Modern Database Management Chapter 2 Test
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
1) The logical representation of an organization's data is called a(n):
A) database model.
B) entity-relationship model.
C) relationship systems design.
D) database entity diagram.
Answer: B
2) A good data definition will describe all of the characteristics of a data object EXCEPT:
A) subtleties.
B) examples.
C) who determines the value of the data.
D) who can delete the data.
Answer: D
3) A fact is an association between two or more:
A) words.
B) terms.
C) facts.
D) nuggets
Answer: B
4) Data modeling may be the most important part of the systems development process because:
A) data characteristics are important in the design of programs and other systems components.
B) the data in a system are generally less complex than processes and play a central role in development.
C) data are less stable than processes.
D) it is the easiest.
Answer: A
5) The most common types of entities are:
A) strong entities.
B) weak entities.
C) associative entities.
D) smush entities.
Answer: A
6) In an E-R diagram, there are/is ________ business rule(s) for every relationship.
A) two
B) three
C) one
D) zero
Answer: A
7) Business policies and rules govern all of the following EXCEPT:
A) managing employees.
B) creating data.
C) updating data.
D) removing data.
Answer: A
8) A ________ defines or constrains some aspect of the business.
A) business constraint
B) business structure
C) business control
D) business rule
Answer: D
9) Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a good business rule?
A) Declarative
B) Atomic
C) Inconsistent
D) Expressible
Answer: C
10) Which of the following is NOT a good characteristic of a data name?
A) Relates to business characteristics
B) Readable
C) Repeatable
D) Relates to a technical characteristic of the system
Answer: D
11) Customers, cars, and parts are examples of:
A) entities.
B) attributes.
C) cardinals.
D) relationships.
Answer: A
12) Which of the following is an entity that exists independently of other entity types?
A) Codependent
B) Weak
C) Strong
D) Variant
Answer: C
13) An entity type whose existence depends on another entity type is called a ________ entity.
A) strong
B) weak
C) codependent
D) variant
Answer: B
14) The following figure shows an example of:
A) a one-to-many relationship.
B) a strong entity and its associated weak entity.
C) a co-dependent relationship.
D) a double-walled relationship.
Answer: B
15) A(n) ________ is the relationship between a weak entity type and its owner.
A) member chain
B) identifying relationship
C) jump path
D) chain link
Answer: B
16) An entity type name should be all of the following EXCEPT:
A) concise.
B) specific to the organization.
C) as short as possible.
D) a singular noun.
Answer: C
17) A property or characteristic of an entity type that is of interest to the organization is called a(n):
A) attribute.
B) coexisting entity.
C) relationship.
D) cross-function.
Answer: A
18) An attribute that must have a value for every entity (or relationship) instance is a(n):
A) composite attribute.
B) required attribute.
C) optional attribute.
D) multivalued attribute.
Answer: B
19) A person's name, birthday, and social security number are all examples of:
A) attributes.
B) entities.
C) relationships.
D) descriptors.
Answer: A
20) An attribute of an entity that must have a value for each entity instance is a(n):
A) optional attribute.
B) composite attribute.
C) required attribute.
D) fuzzy attribute.
Answer: C
21) An attribute that can be broken down into smaller parts is called a(n) ________ attribute.
A) associative
B) simple
C) composite
D) complex
Answer: C
22) The number of entity types that participate in a Unary relationship is:
A) zero.
B) one.
C) two.
D) three.
Answer: B
23) The number of entity types that participate in a relationship is called the:
A) number.
B) identifying characteristic.
C) degree.
D) counter.
Answer: C
24) A relationship between the instances of a single entity type is called a ________ relationship.
A) ternary
B) primary
C) binary
D) unary
Answer: D
25) In the following diagram, what type of relationship is depicted?
A) Unary
B) Binary
C) Ternary
D) Quad
Answer: C
26) In the following diagram, which is true?
A) It depicts a ternary relationship.
