genetics unit 1
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
when did genetics start
8000-`1000 BC with domestication of horses camels, wolves, maize, wheat, rice etc
hippocratic school of medicine and Aristotle tried to explain heredity using the concept of
active humors and vital heat
in the 1600s William Harvey gave what theory
epigenesis
an organism develops from fertilized egg
contrasts with preformation, fertilized egg contains mini adult called a homunculus
cell theory
scheiden and Schwann
proposed that all living organisms are composed of cells and that the cell is the basic unit of life. This theory laid the foundation for modern biology.
natural selection is the driving force for
adaptation
existing species arise from ancestral species by
descent with modification.
the theory of evolution by natural selection was independently was also proposed by
Alfred Russel Wallace.
what did Darwin and Wallace not understand
mode of inheritance
gregor Mendel offered an explanation of inheritance by using
peas
the chromosomal theory of inheritance
sutton and boveri
states that inherited traits are controlled by genes residing on chromosomes
noticed that behavior of chromosomes during meiosis was identical to behavior of genes during gamete formation
_______ explains how genetic information is passed onto the next generation
The theory of inheritance
Avery Macleod and McCarty showed
that dna carried genetic information in bacteria
Hershey and chase showed
that dna carried genetic information in bacteriophage
Watson and crick 1953
discovered the double helix structure of DNA, revealing how genetic information is stored.
dna is an antiparrale double stranded helix
nucleotide
four bases of adenine cytosine guanine and thymine
dna is made up of
sugar, nucleotide, phosphate
transcription
DNA to RNA
transcription occurs in the
nucleus
after transcription occurs in the nucleus
the mrna moves into the cytoplasm where it binds to a ribosome
when the mrna binds to the ribosome it is then turned into
a protein through translation.
what are the largest category of proteins
enzymes
once a protein is made its action or location in a cell plays a role in producing
phenotype
alternate forms of genes are called
alleles.
variation in alleles are the result of
mutations
a set of alleles for a given trait is called
genotype.
restriction enzymes discovered in bacteria that cut viral dna at specific sequences describes
recombinant technology
with the use of _____ restriction enzymes have allowed the advent of recombinant DNA and cloning
vectors
model organisms have what traits
easy to grow
short life cycle
many offspring
genetic analysis is straight forward
what allowed us to see eukaryotic cell structures
development of the transmission electron microscopy in the 1940s-60s
prokaryotic cells do not have
golgi, ER nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
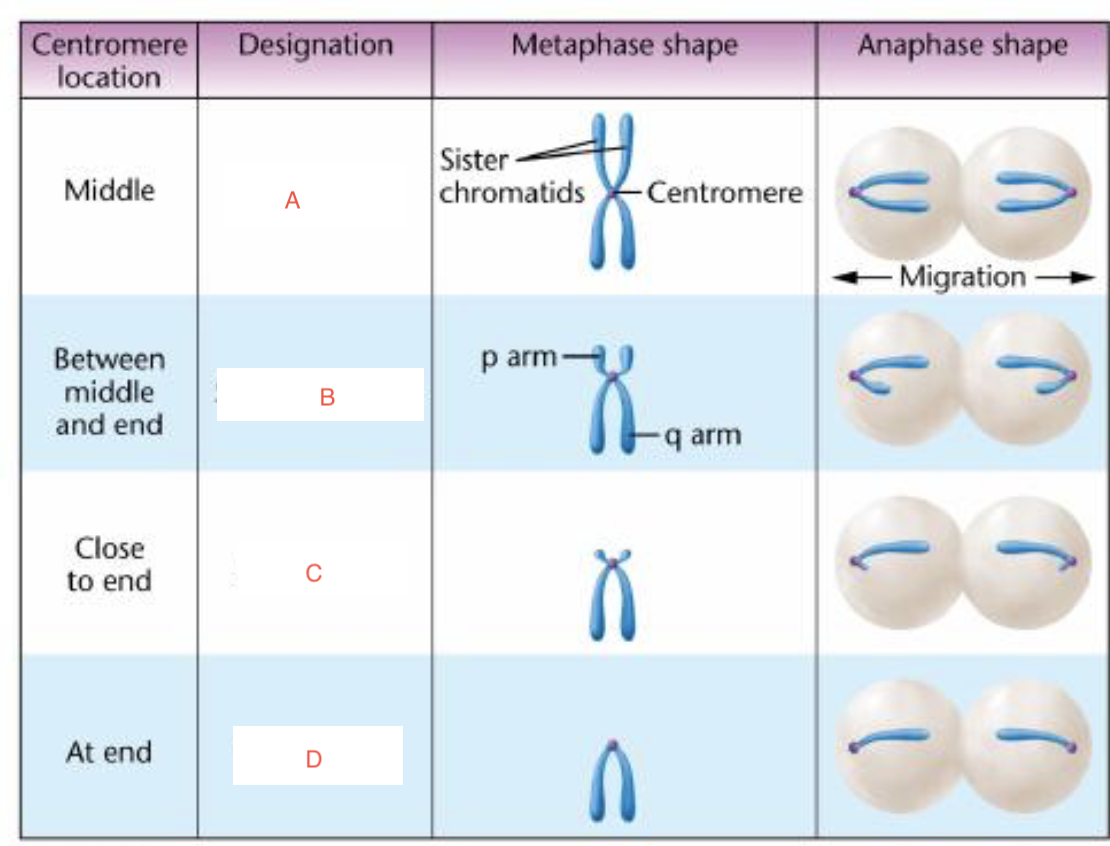
a= metacentric
b= submetacentric
c= acrocentric
d= telocentric
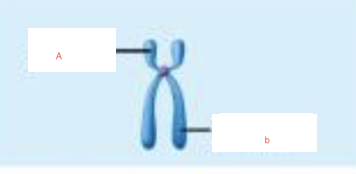
A=p arm
B=q arm
haploid numbers can
vary extensively
humans have how many autosome pairs
22
dogs have 39 chromosomes and what does this mean
not that their genome is bigger, just that they are split up in more fragments
homologous chromosomes
same size and their centromere is the same location
they code for the same genes, but they have different alleles
