biochem hmwk 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
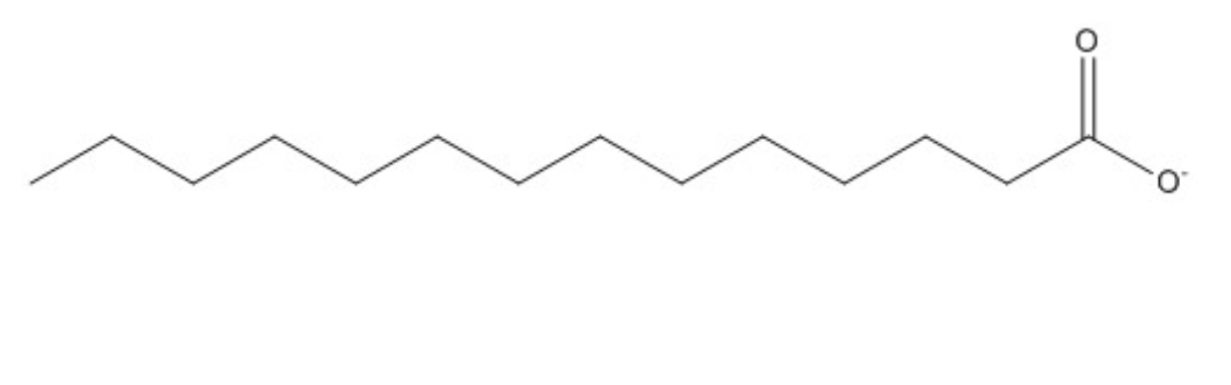
The compound shown below belongs to which of the four major types of biomolecules?
Lipids; fully saturated bc no double bonds on the carbons
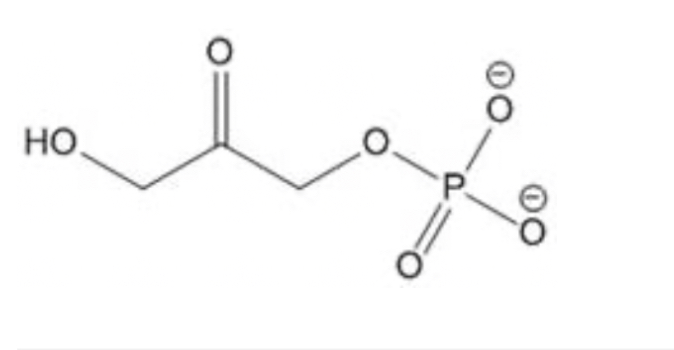
The molecule shown below is dihydroxyacetone phosphate, an intermediate in the biochemical pathways of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. The middle carbon of dihydroxyacetone phosphate is part of what type of functional group?
Ketone; middle carbon is a carbonyl carbon (C=O),
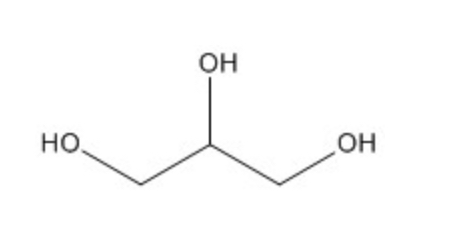
