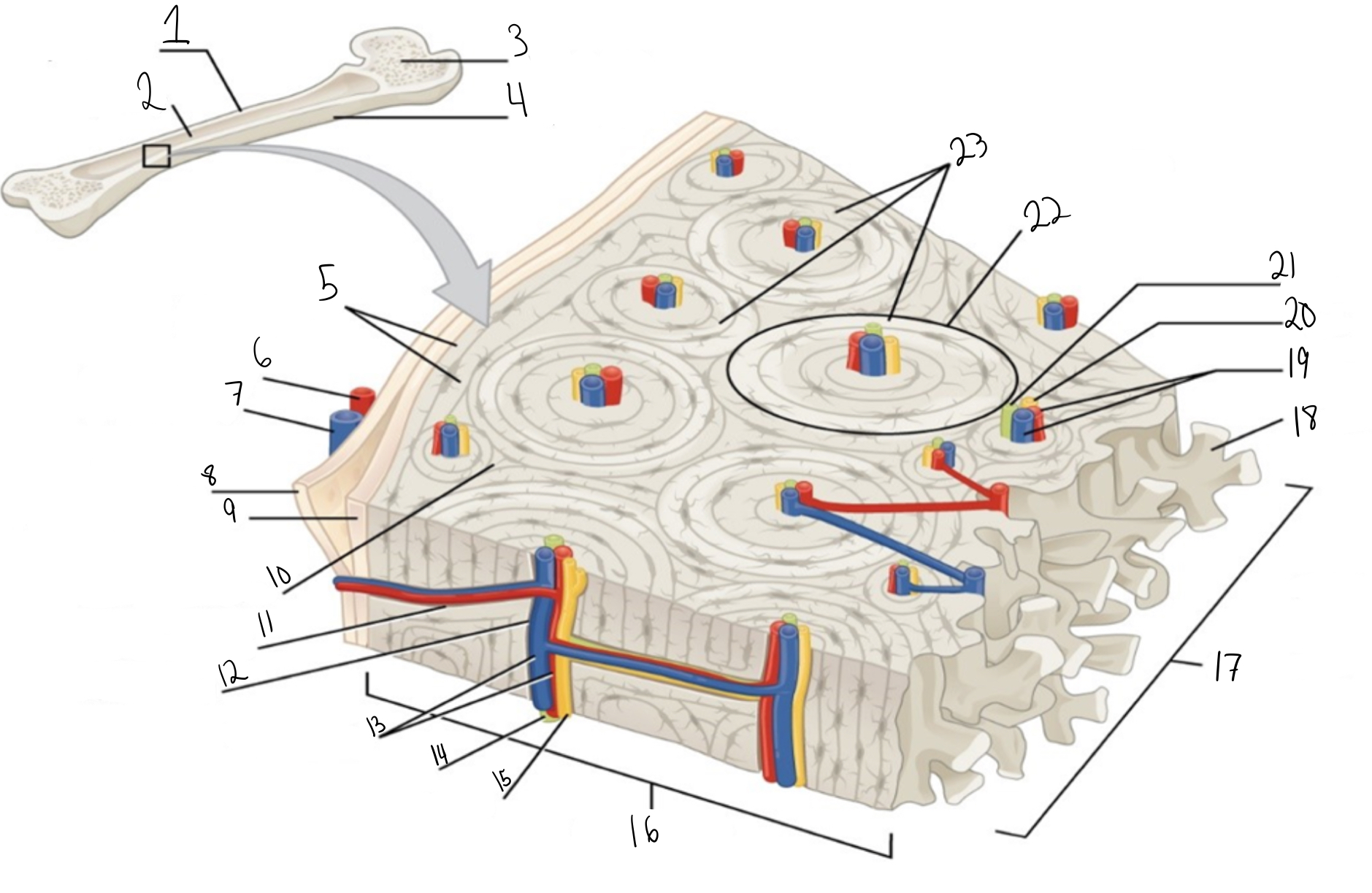
Periosteal artery
Identify #6 on this image.
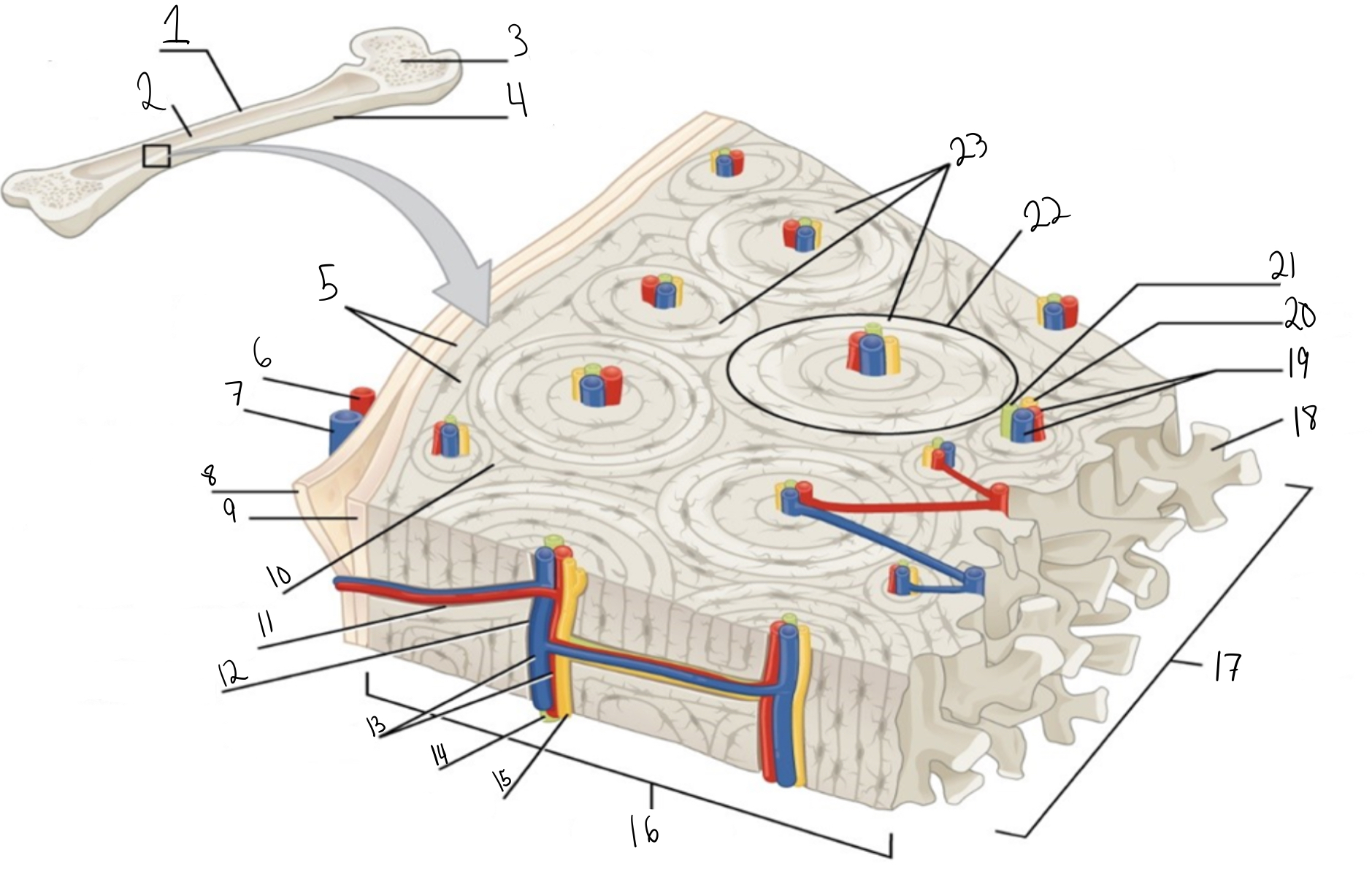
Periosteal vein
Identify #7 on this image.
