4. Competitive and Concentrated Markets (AS)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Last updated 6:42 PM on 4/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
Duopoly
two firms take the majority of the demand *e.g. Pepsi and Cola*
2
New cards
Oligopoly
the existence of a few dominant firms, each market power and seeks to protect and improves its position over time
3
New cards
Working Monopoly
a firm with greater than 25% of total sales
4
New cards
3 things that are used to distinguish between different market structures
1. The number of firms
2. The degree of product differentiation
3. Ease of entry into market
5
New cards
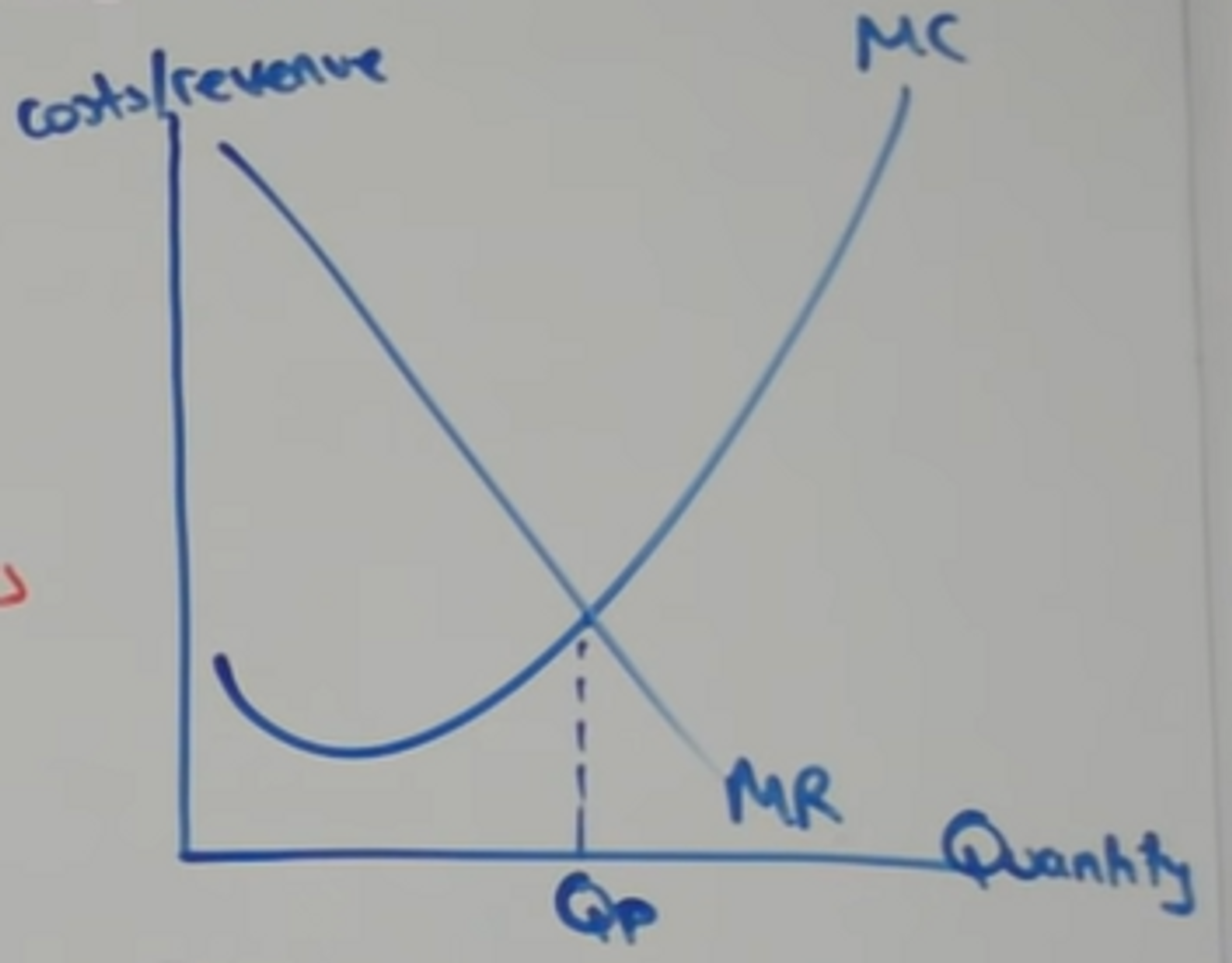
Explain why MC=MR is profit max
MR>MR, profits rise as output increases
MR
MR
6
New cards
Sales Maximisation
AC=AR
7
New cards
Dynamic Efficiency
Improving efficiency in the long run i.e re-investing in the economy
