Orgo Chemistry I: Quiz 2~ IUPAC Naming, Resonance Patterns
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Parent name for Alkane with 1 Carbon
methane
Parent name for Alkane with 2 Carbons
ethane
Parent name for Alkane with 3 Carbons
propane
Parent name for Alkane with 4 Carbons
butane
Parent name for Alkane with 5 Carbons
pentane
Parent name for Alkane with 6 Carbons
hexane
Parent name for Alkane with 7 Carbons
heptane
Parent name for Alkane with 8 Carbons
octane
Parent name for Alkane with 9 Carbons
nonane
Parent name for Alkane with 10 Carbons
decane
Prefix of an alkyne in a ring configuration
cyclo-
What is a constitutional isomer?
Molecules with the same molecular formulas but with different arrangements of molecules that are bonded to each other in different ways
What oribital is an atom in if it can display resonance? Why?
sp2 because it must have an available p orbital
What is it called when there is a lone pair but they cannot exhibit resonance?
The lone pair is localized
Why do molecules exhibit resonance? (not a pattern)
delocalizing the electrons distributes the charge throughout the molecule and lowers the overall energy
Name the 5 patterns that indicate a molecule has resonance
having a lone pair 1 sigma bond away from a pi bond
having a pi bond 1 sigma bond away from a positively charged molecule
having a pi bond 1 sigma bond away from another pi bond
having a lone pair 1 sigma bond away from a positively charged molecule
having a pi bond between 2 atoms with very different electronegativities
What is the highest priority for determining most significant resonance contributor?
All molecules having a complete octet even if they don’t usually have them.
What is the ranks of most important factors for most significant resonance contributors?
first is having complete octets on all atoms, second is having the least amount of formal charges, making sure that the charges align with the electronegativity (e.g oxygen having a negative charge and carbon having a positive charge), and having charges that are closer together in the overall structure
What is the real molecule called that all resonance structures contribute to?
resonance hybrid
What is the definition of an Alkane?
hydrocarbon with only sigma bonds
What suffix do you put in front of an Alkane/ hydrocarbon that has all the carbons in a straight line?
“n-” which stands for normal
What are the greek prefixes for 1-6 in chemistry
mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa
Can you include the molecules in rings in determining the parent Alkane group chain length?
No, you either count in the ring or count a substituent coming off of it
