Conformational Analysis and Thermodynamics of Cycloalkanes and Reactions
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What happens to a cup of coffee as it cools?
It reaches room temperature.
What is the system in the reaction of baking soda and vinegar?
The system is the reaction of NaHCO3 and HC2H3O2.
What is the surroundings in the reaction of baking soda and vinegar?
Everything else outside the reaction.
What is the sign of q for the baking soda and vinegar reaction?
Positive (small).
What is the sign of w for the baking soda and vinegar reaction?
Negative (big).
What is the sign of DE for the baking soda and vinegar reaction?
Negative.
What is the value of DErxn for a reaction that does 255 J of work and absorbs 642 J of heat?
+387 J.
What is the value of DErxn for a reaction that does 350 J of work and releases 230 cal of heat?
-1310 J.
What is the change in enthalpy (DHrxn) for the gas-phase reaction involving C2H2 and HF?
-174 kJ/mol.
What does a negative DHrxn indicate about a reaction?
The reaction is exothermic and enthalpically favored.
How does the carbon-carbon bond length change during the reaction of C2H2?
It increases.
What is the estimated DHrxn for the reaction of diazomethane to form ethene and nitrogen gas?
-422 kJ/mol.
What is the thermodynamic favorability of an endothermic reaction with a positive ∆S?
It is favored at higher temperatures.
What is the thermodynamic favorability of the reaction 2 N2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2 N2O(g)?
It is favored only at higher temperatures.
What are the signs for DGrxn, DHrxn, and DSrxn for a reaction with more product molecules?
DGrxn = Negative, DSrxn = Negative, DHrxn = Negative.
At what temperatures is the reaction thermodynamically favored if it is enthalpically favored and entropically unfavored?
At temperatures of 25 °C and lower.
What is the DGrxn for the reaction I2(g) + H2(g) → 2 HI(g) at 25 °C?
3.4 kJ/mol.
What is the DGrxn for the breakdown of ozone (O3) at -3 °C?
248.1 kJ/mol.
What bond angles are typical for alkanes?
120°, 108°, 90°, 60°
What causes angle strain in cycloalkanes?
Deviations from ideal bond angles.
What causes torsional strain in cycloalkanes?
Eclipsing interactions in molecules.
Which cycloalkane is the least stable?
Cyclopropane
Which cycloalkane is the most stable?
Cyclohexane
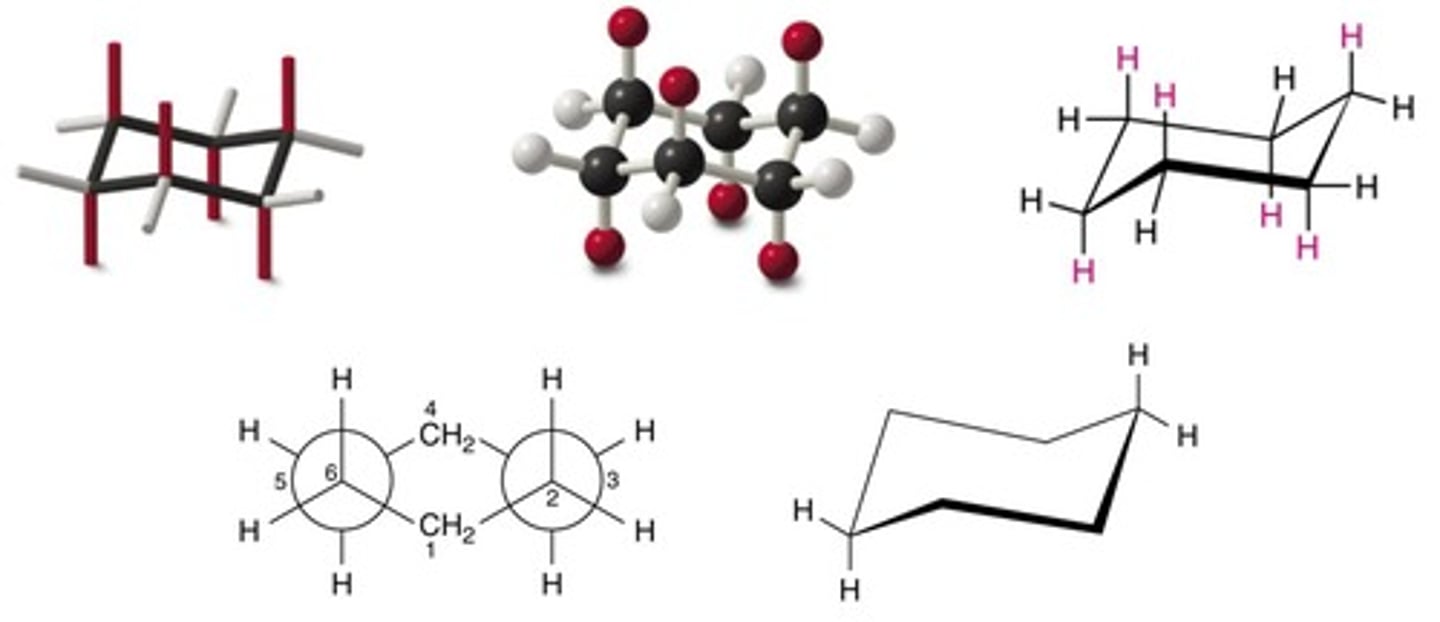
What are the two main conformations of cyclohexane?