Glycerol; aka propane-1,2,3-trill; precursor compound
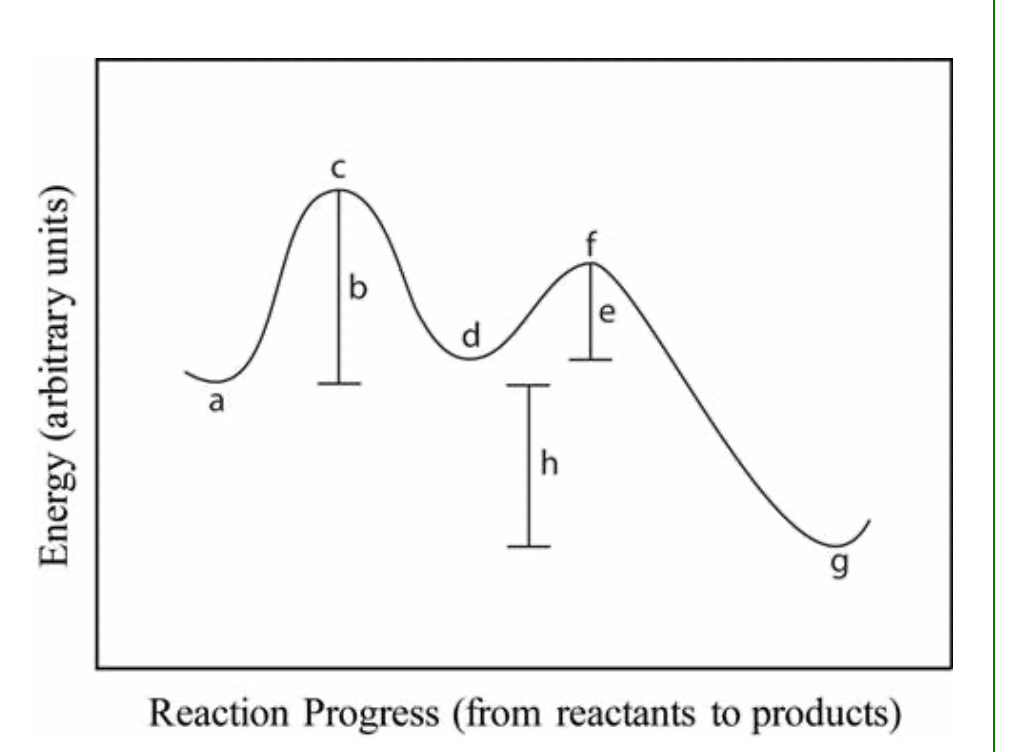
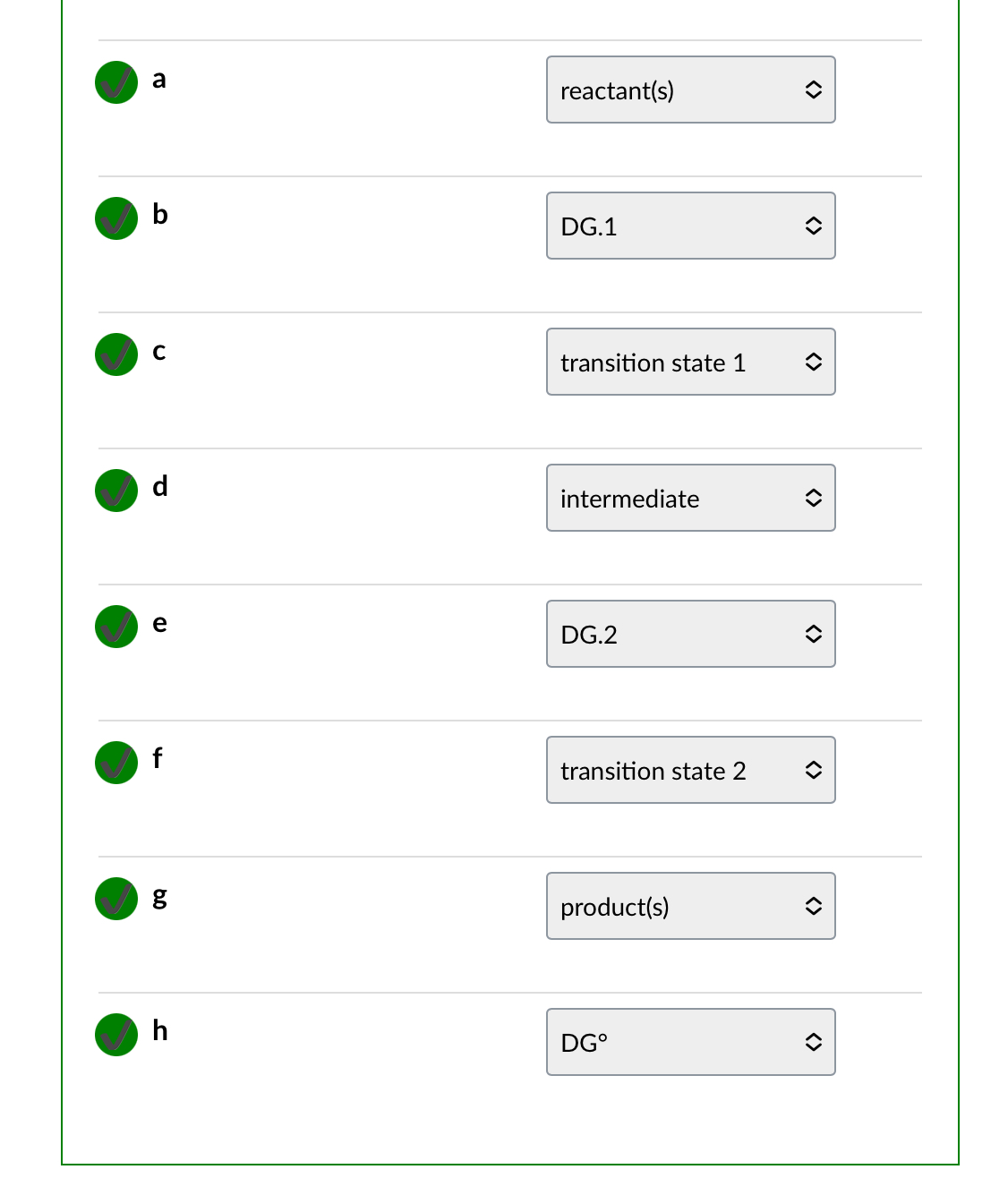
In going from an initial state to a final state it is noted that the surroundings perform 4 J of work on the system, and the system releases 6 J of thermal energy to the surroundings. In a second process, it is noted that in going from the same initial state as above to the same final state as above that the system performs 15 J of work on the surroundings and absorbs 13 J of thermal energy from the surroundings. What are the ΔE values for these processes?
