9- Speech & Language
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Speech
physical ability to produce sounds
Language
system of communication using words and symbols
Phonology
Sound structure
Syntax
Rules system or grammar
Morphology
Smallest units with meaning
Semantics
Meaning or context
Pragmatics
Appropriate use of language
Language is:
-complex system of symbols and rule used for communication
-speaking and understanding (oral), reading and writing, sign language
Speech is:
Pronunciation, fluency, voice, primary mode of expressing language
Communication can be verbal and nonverbal, what are the components of each?
Verbal: linguistic
Nonverbal: paralinguistic, nonlinguistic
Nonverbal communication:
Paraliguistics include:
Pitch, loudness, pause, quality, rate, tone
Nonverbal communication:
Nonliguistics include:
Body language, kinetics, proxemics, haptics, oculesis, posture
What is required for speech production?
Respiration
Phonation: pushing air through vocal chords
Articulation
Resonation
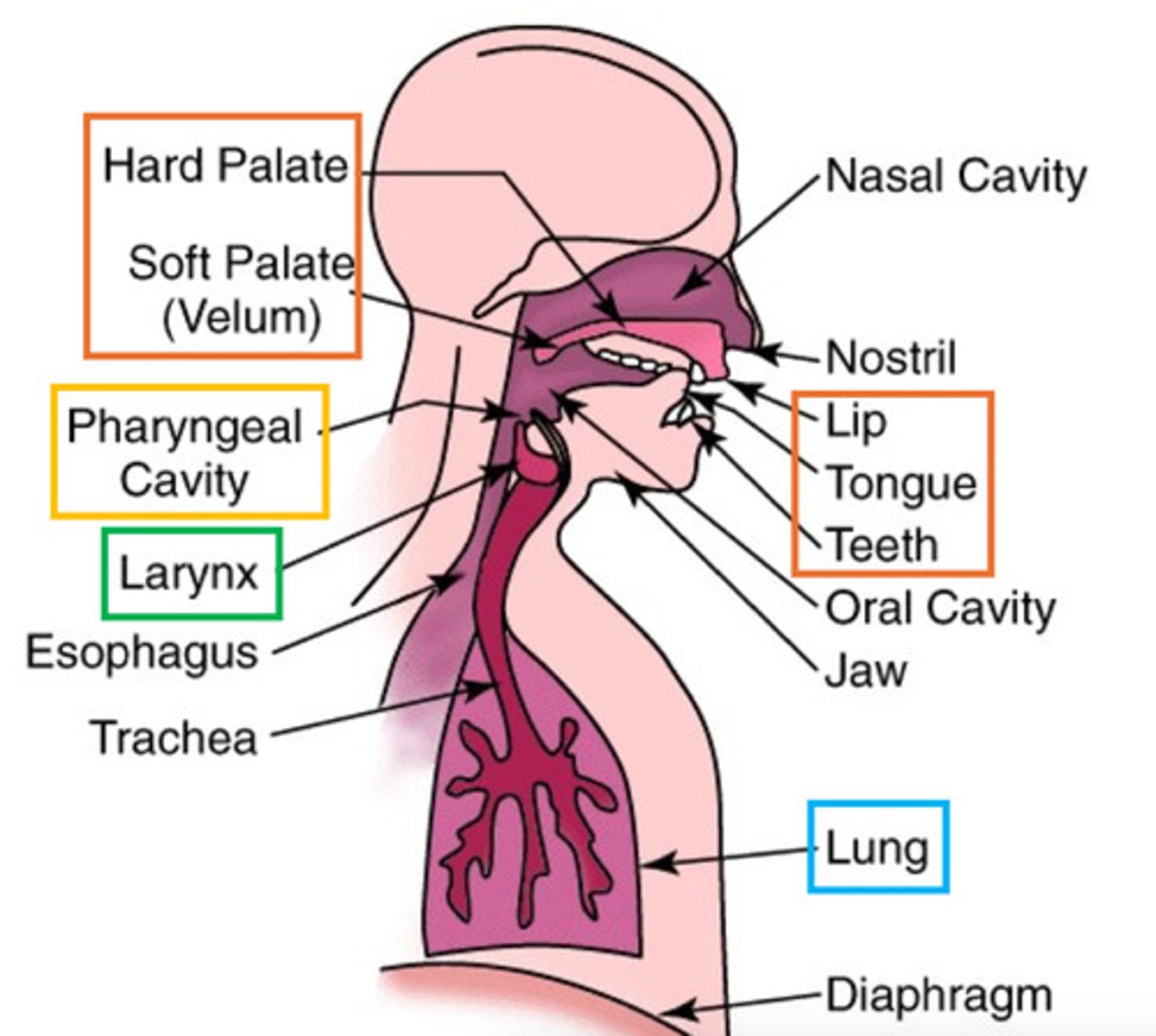
What is the role of the respiratory system/the function of lungs in speech?
