B7: CM H/O Exam 1
1/775
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Hematology/oncology: where the cells are malignant, the prognosis is guarded, and the jokes are still inappropriate.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
776 Terms
Anemia
most common disorder of the blood
1. blood loss
2. destruction of RBC
3. decreased RBC production
the three main causes of anemia
Lasthenie de Ferjol Syndrome
a very rare psychiatric pathology characterized by severe relapsing anaemia due to repeated self-induced hemorrhages
• GI or GU tract; obvious or occult
• Menstrual
• Retroperitoneal
• Nose bleeds, cutting, hematuria
main causes of blood loss that can lead to anemia
• Lack of iron, B12, folate
• Dysfunctional Bone marrow
• Suppressed bone marrow (radiation/chemo)
• Low levels erythropoietin, androgen, thyroid
causes of decreased RBC production that lead to anemia
Bone
where does erythropoiesis occur in adults?
Erythropoietin (EPO)
-enhances growth and differentiation of two erythroid progenitors to normoblasts of
increasing maturity.
Reticulocyte
Normoblast extrudes its nucleus to form a RBC and is identified as a ___________________
1%
Reticulocytes >_____% means bone marrow is working.
Hemolysis
The destruction of red blood cells which leads to the release of hemoglobin from within the red blood cells into the blood plasma
Bi-concave disk
shape of RBC
Normochromic Normocytic
