Sensory Processing
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
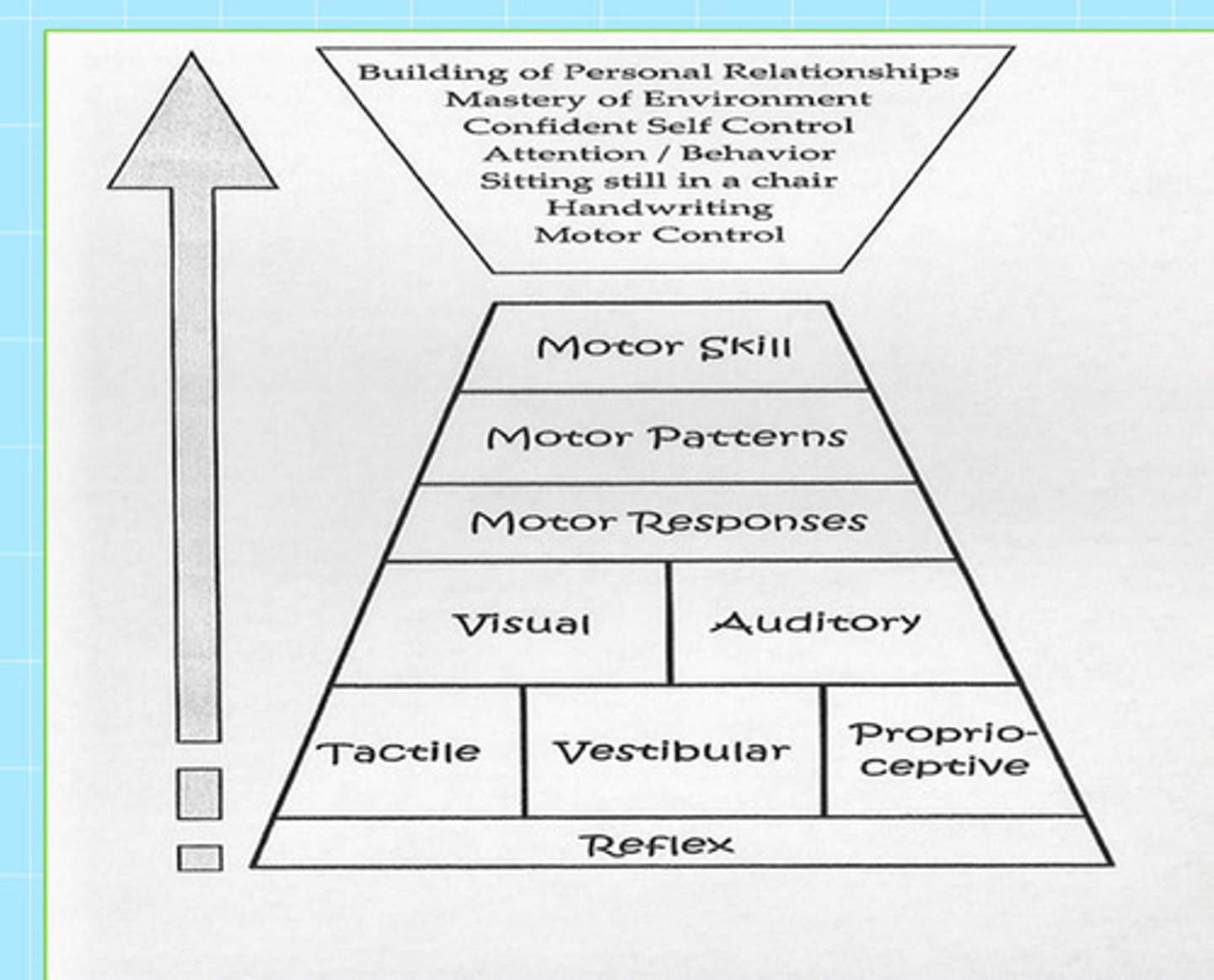
Sensory Input Organization Pyramid (Learning Triangle):
If these prerequisite skills do not work then the outcomes at the top of the triangle will be difficult to achieve
What is peripheral and central to the vestibular system?
-Inner ear
-Vestibular nuclei in pons and medulla of the brainstem
What are 7 ways to stimulate the vestibular system?