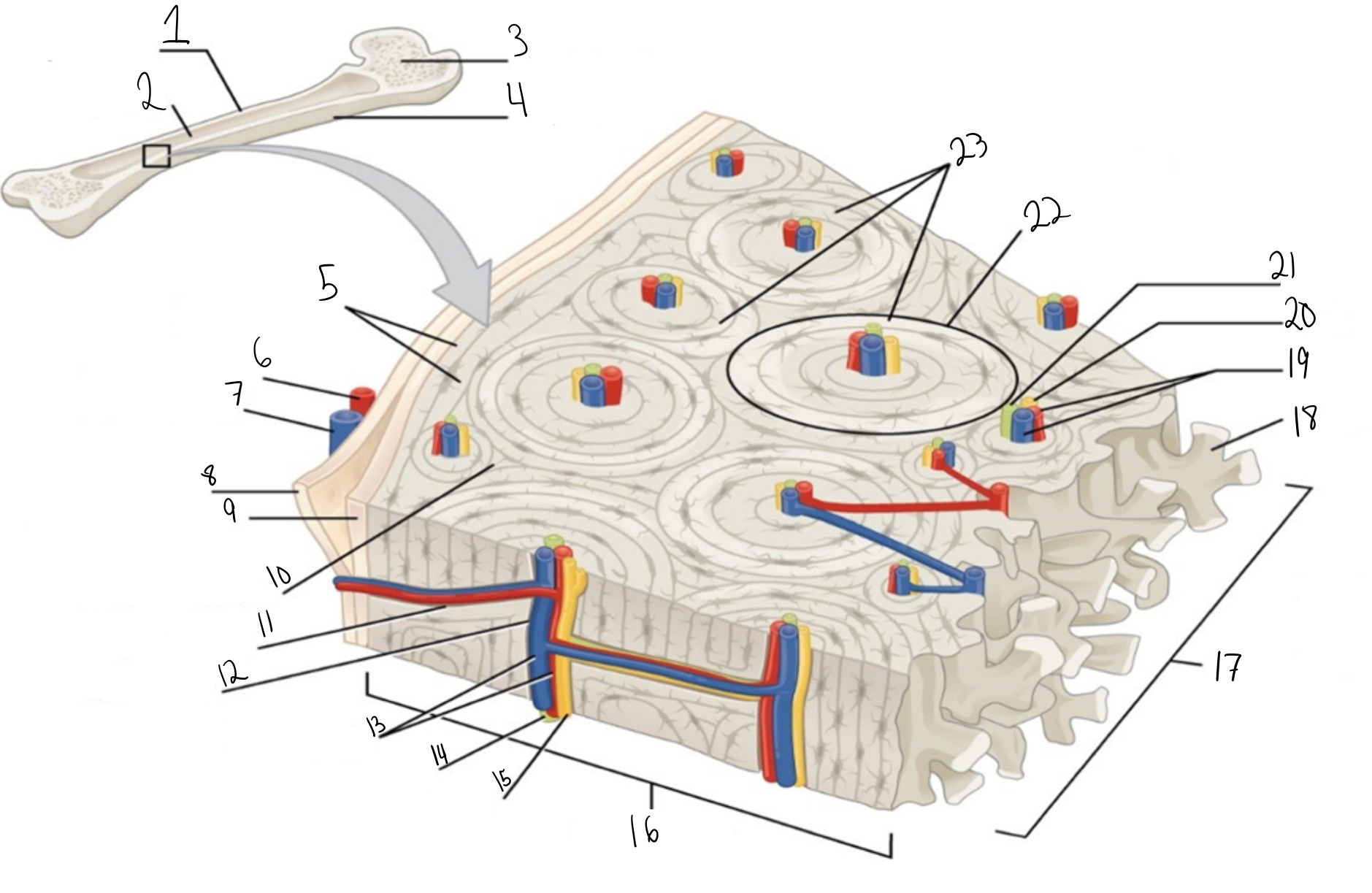
Outer fibrous layer (periosteum)
Identify #8 on this image.
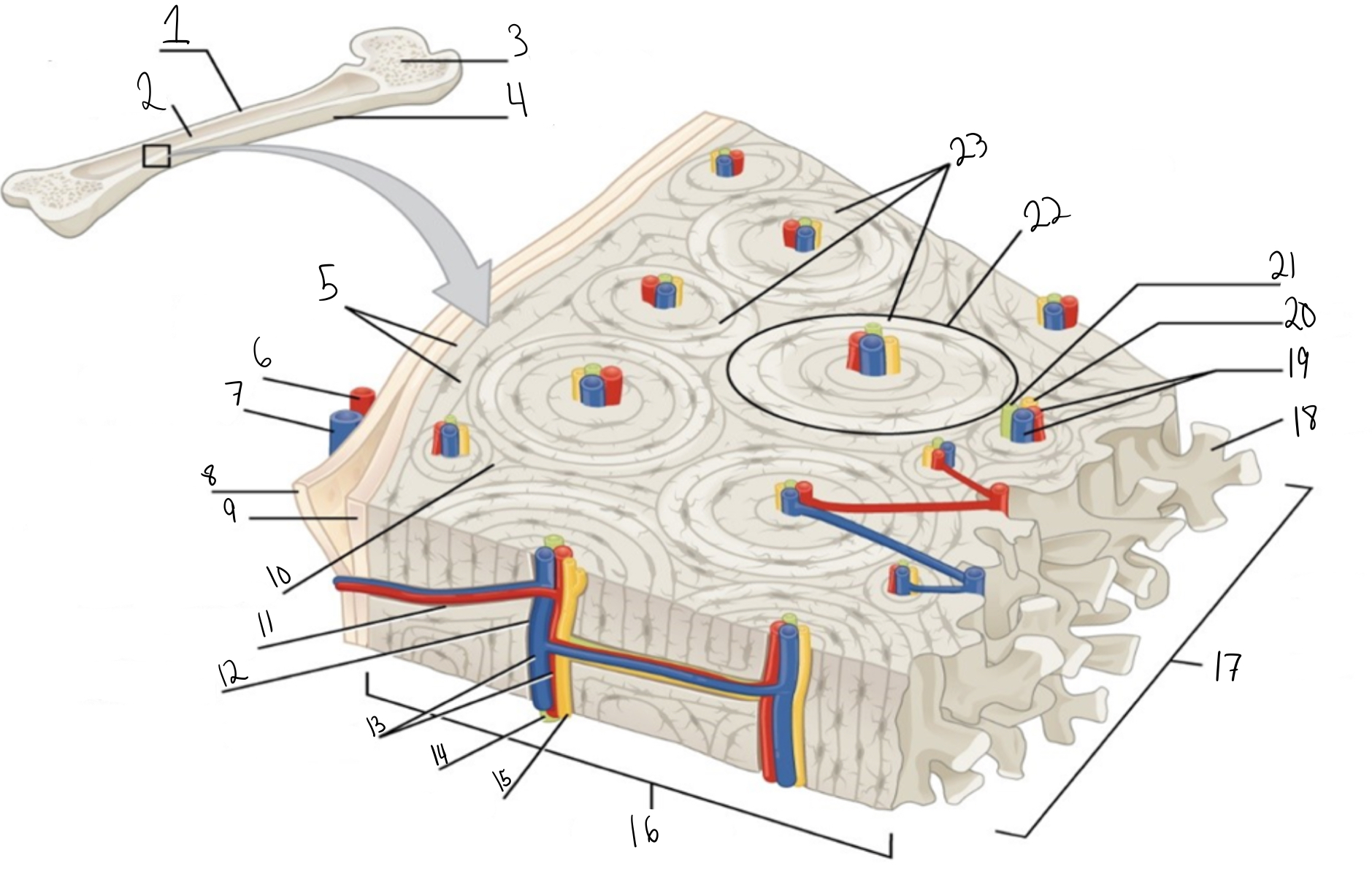
Inner osteogenic layer (periosteum)
Identify #9 on this image.