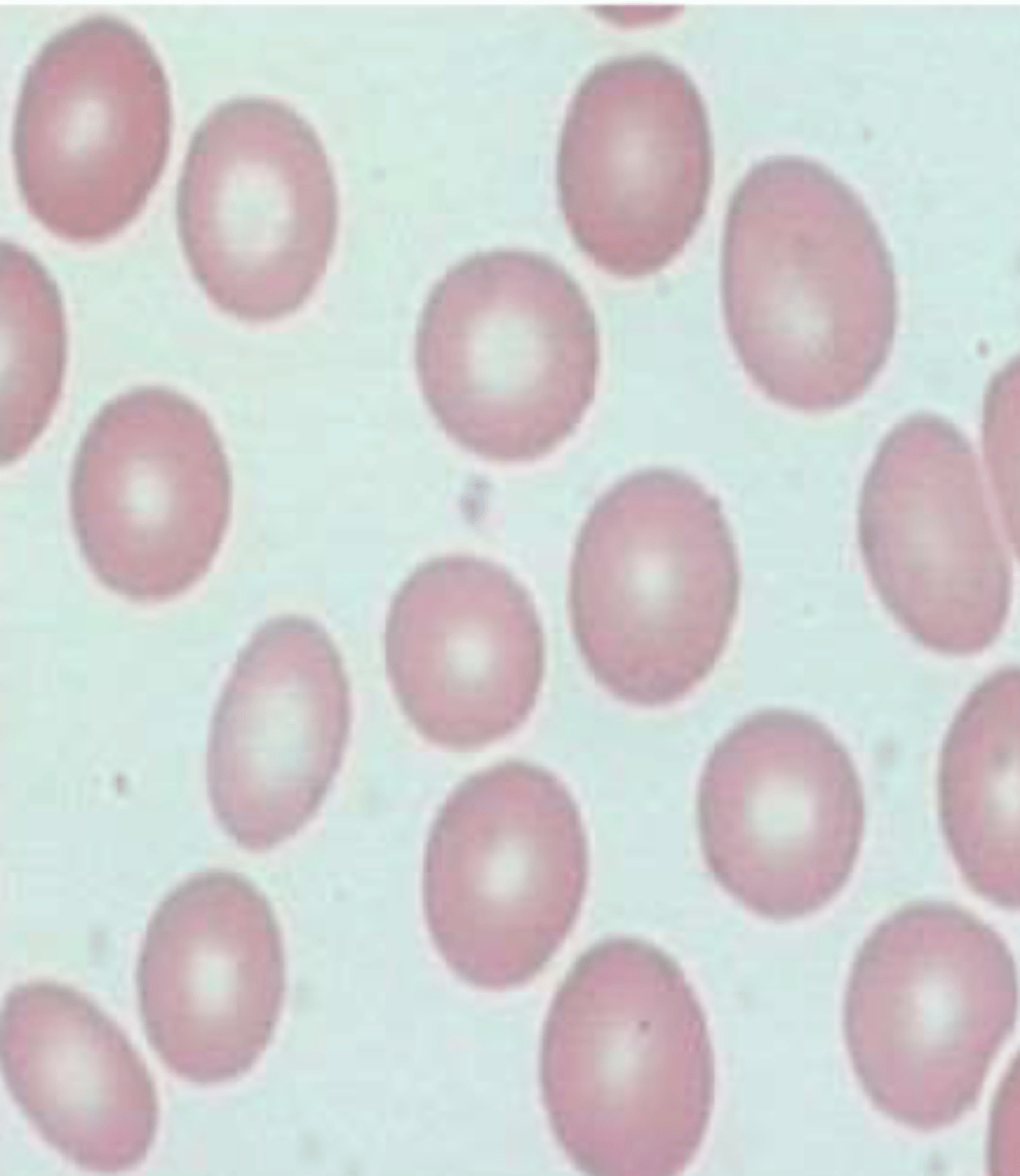
Hypochromic
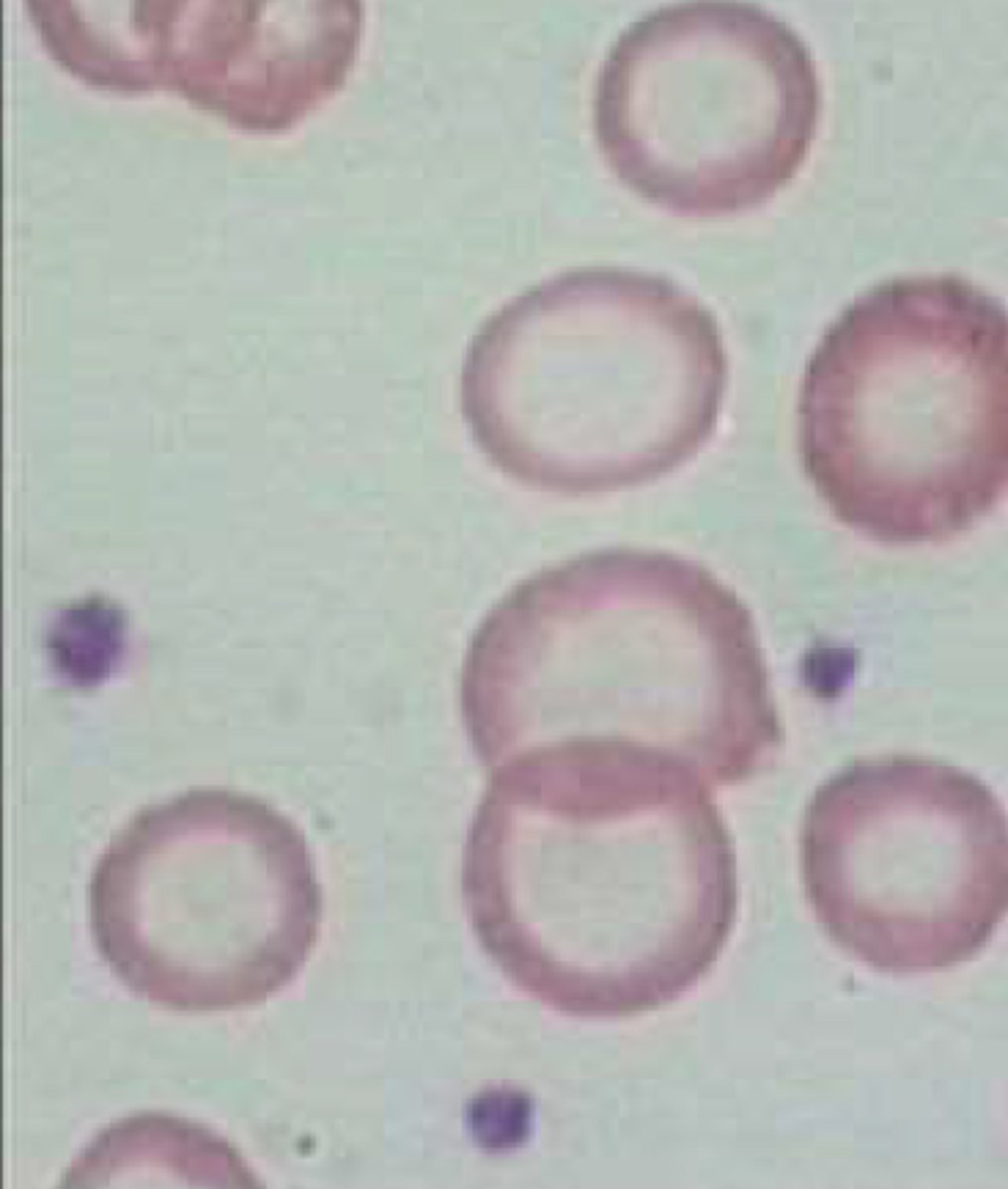
Hyperchromic
Hemoglobin S
variant of hemoglobin found in people with sickle cell
Hemoglobin C (and E)
variant of hemoglobin that causes mild chronic hemolytic anemia
Hemoglobin AS
variant of hemoglobin is heterozygous and causes sickle cell trait
Hemoglobin A (2 & 2)
Most common type of hemoglobin in adults
Oxygen
____________ binding changes structure of porphyrin heme ring
Bohr Effect
-States that in high acid ([H+]) conditions, side chains of Hb take on hydrogen; changes Hb conformation
-Result is LESS Hb oxygen content at given partial pressure of Oxygen
-O2 leaves Hb & goes to tissues
Right
__________ Shift:
-low affinity for O2
-O2 is released to the tissues
Right
__________ Shift:
-decreased pH
-increased CO2
-increased 2,3 BPG
-high temperature
Left
__________ Shift:
-increased pH
-decreased CO2
-decreased 2,3 BPG
Left
______________ Shift:
-high affinity for O2
Hemoglobin
Iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in RBC
Denatures the bond between oxygen and Hemoglobin
How does temp affect hemoglobin affinity for oxygen?
Right
__________ Shift:
acidosis
Left
__________ Shift:
alkalosis
Fetal Hemoglobin
Which has a greater affinity for oxygen?
Fetal or Adult Hemoglobin
Pagophagia
-desire to chew on ice
Pica
Eating non-nutritional items (Iron deficiency anemia)
Vitamin B12
