Chemistry - Basics of Chemistry Test #2
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
definite shape and definite volume
solid
indefinite shape (takes shape of its container) and definite volume
liquid
indefinite shape and indefinite volume( takes shape of its container/ fills container)
gas
matter made of any one type of atom ( pure gold, sulfur, oxygen)
element
matter made up of more than 1 element in a fixed ratio
compound
a mixture that has a consistent composition - solution always the same
homogenous
milk, salt water ,
expls of homogeneous
a mixture with distinct phases - different
heterogenous
oil & vinegar, orange juice, cornstarch & water
expls of heterogenous
Matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction; it can only change forms. The total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products.
law of conservation matter
A chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same fixed ratio by mass, no matter the source or amount.
law of definite proportions
Dalton used these laws to propose that matter is made of indivisible atoms:
The Law of Conservation of Matter suggested atoms are not created or destroyed in reactions.
The Law of Definite Proportions suggested compounds are made of atoms combined in fixed ratios.
How laws contributed to daltons atom theory
All matter is made of tiny atoms.
Atoms of the same element are identical.
Atoms cannot be created or destroyed.
Atoms combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
Chemical reactions rearrange atoms but do not change them
daltons atomic theory
Modern Atomic Theory shows that atoms are divisible into subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons
How Modern Atomic Theory changed the idea that atoms are indivisible
Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons, forming isotopes, so they are not always identical in mass
How Modern Atomic Theory changed the idea that all atoms of the same element are identical
Matter is made of atoms.
Atoms combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
Chemical reactions rearrange atoms rather than creating or destroying them.
parts of daltons theory that are still correct
3 element articles of an atom
protons,neutrons,electrons
Where is the proton located in an atom
nucleus
Where is the neutron located in an atom
nucleus
What is the charge and relative mass of a neutron
charge: 0 (neutral) mass: ~1 amu
What is the charge and relative mass of a proton
charge: +1 Mass: ~1 atomic mass unit (amu)
Where is the electron located in an atom
electron cloud
What is the charge and relative mass of an electron
charge: -1 ,mass: ~1/1836 of an amu
What is the atomic number, and what does it tell you?
The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom. In a neutral atom, it also equals the number of electrons
How do you find the number of neutrons in an atom
Neutrons = Mass number – Atomic number
In hyphen notation, how is an isotope written
[Element name]-[Mass number], e.g., Carbon-14.
In nuclide notation, how is an isotope written
mass number/ atomic number number element symbol

How do you determine the number of electrons in an ion
For a positive ion (cation), electrons = protons – charge.
For a negative ion (anion), electrons = protons + charge
atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, giving them different mass numbers.
isotope
How are isotopes represented in nuclide notation
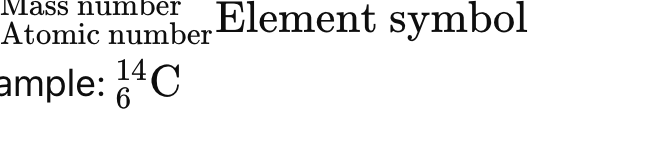
weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes, based on their relative abundances
average atomic mass of an element
how do you calculate average atomic mass

a unit that represents 6.022 × 10²³ particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) of a substance. This number is called Avogadro’s number
mole
What is the relationship between moles and number of particles (atoms/molecules)
number of particles=moles×6.022×10^23 (avogadro’s number)
What is the relationship between moles and mass
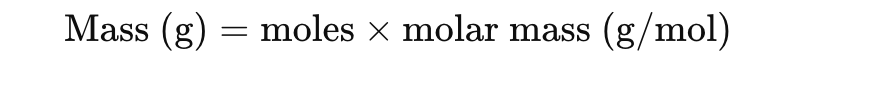
How do you find moles if you know the number of atoms or molecules?
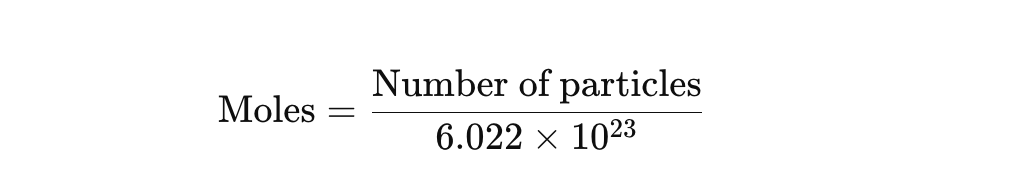
How do you find moles if you know the mass of a substance?
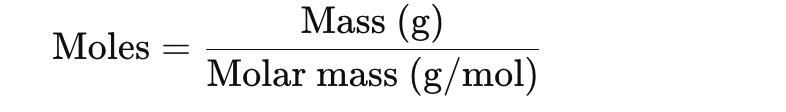
Color
Density
Melting point / Boiling point
Solubility
Hardness
physical properties used to determine substances
Reactivity with acids or bases
Flammability
Oxidation states
Ability to rust or corrode
chemical properties used to identify substances
characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing a substance identity
physical change
characteristics that can only be observed by changing a substance idenity
chemical change
properties that require measurement
quantitative
properties that can be observed without measurement
qualitative
shape, color, texture
qualitative
mass, volume, density
quantitative
flammability, rusting
exps of chemical change
mass, temp, volume
exps of physical change
smallest unit of matter that has its own unique properties
atom
a substance made of 2 or more atoms
molecules
types of molecules ex; water, sugar, salt
compounds
atom, molecule, compound
basic units of matter