EAC 3: AM-FM-PHASE-MODULATION-NOISE PROBLEMS
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
He is recognized as the Father of Electromagnetism
a. Joseph Henry
b. Andre Marie Ampere
c. Hans Christian Oersted
d. Michael Faraday
d. Michael Faraday
An American scientist who discovered electromagnetic self-induction. He was a pioneer of modern forecasting techniques.
a. Joseph Henry
b. Andre Marie Ampere
c. Hans Christian Oersted
d. Michael Faraday
a. Joseph Henry
He discovered Photoelectricity through a photosensitive element, Selenium, that could carry current in direct proportion to the amount of light that struck it.
a. Jonas Jacob Berzelius
b. Charles Babbage
c. James Maxwell
d. Michael Faraday
d. Michael Faraday
The Father of Electrodynamics who exposed the phenomenon of electromagnetism following the discovery of magnet needle by Oersted.
a. Joseph Henry
b. Andre Marie Ampere
c. James Maxwell
d. Michael Faraday
b. Andre Marie Ampere
The range of frequencies represented in a signal.
a. Beam width
b. Crisp
c. Guard band
d. Bandwidth
d. Bandwidth
It refers to the sending, receiving, and processing of information by electronic means.
a. Communications
b. Telemetry
c. Telephony
d. Broadcasting
a. Communications
The big breakthrough in electronics communications came with the invention of the ____________ in 1844.
a. Transistor
b. Phonograph
c. Telegraph
d. Telephone
c. Telegraph
Term for transmission of printed picture by radio (ECE Board April 1998).
a. Facsimile
b. ACSSB
c. Xerography
d. Television
a. Facsimile
A Scottish physicist who established the Theory of Radio or Electromagnetism which held that rapidly oscillating electromagnetic waves exist and travel at the speed of light.
a. James Maxwell
b. Andre Marie Ampere
c. Hans Christian Oersted
d. Michael Faraday
a. James Maxwell
The first words transmitted over the telephone.
a. Mr. Watson, come here, I want you
b. What God has wrought
c. This is the day
d. None of these
a. Mr. Watson, come here, I want you
Most of the communications receiver is in form of ____________ type.
a. Superheterodyne
b. TRF
c. Single-ended
d. High level
a. Superheterodyne
He was the one who developed the wireless telegraph.
a. Edison
b. Armstrong
c. Marconi
d. Bell
c. Marconi
He invented the first practical Multiplex Telegraph and another type of telegraphy codes which consisted of pre-arranged 5-unit dot pulse patterns. This multiplexer allowed signals of up to 6 different telegraph machines to be transmitted over a single wire pair.
a. JM Emile Baudot
b. AC Cowper
c. Thomas Edison
d. Thomas Doolittle
a. JM Emile Baudot
Introduced the first Facsimile Machine or writing telegraph using stylus.
a. JM Emile Baudot
b. AC Cowper
c. Thomas Edison
d. Alexander Graham Bell
Answer: b. AC Cowper
Invented the Microphone transmitter using platinum point bearing against a hard carbon surface.
a. Francis Blake
b. Thomas Watson
c. Thomas Doolittle
d. Henry Hunnings
a. Francis Blake
What type of field does Faraday shield stop?
a. Common
b. Array
c. Electrostatic
d. Magnetostatic
c. Electrostatic
Which of the following is not normally tested in a transmitter?
a. Power
b. Modulation
c. Frequency
d. Amplitude
d. Amplitude
What other term is essentially synonymous with beating?
a. Heterodyning
b. Scrambling
c. Filtering
d. Suppressing
a. Heterodyning
Term in Communication that is referred to “to send in all directions”.
a. Announce
b. Broadcast
c. Transmit
d. Media
b. Broadcast
Invented the telephone transmitter using granular carbon and thin platinum diaphragm and a gold-plated electrode.