__________________ is needed for normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and the formation of red blood cells
Increasing
the body responds to low oxygen in the peripheral blood by ____________ cardiac output
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
-Represents the mean volume of individuals RBCs in blood sample
Microcytosis
defined as a MCV value less than 2 SD below the mean
( <80 fL in adults)
Normocytic
defined as MCV within 2 SD of the mean
Macrocytosis
defined as MCV value more than 2 SD above the mean
(>100 fL in adults)
Medications
Most common cause of macrocytic anemia in children
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Factors that effect ____________ include iron deficiency, lead intoxication, anemia of chronic disease, & hemoglobinopathies (not sickle cell)
RDW (Red Cell Distribution width)
• A measure of the range in the volume and size of RBC
• A quantitative measure of variability of RBC sizes
• Values vary with age, usually ~ 12-14%
• Value increases in conditions in which there is large variation in RBC size.
• Helps differentiate different types of microcytic anemias
Normal
RDW in Thalassemia
>20
RDW in Iron deficiency
RDW (Red Cell Distribution width)
Conditions associated with increased _____________: Iron deficiency anemia, folate deficiency anemia, B-12 deficiency anemia, hemolytic anemia, sideroblastic anemia, transfusion, RBC Fragmentation, Hemoglobin H Disease & Alcohol abuse.
