Analytics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
the application of intelligent data analysis, data mining, and artificial intelligence techniques to analyse cybersecurity problems.
The entire Cyberspace Operating Environment.
The internet, considered as an imaginary, limitless area where people can meet and access any kind of information.
A global domain consisting of interdependent IT infrastructures and resident data, including the internet, telecom networks, computer systems, and embedded processors/controllers.
It enables new opportunities for e-commerce, wider outreach, more efficient business processes, and remote work (WFH).
It opens a new arena for crime such as online banking fraud, hacking, stalking, identity theft, and malware.
Social — collective and group interaction.
People — the actors.
Persona — narrative identity.
Information — the sources.
Network — connectivity infrastructure.
Real world — physical dimension of cyberspace.
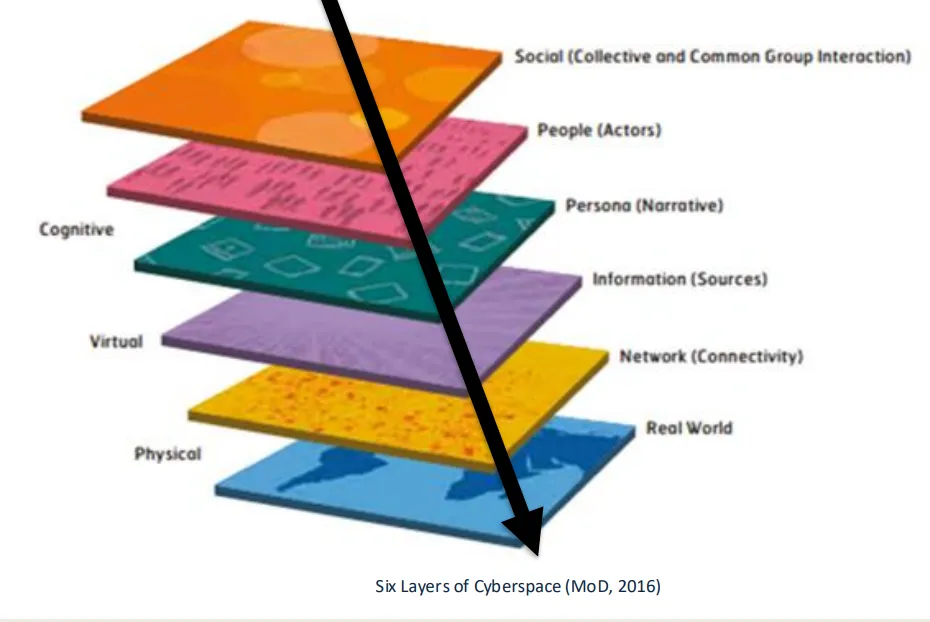
Cognitive
Virtual
Physical
what is the cognitive domain of cyberspace
represents the community, including social, people, and persona layers.
what is the virtual domain of cyberspace
includes software and virtual connections between networks and nodes.
what is the physical domain of cyberspace
the tangible, real-world infrastructure like cables, computers, and hardware.
Each layer and domain within cyberspace generates data that can be collected and analysed using cybersecurity analytics.
Optimisation.
Legal requirements.
Strategic value.
Prediction.
Situational awareness.
It provides insight into asset values, allowing better resource planning and improved efficiency—not just detecting attacks.
Organisations must comply with government regulations, using analytics for auditing, internal investigations, and law enforcement.
Analytics helps define and track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and supports strategic planning through informed risk management, aligning with Board Vision.
It allows organisations to anticipate future attacks based on past events, improving resilience and preparation.
mitigate in advanced
reduce the impact of costly attacks
identify vulnerabilities
It helps identify ongoing attacks and their targets, enabling better decision-making during specific situations.
intelligence
intrustion detection
current status
Network monitoring logs.
Host logs.
Physical logs.
Employee activity.
Suppliers.
Customers.
OSINT (Open Source Intelligence).
They show whether the network is operating securely and can reveal hints of cyberattacks.
firewall
access control
They contain records from machines and terminals that can reveal abnormal or suspicious activity.
logins
event and application data
antivirus
They provide data from physical security systems which can correlate with digital threats.
CCTV
swipe card access
biometrics
Employees may intentionally or unintentionally pose risks, and suspicious behaviour (e.g. on social media) can be an early indicator.
social media
External organisations may introduce vulnerabilities that need to be monitored.
supply chain agreements
Customers can unknowingly interact with malicious content or introduce security risks through compromised accounts.
social media
reviews
Open Source Intelligence like the MITRE ATT&CK framework, which helps compare internal data against known threat patterns.
media
law enforcements
regulators
academic publications
Network architecture
Network scans.
Firewall logs.
IDS logs.
PCAP.
Server/system logs. - Geographical data. - Social media.
Know the analysis techniques.
Understand the data type.
Manage data practicalities.
Prepare for uncertainties.
live or historic analysis
diagnostic or predictive
the focus of the analytical approach
Data quality and reliability.
Granularity.
Whether the dataset is big or small.
Pre-processing the data (e.g., Feature Selection).
Data storage.
Data protection.