Lecture 3: Movement Analysis III: Promoting Learning that Leads to Functional Improvement
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
● Improve mobility and optimize motor skill acquisition.
● Teach patients to solve motor problems.
● Adapt movement strategies to changing task and environmental conditions.
● Resolve, reduce, prevent impairments, and promote health.
● Teach effective self-management strategies
General PT Goals for Motor Learning
The ability of the learner to demonstrate a skill--after a learning period.
○ Not given immediately following training.
○ Eg: W/c to-from mat transfer
RETENTION TESTS
The ability of the learner to modify (adapt) their movement in response to changing environmental demands.
○ Transfers/Ambulation - different surfaces
○ Calm environments to busy environments
○ Increased speed
○ Dual tasks
ADAPTATION TESTS
● Practice leads to learning
● As skill improves, mvt size decreases, speed increases, efficiency increases
Manipulating Practice to Promote Learning
Ways to Manipulate:
○ Distributed versus Massed
○ Variable versus Blocked
○ Closed vs Open
○ Part-task vs Whole-task
○ Transfer (of learning) training
what is intrinsic feedback for manual contacts and verbal cues?
Pt’s internal knowledge
what is extrinsic feedback for manual contacts and verbal cues?
Feedback given by a PT.
i. Delayed FB: Allows for patient self-assessment.
ii. Faded FB: Amt is decreased (faded) over task trainingSummary Feedback:
i. Knowledge of performance: Feedback given about errors made.
1. Concurrent FB: Given during the task.
ii. Knowledge of results: Feedback given about goal achievement
The Types of Practice to Promote Learning
blocked vs random
Part-task/Whole-Task.
Closed/Open Practice: Practice that occurs in a controlled environment.
● Benefit to patients with attention/learning challengesMental practice: Visualize/imagine the task
➢ Activates motor programs
➢ Facilitates learning of skills
what is blocked vs random?
a. Blocked: Constant repetition of a single task.
i. May help those with disorganized mvt.
b. Random: tasks practiced in random order
i. Increased cognitive demand
what is part-task/whole task
a. Part-task: Break down a task into components, train parts.
b. Whole: Practice the entire task
OPTIMAL theory of motor learning:
Optimizing Performance Through Intrinsic Motivation and Attention for Learning
