ENT Final
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
Foregut
forms from stomodeal invagination, lined with chitin, very little digestion
Midgut
formed from mesentral growth, not lined with chitin, main area of digestion
Hindgut
formed from proctodeal invagination, lined with chitin, permeable to some substances
Preoral cavity
Salivary glands open here, grinding of food
Cibarium
important in food ingestion, food storage pouch in front of mouth
Esophagus
Conducts food rearward
Crop
pre-digestive storage
Proventriculus
Valve at end of foregut used for grinding
Ventriculus
Secretes enzymes into stomach
Gastric caeca
tubes that aid in digestion and house microbes
Stomach
main area of midgut, lined with peritrophic membrane
Intestine
receives waste from midgut, excretions from the malphigian tubules
Rectum
Reabsorbs water and salts from waste prodcuts
Anus
Exit for fecal pellet
Peristalsis
Series of muscle contractions moving food down esophagus into crop for storage
Enzymatic digestion
carbohydrases, lipases and proteinases (many insects have specialized enzymes)
Food absorbed from midgut to hemolymph
Peritrophic membrane
Membrane lining midgut that protects epithelial cells from damage
Encloses food, continually formed as digestion occurs, moves along the midgut and into hindgut where it breaks down
Diverticulum
Modified pouch off of the esophagus that allows for liquid storage in some insects
Filter Chamber
allows for passive diffusion of water out of gut
Fat Body
Yellow/white tissue in abdomen with many metabolic functions (storage, synthesis and regulation of blood sugars, synthesis of hemolymph proteins)
Trophocyte
Cell found in fat body, responsible for all metabolic and storage functions
Produced only when needed
Symbionts
Many insects ingest compounds that they can’t digest, these bacteria/yeast digest for them
Malphigian tubules
Small tubes used for liquid excretion, bathed in hemolymph and close in proximity to fat body
Uric Acid
Common nitrogenous waste product, nontoxic and soluble, conserves water
Ammonia
Rare nitrogenous waste product, poisonous and highly soluble, does not conserve water
Circulation
Open circulatory system, 3 major sinuses separated by 2 diaphragms, Aorta and Heart
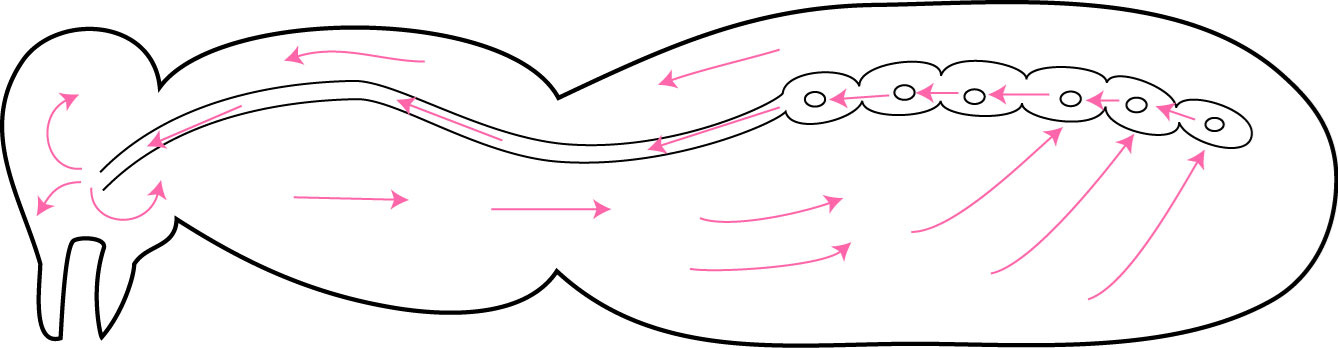
Sinuses
channel flow of hemolymph
Diaphragms
Propel hemolymph through undulations
Aorta
in head, thorax and anterior abdomen, simple conduit for oxygenated hemolymph to get to head
Heart
In abdomen, chambers that draw in hemolymph and pump it towards head
Accessory Pulsate Organs
Contractile, help drive hemolymph to hard to reach areas
Plasma
Aqueous solution of salts and organic compounds that is part of the hemolymph