a. Nikola Tesla
b. Henry Hunnings
c. Thomas Watson
d. AC Cowper
c. Thomas Watson
He introduced the Dial Switching System, transmitting the desired telephone number electrically without the assistance of a human telephone operator.
a. Thomas Edison
b. Almon Strowger
c. JJ Thomson
d. Lee De Forest
b. Almon Strowger
An Italian physicist who invented the first wireless telegraph, initially transmitting messages over a distance of 1 mile but later improved it to 8000 miles in 1902. He also made the first successful transatlantic radio transmission.
a. Francis Blake
b. Ernst Alexanderson
c. KF Braun
d. Guglielmo Marconi
Answer: d. Guglielmo Marconi
The Father of Quantum Theory. He introduced the revolutionary idea that the energy emitted by an oscillator could take only on discrete values or quanta.
a. Guglielmo Marconi
b. John Fleming
c. Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck
d. Christian Hulsmeyer
c. Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck
Who developed the CRT capable of tracing curves on phosphor screen?
a. John Fleming
b. Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck
c. KF Braun
d. Christian Hulsmeyer
c. KF Braun
He invented the superheterodyne receiver.
a. Edwin Armstrong
b. Alec Reeves
c. Veldemar Poulsen
d. Boris Rosing
a. Edwin Armstrong
He developed a simple radio echo device to prevent ship collisions. He was considered as the forerunner of RADAR.
a. Veldemar Poulsen
b. Christian Hulsmeyer
c. Boris Rosing
d. Reginald Fessenden
b. Christian Hulsmeyer
Who invented the Pulse Code Modulator for digital encoding of PCM signals?
a. Alec Reeves
b. Edwin Armstrong
c. Boris Rosing
d. Reginald Fessenden
a. Alec Reeves
He was the one who developed the mathematical solution to a complex repetitive waveform.
a. Carson
b. P. H. Smith
c. J. Fourier
d. Y. Uda
c. J. Fourier
The volume of transaction proceed in a specific unit of time.
a. Response time
b. Throughout
c. Availability
d. Reliability
b. Throughout
____________ is a device that measures the internal open circuit voltage of an equivalent noise generator having an impedance of 600 ohms and delivering noise power to a 600-ohms load.
a. Phosphometer
b. Barometer
c. Reflectometer
d. Voltmeter
d. Voltmeter
Modulation is used to:
a. Increase the carrier power
b. Reduce the bandwidth used
c. Allow the use of practical antennas
d. Shorten the transmission channel
c. Allow the use of practical antennas
Modulation is done at the:
a. Transmitter
b. Receiver
c. Channel
d. Antenna
a. Transmitter
In an AM wave, useful power is carried by:
a. The sidebands
b. The carrier
c. Both
d. Either
a. The sidebands
Which could not be used to remove unwanted sideband in SSB?
a. Filter Method
b. Phase–Shift Method
c. Third Method
d. Balanced Modulator
d. Balanced Modulator
In amplitude modulation, the ____________ of the carrier is varied.
a. Amplitude
b. Phase
c. Frequency
d. Period
a. Amplitude
The output of a balanced modulator is:
a. USB and LSB
b. LSB
c. USB
d. Carrier
a. USB and LSB
A 900 kHz carrier is AM modulated with a 4000 Hz audio tone. What are the lower and upper sideband frequencies?
a. 450 and 1800 kHz
b. 800 and 1000 kHz
c. 896 and 904 kHz
d. 4000 and 8000 kHz
c. 896 and 904 kHz
The HF band covers the frequency range:
a. 3–30 MHz
b. 30–300 MHz
c. 30–300 kHz
d. 300 kHz–3 MHz
a. 3–30 MHz
In AM, if peak signal is 0.5V and carrier peak is 1V, what is the depth of modulation?