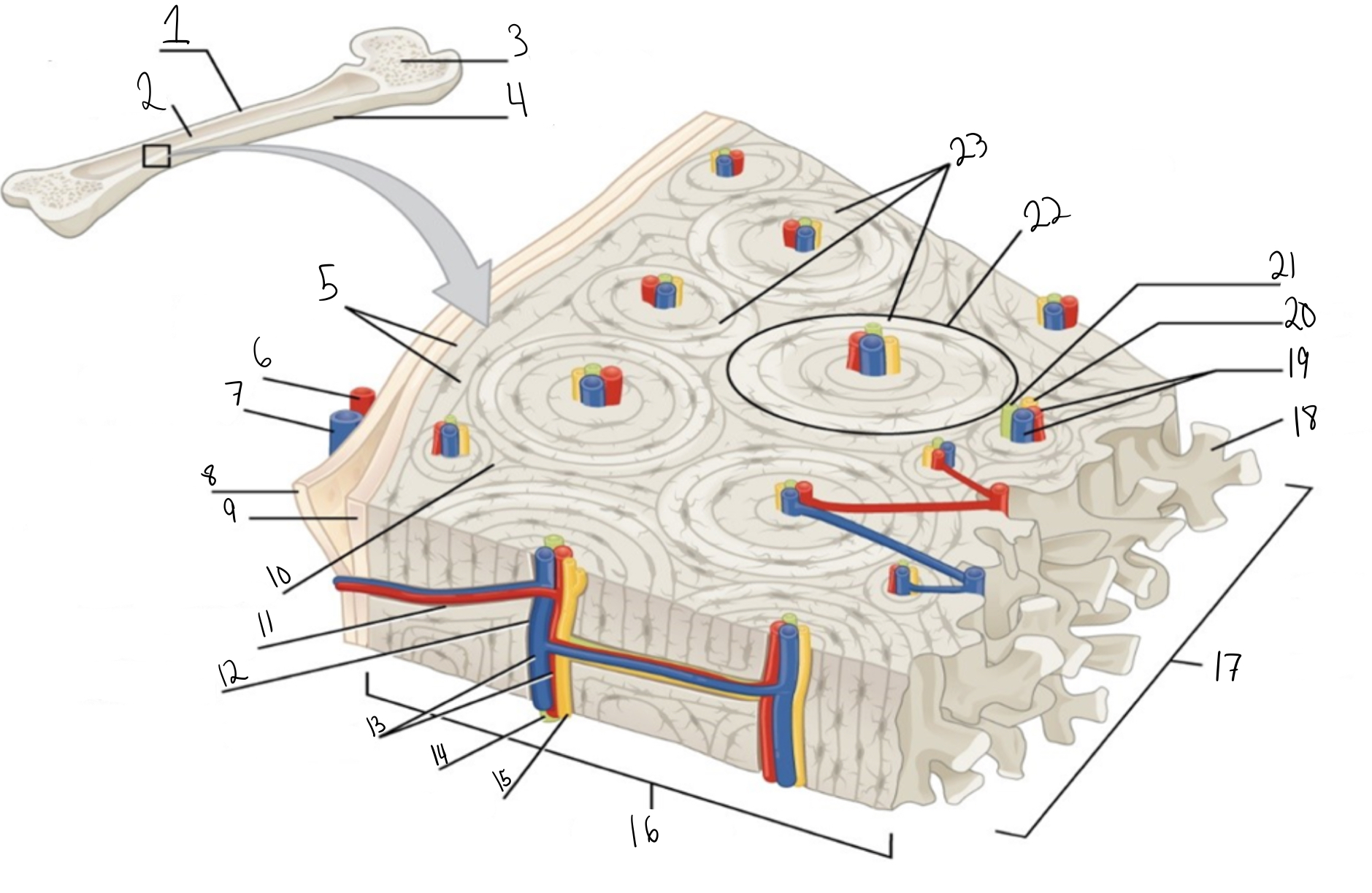
Interstitial lamellae
Identify #10 on this image.
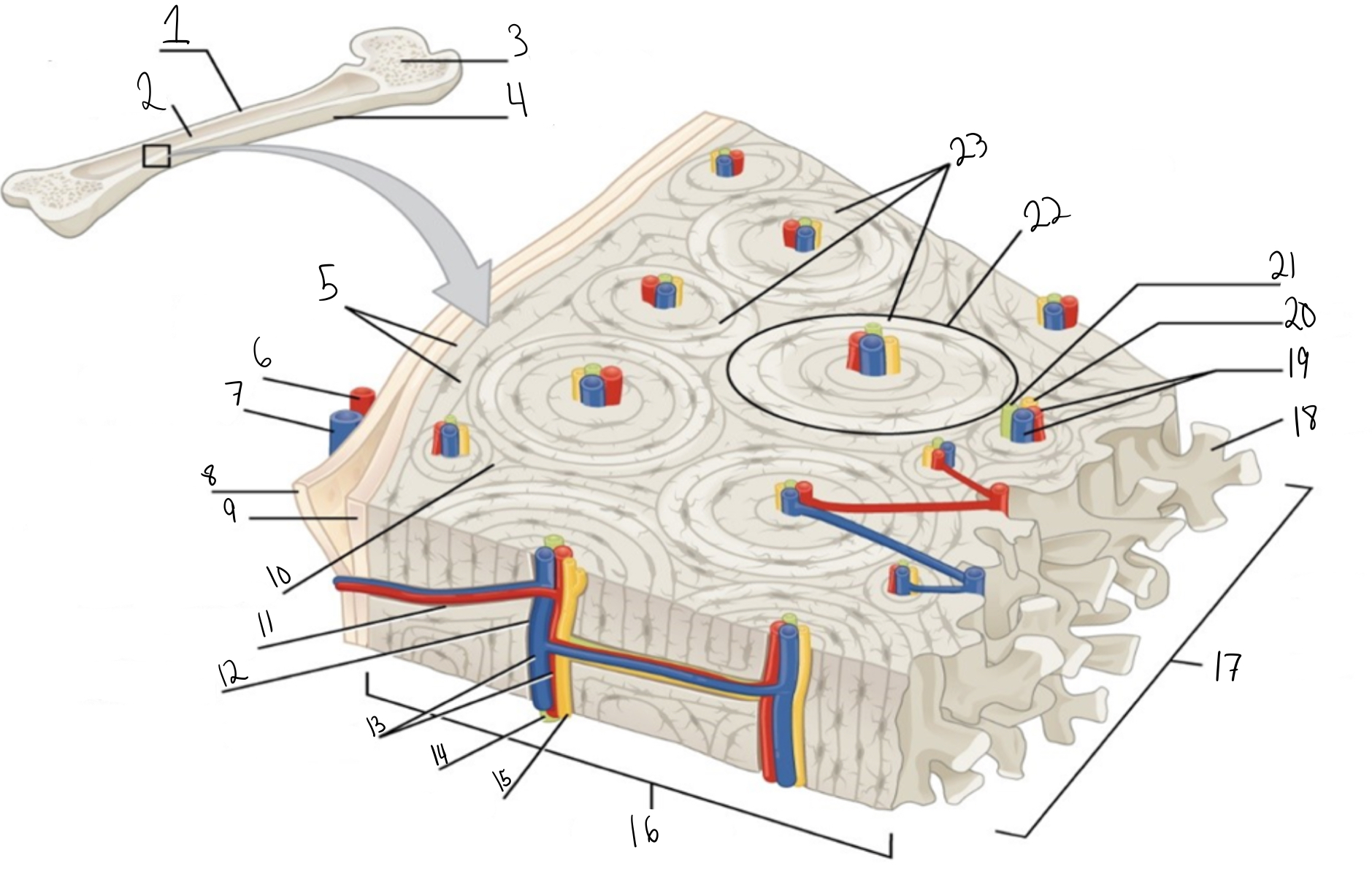
Perforating canal
Identify #11 on this image.