8
New cards
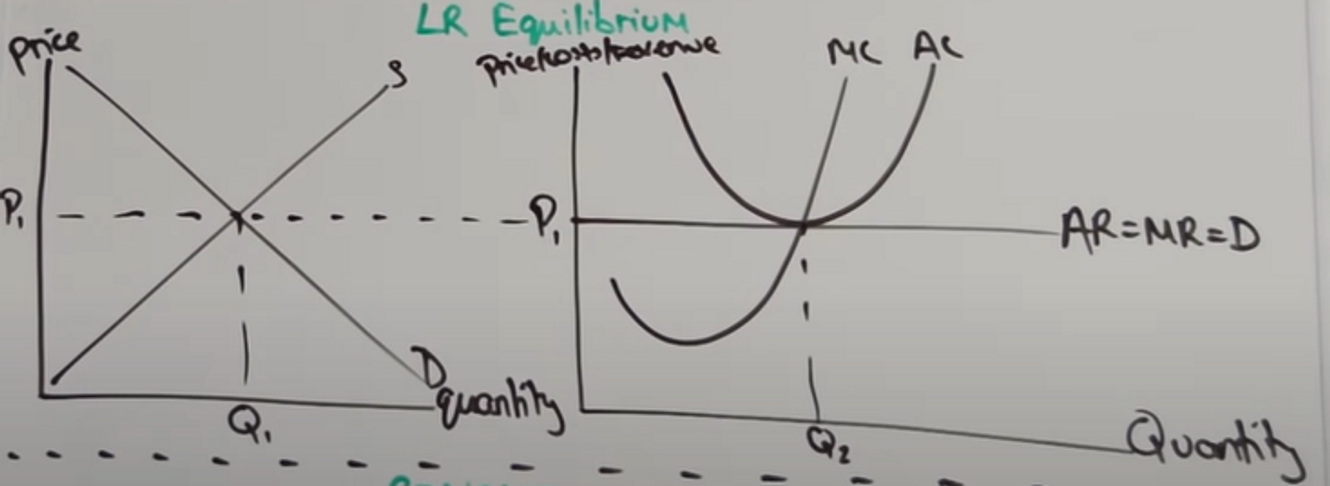
Draw graphs for a perfect competition
9
New cards
Explain concentration ratios
The collective market share of the largest firms in an industry
n (number firms we are working out the concentration ration)
n : total market share
***A:25%, B:10%, C15%, D20% 4:70***
**Don’t add up ‘others’**
n (number firms we are working out the concentration ration)
n : total market share
***A:25%, B:10%, C15%, D20% 4:70***
**Don’t add up ‘others’**
10
New cards
legal Monopoly
25% market share or more
11
New cards
Conditions for monopolistic market
* Price makers
* high barriers to entry
* advertising and product differentiation
* Few competitors
* profit maximiser
* imperfect information
* high barriers to entry
* advertising and product differentiation
* Few competitors
* profit maximiser
* imperfect information
12
New cards