1. Slow
2. Fast
3. Rhythmical
4. Erratic
5. Linear
6. Rotary
7. Inverted
Is vestibular input powerful?
Yes, very powerful
What 3 body systems does vestibular input work together with?
1. Proprioceptive system
2. Visual system
3. Auditory system
What is the vestibular system a primary organizer of?
Sensory information
At what level does the vestibular system integrate input?
At the brainstem level or cerebellum
Visual of Vestibular System:
Slide 7
brainstem sends vestibular input to cerebellum, oculomotor nuclei, thalamus and cortex, and spinal cord
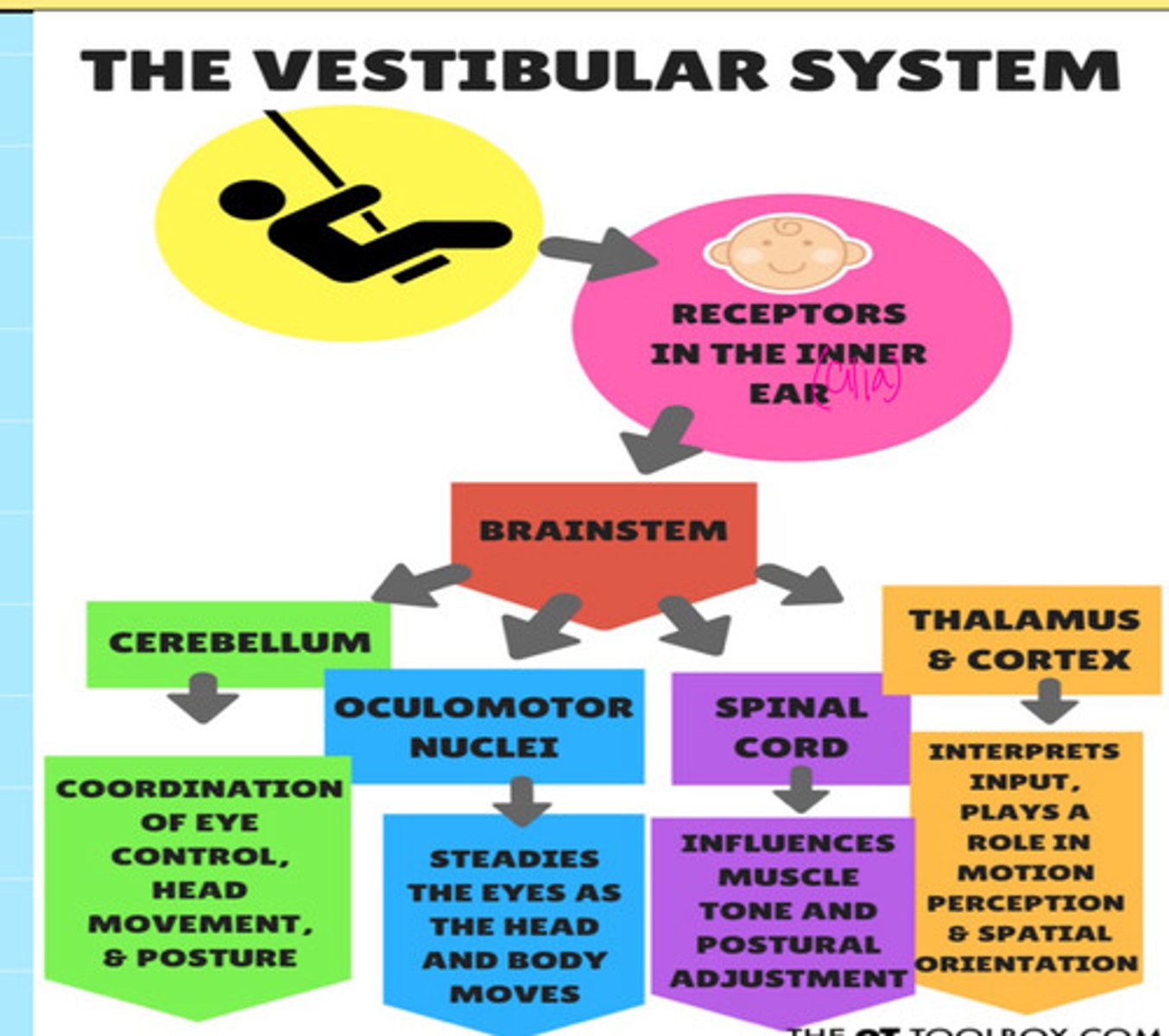
What are the 4 functional processes of the cerebellum in the vestibular system?