−2 J for process 1 and –2 J for process 2
exergonic
Negative change in free ENERGY of the system
Exothermic
Negative change in ENTHALPY of the system
Endothermic
positive change in ENTHALPY of the system
Endergonic
Positive change in free ENERGY of the system
Many textbooks use J and kJ, but many biochemists are stubborn and use cal and kcal; the conversion between J and cal is: 1 cal = 4.184 J. Therefore, if a person wanted to convert between kJ and kcal, they should use following conversion factor (to four significant figures): 1 kcal = 4.184 kJ.
Not true
To four significant figures, the value of the gas constant is 8.314 J/K⋅mol. Given this information, the value of the gas constant (in terms of cal/K⋅mol) is 1.987 cal/K⋅mol (to four significant figures).
True
When Q is greater than Keq for a particular reaction, then the reaction is not thermodynamically favorable (or spontaneous). Hint: you know an expression that involves Q and an expression that involves Keq. Combine the two expressions and simplify algebraically such that you can evaluate the effects on ΔG when Q is less than Keq.
True
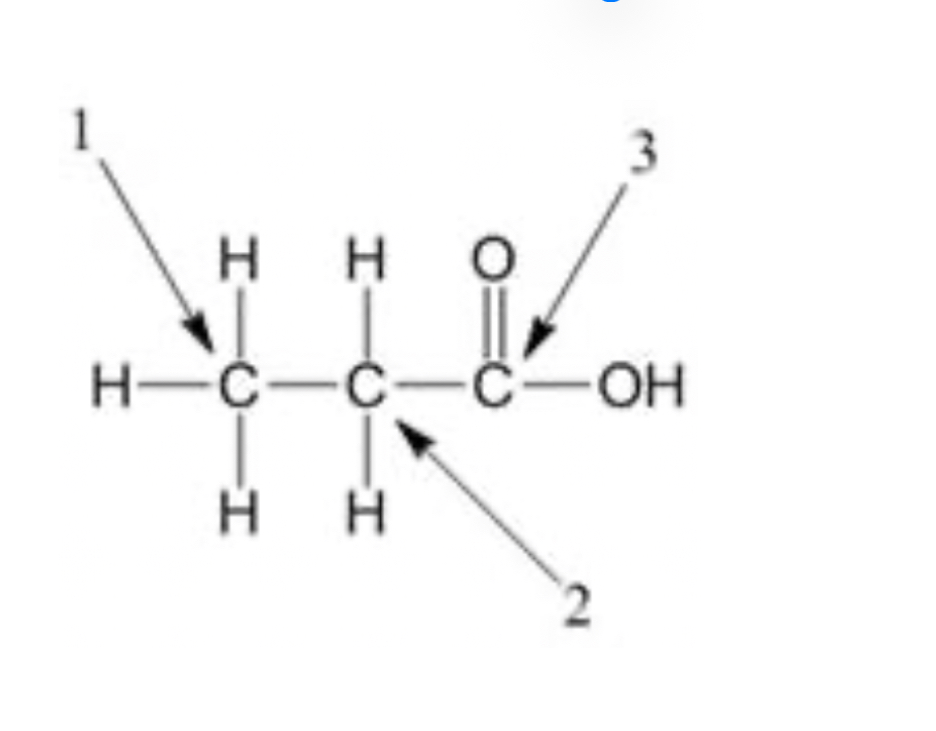
In the figure below, which of the arrows is pointing to the methylene carbon?