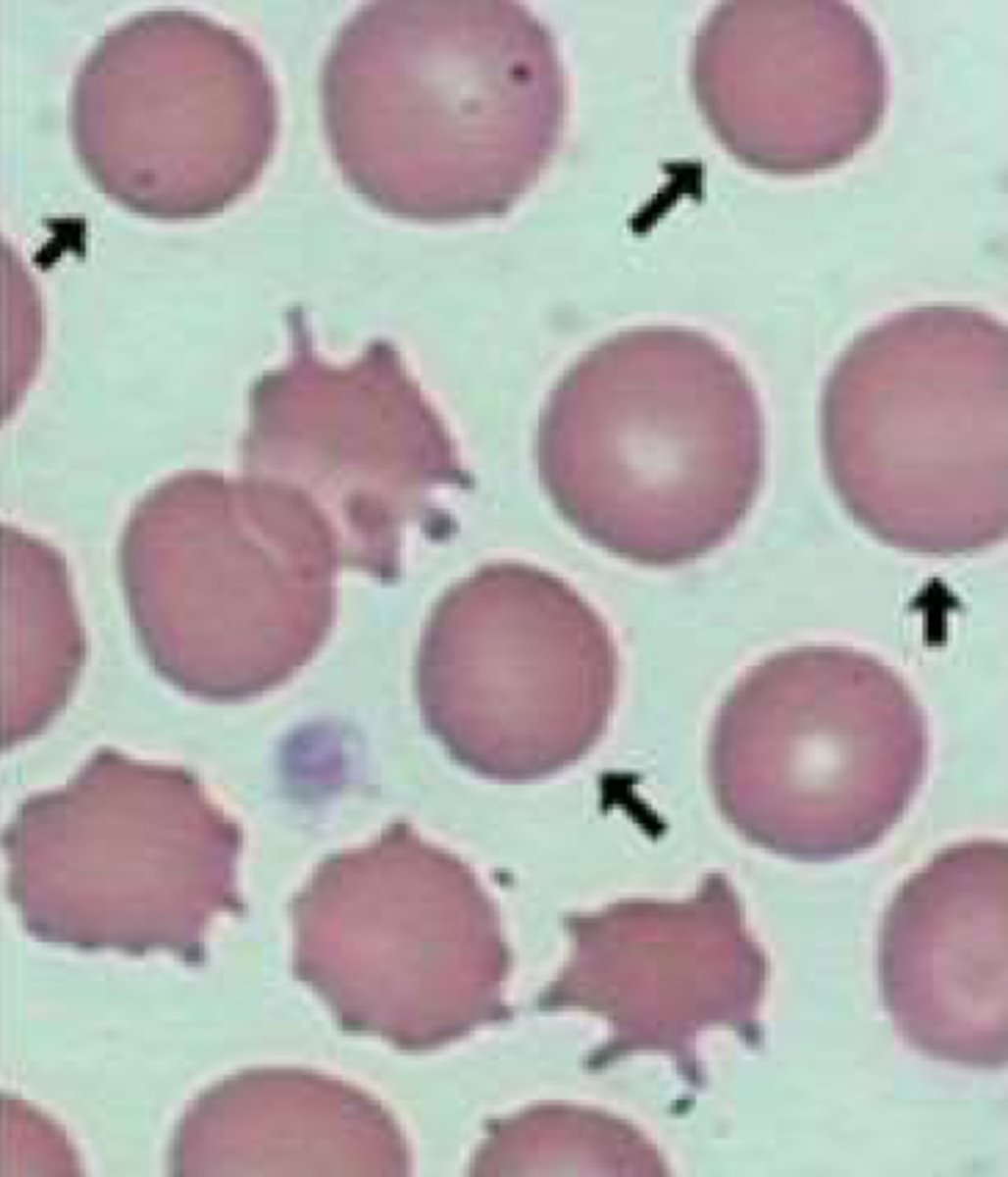
Anisocytosis
cells of different sizes
Poikilocytosis
cells of different shapes
Spherocytosis & reticulocytes
cells that are hyperchromic
1/3
Normocytic central pallor is ~ _________ the RBC diameter
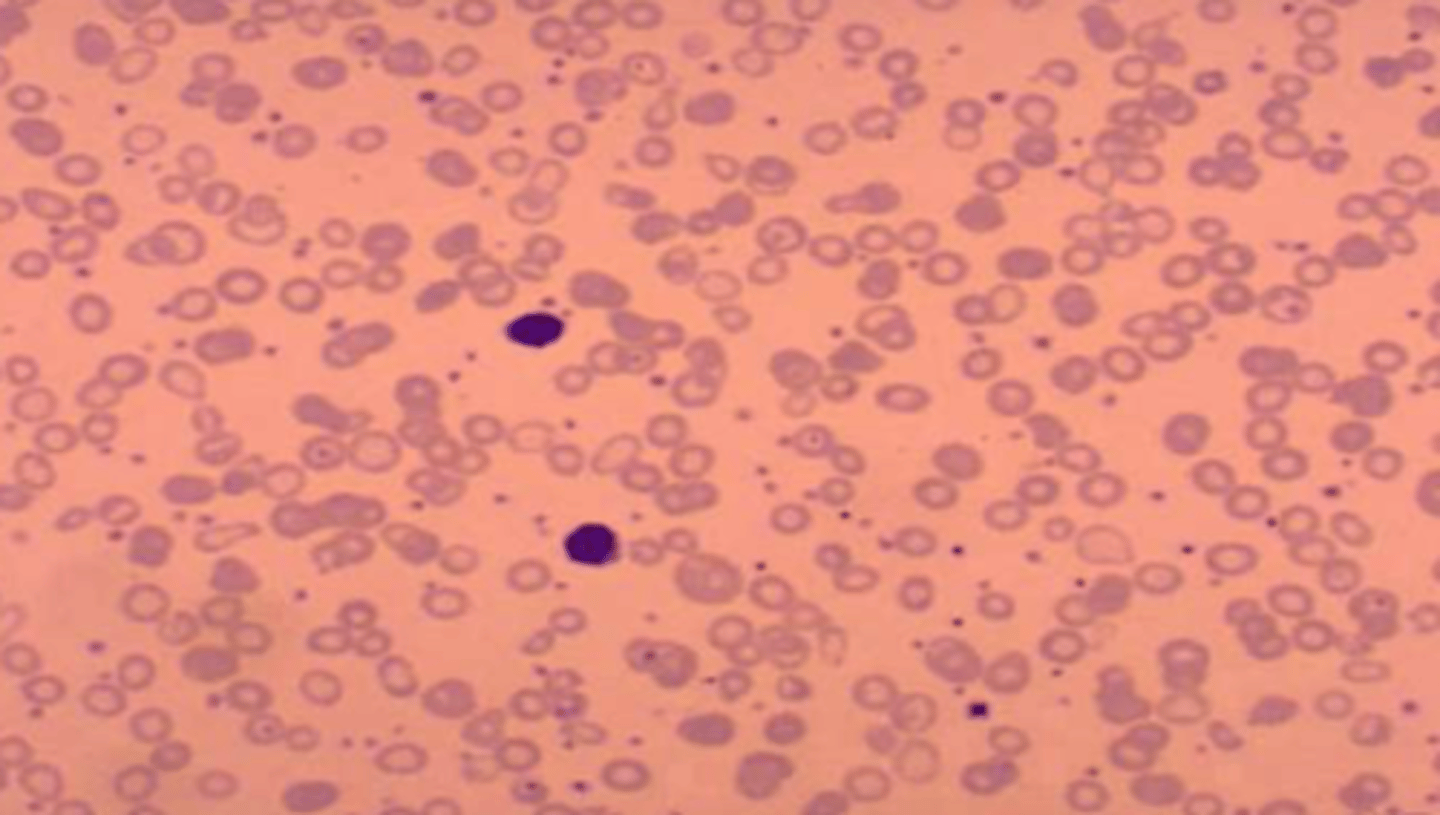
Infection
if there is increased neutrophils on a peripheral smear, there is a concern for __________________
Leukemia or Lymphoma
if there are blasts on a peripheral smear, there is a concern for ________________________
Normal
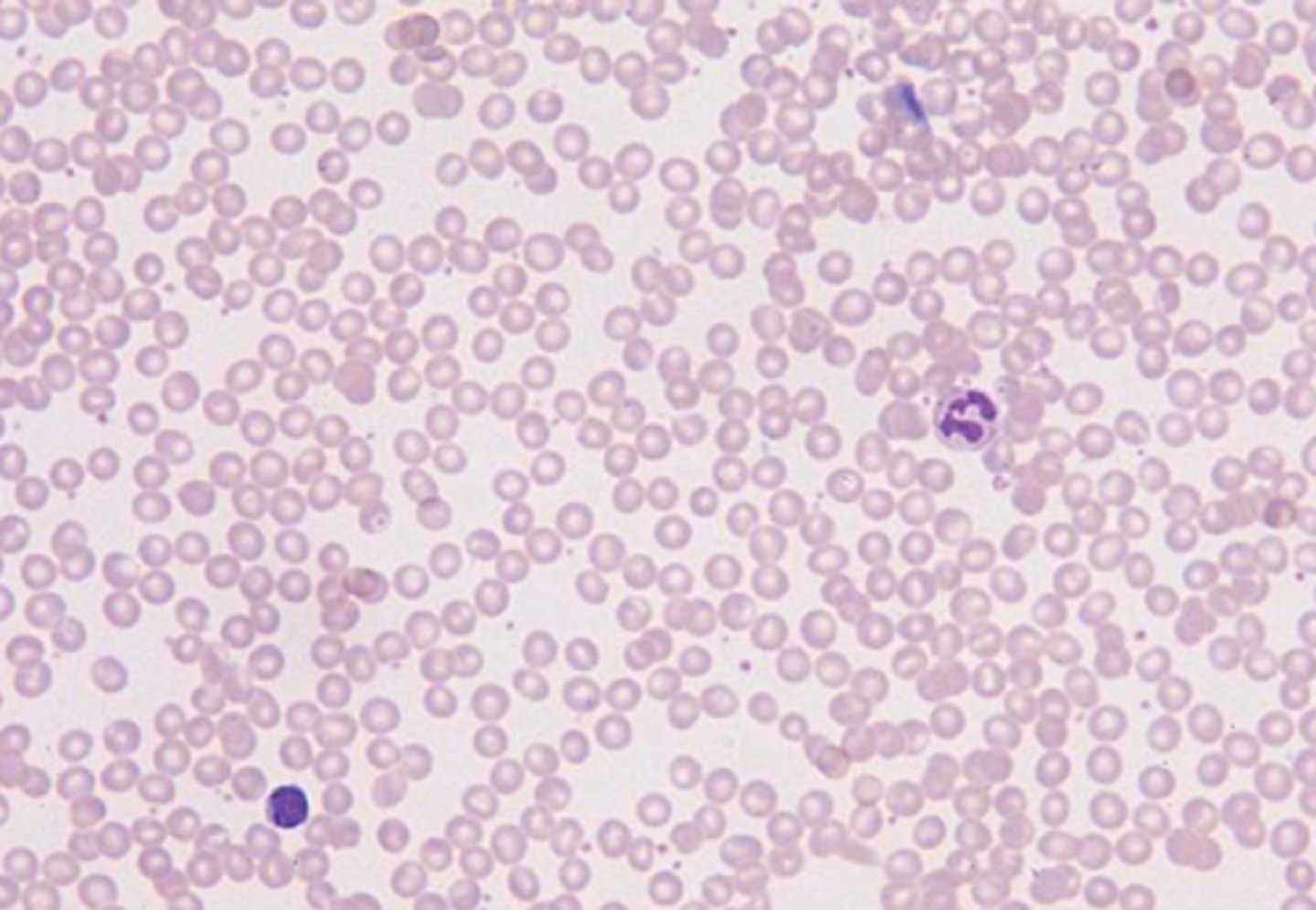
Reticulocyte Count
Allows critical distinction between anemia arising from failure of RBC production versus that from increased RBC destruction
High
_____________ reticulocyte count with low hgb suggests the body is making RBCs
- anemia is due to blood loss or hemolysis
Low