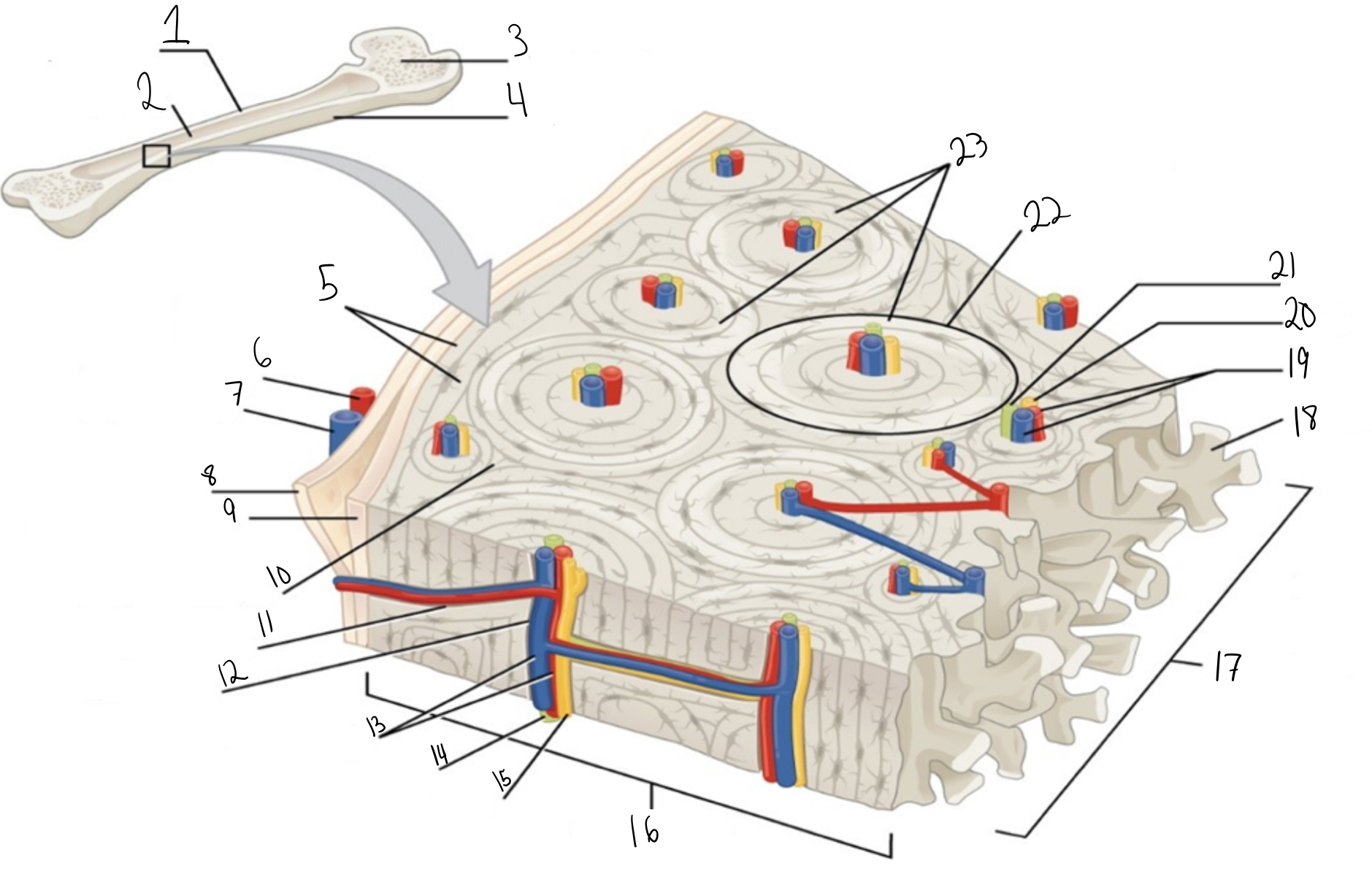
Central canal
Identify #12 on this image.
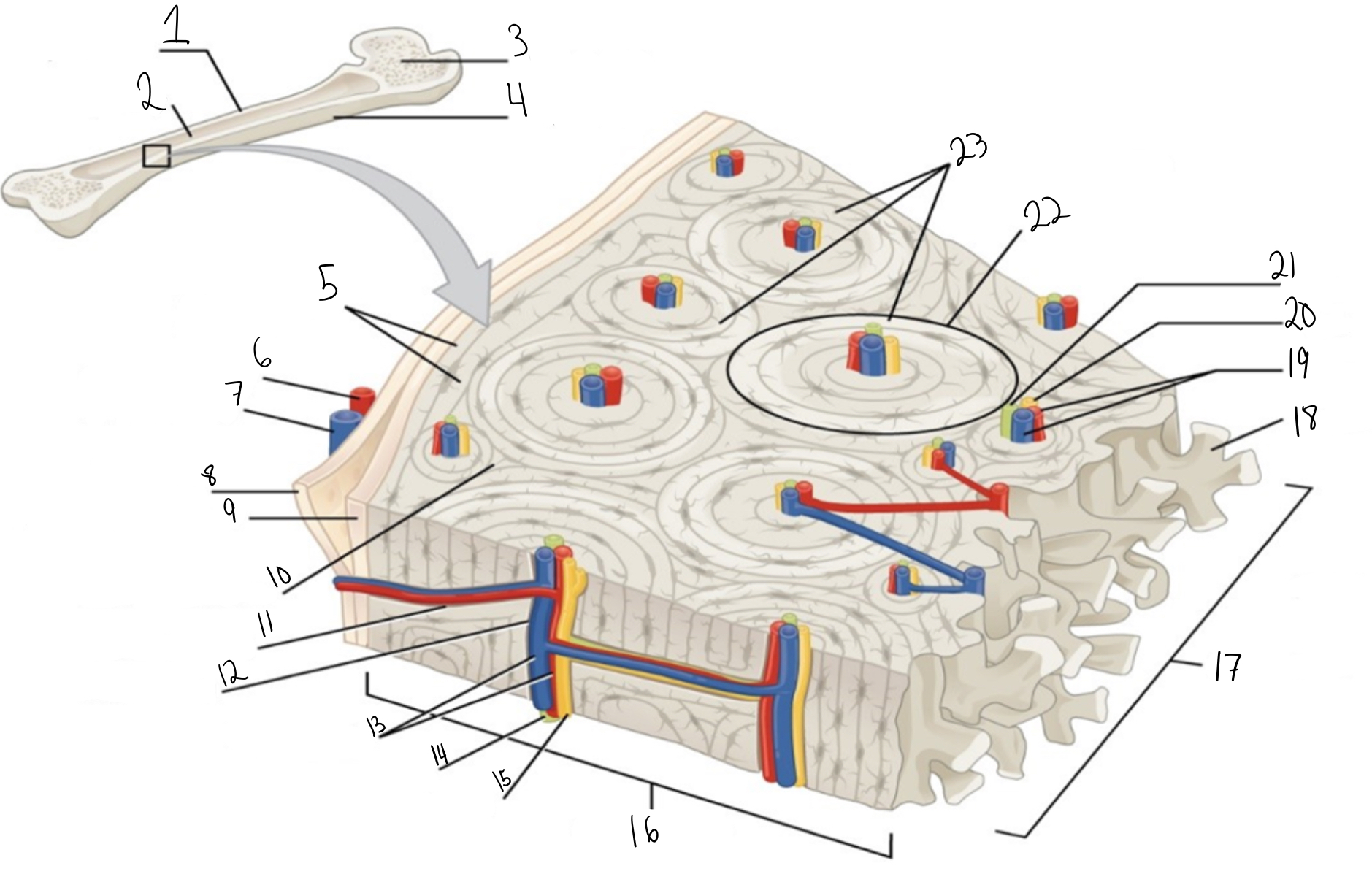
Blood vessels
Identify #13 on this image.
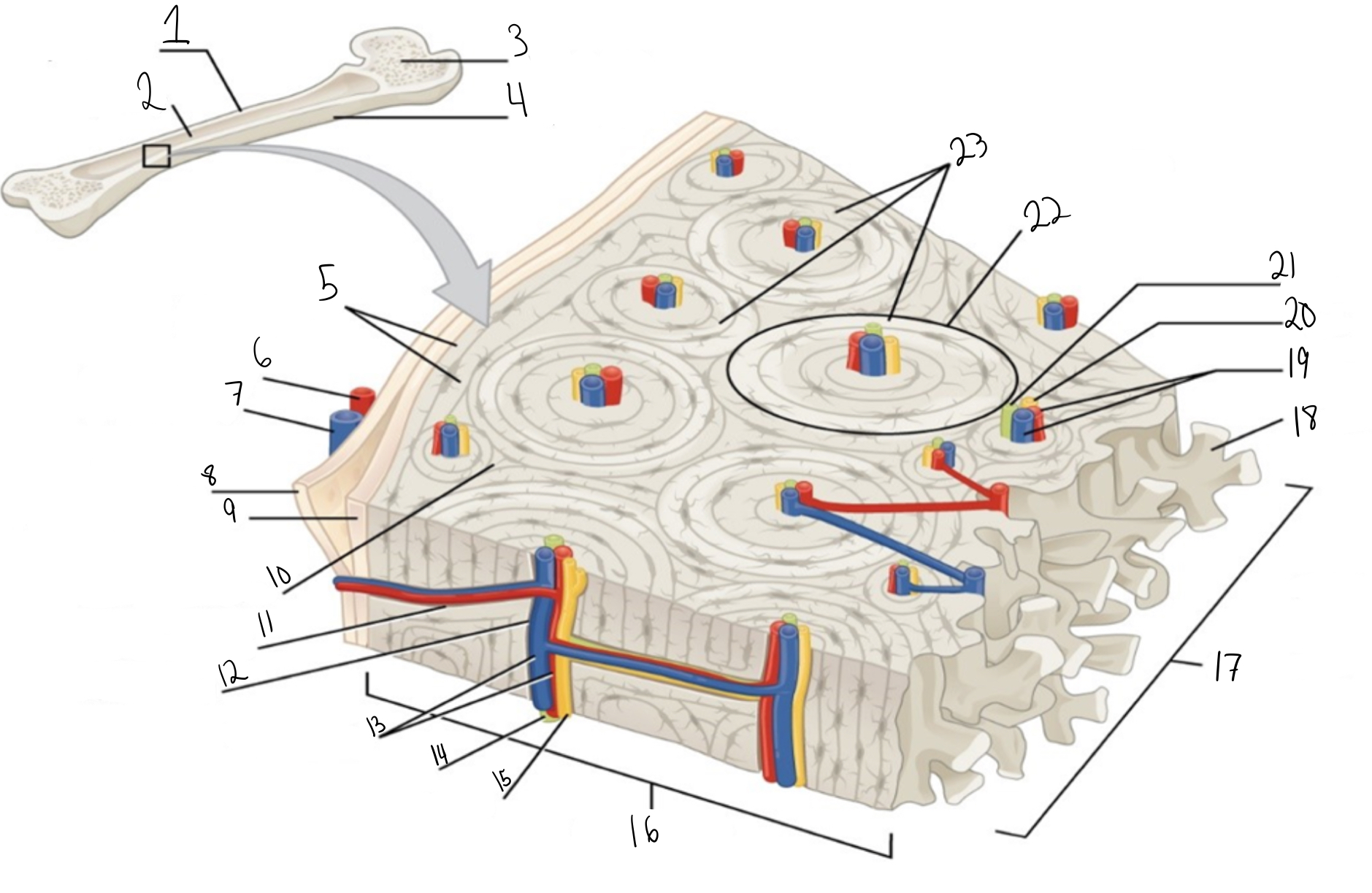
Lymphatic vessel
Identity #14 on this image.