-Air supply: provides airflow for sound production (vocal folds in larynx vibrate)
-Breath control: regulates airflow to control volume and pitch (changes in airflow modalities pitch and lowness of the voice)
Vocal cords addition function
To prevent aspiration of fluid into the lungs
What structure is the primary articulator?
Tongue
What are the key structures for sound production?
- Larynx: voice box that houses the vocal folds
- Vocal folds: muscular structures that vibrate to produce sound
What 2 things are important for sound production?
- Airflow: air from lungs pass through trachea into larynx
- Vocal fold vibration: air pressure causes vocal folds to rapidly open/close, creating sound waves
What 2 types of control are used for the modulation of sound?
- Pitch control: adjust tension and length of vocal folds to alter pitch
- Volume control: increased airflow = louder sounds
What is Resonance?
Sound waves in vocal tract
What is Articulation?
Movement of the tongue, lips, and soft palate shapes sound into recognizable speech
key structures of the articulatory system
-Tongue: Primary articulator
-Lips: bilabial sounds ("p", "b")
-Teeth: dental sounds ("t", "d")
-Palate: Hard and soft palate create different sounds
-Jaw: Adjusts position of mouth for various sounds
Consonant is a type of sound produced with ___________
obstructed airflow
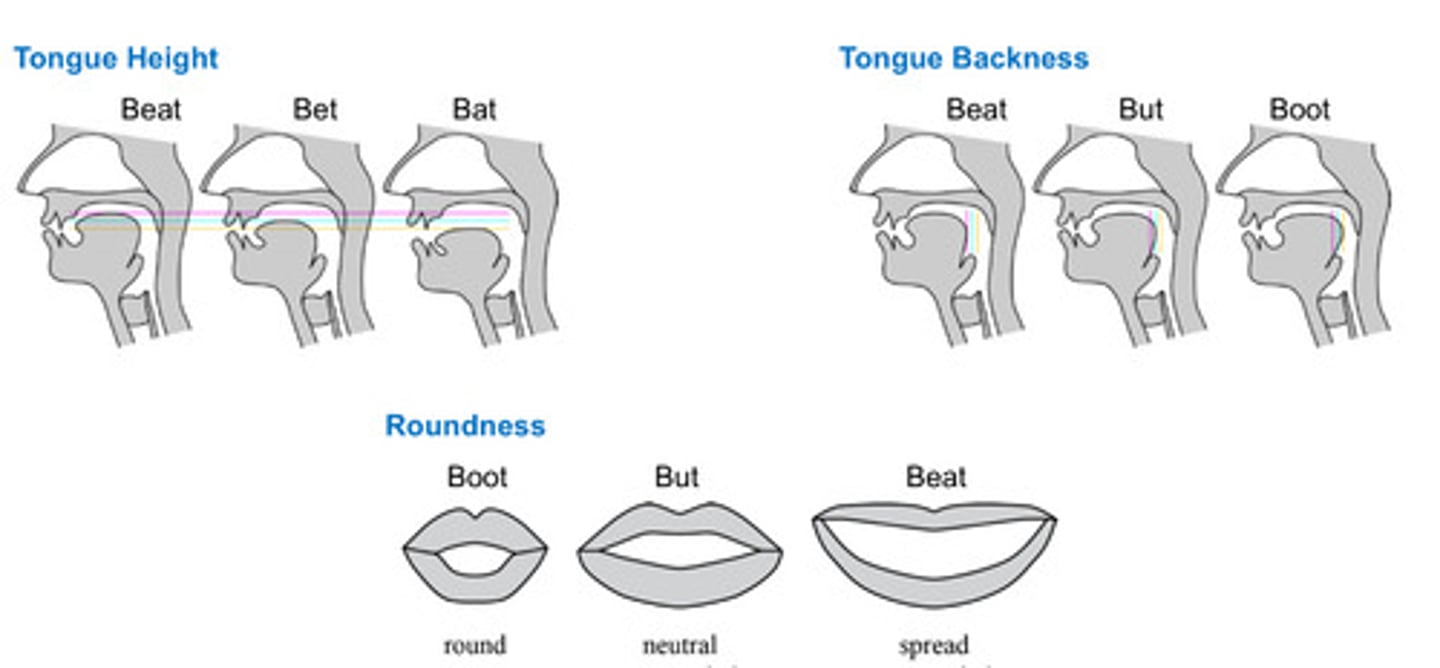
Vowels produced with _____________, shaped by _____________
open airflow, position of the tongue and lips
Vowels produced are influenced by ___________
tongue height, tongue backness, and mouth roundness
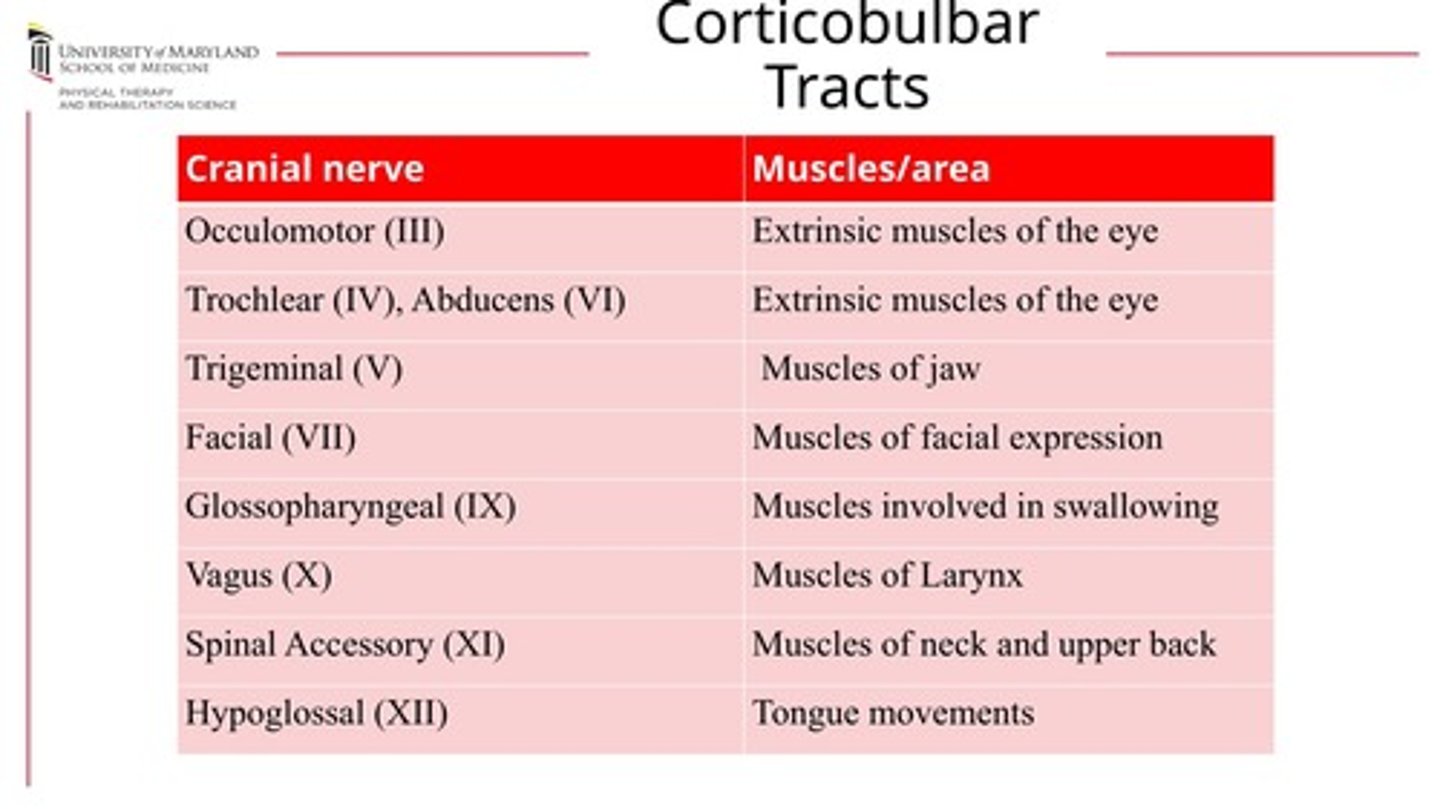
Corticobulbar tract controls?