Hemocytes
Blood cells, phagocytize small particles, encapsulates invaders, coagulates
Hemolymph Function
Transportation of food/waste
Storage
Cellular defense
Wound healing
Tracheal System
System of tubes allowing for direct diffusion of air into almost all body cells
Spiracles
Openings for tracheal system into integument
Trachaea
Air filled tubes that conduct gas into tracheoles and eventually cells
Tubes
Extension of body to water surface for respiration
Bubble
Air is captured at surface and carried under water for respiration
Plastron
Air bubble acts as gills, oxygen diffused in as co2 diffuses out
Blood Gills
Oxygen diffuses through gill integument to hemolymph then to a respiratory system
Tracheal Gills
O2 diffuses through gill integument into tracheal system
Cuticular Gills
O2 diffuses through integument into air pocket then to tracheal system
Muscular Bundles
Skeletal muscles, origins and insertions on integument
Muscular Sheets
circular and longitudinal muscles wrapped around gut
Muscle Networks
Branching network of muscle units spread around the esophageal diverticulum
Tergo-sternal muscles
Muscles that run from the tergum to the sternum
Dorsal longitudinal muscles
Muscles that run longitudinally along the dorsal length of the body
Ventral longitudinal muscles
Muscles that run longitudinally along the ventral length of the body
Direct muscle control
Muscles connected directly to wings; contraction and relaxation of muscles results in movement of wings
Indirect muscle control
Muscle contraction and relaxation causes movement of thorax and movement of flight muscles
Dendrite
Part of neuron that receives signal
Axon
Part of neuron that transmits signal
Sensory Neurons
Receive stimuli from environment, transmits to nervous system
Interneurons
Receive information, transmit to other neurons
Motor Neurons
Receive information from interneurons, transmit to muscles
Neuroendocrine cells
Modified neural cells that produce hormones
Neurotransmitters
transmit impulses between neurons and from neurons to muscles
Reflexes
Transmit impulses from sensory to motor neurons
Central Nervous System Components
Brain, main ventral nerve cord, all ganglia
Peripheral Nervous System Components
Skeletal and Visceral System
Protocerebrum
innervates compound eyes and ocelli
Dueterocerebrum
Innervates antennae
Tritocerebrum
Connects to the visceral nervous system
Frontal Ganglion
helps to process stimuli; innervates labrum
Subesophageal ganglion
innervates mandibles, maxillae and labium
Thoracic ganglia
innervate muscles, legs, wings
Abdominal Ganglia
innervate musculature and genitalia
Skeletal System
innervates sensory organs and muscles related to the integument