1. Postural control
2. Head and eye movement
3. Equilibrium
4. Motor control (specifically sequencing, timing, motor planning of movement)
What structure of the brainstem assists the vestibular system in head righting and equilibrium?
The reticular formation
What type of affect does the reticular formation have on the vestibular system?
Autonomic effect (due to connection with brainstem)
-Very powerful, must watch vestibular input?
What changes can the autonomic affect of the reticular formation cause in the vestibular system?
Changes in arousal and REM sleep
Where does the reticular formation project to?
The limbic system (causing strong emotional reactions)
What is the reticular system a gateway between?
Sensory and cortical information for somatic motor activity, autonomic function, and consciousness
What does the reticular formation control?
Release of neurotransmitters
What are ways to incorporate vestibular input?
-Swinging (prone, seated, and standing)
-Movements (linear, vertical, rotary, angular, upside down, horizontal)
-Challenges to balance
-Inverted head
-Unstable base of support
-Starts and stops in motion
-Changes in direction
-Changes in speed
What is the most mature body system at birth?
Proprioceptive system
What is the proprioceptive system responsible for?
-Motor programming
-Timing and adequacy for our movements
-Nervous system modulator
What are ways to incorporate proprioceptive input?
-Weightbearing walks (animal and wheelbarrow)
-Jumping
-Weightbearing activities
-Resistance activities
-Heavy lifting
-Cardiovascular activities
-Swimming
-Karate
-Climbing
-Yoga
-Chewing gum
What system does the spinothalamic system and dorsal column medial lemniscus system make up?
The tactile system
Why is the spinothalamic system fast reacting but slower processing and responding?
Because of its diffuse synapse areas and because it's myelinated earlier
What is the spinothalamic system involved in?
-Protective (from pain, temp, etc)
-Pain
-Temperature
-Light touch
-Implicated in sensory defensiveness (kids with sensory defensiveness have deficits in tactile system)
What does the dorsal column medial lemniscus system discriminate?
Touch, pressure, kinesthesia, and vibration
What is the dorsal column medial lemniscus system also called?
Discriminative system
What is the dorsal column medial lemniscus system important for?
-Feedforward
-Planning
-Executive of motor task
What is the dorsal column medial lemniscus system implicated in?
Motor planning
What are ways to incorporate tactile input?
-Playing in textures (rice, beans, sand)
-Sensory bins
-Walking on hands (and wheelbarrow walking)
-Deep pressure
-Hand squeezes
-Massages
-High fives
-Vibrating toys
-Weighted blanket
-Lap pad
-Messy play (get hands dirty)
-Arts and crafts
Who was the term "sensory integration" developed by?
Jean Ayres, OT, PhD
What 2 things is sensory integration referred to as?
1. The way sensory information interacts and is organized in the nervous system to produce a motor output
2. A frame of reference for OT treatment
Why has the sensory integration frame of reference undergone major revisions since its inception in the 1960's?
-Due to increasing knowledge of the nervous system
-Due to clinical and theoretical research
What was sensory integration originally developed as?
A treatment approach to "ameliorate associated learning and behavior problems"
What does the sensory integration frame of reference put emphasis on in child development?
The importance of vestibular, tactile, and proprioceptive senses and their importance to development and occupations
What are 3 initial concepts of sensory integration Jean Ayres developed?
1. Sensory integration
2. Adaptive responses
3. Praxis
Ayres classic books she wrote:
-Sensory Integration and Learning Disorders
-Sensory Integration and the Child
What are 4 neurobiologically based concepts of sensory integration?
1. Sensory support for development and brain function
2. Adaptive response
3. Neural plasticity
4. Central nervous system organization
What 2 types of sensory support are important for development and brain function?
1. Sensory nourishment
2. Sensory diet
What does an adaptive response result in?
A more organized state, and the capacity for further sensory integration is enhanced
What does an adaptive response imply?
Implies that the child is an active participant
What does an adaptive response use?