Chair and Boat.
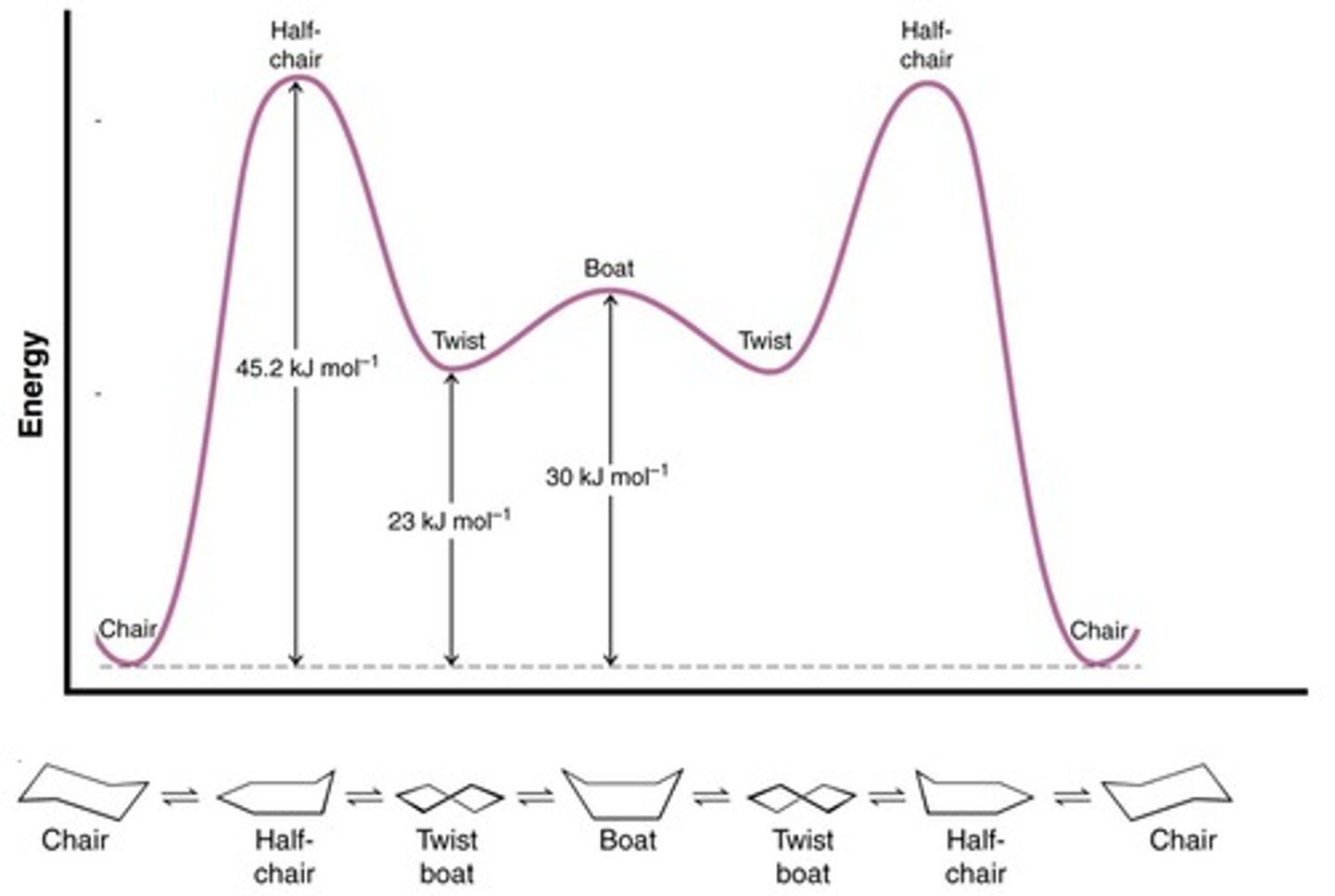
What is the highest energy conformation of cyclohexane?
Half Chair.
What type of strain is associated with all staggered conformations?
Torsional strain.
What interactions are involved in cyclohexane's chair conformation?
1,3-Diaxial interactions.
What defines an axial bond in cyclohexane?
A bond that extends perpendicular from the ring.
What defines an equatorial bond in cyclohexane?
A bond that extends parallel from the ring.
What is the preferred position for a methyl group in methylcyclohexane?
Equatorial position.
What percentage of methylcyclohexane adopts the lower energy conformation?
95%.
What is the A-value for chloro in 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane?
1.8 kJ/mol.
What is the A-value for methyl in 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane?
7.1 kJ/mol.
What is the Gibbs Free Energy equation for conformational exchange?
DGconformational = -RT ln K.
What is the A-value for phenyl in conformational analysis?
13 kJ/mol.
What is the A-value for amine in conformational analysis?
6.7 kJ/mol.
What is the A-value for hydroxyl in conformational analysis?
3.6 kJ/mol.
What is the A-value for fluoro in conformational analysis?
0.63 kJ/mol.
What are cis groups in cycloalkanes?
Groups on the same side of a molecule.
What are trans groups in cycloalkanes?
Groups on opposite sides of a molecule.
What is the energetically favored conformation for cis-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane?
The two conformations are equally favored.