a. 25%
b. 50%
c. 75%
d. 78.5%
b. 50%
In a communications system, noise most affects the signal at the:
a. Transmitter
b. Channel
c. Information source
d. Destination
b. Channel
Another term for Amplitude Modulation is:
a. DSBSC
b. SSBSC
c. DSBFC
d. SSBFC
c. DSBFC (Double Sideband Full Carrier)
Bandwidth of an AM transmitter if carrier = 1000 kHz and modulation frequency varies from 1 kHz to 10 kHz?
a. 2000 kHz
b. 2 kHz
c. 20 kHz
d. 20.1 kHz
c. 20 kHz
If the modulation index of an AM wave increases from 0 to 1, the transmitter power will be:
a. Unchanged
b. Increased by 50%
c. Increased by 100%
d. Decreased by 50%
b. Increased by 50%
When modulation index = 1, the amplitude of carrier is ____________ the modulating signal.
a. Greater than
b. Equal to
c. Less than
d. Double
b. Equal to
Overmodulation results in:
a. Weakening of the signal
b. Excessive carrier power
c. Distortion
d. Either a or b
c. Distortion
If AM modulation index is 0.80, the % modulation is:
a. 20%
b. 80%
c. 0.80
d. 0.20
b. 80%
Both frequency and phase modulation are types of ____________ modulation.
a. Phase
b. Amplitude
c. Digital
d. Angle
d. Angle
The maximum percentage modulation without distortion in AM is:
a. 20%
b. 50%
c. 110%
d. 100%
d. 100%
Form of AM where carrier is transmitted at full power but only one sideband is transmitted?
a. SSBFC
b. SSBSC
c. DSBFC
d. DSBSC
a. SSBFC
Emission with only one sideband transmission?
a. A3E
b. J3E
c. 11BE
d. H3E
b. J3E
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of FM over AM?
a. Better noise immunity
b. Lower bandwidth required
c. Transmitted power is useful
d. Less modulating power
FM actually requires higher bandwidth
Answer: b. Lower bandwidth required
In an FM Stereo Multiplex transmission, the:
a. Sum signal modulates the 19 kHz subcarrier
b. Difference signal modulates the 67 kHz subcarrier
c. Difference signal modulates the 38 kHz subcarrier
d. Difference signal modulates the 19 kHz subcarrier
38 kHz is for difference signal
Answer: c. Difference signal modulates the 38 kHz subcarrier
When modulating frequency is doubled, the modulation index is halved. What is the modulation system?
a. AM
b. PAM
c. FM
d. PM

Pre-emphasis and de-emphasis are used in FM stereo multiplex to improve:
a. SWR
b. Power ratio
c. S/N
d. CMMR
Increases signal-to-noise ratio
Answer: c. S/N
The commercial FM radio broadcast band is:
a. 535 – 1605 kHz
b. 27 – 29 kHz
c. 88 – 108 MHz
d. 300 – 3000 MHz
Standard FM broadcast is 88 to 108 MHz
Answer: c. 88 – 108 MHz
For an FM broadcast station, the maximum deviation by audio modulation is 45 kHz. What is the percent modulation?
a. 10
b. 45
c. 60
d. 100
45 kHz out of 75 kHz max deviation = 60%
Answer: c. 60
The modulation index of an FM signal is half if the modulating frequency is:
a. Doubled
b. Halved
c. Increased
d. Decreased
If fmfmfm doubles, mfmfmf halves
Answer: a. Doubled
An FM signal passed through a frequency tripler will have modulation index of:
a. mf/3
b. mf
c. 3mf
d. 9mf
Multiplied by 3
Answer: c. 3mf
Which of the following is an indirect method of generating FM?
a. Reactance FET Modulator
b. Varactor Diode Modulator
c. Armstrong Modulator
d. Reactance BJT Modulator
Armstrong method uses phase modulation to create FM
Answer: c. Armstrong Modulator
What is the deviation ratio for the station in the commercial FM broadcast band?
a. 5.5
b. 5
c. 4
d. 6
Standard deviation ratio is 5
Answer: b. 5
What frequency deviation is needed for 80% modulation in FM broadcast?