_____________ reticulocyte count with low hgb suggests inadequate RBC production anemia is due to marrow failure (i.e. aplastic anemia)
0.5 - 2.0 %
normal reticulocyte count for adults
~100-120 days
how long do RBCs survive?
Methylene blue
reticulocytes can be counted manually when stained with _________________
Retic Index
corrected percentage for reticulocyte count
reticulocyte count x (hct/normal hct)
Inadequate
RPI < 3% with anemia = _______________ response of marrow
Appropriate
RPI > 3% with anemia = ______________ marrow response
<3%
RPI ___________% with anemia:
decreased production of reticulocytes (Myelodysplastic) & therefore RBCs.
>3%
RPI ___________% with anemia:
indicates loss of RBCs (from causes such as destruction, bleeding, etc.), with an increased
compensatory production of reticulocytes to replace lost RBCs.
Colon Cancer
when considering a diagnosis of Iron deficiency Anemia, you must rule out ____________________
Iron deficiency Anemia
-Hypochromic and microcytic cells
-most of the red cells are much smaller than the lymphocytes
-increased
platelet count
Duodenum and Upper Jejunum
Iron absorption occurs predominantly where?
pH
the absorption of iron is highly dependent on the __________ of the duodenum and upper jejunum
Iron deficiency Anemia
• Low iron,
• high TIBC (Total Iron Binding Capacity)
• Ferritin Low (High in anemia of chronic disease)
Iron deficiency Anemia
Ferritin
acute phase reactant protein that helps store iron in your body
-low level indicates a low level of stored iron
Transferrin Saturation
the ratio of serum iron and total iron-binding capacity
-his value tells a clinician how much serum iron are actually bound.