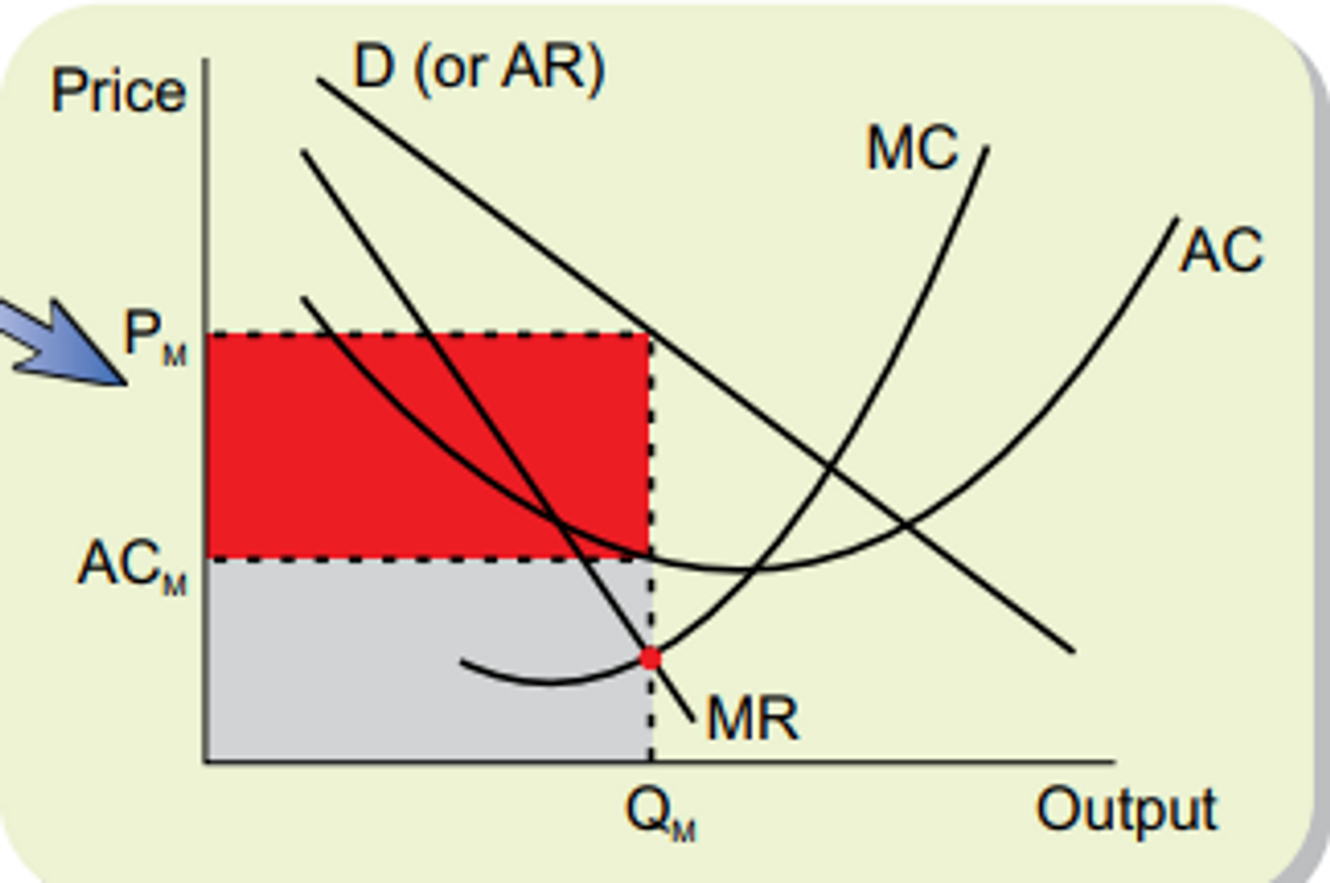
Draw diagrams for a monopolist
13
New cards
Why can a monopolist make supernormal profits even in the long run
The barriers to entry are high, so no new firms enter the market, this way supernormal profit is not competed away
14
New cards
inefficiencies of monopolies and why
in the long run equilibrium position, MC Isn’t equal to AC, meaning it isn’t productively efficient
The price being charged is also greater than MC, meaning it is not allocatively efficient
They are producing above their AC curve, allowing for waste and excess costs. This is because there isn’t competitive drive and it is hard to reduce waste.
The price being charged is also greater than MC, meaning it is not allocatively efficient
They are producing above their AC curve, allowing for waste and excess costs. This is because there isn’t competitive drive and it is hard to reduce waste.