a. 75 kHz
b. 75 MHz
c. 60 kHz
d. 60 MHz
80% of 75 kHz = 60 kHz
Answer: c. 60 kHz
In FM, noise affecting amplitude can be eliminated using:
a. Oscillator
b. Integrator
c. FM limiter circuit
d. Differentiator
Limiter removes amplitude variations
Answer: c. FM limiter circuit
In FM, if a carrier is modulated by a single frequency, the number of sidebands produced is:
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. Greater than 3
FM generates infinite sidebands theoretically
Answer: d. Greater than 3
Maximum frequency deviation of standard FM broadcast station?
a. 25 kHz
b. 40 kHz
c. 75 kHz
d. 200 kHz
Maximum allowed deviation = 75 kHz
Answer: c. 75 kHz
The modulation index of an FM signal with 100 kHz swing and 2 kHz modulating frequency?
a. 75
b. 25
c. 50
d. 0.5
Swing/2 = deviation 50 kHz / 2kHz = 50
Answer: c. 50
In FM stereophonic transmission, suppressed subcarrier frequency is:
a. 19 kHz
b. 67 kHz
c. 38 kHz
d. 69 kHz
38 kHz is the suppressed carrier
Answer: c. 38 kHz
Maximum FM deviation is 75 kHz; max modulating frequency is 15 kHz. What is max bandwidth?
a. 180 kHz
b. 160 kHz
c. 140 kHz
d. 90 kHz
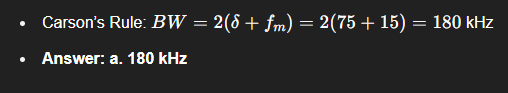
An FM signal passed through a mixer reducing frequency fivefold. Output deviation is:
a. 5δ
b. Indeterminate
c. δ/5
d. δ
Deviation is divided by 5
Answer: c. δ/5
Permissible maximum modulating index range for commercial FM (30 Hz–15 kHz)?
a. 5 and 2500
b. 50 and 250
c. 50 and 2500
d. 5 and 50
FCC allows 50–2500 modulation index
Answer: c. 50 and 2500
Carrier swing necessary for 80% modulation in FM broadcast band?
a. 150 kHz
b. 120 kHz
c. 75 kHz
d. 60 kHz
80% of 75 kHz swing = 60 kHz
Answer: d. 60 kHz
Modulation means ____________.
a. Varying carrier parameters like amplitude to transmit info
b. Transmit pulses in DC form over copper wire
c. Varying information
d. Utilization of a single transmission channel
Modulation varies carrier parameters to carry information
Answer: a. Varying carrier parameters like amplitude to transmit info
The modulation system used for telegraphy is ____________.
a. Single tone modulation
b. Two-tone modulation
c. Frequency-shift keying (FSK)
d. Pulse code modulation (PCM)
Telegraphy uses frequency-shift keying
Answer: c. Frequency-shift keying (FSK)
A process that occurs in the transmitter.
a. Demodulation
b. Modulation
c. Mixing
d. Beating
Modulation happens at the transmitter
Answer: b. Modulation
A process that occurs in the receiver.
a. Beating
b. Modulation
c. Mixing
d. Demodulation
Demodulation happens at the receiver
Answer: d. Demodulation
What amount of carrier swing necessary to produce 80% modulation for TV audio?
a. 40 kHz
b. 50 kHz
c. 20 kHz
d. 25 kHz
80% modulation corresponds to 40 kHz swing
Answer: a. 40 kHz
The letter number designation B8E refers to:
a. Pilot-carrier system
b. Independent sideband emission
c. LINCOMPEX
d. Vestigial sideband transmission
B8E = Independent sideband emission
Answer: b. Independent sideband emission
Which symbol indicates that only one sideband is transmitted?
a. A3E
b. B8E
c. C3F
d. H3E
H3E = single sideband reduced carrier
Answer: d. H3E
Emission designation for facsimile transmission?
a. J3E and F4E
b. A3J and A4E
c. A3C and F3C
d. R3E and A3E
Facsimile is F3C (FM facsimile) or A3C (AM facsimile)
Answer: c. A3E and F3C
Double sideband full carrier emission?
a. A3E
b. A3J
c. F3
d. R3A
A3E = double sideband full carrier
Answer: a. A3E
What is the emission of F3F?
a. Facsimile
b. Modulated CW
c. RTTY
d. Television
F3F = Television (FM type)
Answer: d. Television
In a J3E filter system, how many circuits must be balanced?