Total iron-binding capacity (TIBC)
medical laboratory test that measures the blood's capacity to bind iron with transferrin (may be HIGH if iron level is LOW).
Oral iron
Which treatment for iron deficiency anemia:
• Time consuming
• GI side effects are common
-150-200mg a day (3 pills a day)
IV Iron
Which treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia
• Many formulations and dosing schemes
• Watch for reactions
• Much faster - can replete a years worth of iron in a dose or two
Anemia of Inflammation/ Anemia of Chronic Disease
acquired condition that is commonly observed in the clinical settings of:
• Infection
• Arthritis
• Malignancy
• trauma
• organ failure.
Anemia of Inflammation/ Anemia of Chronic Disease
What disorder:
-Initially anemia is mild, characterized primarily by a decrease in the number of RBCs
• Over time, the anemia becomes more severe, with hypochromic, microcytic erythrocytes
-results from a host-defense mechanism designed to sequester iron from the invading pathogens
Anemia of Inflammation/ Anemia of Chronic Disease
Pathogenesis:
• First, there is a modest (<10%) shortening of red cell survival which creates a demand for a slight increase in bone marrow red cell production.
-The bone marrow cannot respond adequately owing to impaired erythropoiesis and impaired mobilization of iron from the reticuloendothelial cells
Hepcidin
an endogenous antimicrobial peptide secreted by the liver, has been identified as controlling the level of plasma iron by regulating the intestinal absorption of dietary iron as well as the release of macrophages and the transfer or iron stored in the hepatocytes
Hepcidin
Increase in _____________level in the course of inflammatory disease may be a significant mediator of the accompanying anemia
Lead Toxicity
-Basophilic Stippling
-hct and hb moderately low
-normochromic and normocytic or hypochromic and microcytic
-Eosinophilia
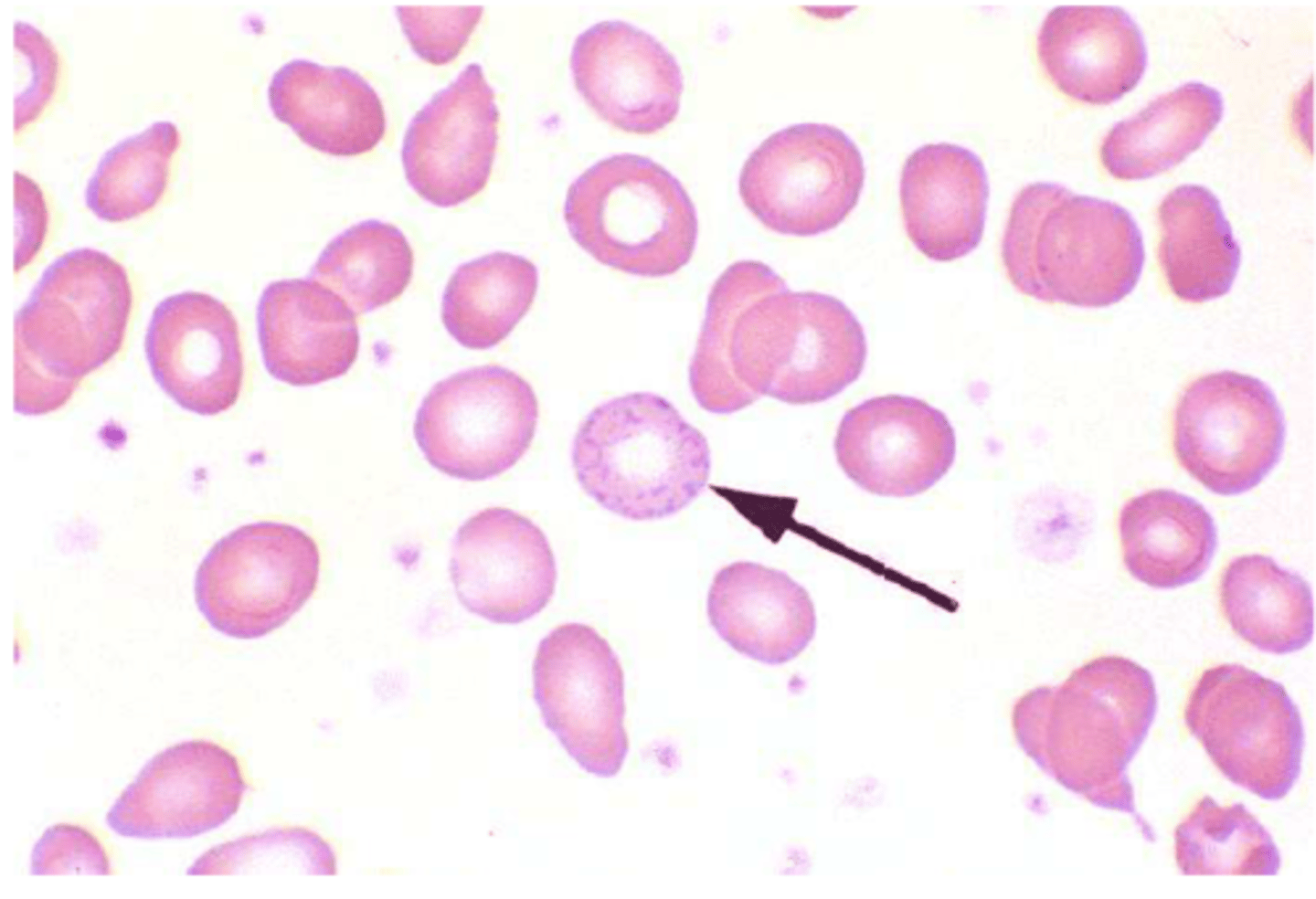
Sideroblastic Anemia
What disorder:
-rare blood disorder characterized by the bone marrow's inability to manufacture normal red blood cells
-normocytic-normochromic anemia with high RDW
-microcytic-hypochromic anemia, particularly with increased serum iron, ferritin, and transferrin saturation
Hereditary Sideroblastic Anemia
-X-linked Recessive
-more commonly in young males, maternal uncles and cousins.
-generally manifests during the first three decades of life especially during adolescence