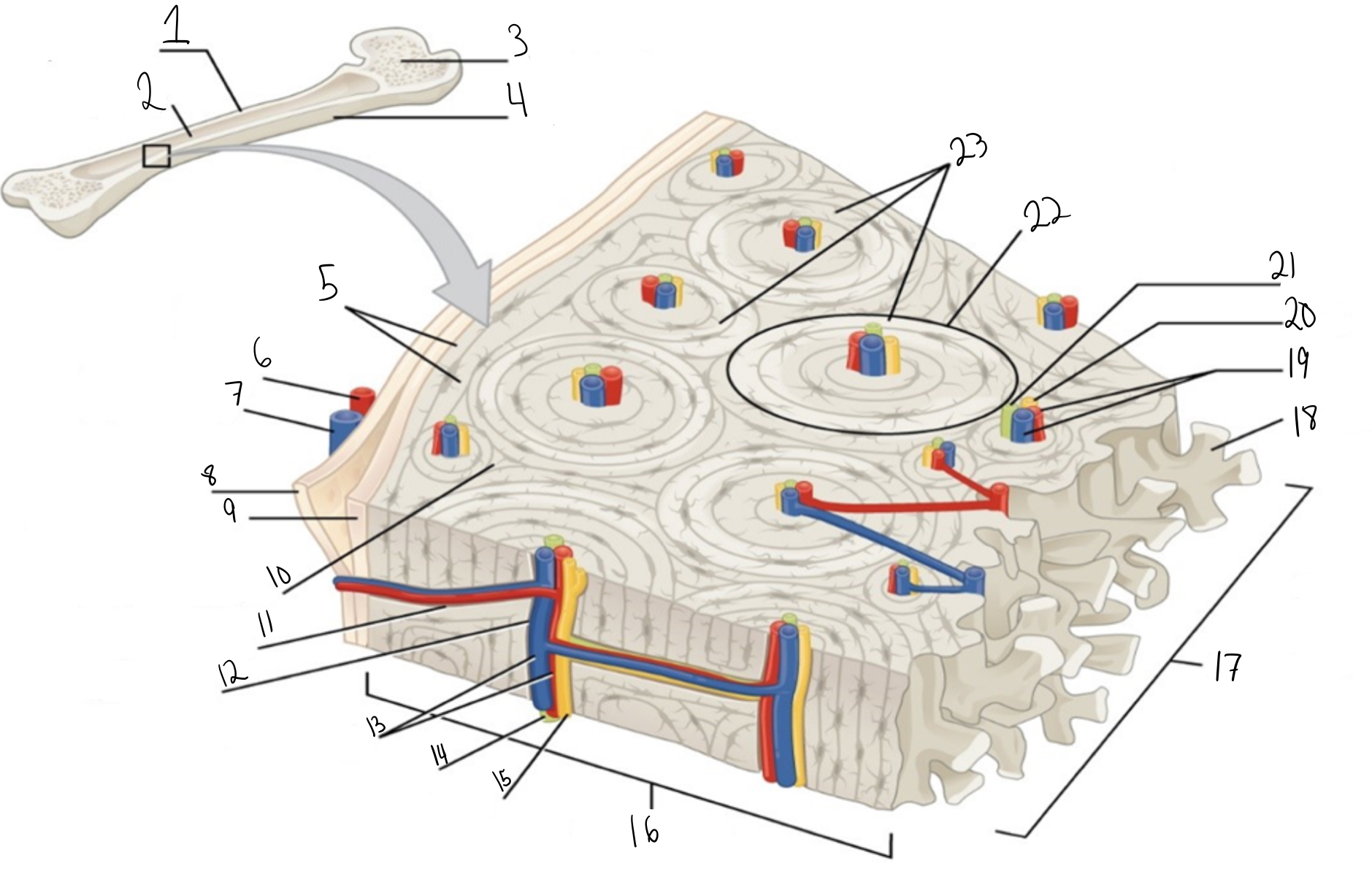
Nerve
Identify #15 on this image.
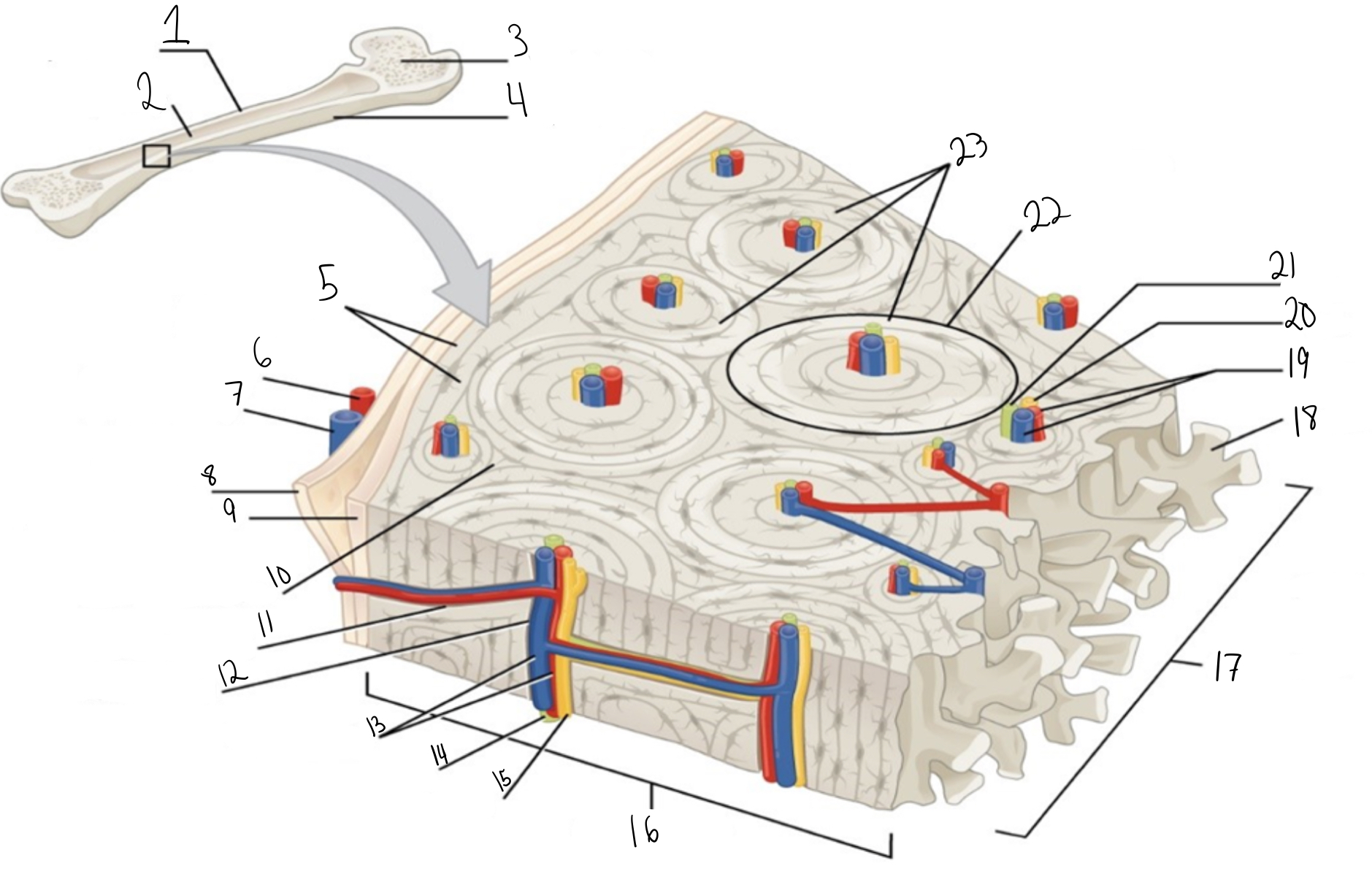
Compact bone
Identify #16 on this image.

