Unit 1- Electrical and Computer Engineering
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What are the two functions needed for devices to operate?
1. Energy to operate (EE)
2. Info to know what do do (CE)
What happens in a circuit?
What is the best analogy for each of the 3 parts of Energy?
A circuit consists of electrons flowing out the negative lead (anode) of a power source through the components in the circuit
1. Voltage is the PUSH of electrons through a circuit (like water pressure)
2. Current is the flow rate of electrons (water flow rate)
3. Resistance OPPOSES electron flow (slows current down)
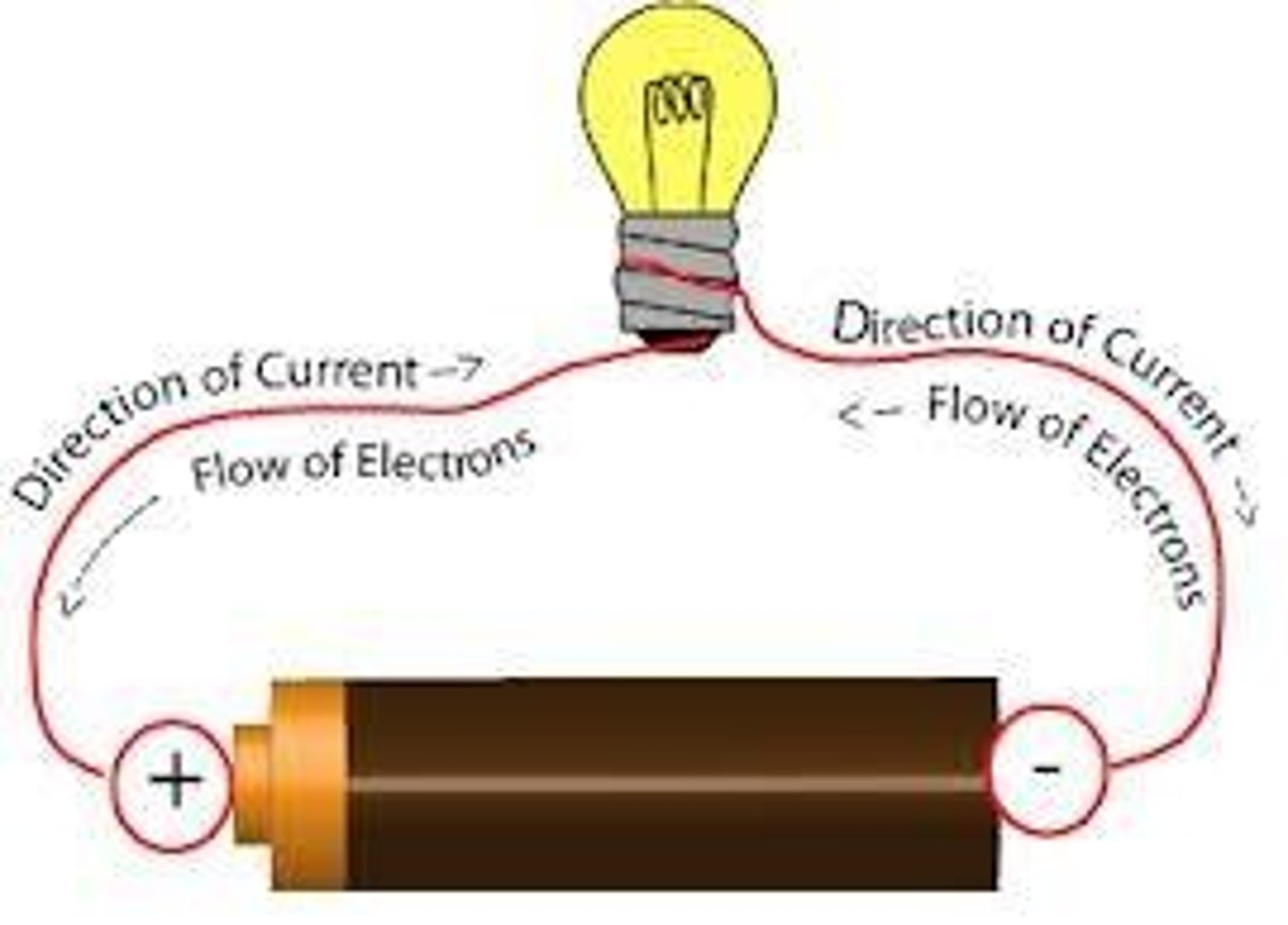
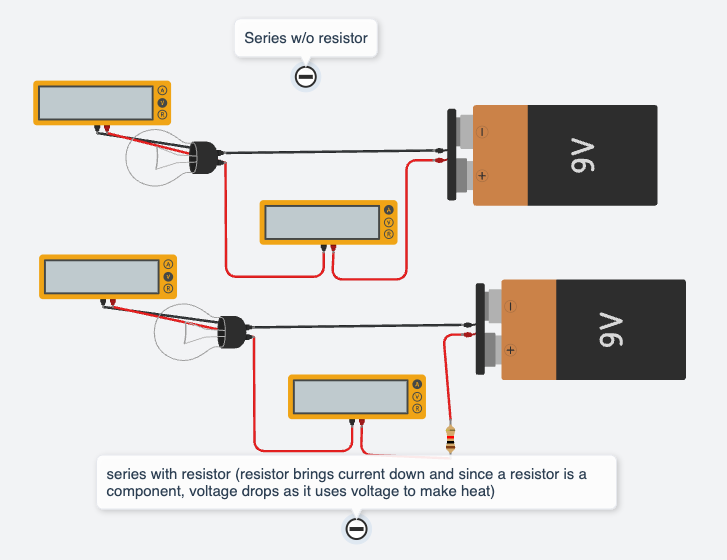
What Is Voltage, Current, and Resistance measured in and HOW do we measure it?