B) It depicts a many-to-many relationship.
C) Item represents a column.
D) BOM_STRUCTURE represents a row.
Answer: B
27) A simultaneous relationship among the instances of three entity types is called a ________
relationship.
A) ternary
B) tertiary
C) primary
D) binary
Answer: A
28) The following figure shows an example of:
A) a composite attribute.
B) a relational attribute.
C) a derived attribute.
D) a multivalued attribute.
Answer: A
29) In the figure below, which attribute is multivalued?
A) Years_Employed
B) Employee_ID
C) Skill
D) Address
Answer: C
30) In the figure below, which attribute is derived?
A) Years_Employed
B) Employee_ID
C) Skill
D) Address
Answer: A
31) An attribute that can be calculated from related attribute values is called a ________
attribute.
A) simple
B) composite
C) multivalued
D) derived
Answer: D
32) The total quiz points for a student for an entire semester is a(n) ________ attribute.
A) derived
B) mixed
C) stored
D) addressed
Answer: A
33) Which of the following criteria should be considered when selecting an identifier?
A) Choose an identifier that is not stable.
B) Choose a null identifier.
C) Choose an identifier that doesn't have large composite attributes.
D) Choose the most complex identifier possible.
Answer: C
34) An attribute that uniquely identifies an entity and consists of a composite attribute is called a(n):
A) composite attribute.
B) composite identifier.
C) identifying attribute.
D) relationship identifier.
Answer: B
35) An entity that associates the instances of one or more entity types and contains attributes specific to the relationships is called a(n):
A) associative entity.
B) build entity.
C) gateway entity.
D) smush entity.
Answer: A
36) A ________ specifies the number of instances of one entity that can be associated with each instance of another entity.
A) degree
B) cardinality constraint
C) counter constraint
D) limit
Answer: B
37) A relationship where the minimum and maximum cardinality are both one is a(n) ________relationship.
A) optional
B) unidirectional
C) mandatory link
D) mandatory one
Answer: D
38) A mutually exclusive relationship is one in which:
A) an entity instance can participate in many different relationships.
B) an entity instance can participate in only one of several alternative relationships.
C) an entity instance cannot participate in a relationship with another entity instance.
D) an entity instance bridges other XML documents.
Answer: B
39) In the figure shown below, which of the following is true?
A) A person can marry at most one person.
B) A person has to be married.
C) A person can marry more than one person, but that person can only be married to one person.
D) A person can marry more than one person.
Answer: A
40) For the relationship represented in the figure below, which of the following is true?
A) An employee can work in more than one department but does not have to work for any
department.
B) A department must have at least one employee.
C) A department can have more than one employee.
D) An employee has to work for more than one department.
Answer: C
41) In the following diagram, which of the answers below is true?
A) Each patient has one or more patient histories.
B) Each patient has one and only one visit.
C) Each patient history belongs to zero and one patient.
D) Each patient history belongs to many patients.
Answer: A
42) In the figure shown below, which of the following business rules would apply?
A) Each vendor can supply many parts to any number of warehouses, but need not supply any
parts.
B) Each part must be supplied by exactly one vendor to any number of warehouses.
C) Each warehouse can be supplied with any number of parts from more than one vendor, and
each warehouse could be supplied with no parts.
D) VENDOR is not allowed
Answer: A
43) In the following diagram, which answer is true?
A) Each employee can supervise one employee, no employees or many employees.
B) Each employee can manage many departments.
C) Each employee works in more than one department.
D) Each employee was fired.
Answer: A
4) A student can attend five classes, each with a different professor. Each professor has 30 students. The relationship of students to professors is a ________ relationship.
A) one-to-one
B) many-to-many
C) one-to-many
D) strong
Answer: B
45) A value that indicates the date or time of a data value is called a:
A) value stamp.
B) time stamp.
C) checkpoint.
D) check counter
Answer: B
46) The E-R model is used to construct a conceptual model.