Stomodeal System
Innervates heart, foregut, and midgut
Ventral nerves
innervate spiracles
Caudal System
Innervates hindgut and reproductive organs
Neuroendocrine system
system that controls molting, excretion, metabolic rate, etc
Neurosecretory Cells
Excrete brain hormones into hemolymph
Thoracic glands
Release Ecdysone into hemolymph
Ecdysteroids
Any steroid with molt promoting activity obtained from food
Juvenile Hormones
Control metamorphosis, regulate reproductive development
Neurohormones
Master regulators of insect development, metabolism, reproduction, regulate Juvenile Hormone and ecdysone
Tormogen Cell
Forms Socket for sensory neuron
Trichogen Cell
Forms the seta within the socket
Sensory neuron
Dendrite rests directly on seta
Stimulation of seta causes movement of dendrite and stimulation of axon
Mechanoreceptors
Sense touch, hearing
Chemoreceptors
Sense smell, taste
Hygroreceptors
Sense humidity
Thermoreceptors
Sense radiant, convective heat
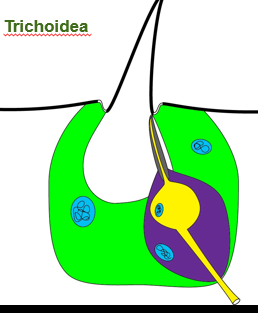
Sensillum Trichoidea
seta in socket, innervated by a single sensory neuron
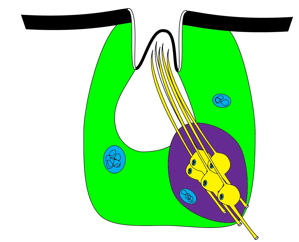
Sensillum Basiconica
Sensory pegs in socket; innervated by many sensory neurons
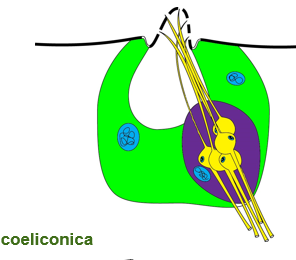
Sensillum Coeliconica
Like Basiconica except the peg is sunken into a cavity
Sensillum Campaniformia
External area is dome-like; innervated by a single sensory neuron
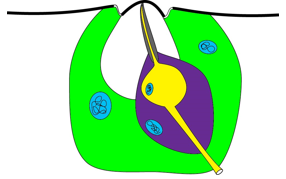
Sensillum Placodea
External area is a thin cuticular plate; innervated by many sensory neurons
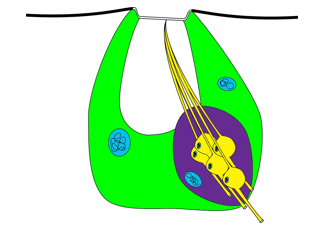
Taste
Located on mouthparts and tarsi, chemoreception
Smell
Located on antenna, airborne chemoreception
Sensillum Basiconica allows entry of many volatile chemicals
Johnston’s Organ
in 2nd antennal segment of male mosquitos to pick up on wing frequency
Tympanal organs
made of thin cuticular membrane stretched across thin airspace
Stemmata
Visual organs of larval homometabolous insects
Can discriminate between light and dark, low resolving powers
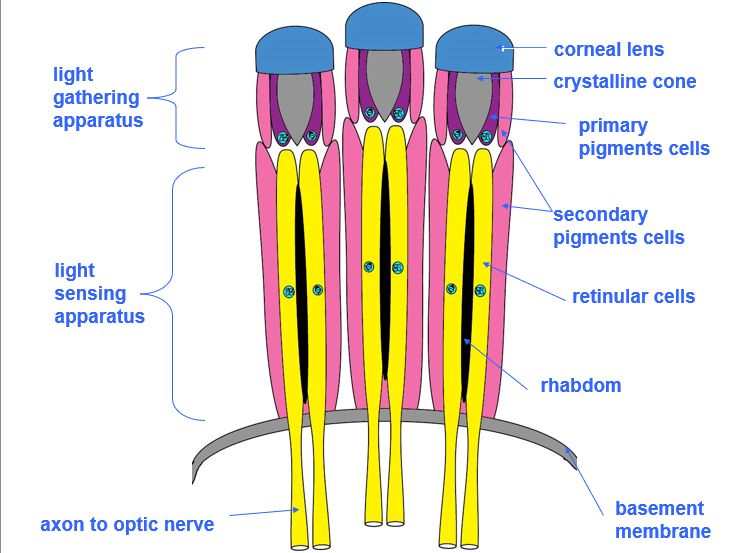
Ommatidia
Small repeating units that make up compound eye compose of a lens, cone, pigment cells and sensory neurons
Ocelli
light sensing organs
thin cuticle allows light to pass through to sensory neurons which relay directly to brain
Help navigate, can discriminate between light and dark
Compound eye
Made of apposition (daylight) and superposition (nighttime) ommatidium
Forms composite images
Can discriminate between color, distance and direction and very sensitive
Pheromones
Hormones transmitted through air to attract opposite sex
Visual Displays
Use to attract via long distance visual signals (ex. fireflies)