What does resistance affect?
Voltage is measured in VOLTS
Measured by stringing a new parallel circuit off a series circuit (or else multimeter STEALS voltage from circuit cus its a component)
Current is measured in AMPS
Measured within a series circuit (splice + wire and put multimeter in between) with a device drawing power
Resistance is measured in OHMS
Must be connected directly to component leads (multimeter has a battery for this)
--> Resistance lowers the current in a system and lowers voltage as it is a Component that uses voltage to make itself hot
What is the relationship between Volts, Amps and Ohms in the Ohms law formula? (V=IR)
Voltage in directly proportional to Resistance if Current (I) is constant
Current is inversely proportional to Resistance if Voltage is constant
|
—> There are many relationships for different cases where on part of V= IR is constant. Always think of V= IR and rearrange the formula with your givens to find the proportionality.
EX: What happens if voltage stays the same but Resistance goes up?
—> R = V/I and I needs to get smaller to match increasing R
What is the difference between Analog and Digital?
Analog = something with continuous or INFINITE states (like a XBOX controller joystick beacause there are infinite positions you can put it in)
|
Digital = someting with 2 DISCRETE states: ON or OFF (little button controls on phone)
What is the difference between AC and DC voltage?
DC = one direction (unidirectional) energy that has 2 fixed polarities + and - (produced by everything BUT wall outlets)
|
AC = we didn’t learn….
What is a resistor?
A resistor is a arrangement of material (ceramic) that electrons have difficulty getting through (stays in material and makes it HOT)
What is Kirchoff’s Voltage Law in Series vs Parallel?
Series: Total voltage supplied by the battery must equal the voltage drop across the components (Vt = V1 + V2)
|
Parallel: Voltage remains the same through branches (Vt = V1 = V2 = V3)
What is Kirchoff’s Current Law in Series vs Parallel?
Law: The total current entering the circuit and a junction equals the total current leaving it.
|
Series: Since there are 0 junctions, current is the same everywhere (It = I1 = I2 = I3)
|
Parallel: Since there are junctions, current divides like volts in series (It = I1 + I2+ I3)
What are the characteristics of Resistance Series vs Parallel? (no Kirchoff Law for this 😔)
Series: Resistance divides among components (Rt = R1 + R2)
|
Parallel: Resistance gets smaller per branch added (1/Rt = 1/R1 = 1/R2 = 1/R3)
(resistance in parallel is like adding more lanes on a busy highway —>)
reduces traffic (resistance)
increases traffic flow (current)
What is Voltage Sag?
Voltage SAG = when voltage of POWER SOURCE (typically a DC one) drops below its normal/expected amount as you draw CURRENT
(think of it as you opening many showers at home and then water pressure drops)
what are the chracteristics of V I R in series and parallel circuits?
Series
Voltage divides
Current stays the same
Resistance divides
Parallel
Voltage stays the same across all branches
Current divides
Resistance divides into smaller bits (1/Rt = 1/R1 = 1/R2 = 1/R3)
What do the 3 acronyms means for Series and Parallel Circuits?
Series:
SCSC = Series Circuit Same Current
SVSV= Same Current Split Voltage
Parallel:
SVSC = Same Voltage Split Current