- motor control of muscles for SPEECH!
- movement of face, neck, tongue, and parts of the extraocular eye muscles
- skilled voluntary movement of muscles related to the execution of speech
- 3,4,5,6,7,9,10,11,12 all in corticobulbar tract but not all control speech
Explain the path of the corticobulbar tract
Descends through internal capsule going to midbrain, pons, and medulla where it projects ipsilaterally and contralaterally (lateral aspect of temporal lobe)
What artery is controlling info of the neck, brow, eyelid, nose, lips, tongue, larynx?
MCA
What CN are involved in speech?
CN 5, 7, 9, 10, 12 *double check!
Corticobulbar tracts: CN and the muscle it innervates
The left hemisphere of the brain mediates:
Language functions, analytical, logical (dominant language hemisphere)
The right hemisphere of the brain mediates:
Perceptual, prosodic, pragmatic, spatial functions
The two hemispheres work together in complementary manner. T/F?
True
In most people, language is processed in the _______ hemisphere (dominant) but dominant hemisphere depends on ____________
left, handedness
A person who is right handed is language function dominant in what hemisphere?
Left
A person who is left handed has dominant language function in what hemisphere?
Some in right & left
What are important areas in the Left hemisphere?
Broca’s (in frontal lobe)
Wernicke’s (in temporal parietal area)
Heshl’s gyrus
Angular gyrus
Arcuate fasciculus
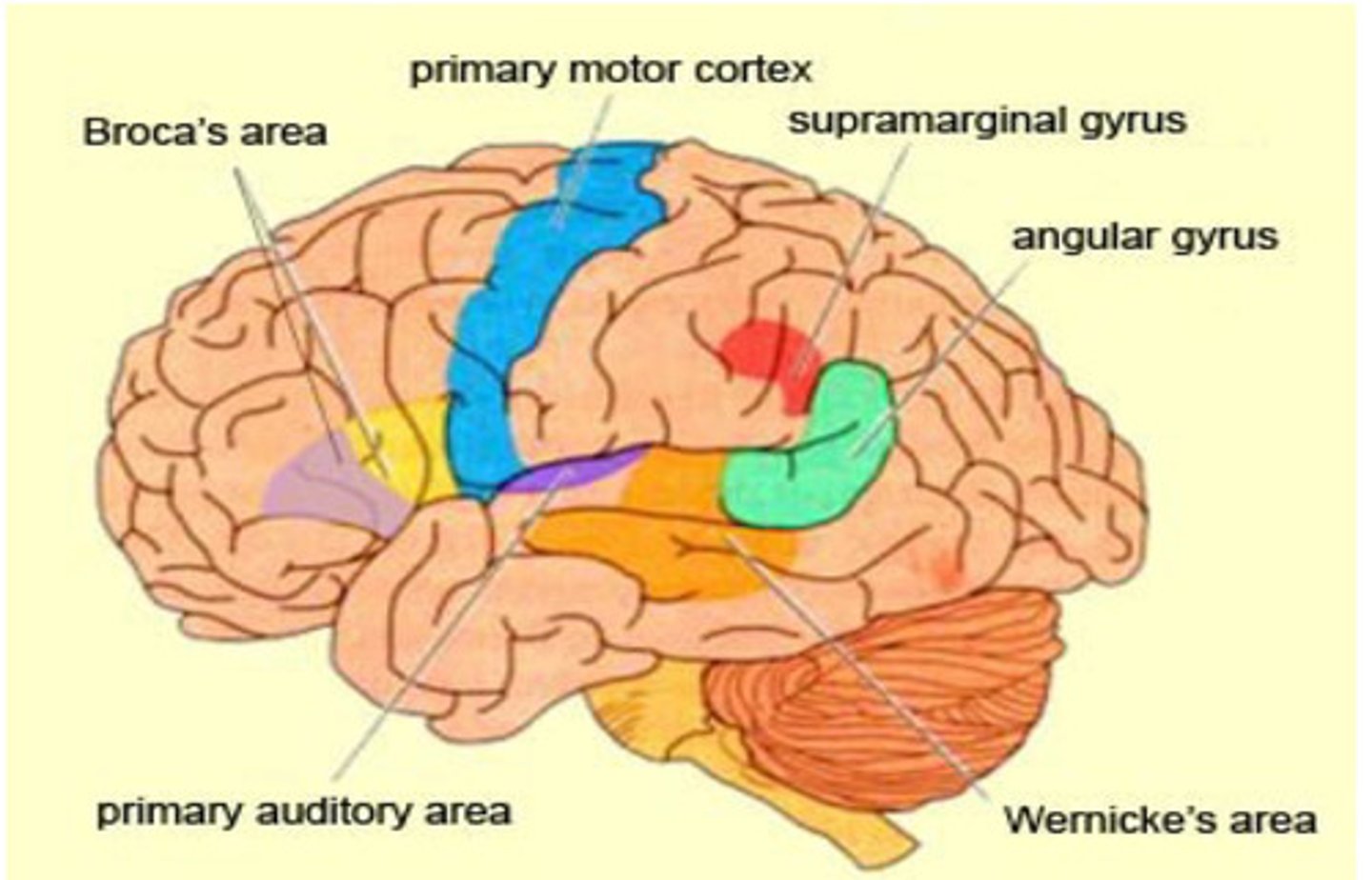
Broca's area is responsible for:
Speech production and language processing, grammar and sentence structure
Wernicke’s area is responsible for:
Language comprehension; processes the meaning of words and sentences
Heshl's gyrus (superior temporal gyrus) is responsible for:
Processing auditory info, including spoken language sounds
Angular gyrus (area between Wernicke’s and parietal) is responsible for:
Integrates sensory info and plays a role in reading and writing
Arcuate fasciculus (white matter pathway of axons from Wernickes area to brocas) is responsible for:
bundle of nerve fibers connecting Broca's and Wernicke’s areas, essential for repeating heard speech
Neurogenic communication disorders are cause by:
Damage to the CNS and PNS
Most often caused by CVAs (strokes), tumors, TBI, infectious diseases
Blood supply
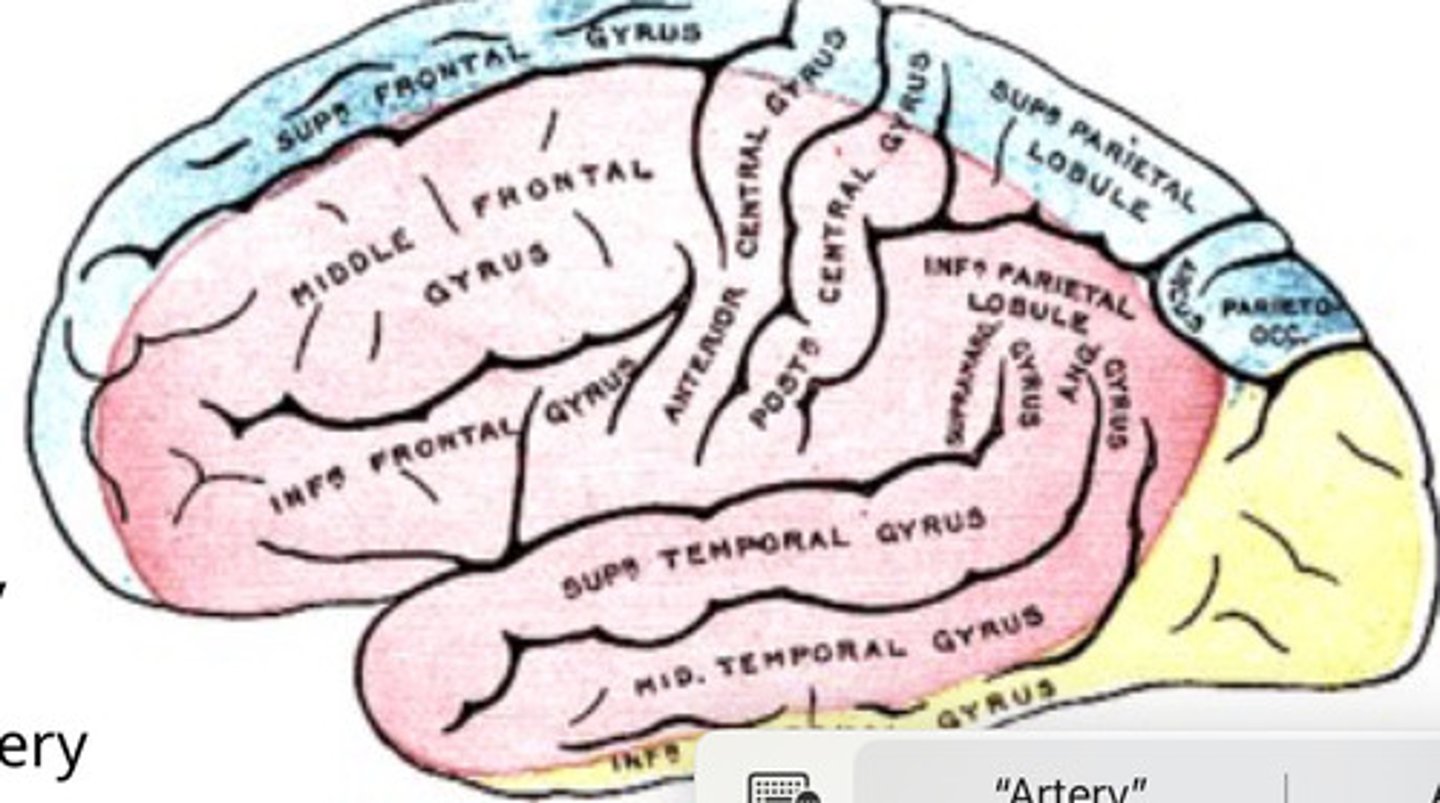
Blue = Anterior Cerebral Artery
Pink = Middle Cerebral Artery
Yellow = Posterior Cerebral Artery

What are examples of neurogenic communication disorders?
Aphasia/Dysphagia, Apraxia, Right Hemisphere Disorder, Dysarthria
Aphasia/Dysphasia
Loss or impairment of language function caused by brain damage (language content, comprehension, reading and writing)
Fluent
Receptive aphasias (ex. Wernicke’s)
Non-fluent
Expressive aphasias (ex. Broca’s)
What are the components of Broca's Aphasia?
•Non-fluent speech
•Agrammatism, Telegraphic, Effortful speech
•Phenomic paraphasias
•Some degree of comprehension deficit
•Agraphia with/without alexia
• Writing and possible reading deficits
•Repetition abnormal - drops function words
•Buccofacial apraxia, right hemiparesis
Semantic paraphasias examples
Fork/knife
Brush/comb
Phonemic paraphasias examples
Nuzzle/muzzle
Prograther/protractor
What are the components of Wernickes aphasia?
•Fluent, nonsensical speech
•Impaired comprehension
•Phonemic and semantic paraphasias
•Incapable of monitoring own output
•Grammar better preserved than in Broca's Aphasia