Spongy bone
Identify #17 on this image.
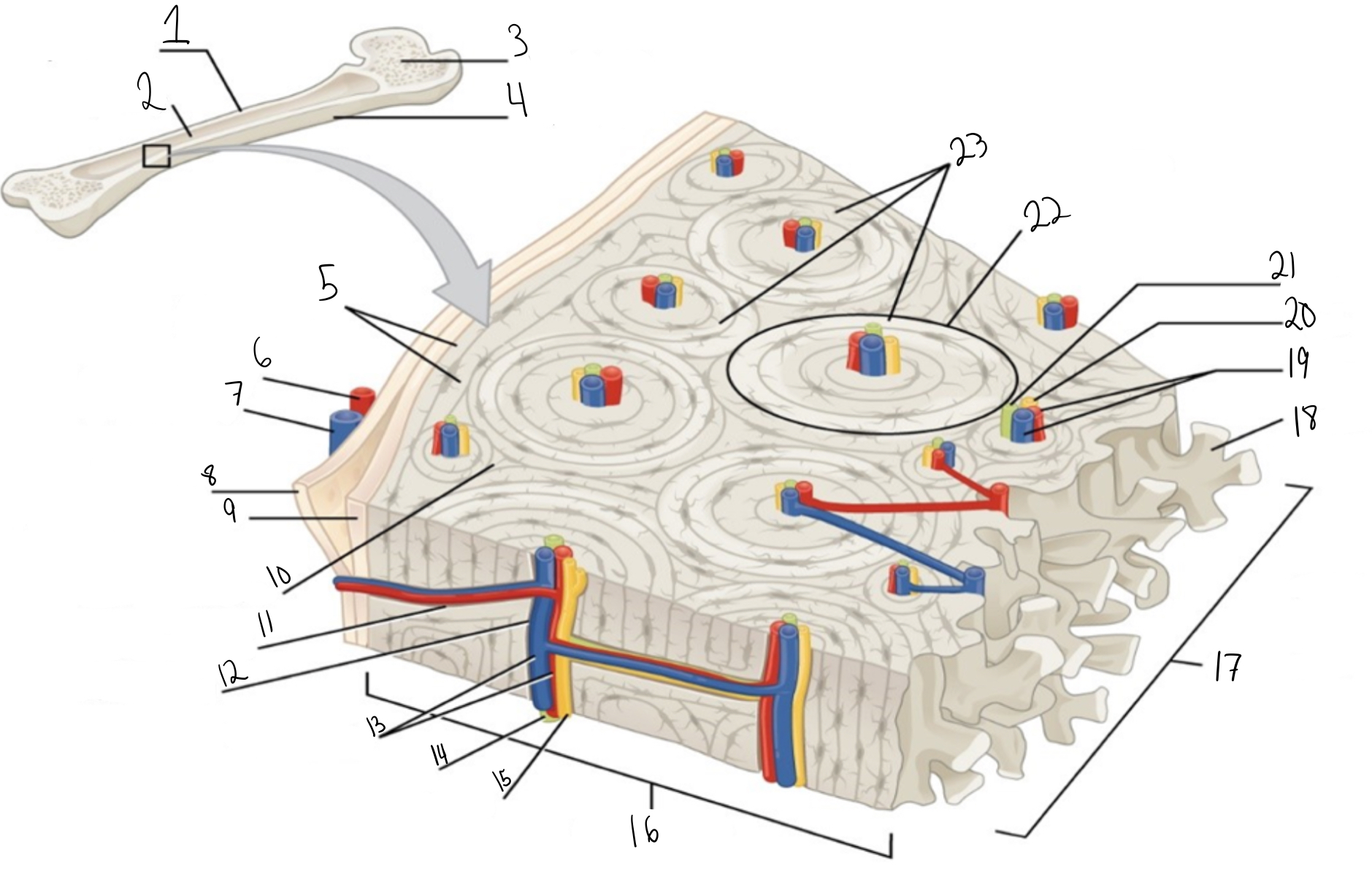
Trabeculae
Identify #18 on this image.
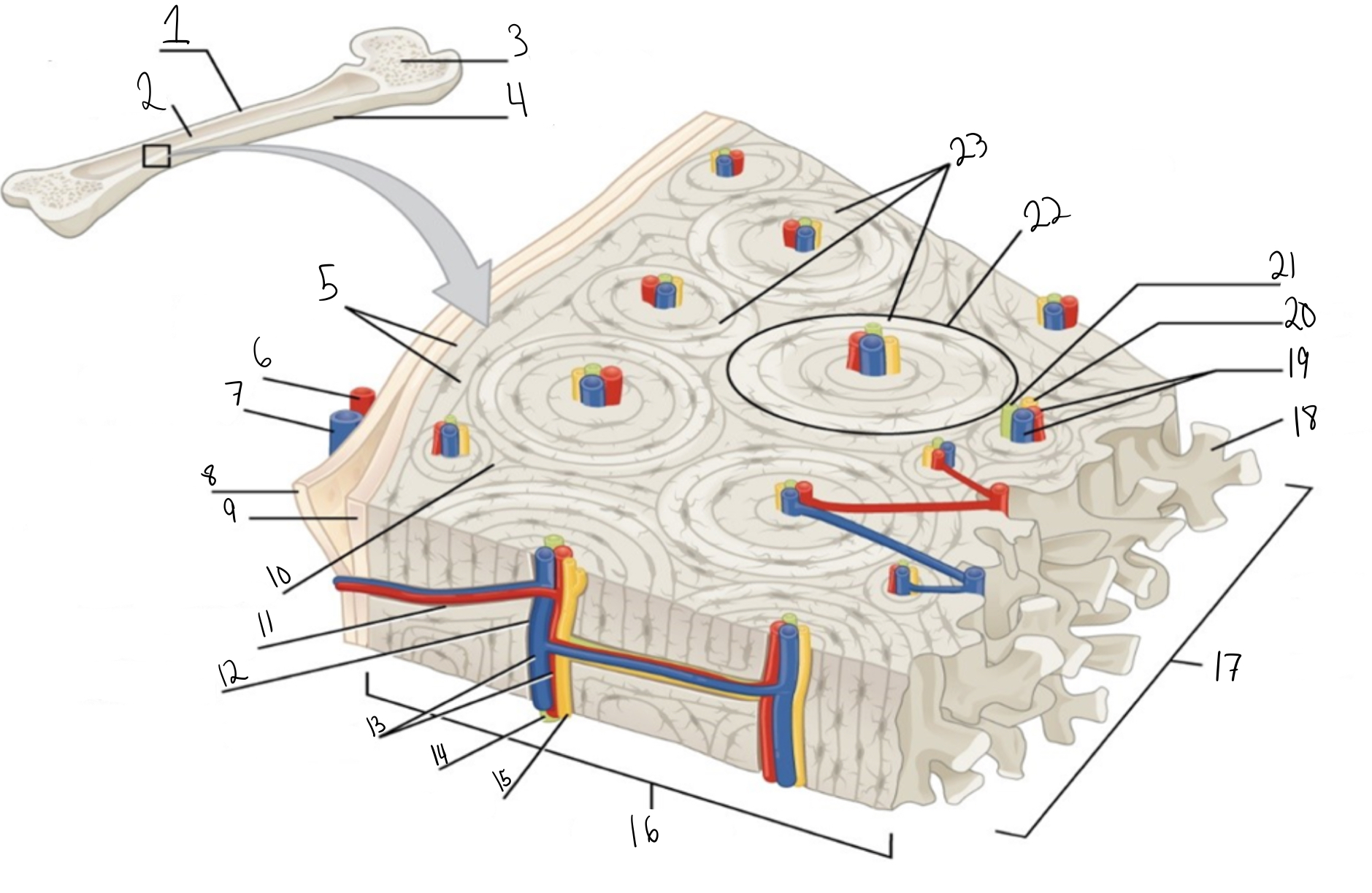
Blood vessels
Identify #19 on this image.
