Recap of brain structures and neurotransmitters
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
neuropsychiatric disorders
Biological basis is poorly understood
Not disorders of a specific brain region —> difficult to treat
Hard to diagnose as the main diagnostic method is through self reporting
Theories suggesting rather than looking for some specific disorder its more about looking for a continuum of neuropsychiatric disturbance
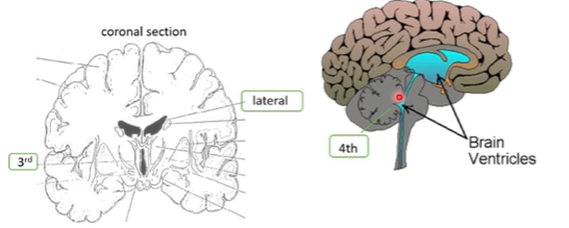
ventricles
4 Ventricles in the middle of the brain: 2 lateral, a 3rd and a 4th ventricle
Filled with CSF – can be useful to sample as they contain neurotransmitters
Ventricles will expand to fill the space when parts of the brain decay/atrophy
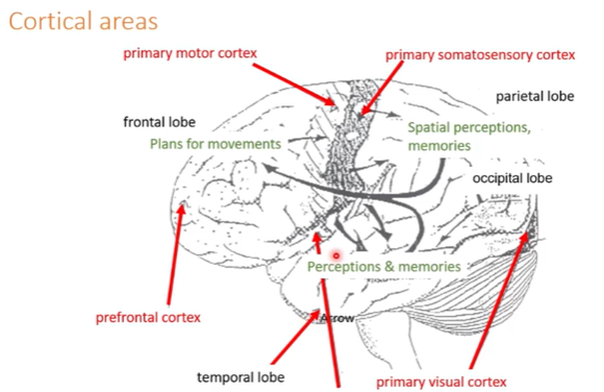
cortex
Temporal lobes become very active in schizophrenia patients who have hallucinations
Prefrontal cortex not essential to live Eg: Phinneas Gage
Big feedback loop for spatial information, planning and execution of movement
limbic system
Number of different nuclei: hippocampus, amygdala and hypothalmus
Regulation of emotion and behaviour
Hippocampus function changes along the longitudinal axis
Ventral – more interlinked with amygdala and more associated with anxiety
Dorsal – more interlinked with the cortex more important for spatial information
Amygdala sits at the end of the hippocampus
Hypothalamus linked with the pituitary
amygdala
Involved in fear and emotional response to face recognition a can induce sham rage
Urbach Wiethe disease where calcium deposited in the amygdala and patients with bilateral amygdala lesions cant discriminate emotions in facial expressions
hemispheres
Connected by the corpus callosum, made up of many neurons
The brain functions as a single unit in most people, evidence of lateralisation
Not essential – can be removed in epileptic patients who have whole brain epilepsy
However, does have side effects E.g: if a water bottle is perceived on the right side, you could see a water bottle but wouldn’t be able to say it’s a water bottle
In some patients with reduced hemisphere asymmetry, there's an increased risk for schizophrenia (as the left brain is responsible for linguistic ability, whilst the right side of the brain Is responsible for perception)
Potentially reduced asymmetry in patients with neuropsychiatric disorders
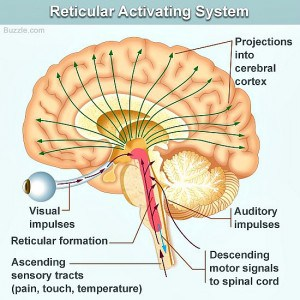
thalamus
Sensory information ascending the spinal chord synapse in the thalamus, new neurons ascend up to the cortex
Reticular activating system is ascending information which is non specific – more a general state of arousal
Also has very diffuse innervation
Main sensory afferents have projections which form the reticular activating system
Has a circuit loop which acts as a relay station for sensory info
Provides all parts of the corte with information and in turn takes input from the cortex
Ascending info sent to the thalamus —> cortex —> descending info to the striatum —> thalamus
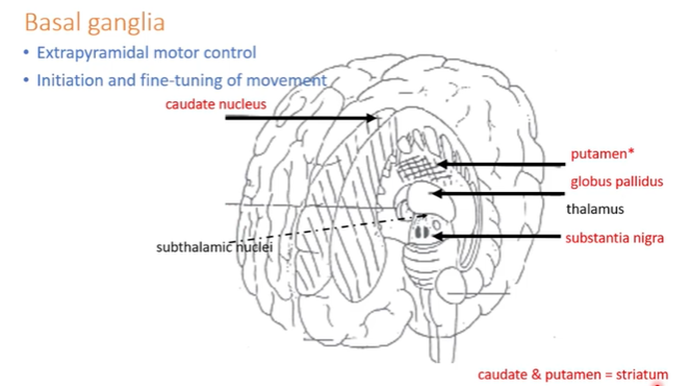
basal ganglia
Middle of the brain
Causes disorders of movement
Extrapyramidal motor control causes involuntary movement, control of initiation of movement
Pyramidal motor control is responsible for voluntary movement
The caudate and the putamen make up the striatum (part of the basal ganglia which recieves decending info from cortex) —> dopaminergic neurons dark in colour so stripy
Challenges of antipsychotics is not inducing Parkinson’s
catecholamines - Noradrenaline
adrenaline
noradrenaline
dopamine
*Catechol group is a benzene ring with 2 hydroxyl groups on each side
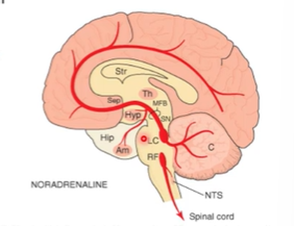
NORADRENALINE
Long tracts, small, highly branched, unmyelinated
Diffuse innervation pattern
Nadr neurons originate from a single nucleus: locus coerelius (part of the reticular activating system – role in general arousal)
Have lots of neuromelanin – sometimes appear blue
Ascending Nadr pass through the medial forebrain bundle, affect hormone secretion
Innervate limbic regions
Very specific subgroups of neurons in subregions of LC, might not be as long and barnched as we think they are
catecholamines - Dopamine
adrenaline
noradrenaline
dopamine
DOPAMINE
3 regions in the brain that have dopaminergic neurons, can control behaviour, motor control and hormone secretion
Substantia Nigra (part of the basal ganglia): cell bodies in SN and project to the striatum
Ventral Tegmetal area: form mesolimbic pathway —> innervates nucleus accumbens, involved in reward. Also mesocortical pathway where neurons from VTA innervate the cortex
Arcruate nucleus send neurons down to the pituitary
5HT
5HT
Monoamine – not chatecholamine
Synthesised in the rafe nuclei – small all located in the region of the midbrain
Send afferents all over the brain so can affect limbic and cortical areas
Activity of neuros goes up when animals are aroused as the Rafe nuclei located in the path of the reticular activating system
Level of activity of nuclei increases immediately prior to and during periods of activity.
Acetylcholine
2 main types of neurons
One type has long projections – originates from the nucleus Basalis of myenert —> innervate the cortex, linked to cognitive function
One has short projections and are interneurons – found round the basal ganglia, control and modulate levels of local information
GABA/Glutamate
Ubiquitous
Can't modulate them
Control information within the brain a drive most of the function, other neurotransmitters that we’ve talked about more modulating the function.