•Alexia without agraphia: reading impairment often present; writing is legible - letters formed (rarely have a concomitant
hemiplegia), but disjointed, repetitive text, few nouns and
verbs
•May be aware or unaware of deficit
•Repetition poor
What are the components of Global Aphasia?
•Deficits in repetition, naming, fluency and comprehension
•Gradations of severity exist
•May communicate prosodically
•Involve (typically) large lesions
•Outcome poorest
Dysarthria
impairment of the structures involved in speech production (tongue, throat, lips)
Aphasia and Speech Apraxia are a disorders of
Language
Dysarthria is a disorder of (the motor control) of
Speech (closely tied to swallowing function)
CNS disorders
- Aphasia: Wernicke's (receptive); Broca's (expressive); Global
- Cognitive/Linguistis (due to dementia or TBI; Problems with attention, memory, planning)
What are the key components of speech production?
Respiration, larynx and vocal folds (producing sounds), articulation, resonance
Describe the role of 2 key brain regions in speech and language
Broca’s: expressive nonfluent aphasia
Wernicke’s: receptive fluent aphasia
What is the difference between speech and language?
Speech: ability to produce the sounds
Language: involves symbols and rules
Peripheral disorders
Dysphagia, Tracheostomies, Voice disorders, Cranial Nerves (Muscles of jaw, face & tongue, pharynx), Dysarthria
What is the role of a PT in individuals with speech and language disorders?
- Slower and more deliberate speech when providing patient education
- Allow processing time (when taking history, switching tasks)
- Reduce background noise and interference
- Reduce dual tasking
- Don't assume speech disorder = cognitive disorder