15
New cards
efficiencies of monopolies
Dynamic Efficiency → There are long run supernormal profits
16
New cards
4 Disadvantages of monopolies
→ narrow product range
→ charge high prices
→ Reduces consumer surplus
→ can exploit suppliers
→ charge high prices
→ Reduces consumer surplus
→ can exploit suppliers
17
New cards
Advantages of Monopolies
→ can gain advantage from economies of scale
→ Intellectual property rights, like patents and copyrights, means consumers can benefit from better quality, innovative products, but also reward the entrepreneur.
→ financial security: stable employment
→ Intellectual property rights, like patents and copyrights, means consumers can benefit from better quality, innovative products, but also reward the entrepreneur.
→ financial security: stable employment
18
New cards
Explain 4 barriers to entry for monopolies
1. Legal → patents, licence, red tape, insurance
2. Technical → start up costs, sunk costs, economies of scale
3. Strategic → predatory pricing, heavy advertising
4. brand loyalty
19
New cards
Draw the LRAC for a monopoly and explain why
The LRAC curve will be downwards sloping for a huge quantity range because to minimise the Average, it takes a lot of quantity, a TC is so high (AC = TC/Q)
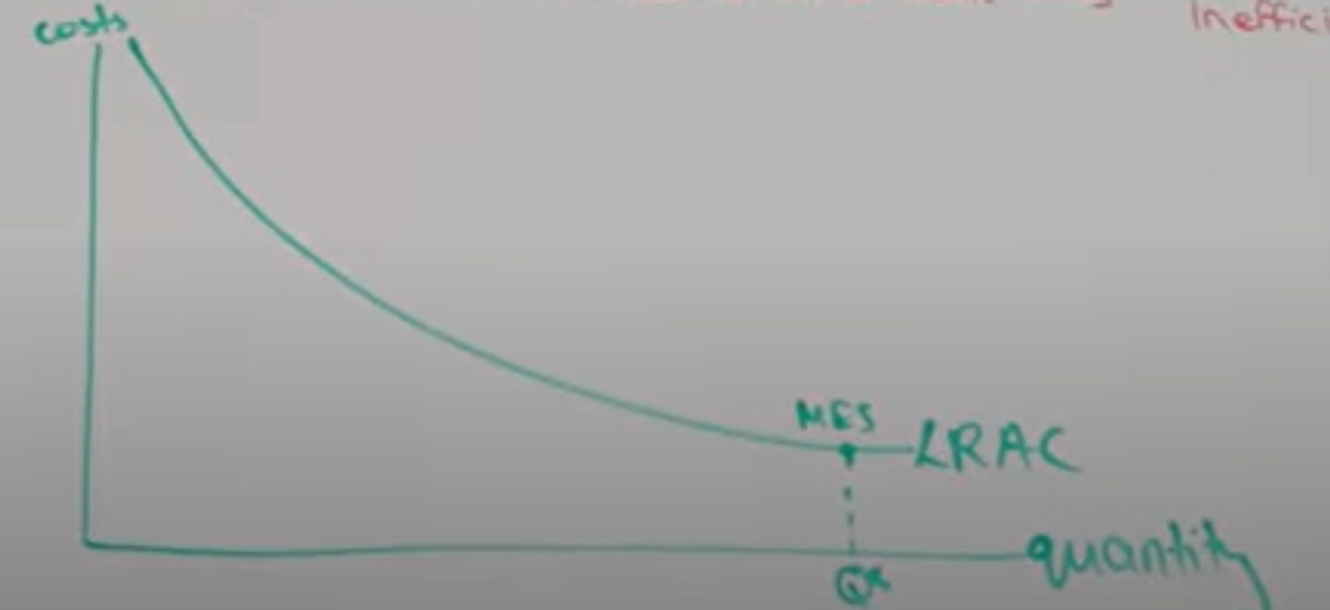

20
New cards
X efficiency
Where a business is minimising its waste *i.e. there are no excess costs. any point in its AC curve*
21
New cards
Consumer Surplus
The difference between the price consumers are willing and able to pay for a good/service and the price they actually pay