The child's inner drive
What are 3 major components and postulates of the sensory integration frame of reference?
1. Development and typical sensory integration functioning
2. Sensory integration dysfunction (SID) or sensory processing disorder (SPD)
3. Treatment
What is development and typical sensory integration functioning dependent on?
Learning is dependent on the ability to take in and process sensations from movement and environment and use it to plan and organize behavior
What is sensory integration dysfunction (SID)/ sensory processing disorder (SPD)?
Individuals with decreased ability to process sensation also may have difficulty producing appropriate actions, which may interfere with learning and behavior
What does treatment for sensory integration involve?
Enhanced sensation, as part of meaningful activity that yields an adaptive interaction, improves the ability to process sensation, thereby enhancing learning and behavior
What are 5 assumptions of the sensory integration frame of reference?
1. The central nervous system is plastic
2. Sensory integration develops
3. Brain functions as an integrated whole
4. Adaptive interactions are critical to sensory integration
5. People have an inner drive to develop sensory integration through participation in sensorimotor activities
What are 6 guiding principles of the sensory integration frame of reference?
1. Sensory input can be used systematically to elicit an adaptive response
2. Registration of meaningful sensory input is necessary before an adaptive response can be made
3. An adaptive response contributes to the development of sensory integration
4. Better organization of adaptive responses enhances the child's general behavioral organization
5. More mature and complex patterns or behavior involve consolidations of more primitive behaviors
6. More inner-directed a child's activities are, the greater the potential for improving neural organization
When do problems in sensory integration occur?
-Behaviorally
-Socially
-Academically
-Motor coordination
What may behavioral, social, academic, or motor coordination problems be a result of?
Poor sensory processing
What do children with poor sensory processing tend to avoid or reject?
Simple sensory or motor challenges
What do long-term patterns of poor sensory processing lead to?
Missing important activities of development
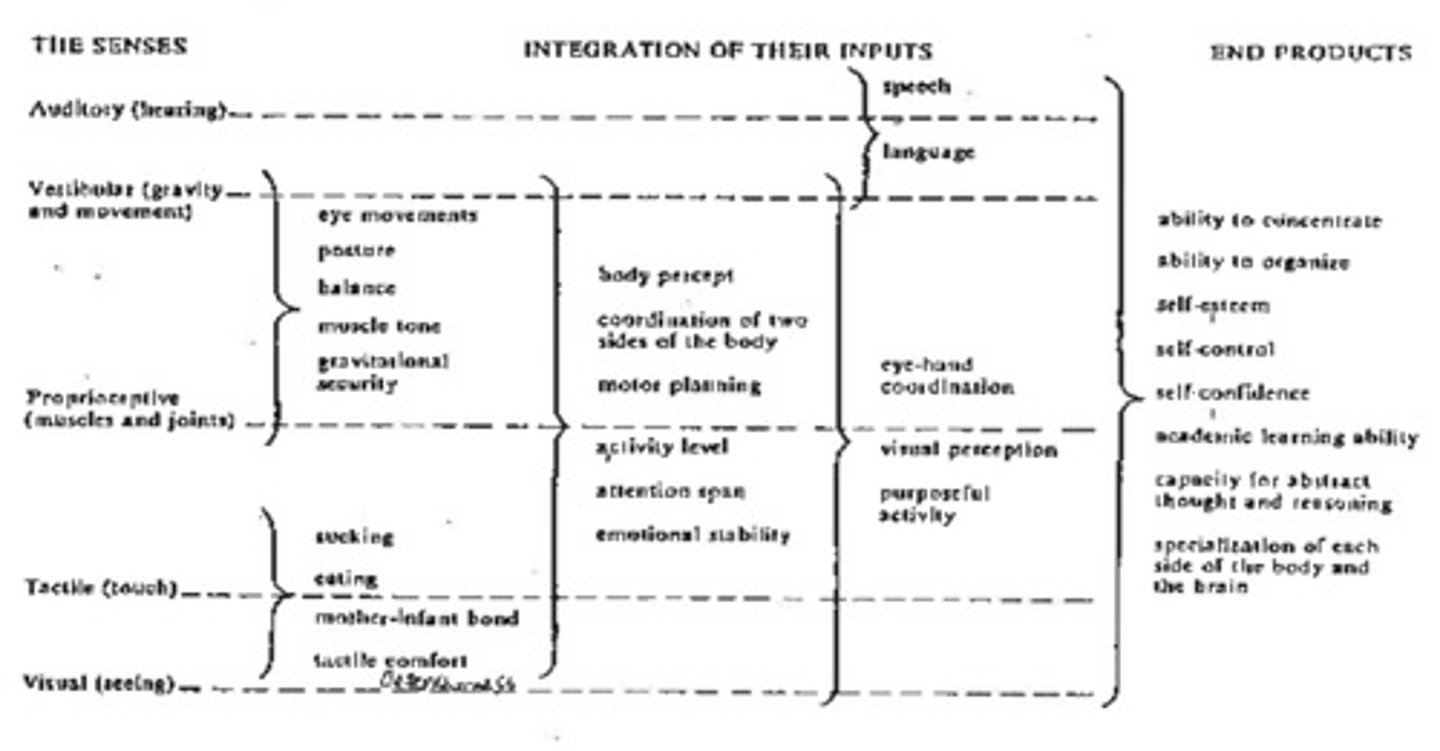
Sensory Systems and End Products Diagram:
Progression of sensory system and why it's important
-slide 23
What areas of occupation do OTs see challenges/ symptoms in with clients with SPD?
-Play, leisure, and social participation
-ADLs & IADLs
-Rest & Sleep
-Education & Work
What challenges/ symptoms do OTs see in play, leisure, and social participation in those with SPD?
-Decreased quality and quantity of play skills (for children with DCD, most related to physical play)