2
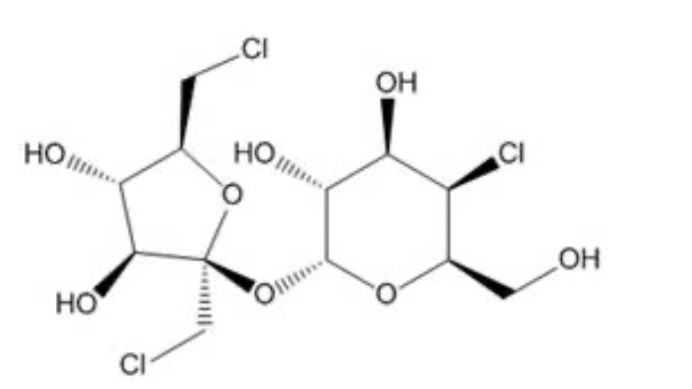
Functional group?
Alkyl halide (haloalkane) ; chlorines
1 step exergonic ran
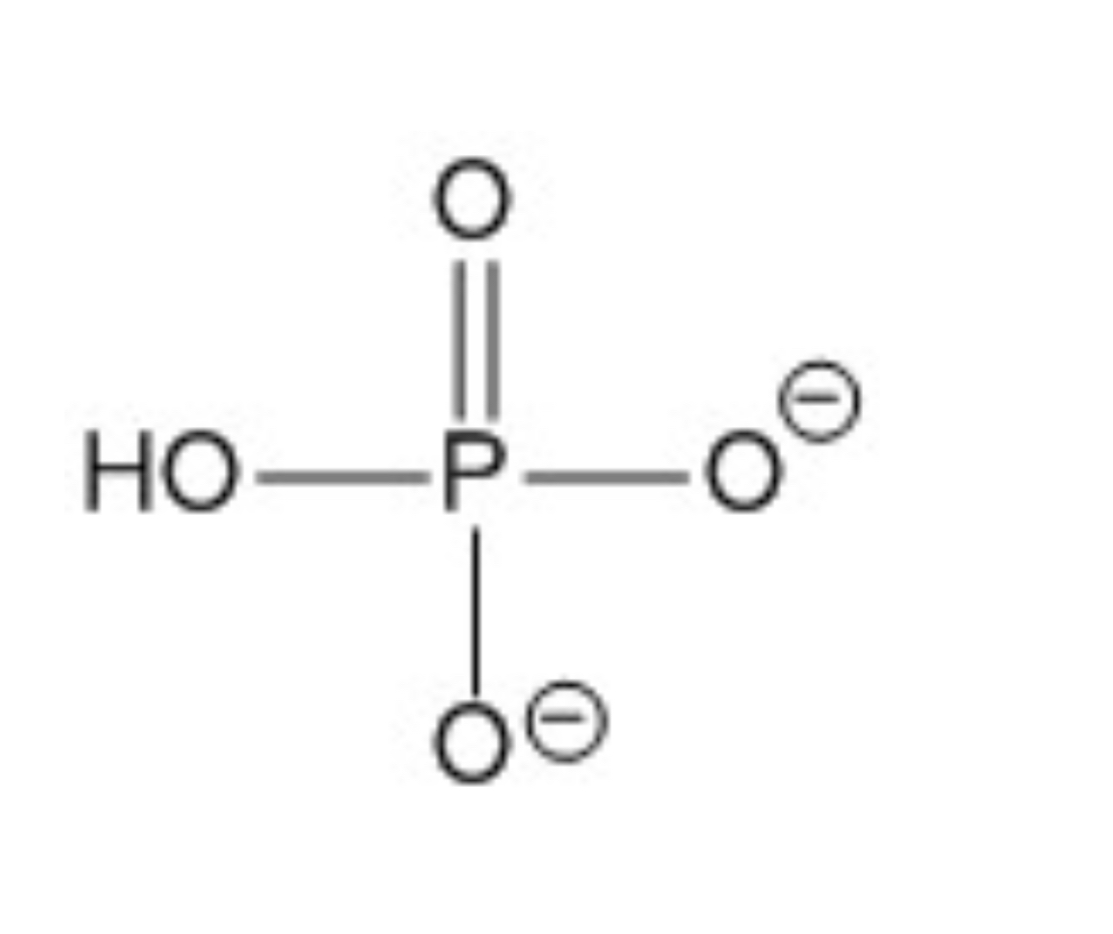
Name?
Inorganic phosphate; precursor compound
The First Law of Thermodynamics allows for the possibility of a perpetual motion machine.
Not true
Exergonic
ΔG of the system is _____.
negative
Many textbooks use J and kJ, but many biochemists are stubborn and use cal and kcal; the conversion between J and cal is: 1 cal = 4.184 J. Therefore, if a person wanted to convert between kJ and kcal, they should use following conversion factor (to four significant figures): 1 kcal = 4.184 kJ.
True
To four significant figures, the value of the gas constant is 1.987 cal/K⋅mol. Given this information, the value of the gas constant (in terms of J/K⋅mol) is 0.4749 J/K⋅mol (to four significant figures).