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
TRUE
47) A business rule is a statement that defines or constrains some aspect of the business.
TRUE
48) One of the roles of a database analyst is to identify and understand rules that govern data.
TRUE
49) The intent of a business rule is to break down business structure.
FALSE
50) Enforcement of business rules can be automated through the use of software tools that can interpret the rules and enforce them.
TRUE
51) When systems are automatically generated and maintained, quality is diminished.
FALSE
52) A business rule is a statement of how a policy is enforced or conducted.
FALSE
53) While business rules are not redundant, a business rule can refer to another business rule.
TRUE
54) A business rule should be internally consistent.
TRUE
55) Business rules are formulated from a collection of business ramblings.
FALSE
56) Data names should always relate to business characteristics.
TRUE
57) An example of a term would be the following sentence: "A student registers for a course."
FALSE
58) A fact is an association between two or more terms.
TRUE
59) A good data definition is always accompanied by diagrams, such as the entity-relationship diagram.
TRUE
60) An entity is a person, place, object, event, or concept in the user environment about which the organization wishes to maintain data.
TRUE
61) A single occurrence of an entity is called an entity instance.
TRUE
62) In the figure below, Name would be an ideal identifier.
FALSE

63) When choosing an identifier, choose one that will not change its value often.
TRUE
64) Most systems developers believe that data modeling is the least important part of the systems development process.
FALSE
65) Data, rather than processes, are the most complex aspects of many modern information systems.
TRUE
66) Data modeling is about documenting rules and policies of an organization that govern data.
TRUE
67) The purpose of data modeling is to document business rules about processes.
FALSE
68) In an E-R diagram, strong entities are represented by double-walled rectangles.
FALSE
69) In an E-R diagram, an associative entity is represented by a rounded rectangle.
TRUE
70) Data names do not have to be unique
FALSE
71) The relationship between a weak entity type and its owner is an identifying relationship.
TRUE
72) An entity type on which a strong entity is dependent is called a covariant entity.
FALSE
73) An entity type name should always be a singular noun.
TRUE
74) The name used for an entity type should never be the same in other E-R diagrams on which the entity appears
FALSE
75) Some examples of attributes are: eye_color, weight, student_id, STUDENT.
FALSE
76) A simple attribute can be broken down into smaller pieces.
FALSE
77) An attribute whose values can be calculated from related attribute values is called a derived attribute.
TRUE
78) A multivalued attribute may take on more than one value for a particular entity instance.
TRUE
79) Relationships represent action being taken using a verb phrase
TRUE
80) Participation in a relationship may be optional or mandatory.
TRUE
81) A ternary relationship is equivalent to three binary relationships.
FALSE
82) The degree of a relationship is the number of attributes that are associated with it.
FALSE
83) The relationship between the instances of two entity types is called a binary relationship.
TRUE
84) The relationship among the instances of three entity types is called a unary relationship.
FALSE
85) It is desirable that no two attributes across all entity types have the same name.
TRUE
86) It is not permissible to associate attributes with relationships.
FALSE
87) A relationship instance is an association between entity instances where each relationship
instance includes exactly one entity from each participating entity type.
FALSE
88) One reason to use an associative entity is if the associative entity has one or more attributes in addition to the identifier.
TRUE
89) In the figure below, the name of the relationship follows the guidelines for naming a relationship.
FALSE
90) A cardinality constraint tells what kinds of properties are associated with an entity.
FALSE
91) The maximum criminality of a relationship is the maximum number of instances of entity B that may be associated with each instance of entity A.
FALSE
92) In the figure shown below, a person has to be married.