-Poor social competence and participation
-Scores on Test of Playfulness lower for children identified with sensory processing disorder using the Short Sensory Profile
What challenges/ symptoms do OTs see in ADLs & IADLs in those with SPD?
-Poor performance in functional ADL and IADL tasks
-Avoidance of functional tasks- children with sensory hypersensitivity
What challenges/ symptoms do OTs see in rest & sleep in those with SPD?
-Disturbances in sleep
(children with tactile sensitivity)
-Decreased arousal (children that are underresponsive)
What challenges/ symptoms do OTs see in education & work in those with SPD?
-Lower participation in school
-Decreased academic achievement and attention
-Higher risk for learning difficulties
What is dyspraxia correlated with in younger children?
Poor arithmetic performance
What is dyspraxia correlated with in older children?
Reading difficulty
What client factors and performance skills do OTs see challenges/ symptoms in with clients with SPD?
-Postural control
-Stereotyped Movement (SM)
-Gravitational insecurity
-Praxis
-Pain
-Tactile Over-sensitivity
What challenges/ symptoms do OTs see in postural control in those with SPD?
Children with sensory processing disorder have poorer stance control in variable sensory conditions (ex: carpet and tile)
Children with what conditions in addition to sensory processing disorder experience challenges in stereotyped movement?
Children who have autism, intellectual disability, vision, or hearing disabilities, or are typically developing
What is gravitational insecurity?
A sensory modulation issue where fear response to movement or postural challenge is out of proportion to child's postural deficits
-Thought to be related to poor otolithic vestibular processing
-Gravitational Insecurity Assessment pilot study to identify it
What is praxis?
The ability to plan and execute coordinated movements (conceptualize, plan, and execute nonhabitual motor act)
-Conceptualizing the motor act = ideation
-Pilot study of the development of Test of Ideational Praxis (TIP)
What did Jean Ayres (1985) characterize praxis issues in children as?
Developmental dyspraxia
Sensory modulation issues did not appear to be due to increased sensitivity, but rather what?
More averse reactions, suggesting central nervous system processing issues (pain)
-ex: hypersensitive/ over firing
What are 4 tactile sensations that most bothered children?
1. Tags in clothing (39%)
2. Cutting finger or toe nails (19%)
3. Hair brushing (16%)
4. Mud (11%)
What are 4 tactile sensations that least bothered children?
1. Light stroking touch (1%)
2. Play dough (1%)
3. Getting dressed (2%)
4. Finger painting (2%)
What is a trick for cutting finger or toe nails to make it less bothersome?
Do it after bath time (they are soft)
What is a trick for brushing hair to make it less bothersome?