the basis for asexual reproduction in many single celled organisms
mitosis
the development of a zygote into an adult through mitosis is called
asexual reproduction
wound healing, blood and skin cell production and tumor development occurs through
mitosis
the typical human cell has a cell cycle that lasts
24 hours
the cell cycle process
G1 → S → G2 → M
G0 step
the non dividing phase, where cells can opt out of the cell cycle either permanently or temporarily
interphase includes
S phase
two gap phases (G1 and G2)
G0 withdrawal from the cycle
G1
cell growth
metabolic activity
cell differentiation
no DNA replication
S phase
cell growth
metabolic activity
cell differentiation
DNA replication
G2 phase
cell growrth
metabolic activity
cell differentiation
no DNA replication
when do cells enter G0 or commit to entering the S and completing another cell cycle
in late G1
______ cells are characterized by uncontrolled cell division, they apparently never enter G0 or they pass through it very quickly
Cancer
chromosomes are extended and uncoiled forming chromatin
interphase
chromosomes coil up and condense; centroioles divide and move apart
prophase
chromosomes are clearly double structures; centrioles reach the opposite poles; spindle fibers form
pro metaphase
chromosomes align on metaphase plate
metaphase
centromeres split and daughter chromosomes migrate to opposite poles
anaphase
daughter chromosomes arrive at the poles; cytokinesis commences
telophase
factors of prophase
migration of centrioles to establish poles
break-down of nuclear envelope
disintegration of nucleolus
chromosome condensation
migration of chromosomes to metaphase plate happens during
prometaphase and metaphase
movement of chromosomes happens in _____ where completion of movement happens in
prometaphase metaphase
which phase do sister chromatids separate and migrate to opposite ends of the cell and requires kinetochore and spindle fiber attachment
anaphase
telophase factors
cytokinesis
chromosomes begin to uncoil
nuclear envelope reforms
single fibers disappear
nucleolus reforms
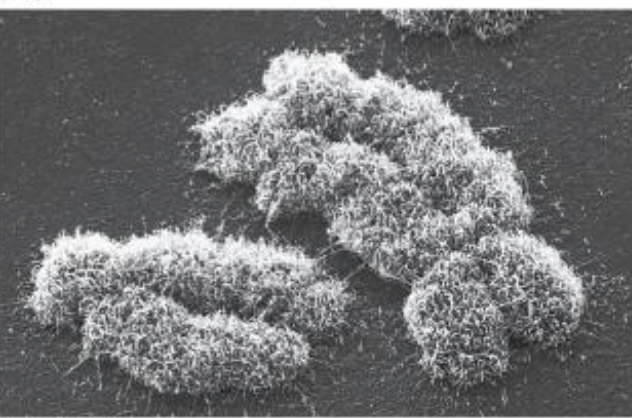
chromosome
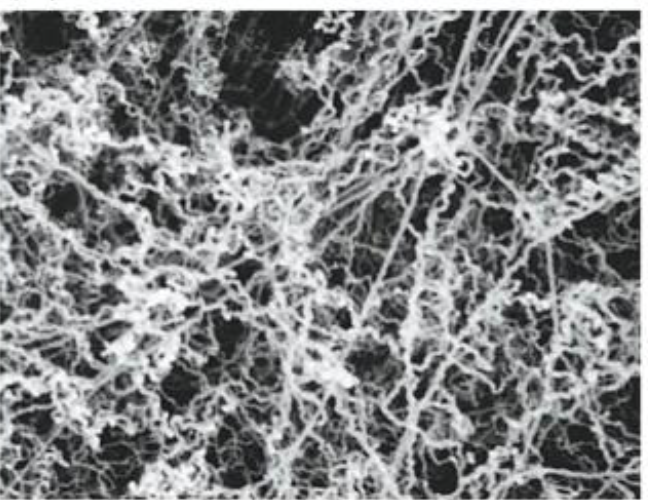
chromatin
folded fiber model
two sister chromatids joined at centromere
each chromatid is a single fiber wound like a skein of yarn
fiber is tightly coiled DNA and protein
5000x compaction in the length of the DNA during transition from interphase to prophase
_____ produces two daughter cells that are genetically identical to their parent cell
Mitosis
_____ produces four gametes or spores with only a haploid set of chromosomes
Meiosis
______ is highly specific because each gamete must contain precisely one member of each homologous pair of chromosomes
Meiosis
when do two gametes fuse to reconstitute a diploid complement of chromosomes
during sexual reproduction
the two features of meiosis generating variation
segregation and independent assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes during Meiosis I
crossing over or genetic exchange between members of a homologous pair
meiosis consists of how many rounds of duplication and how many rounds of cell division resulting in haploid cells
one round of cell duplication and two rounds of cell division
meiosis reduces the amount of genetic material by one half to produce haploid gametes or spores containing one member of each _____ of chromosomes
homologous pair