➔ The learner is influenced by enhanced expectancies, autonomy, and, an external focus of attention.
Enhanced expectancies:
a patient’s sense of confidence, based upon past experience.
➢ PT implications: Can augment confidence though compliments
Autonomy:
Practice conditions should support autonomy/ self-determination.
➢ PT implications: Giving choices during therapy benefits performance.
Eg: “show me what you think you should do when you transfer”
External focus of attention:
➢ PT implications: Move the patient’s attention from their own body to
the intended movement effect.
➢ Eg: Move toward a target, exerting force against an object.
➢ Eg: Standing on a rocker board...”Keep the board level”, not “Push your
toes down.” Instead “Push the edge down”
Mobility - Impairments that Drive Abnormal Patterns ➔ Other Considerations:
Perception/Sensation
Vision, hearing, joint and muscle afferents
Pain
Cognition
Executive function (awareness, attention, memory)
Dual-task
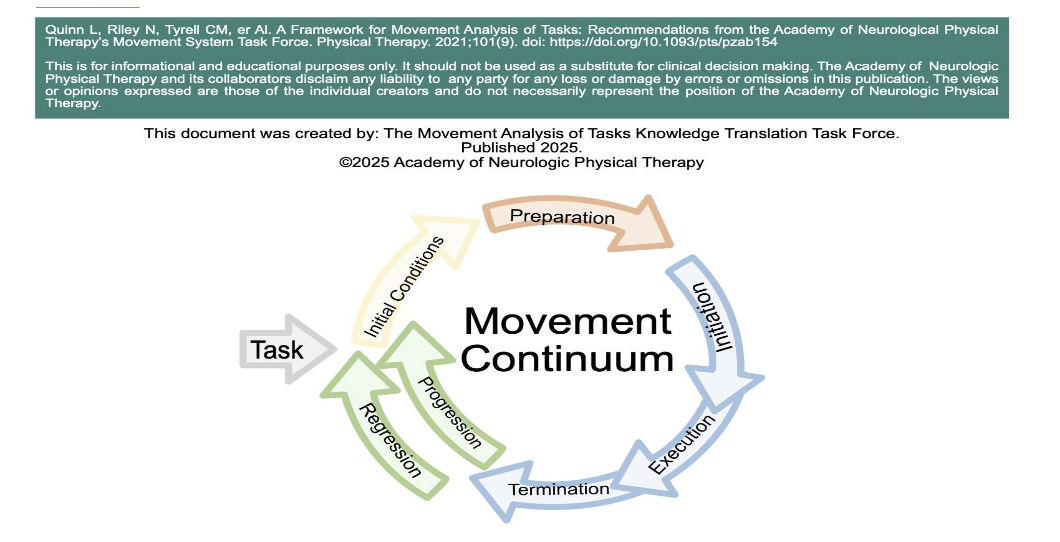
Ok, So How Do We Analyze Movement? chart

For Identifying and describing movement
1. Principle 1: Use it or Lose it
2. Principle 2: Use it and Improve it
3. Principle 3: Specificity matters
4. Principle 4: Repetition matters
5. Principle 5: Intensity matters
6. Principle 6: Time matters
7. Principle 7: Salience matters
8. Principle 8: Age matters
9. Principle 9: Transference
10. Principle 10: Interference
Promoting Neuroplasticity Through Experience Dependent Rehab (644!)
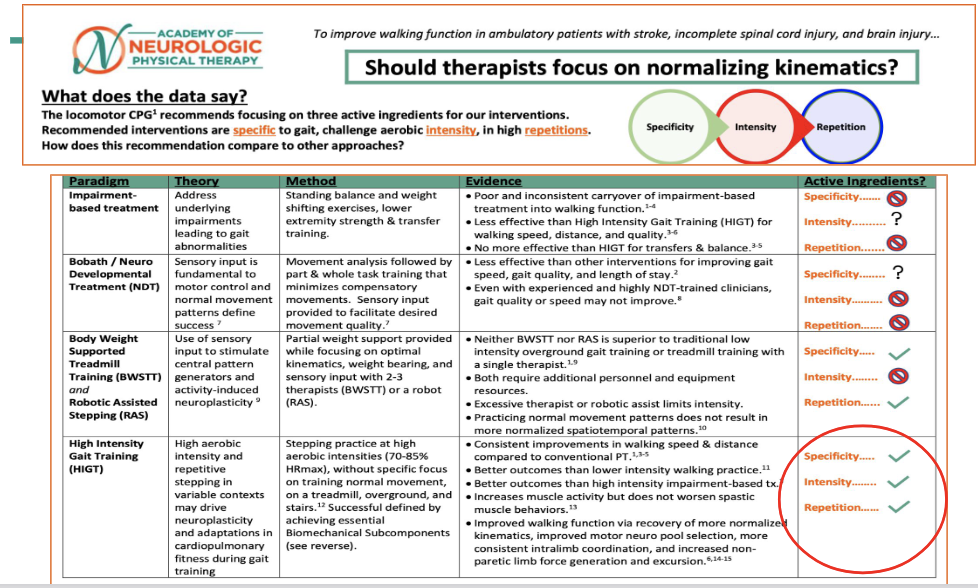
Walking - What should we do - History Lesson
● The ability of the learner to demonstrate a skill--after a learning period.
○ Not given immediately following training.
○ Eg: W/c to-from mat transfer
RETENTION TESTS
● The ability of the learner to modify (adapt) their movement in response to changing environmental demands.
○ Transfers/Ambulation - different surfaces
○ Calm environments to busy environments
○ Increased speed
○ Dual tasks
ADAPTATION TESTS
● Learning in enhanced by applying the OPTIMAL Theory of
Motivation and Attention in humans.
● Practice conditions and feedback strategies must be
considered on an individual basis.
● Practice must be specific, intense, and have sufficient to
promote learning
● Learning has not happened unless there is a test
(adaptation or retention) to demonstrate success
Summary