FALSE
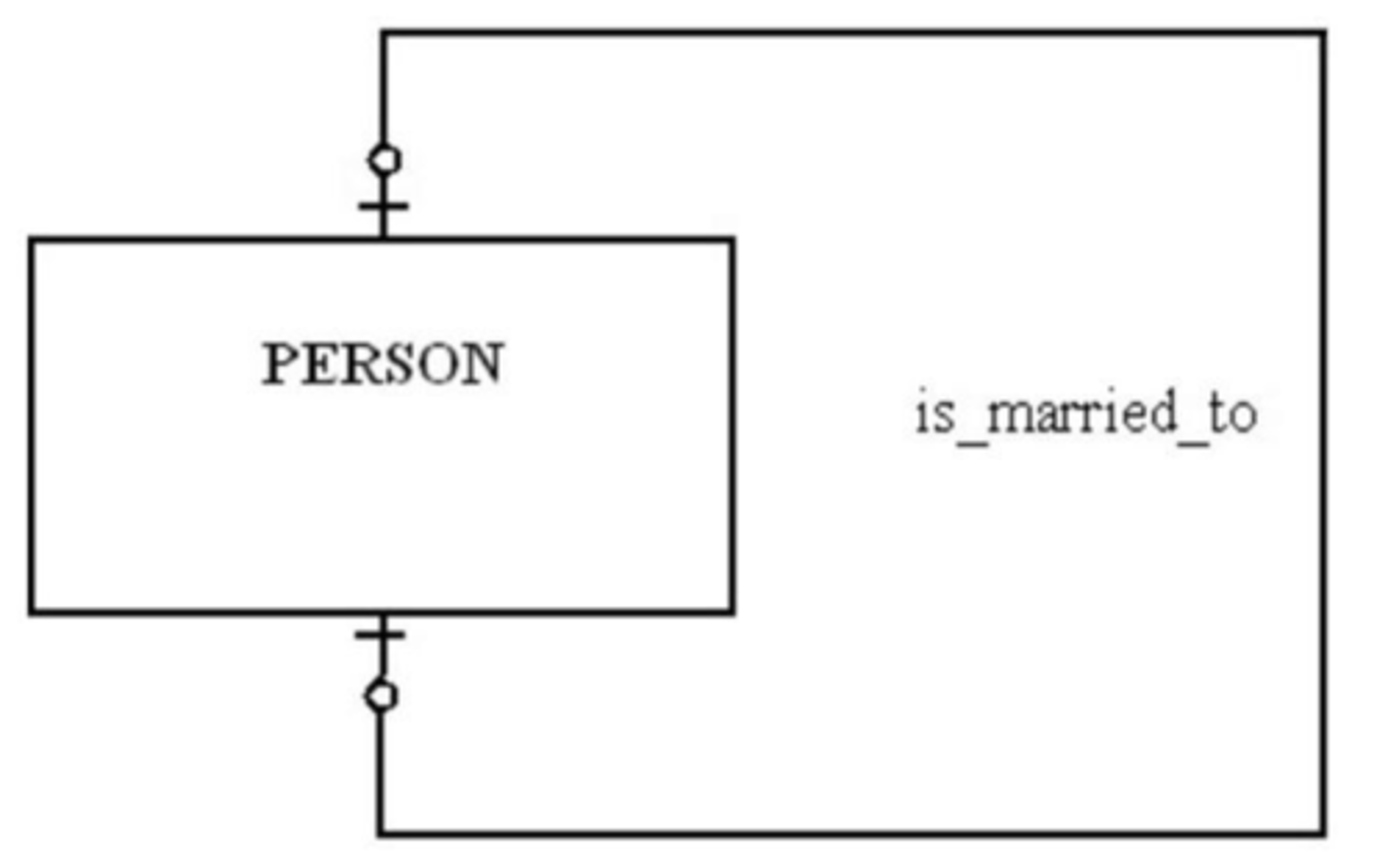
93) For the relationship represented in the figure below, a department can have more than one employee.
TRUE
94) A customer can order many items, and an item can be ordered by many customers is an example of a recursive relationship.
FALSE
95) A time stamp is a time value that is associated with a data value.
TRUE