what restores the diploid number in meiosis
fertilization
how does meiosis maintain genetic continuity from generation to generation and gives rise to genetic variation in gametes
crossing over
unique combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes
when do sister chromatids separate
anaphase II
In humans, what is a fundamental difference between the production of female gametes and male gametes?
During the production of female gametes, one daughter cell contains most of the cytoplasm, and two or more polar bodies contain only a small amount of cytoplasm.
What is the significance of the formation of polar bodies?
Polar bodies allow for the unequal distribution of cytoplasm during oogenesis, ensuring that the ovum has sufficient resources for early development.
meiosis begins with
diploid cell - dna duplicated during interphase, chromosomes made up of sister chromatids
prophase I is a process similar to mitotic prophase, except that
homologous chromsomes pair up (synapsis)
______ gives rise to a tetrad with overlapping of non sister chromatids
synapsis (prophase I)
tetrad
two pairs of sister chromatids
during prophase I there is an exchange of genetic material through
recombination
what happens in prophase I
nuclear envelope and nucleolus break down
two centromeres of the tetrad attach to the spindle fibers
what happens in metaphase I
chromosomes have maximally shortened and thickened
chiasmata are visible and holding sister chromatids together
alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate is random; half of each tetrad is pulled randomly to opposite poles…. which phase is this?
Anaphase I
what is marked with the reappearance of the nuclear membrane and a short interphase?
telophase I
chromosomes do not replicate because they already consist of sister chromatids…. which process is this?
meiosis I
what is the ploidy of cells in meiosis I at the end
haploid
prophase II
chromosomes are composed of one pair of sister chromatids attached by a common centromere
metaphase II
centromere is positioned at the metaphase plate
anaphase II
centromeres divide; sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles
telophase II
similar to mitotic telophase
cytokinesis results in four haploid gametes with equal cytoplasm containing combination of maternal and paternal genes
male vs female gamete production
spermatogenesis and oogenesis
in spermatogenesis an undifferentiated germ cell called ______ enlarges to become a primary spermatocyte
spermatogonium
in spermatogenesis the primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I to produce ________
HAPLOID secondary spermatocytes
secondary spermatocytes under go meiosis II to produce ________ that undergo a series of developmental changes, ______ to become highly specialized, motile spermatozoa or sperm
four haploid spermatids; spermiogenesis
an undifferentiated germ cell called an _____ enlarges to become a primary oocyte
oogonium
meiosis I of oogenesis results in
one haploid secondary oocyte and one polar body
polar body
the cell with little or almost no cytoplasm and will disintegrate
the secondary oocyte undergoes meiosis II to produce
two haploid cells: an ootid with bulk of cytoplasm and a second polar body
polar bodies
first may or may not divide - eventually all disintegrate with only one functional cell remaining
meiosis II is completed only after
fertilization