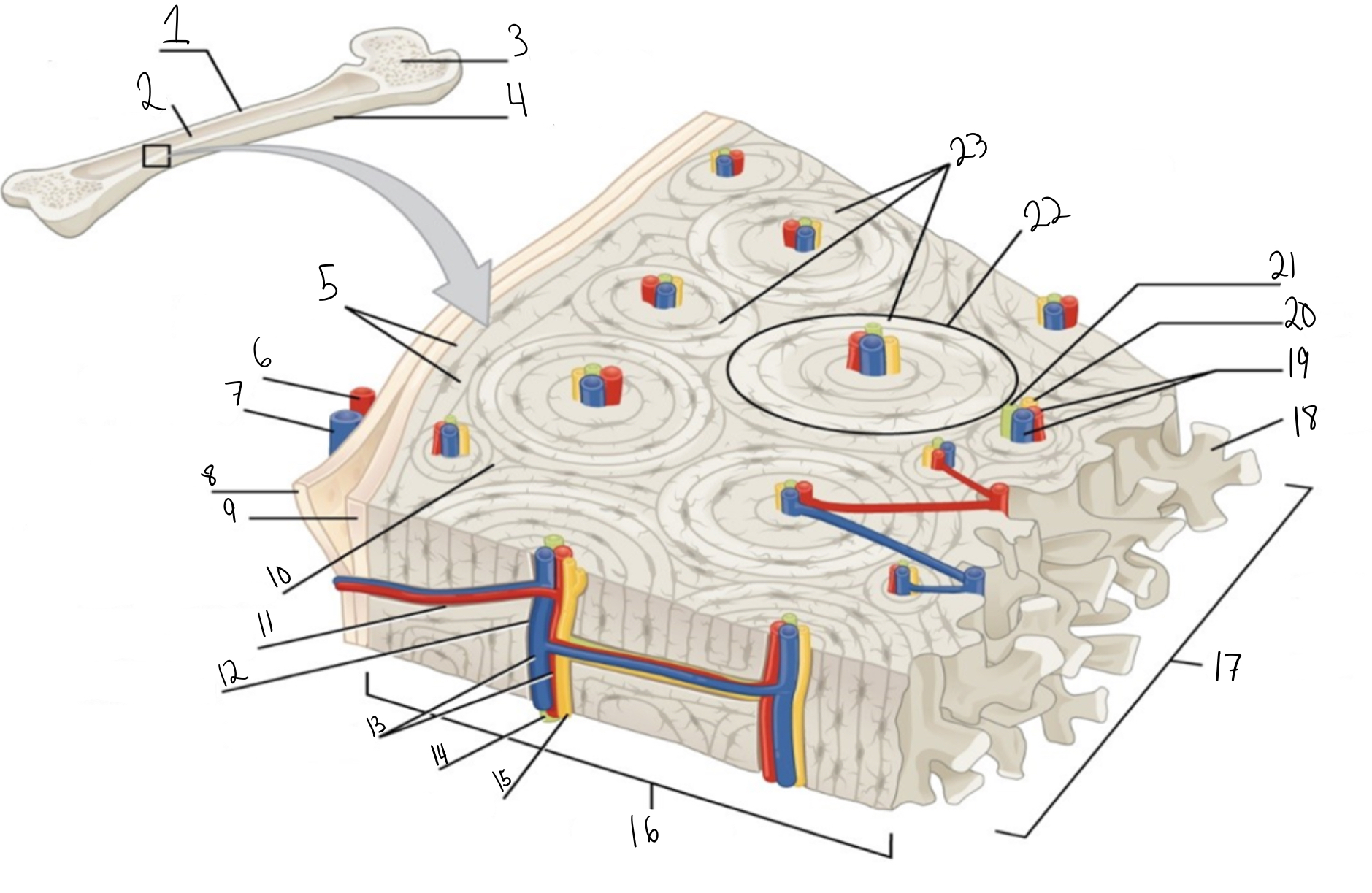
Nerve
Identity #20 on this image.
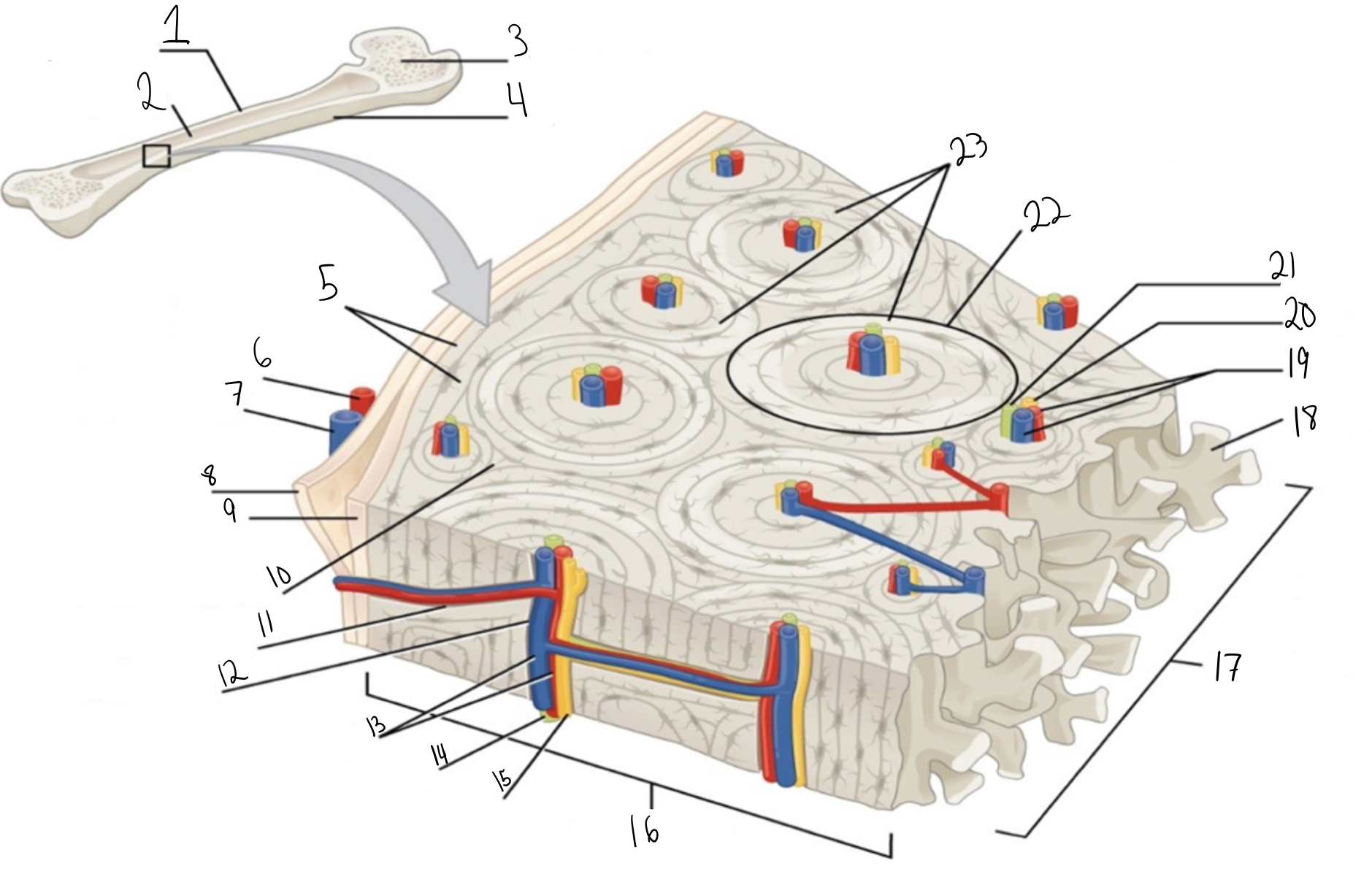
Lymphatic vessels
Identify #21 on this image.