Not true
When Q is less than Keq for a particular reaction, then the reaction is not thermodynamically favorable (or spontaneous). Hint: you know an expression that involves Q and an expression that involves Keq. Combine the two expressions and simplify algebraically such that you can evaluate the effects on ΔG when Q is less than Keq.
Not true

Ester
Polymers to monomers
Proteins → amino acids
Polysaccharides → monosaccharides
Nucleic acids → nucleotides
Lipid bilayers → non polymeric associations of lipids
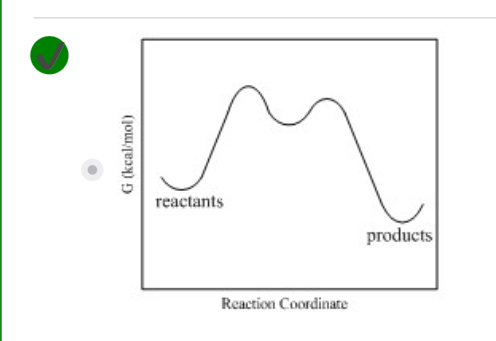
Two step exergonic
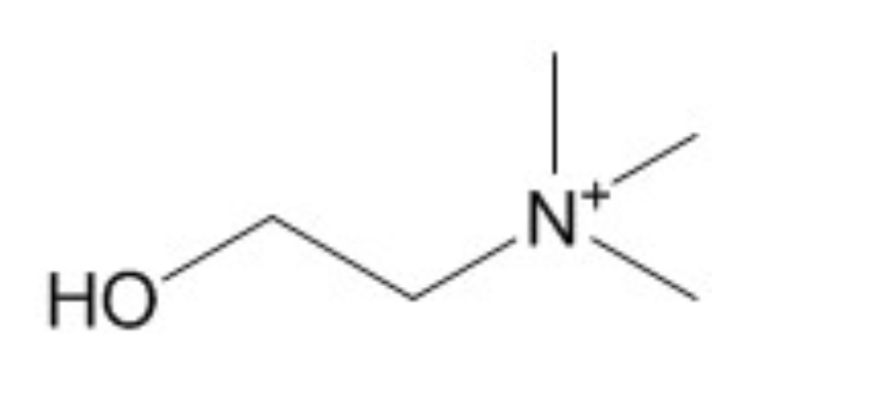
Who?
Choline
The value of the gas constant (R) is 8.314 J/K⋅mol to four significant figures. If you needed to use the gas constant in a calculation such that the desired units were kJ/K⋅mol, then you would use the following: R = 0.008314 kJ/K⋅mol (to four significant figures).
True
The reaction quotient (Q), based on the initial concentrations of reactants and products, is known to be 300. The equilibrium constant (Keq) for the same reaction is known to be 10,000. Given this information (and conditions), will the reaction be spontaneous?
Yes, will be spontaneous
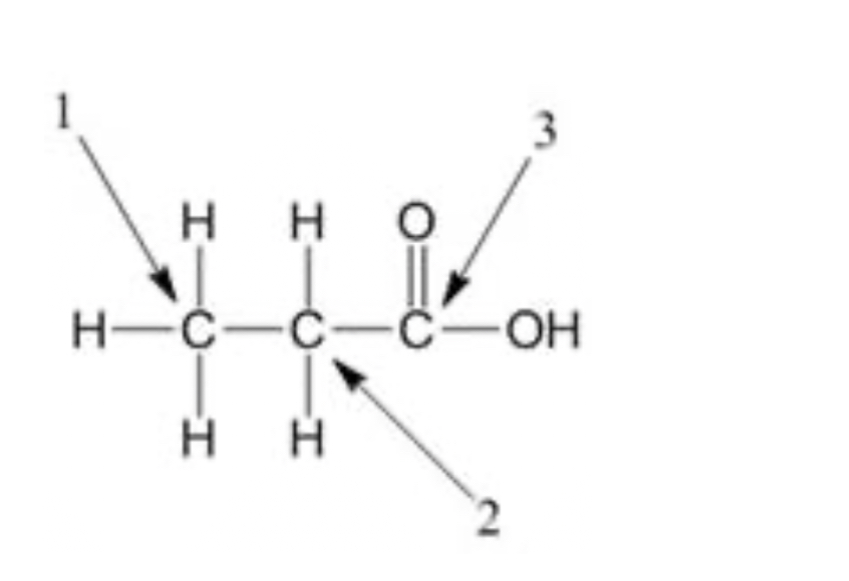
Alcohol carbon
3