Do it after a shower; in the morning your senses are just waking up so could be more bothersome
True or False: Children have differences in their sensory responses at home as compared to at school.
True
(usually more comfortable at home than school, causing more of a reaction at school)
What are the 3 subtypes of sensory integration dysfunction (SID)/ sensory processing disorder (SPD)?
1. Pattern 1- Sensory modulation disorder
2. Pattern 2- Sensory-based motor disorder
3. Pattern 3- Sensory discrimination disorders
What are the characteristics of Pattern 1- Sensory modulation disorder?
-Sensory over-responsivity
-Sensory under-responsivity
-Sensory seeking/craving
What are the characteristics of Pattern 2- Sensory-based motor disorder?
-Dyspraxia
-Postural disorders
What are the characteristics of Pattern 3- Sensory discrimination disorders?
Disruptions in:
-visual
-tactile
-vestibular
-auditory
-proprioception
-taste/smell
What is sensory registration?
Behavior of noticing sensory stimuli in the environment
What is sensory modulation?
Producing responses that match the demands and expectations of the environment (graded and adaptive)
What is sensory integration?
"Neurological processes that organizes sensation from one's own body and from the environment and makes it possible to use the body effectively within the environment" -Ayres
What can occur in individuals with sensory modulation dysfunction?
-Different arousal or response levels occur between individuals
-Different arousal or responses occur within individuals between sensations
-People can be under-response (hyporesponsive) or over-responsive (hyperresponsive)
How can responsiveness be represented?
On a continuum
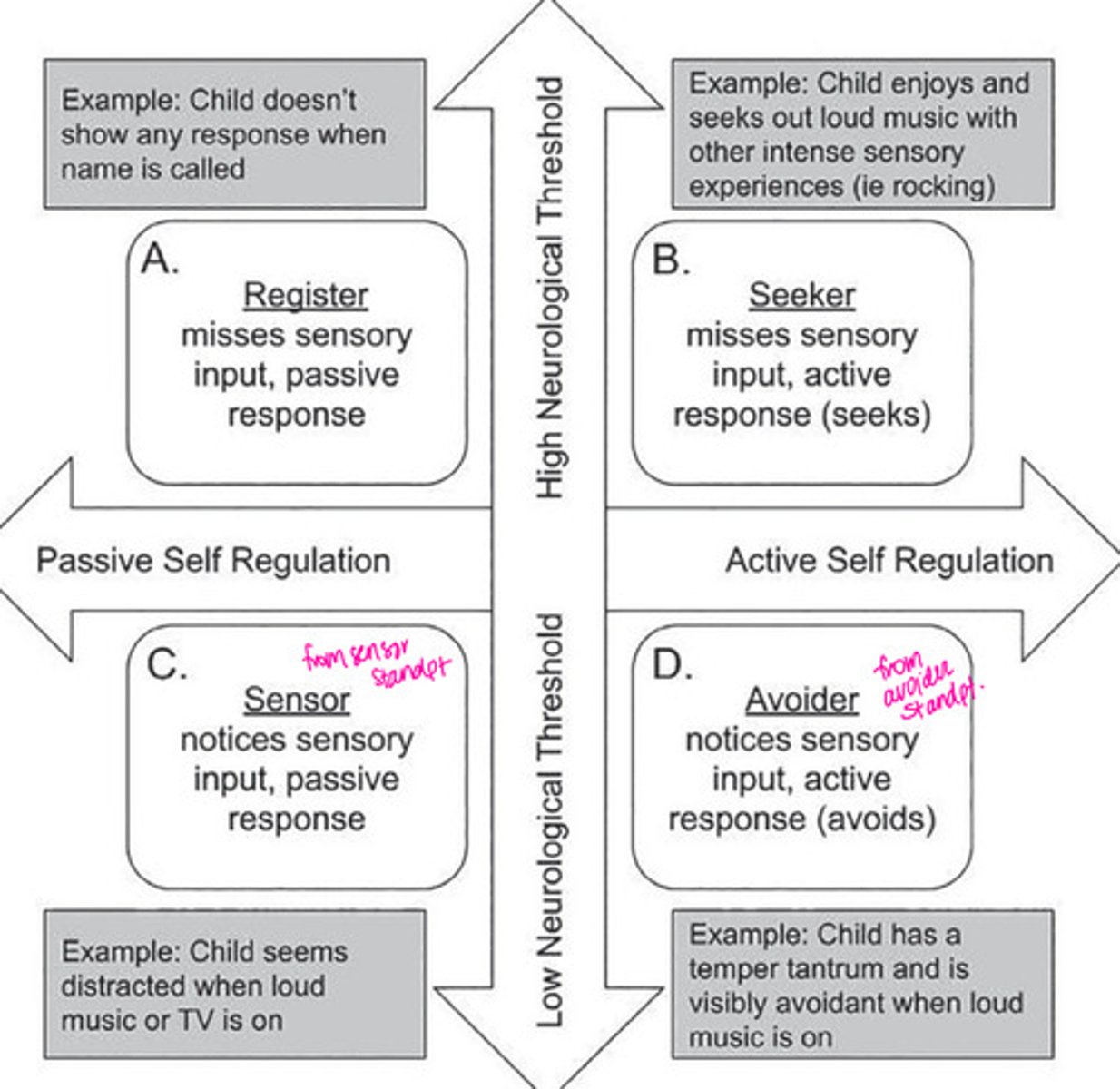
Types of Sensory Modulation Disorder- Dunn's Model (2014):
Slide 36
What are 3 programs that OTs created to teach regulation?