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
2 circuits must be balanced in J3E filter systems
Answer: c. 2
Independent sideband emission?
a. H3E
b. R3E
c. J3E
d. B8E
B8E = Independent sideband
Answer: d. B8E
Emission when an AM transmitter is modulated by a TV signal?
a. F3F
b. A3C
c. F3C
d. A3F
A3F = AM modulated by TV signal
Answer: d. A3F
Output of a balanced modulator?
a. AM
b. FM
c. SSB
d. DSB
Balanced modulator output = DSB (Double Sideband)
Answer: d. DSB
Emission designation for FM telephony?
a. F3E
b. G3E
c. J3E
d. H3E
FM telephony = F3E
Answer: a. F3E
Maximum output power of an A3E emission?
a. 4 W
b. 10 W
c. 3 kW
d. 10 kW
Standard A3E maximum power is 10 kW
Answer: d. 10 kW
If the modulation index of AM wave is doubled, antenna current is doubled. AM system type?
a. A5C
b. A3J
c. A3H
d. A3
A3 = Double Sideband Full Carrier (standard AM)
Answer: d. A3
Power saving in J3E system at 100% modulation?
a. 33%
b. 100%
c. 83.3%
d. 66.67%
83.3% of carrier power is saved
Answer: c. 83.3%
Letter number designation for FM facsimile?
a. F3E
b. F3C
c. A3E
d. C3C
FM facsimile = F3C
Answer: b. F3C
Which symbol indicates that only one sideband is transmitted?
a. A3E
b. B8E
c. C3F
d. H3E
H3E = Single Sideband Reduced Carrier
Answer: d. H3E
Vestigial sideband emission is:
a. C3F
b. R3E
c. J3E
d. B8E
Vestigial Sideband = C3F
Answer: a. C3F
Third symbol in radio emission for telephone transmission (including sound broadcasting)?
a. W
b. F
c. C
d. E
Telephone transmission is represented by E
Answer: d. E
Shape of trapezoidal pattern at 100% modulation?
a. Circle
b. Square
c. Triangle
d. Rectangle
Perfect rectangle at 100% modulation
Answer: d. Rectangle
Maximum sideband suppression using filter system?
a. 50 dB
b. 60 dB
c. 40 dB
d. 30 dB
Maximum suppression = 60 dB
Answer: b. 60 dB
Test instrument that displays carrier and sidebands amplitude versus frequency?
a. Oscilloscope
b. Spectrum Analyzer
c. Frequency Analyzer
d. Amplitude Analyzer
Spectrum analyzer shows amplitude vs frequency
Answer: b. Spectrum Analyzer
In what transmitters are balanced modulators used?
a. SSB
b. A3E
c. F3E
d. FM
SSB uses balanced modulators
Answer: a. SSB
Emission C3F corresponds to:
a. Facsimile
b. Modulated CW
c. RTTY
d. Television
C3F = Vestigial sideband Television
Answer: d. Television
Emission that transmits lower sideband and half of upper sideband?
a. A5C
b. J3E
c. A3J
d. A3H
A3H = lower sideband + half upper
Answer: d. A3H
Single sideband reduced carrier emission type?
a. H3E
b. R3E
c. J3E
d. B8E
H3E = Single Sideband Reduced Carrier
Answer: a. H3E
Phase modulation type?
a. F3E
b. F3C
c. F3F
d. G3E
Phase modulation = G3E
Answer: d. G3E