What does an R group mean in terms of identifying functional groups?
the remainder of the compound which is usually just carbon and hydrogen atoms
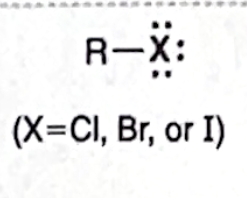
Identify this functional group
alkyl halide
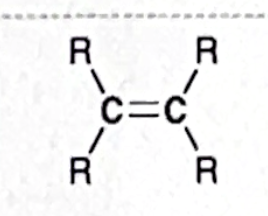
Identify this functional group
Alkene
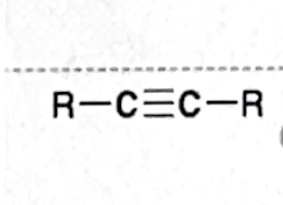
Identify this functional group
Alkyne
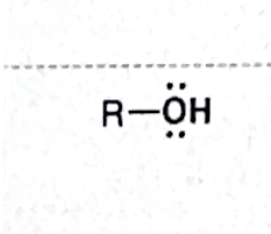
Identify this functional group
Alcohol
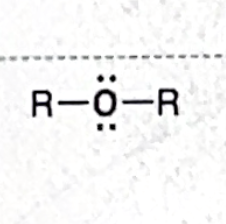
Identify this functional group
Ether
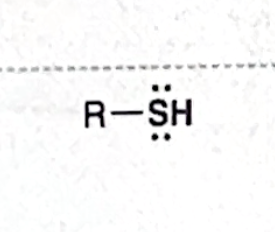
Identify this functional group
Thiol
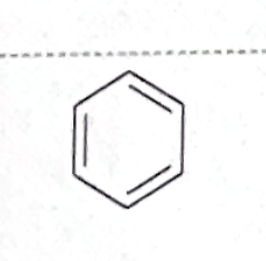
Identify this functional group
Aromatic (or arene)
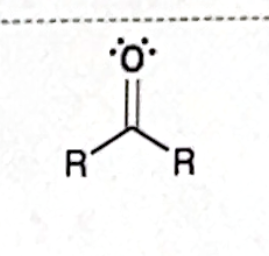
Identify this functional group
Ketone
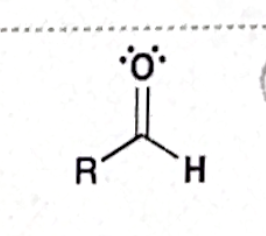
Identify this functional group
Aldehyde
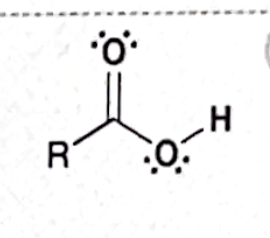
Identify this functional group
Carboxylic acid
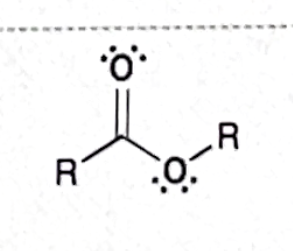
Identify this functional group
Ester
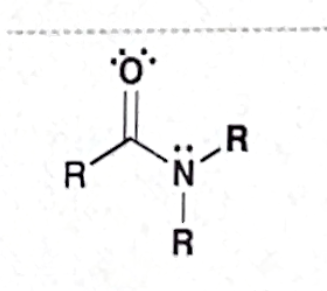
Identify this functional group
Amide
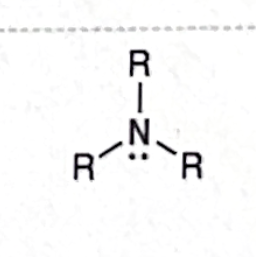
Identify this functional group
Amine
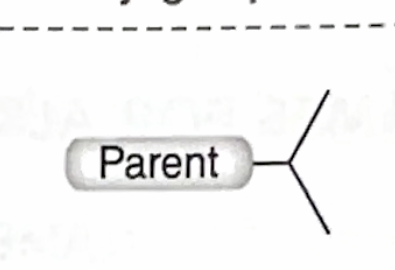
Identify this branch Alkyl substituent
Isopropyl
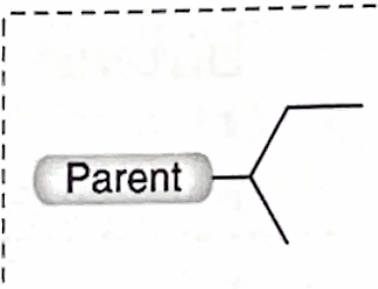
Identify this branch Alkyl substituent
sec-Butyl
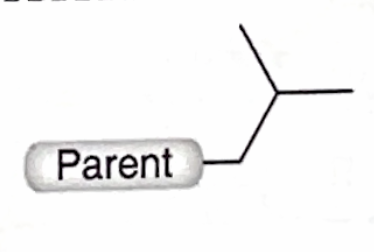
Identify this branch Alkyl substituent
Isobutyl
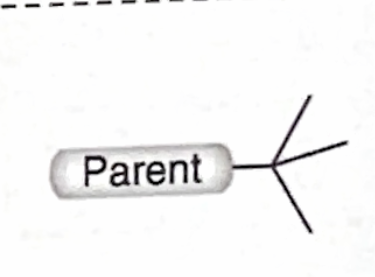
Identify this branch Alkyl substituent
tert-Butyl
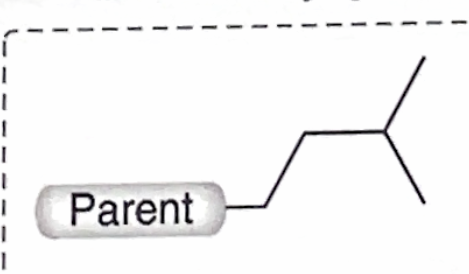
Identify this branch Alkyl substituent
Isopentyl
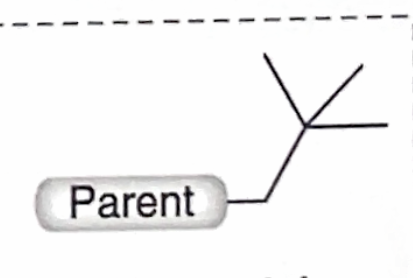
Identify this branch Alkyl substituent
Neopentyl
Are gouche interactions favored?
they are more energetically unfavorable than anti interactions due to increased steric strain and decreased orbital overlap
What is a gouche interaction?
a type of steric strain that occurs when two bulky substituents on adjacent carbon atoms in an alkane are oriented in a gauche (60° dihedral angle) conformation
What is steric strain? What does this only really apply to
the increase in potential energy of a molecule due to repulsion between electrons in bulky substituents that are not directly bonded to each other. Only really applies to bulky substituents and not just hydrogens.
What is torsional strain also known as and what is it? When does it only exist?
It is also known as eclipsing strain and it is the increase in potential energy of a molecule due to repulsion between electrons in bonds that do not share an atom. Only exists in eclipsed confirmations and not staggered ones.