1. Williams and Shellenberg- "How Does Your Engine Run?"
2. Kupers program- "The Zones of Regulation"
3. Can work in conjunction with Michelle Garcia "Winner's Social Skills Curriculum"
What does "How Does Your Engine Run" teach children?
To start monitoring their arousal and teaching strategies to help them regulate their arousal
What are 2 praxis problems?
1. Dyspraxia
2. Somatodyspraxia
What is dyspraxia?
Difficulty with praxis (conceptualizing, planning, executing nonhabitual motor act) not explained by another medical diagnosis or developmental disability
What is somatodyspraxia?
Poor praxis involving impaired tactile and proprioceptive processing
How do individuals with somatodyspraxia present?
-Clumsy, awkward
-Difficulty relating to objects in space
-Poor body awareness
-Poor timing
-Poor sequencing
-Poor directionality
-Novel motor activities performed poorly
-Can have difficulty with ideation see with poor initiation of motor sequences
Praxis Model:
-Task
-Ideation
-Memory, neuronal model, schema
-Develop plan
-Execute
-Action complete
*simultaneous reaction of internal feedback, efferent monitoring, preview of action, feedback/feedforward
-slide 39
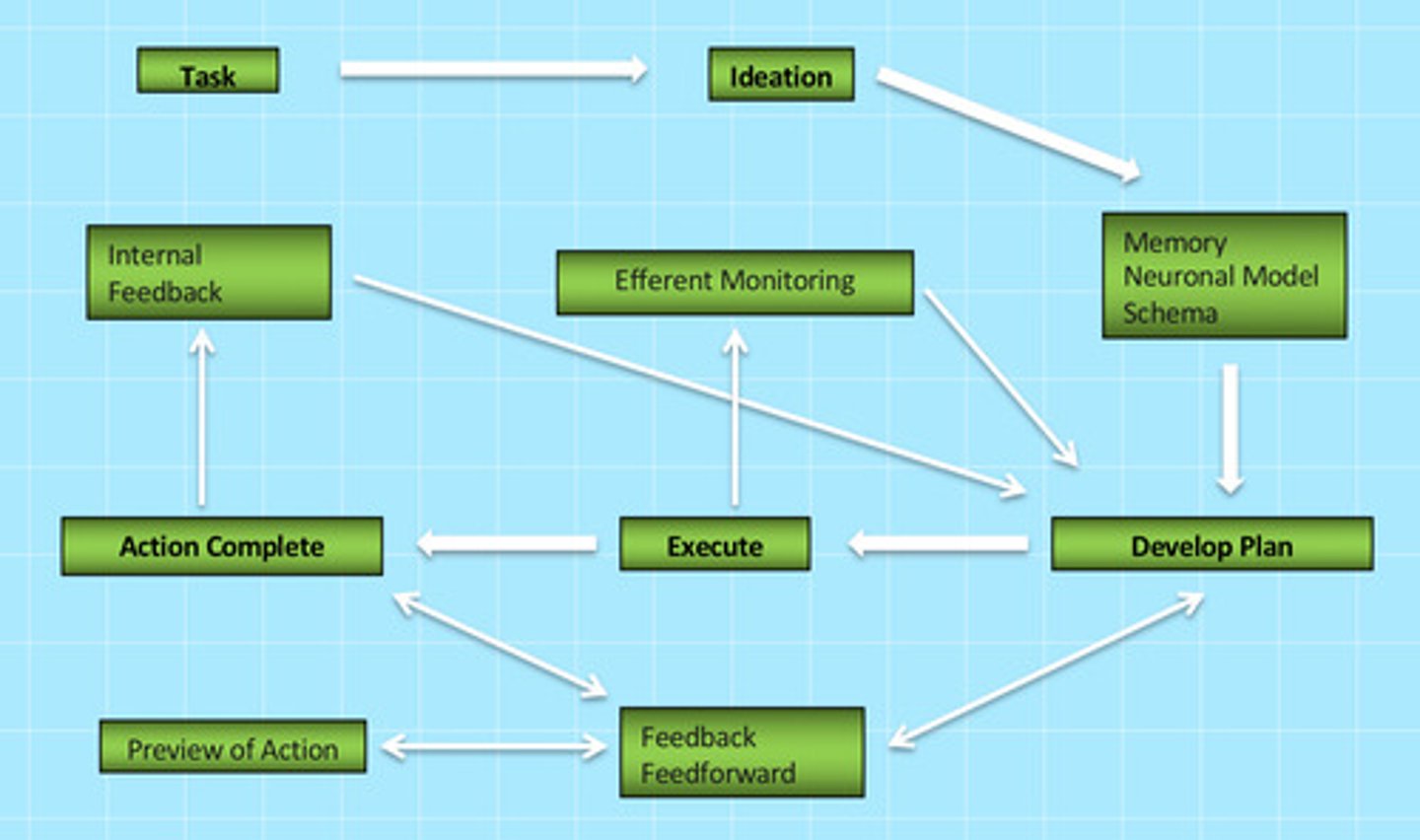
What condition is easily overlooked as it is a frequently mild disorder?
Bilateral integration and sequencing dysfunction
What do bilateral integration and sequencing problems in the vestibular and proprioceptive system cause?
-Poor equilibrium reactions
-Low muscle tone
-Poor eye hand coordination
-Poor postural stability
3 terms used over time for bilateral integration and sequencing problems:
1. Postural and bilateral integration dysfunction
2. Vestibular-bilateral integration dysfunction
3. Bilateral integration and sequencing dysfunction
Fisher (1991) added a concept of projection action sequences to describe what?