-inability of bone marrow to make normal RBCs
Acquired Sideroblastic Anemia
anemia due to prolonged exposure to toxins like alcohol, lead, drugs or nutritional imbalances such as deficiency in folic acid, deficiency in copper or excess zinc
-usually seen in patients over 65 year of age but it can be present as early as mid to late fifties
Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)
Idiopathic Sideroblastic Anemia is aka:
Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)
bone marrow dysfunction disorder which can develop into aplastic anemia requiring bone marrow or stem cell transplantation
Sideroblastic Anemia
• Serum iron increased
• transferrin iron saturation percentage increased
• ferritin increased
• transferrin is decreased.
• TIBC is normal to decreased; serum transferrin receptor is normal to high
-MCV normal to slightly increased
-RDW increased
-White blood cells and platelets are decreased.
Blood Transfusions
Treatment for Sideroblastic anemia if the cause of the pts anemia cannot be determined
Pyridoxine (b6)
In rare instances of sideroblastic anemia, treatment with oral ________________________ benefits patients whose who have had the condition since birth
anemia
a serious sign of disease, NEVER NORMAL
Romberg sign
loss of balance standing with eyes closed
angular cheilitis (cracking at corners of mouth), glossitis, jaundice
oral/skin findings of macrocytic anemia
CBCwd, peripheral smear, reticulocyte count
basic initial labs for anemia
b12 level, folate level, MMA and homocysteine
focused initial labs for anemia
WBC, RBC, H&H, MCV
most important aspects of CBC to look at in anemia workup
MCV
Represents the mean volume of individuals RBCs in blood sample
macrocytosis
MCV value more than 2 SD above the mean (>100 fL in adults)
-RBC larger than normal at all stages
-classified as megaloblastic or non-megaloblastic
normocytic
MCV within 2 SD of the mean
microcytosis
MCV value less than 2 SD below the mean( <80 fL in adults)
medications
most common cause of macrocytic anemia in children
megaloblastic anemia
caused by impaired DNA synthesis
-Deficient Thymidylate leads to arrest in cell maturation
-Marked increase in MCV is common (MCV >110)
b12 deficiency
folate deficiency
medication associated
hereditary orotic aciduria
causes of megaloblastic anemia
Reticulocytosis
Hypothyroidism
Liver disease
Postsplenectomy anemia
Myelodysplastic syndromes
Aplastic anemia
Dyserthropoetic anemia
Down syndrome
causes of non-megaloblastic anemia