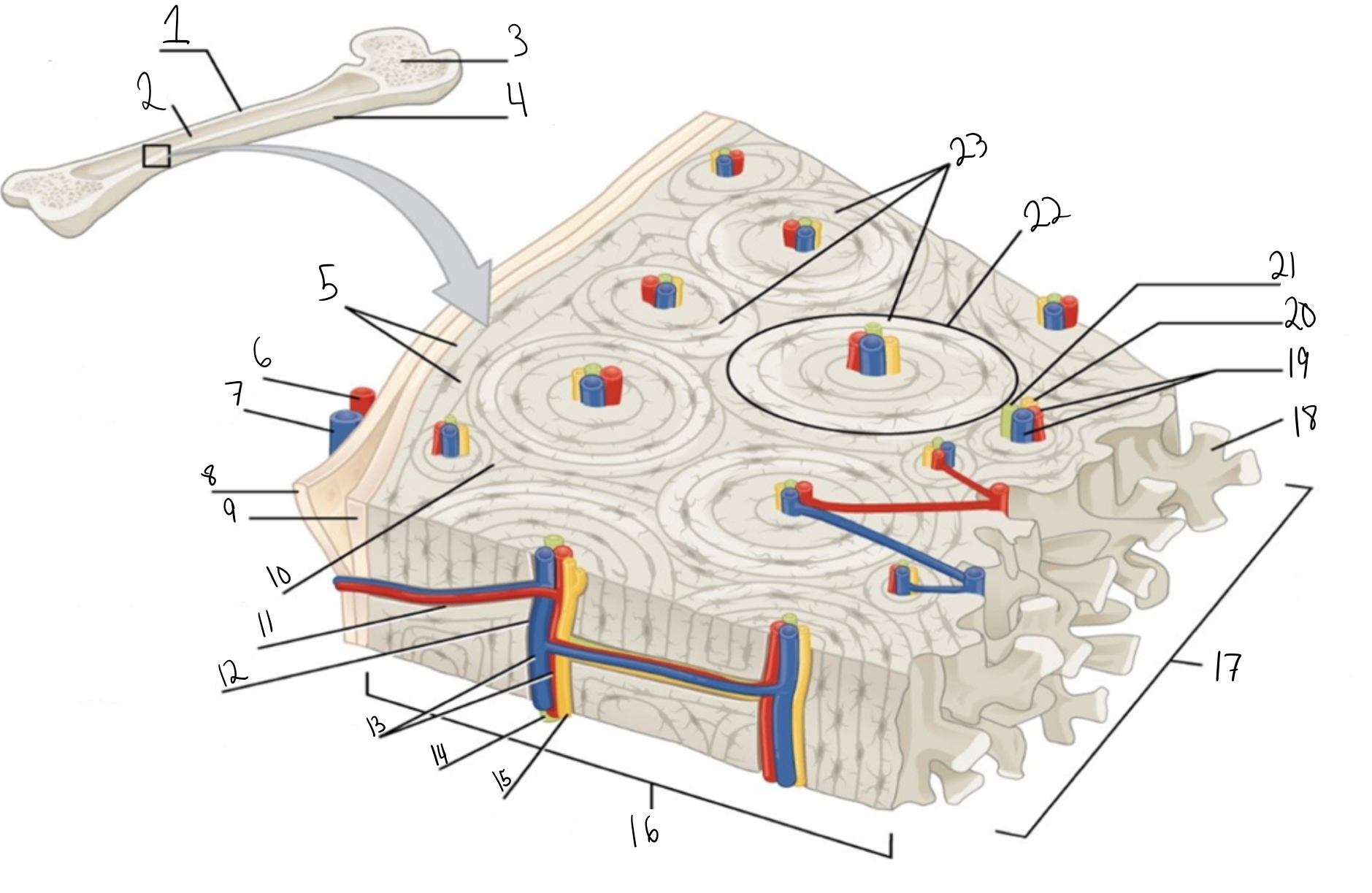
Osteon
Identify #22 on this image
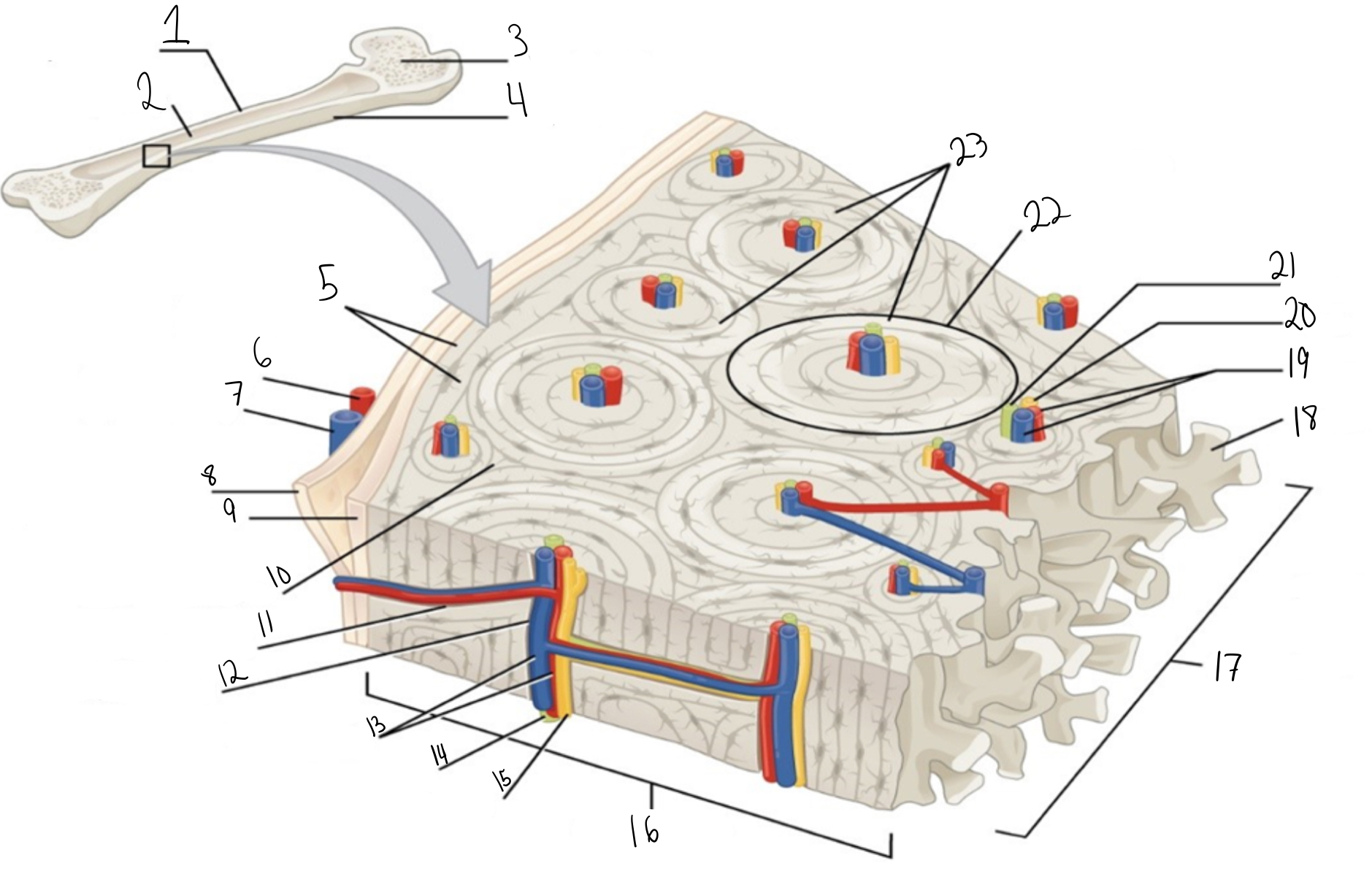
Concentric lamellae
Identify #23 on this image.
206 bones
How many bones in the adult Skeleton?
80 bones
How many bones are part of the axial skeleton?
126 bones
How many bones are part of the appendicular skeleton?