Difficulty anticipating how to move to adapt to changes in the spatial relationships to the environment
What problems do individuals with sensory discrimination and perception problems have?
-Tactile
-Proprioceptive
-Visual perceptual
-Other perceptual problems
What do individuals with tactile sensory discrimination and perception problems have difficulty with?
-Interpreting tactile information
-Poor motor planning
-Poor fine motor skills for ADL and play (ex: handwriting, fastening buttons)
-Developing manipulation and mature grasp patterns
-Poor eye hand coordination
What are tactile sensory discrimination and perception problems commonly seen with?
Visual perceptual issues
What do individuals with proprioceptive sensory discrimination and perception problems have difficulty with?
-Interpreting proprioceptive information
-Gross and fine motor skills
What do proprioceptive sensory discrimination and perception problems present as?
-Clumsy
-Awkward
-Poor grading of force of movement
What do proprioceptive sensory discrimination and perception problems seek for gross and fine motor skills?
They may seek heightened input resulting in disruptive behavior
What do visual perceptual sensory discrimination and perception problems have difficulty with?
-See previous discussion of visual perception
What are visual perceptual sensory discrimination and perception problems commonly seen in?
Children with sensory integrative disorder but may or not may not be part of a sensory integrative disorder
What other problems do those with sensory discrimination and perception problems have?
-Central auditory processing problems may or may not be related to sensory integrative dysfunction
-Combinations of multisensory problems
What do the secondary problems to sensory integration dysfunction have a major influence on?
Occupational performance