HRM 401 Exam 2
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Benefits of Diversity
-Higher Creativity in decision making
-Better understanding and service of customers
-More satisfied workers
-Higher stock prices
-Lower litigation expenses
-Higher company performance
Equality
Belief that all people have the same opportunities to succeed
Equity
Seeks to even the playing field by recognizing that not all people start at the same place
Why Is It Hard to Work Together? (Diversity)
-ASA
-Inaccurate stereotypes or prejudice
-Unsupportive/hostile work enviornment
-Lack of Experience
-Fears of reverse discrimination
-Diversity Fatigue
-Resistance to Change
Deep Level Diversity
Difference in values, attitudes, and beliefs
Surface Level Diversity
Differences in gender, race, age, and physical disabilities
Individualistic Cultures
-Looser ties with their groups
-Familial bonds are less important; family is defined more narrowly
-Changes groups more often
-Individual differences are valued
-Prefers individual rewards
Collectivism
-People define themselves in terms of the groups they are a part of and stronger bonds with their groups
-Family bonds are influential and family is defined in a broader sense
-Individuals try to stay with their groups and are more permanently attached
-Being different from the group is undesirable
-Prefers group rewards
Belonging Occurs When…
People are valued, respected and supported and when people have access to opportunities and resources
Behaviors that Support Inclusion:
-Language
-Situations
-Relationships
How to Increase Belonging at an Individual Level
-Possess self-awareness of motives and comfort level with diversity
-Engage in continuous learning
How to Increase Belonging at an Organizational Level
-Belonging must be tired to organizational value with measurable goals
-Focus on core learning goals for employees with personalized training that employees volunteer to complete
-Focus on specific behaviors for inclusion
Openness to Experience (Big 5)
The extent to which someone seeks new experiences and is tolerant of change.
-imagination, complexity, change, scope
Low: implements plans, prefers simplicity, wants to maintain existing methods, and is attentive to details
High: creates new plans and ideas, seeks complexity, readily accepts changes and innovations, prefers a broad view and resists details
Conscientiousness (Big 5)
How an individual approaches goals (achievement-orientation)
-Perfectionism, organization, drive, concentration, methodical
Low: low need to continually refine or polish, comfortable with little formal organization, satisfied with current level of achievement, shifts easily between ongoing tasks, operates in a more spontaneous mode
High: perfectionism, keeps everything organized, craves even more achievement, prefers completing tasks before shifting, develops plans for everything
Extraversion (Big 5)
The degree to which a person can tolerate sensory stimulation from people and situations
-Enthusiasm, social ability, energy mode, taking charge, trust of others, tact
Low: holds down positive feelings, prefers working alone, prefers being still in one place, prefers being independent of others, skeptical of others, speaks without regard for consequences
High: shows a lot of positive feelings, prefers working with others, prefers to be physically active, enjoys the responsibility of leading others, readily trusts others, carefully selects the right words
Agreeableness (Big 5)
The degree to which we take others’ opinions into account
-Service, agreement, deference, reserve, reticence
Low: more interested in self needs, welcomes engagement, wants acknowledgement, usually expresses opinions, enjoys being out front
High: more interested in others’ needs, seeks harmony, uncomfortable with acknowledgement, keeps opinions to self, and prefers the background
Neuroticism/Emotional Stability (Big 5)
How we respond to stress/negative experiences (anxiousness)
-Sensitivity, intensity, interpretation, rebound time
Low: at ease most of the time, usually calm, optimistic explanations, rapid rebound time
High: worrying, quick to feel anger, pessimistic explanations, longer rebound time
Locus of Control
Beliefs about what causes things to happen- either the person (internal) or other people/things (external)
Self-Efficacy
A belief that one can perform successfully- may be either task specific or general
Self-Esteem
The degree to which a person has overall positive feelings about oneself
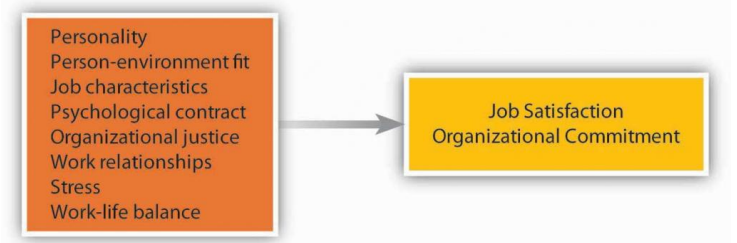
What Factors Lead Toward Job Satisfaction & Organizational Commitment?
Personality
Person-enviornment fit
Job characteristics
Psychological contract
Organizational justice
Work Relationships
Stress
Work-life balance
Cognitive Dissonance
Experiencing inconsistency between attitudes and behaviors
How do you reduce Cognitive Dissonance?
-Change your behavior and attitudes
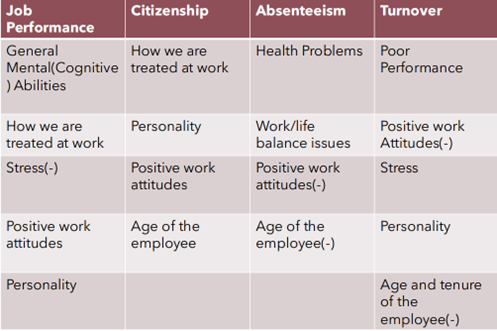
Major Predictors of Job Performance
OCB
Organizational Citizenship Behaviors
-voluntary behaviors employees perform to help others benefit the organization
Responses to Dissatisfaction (Hirschman)
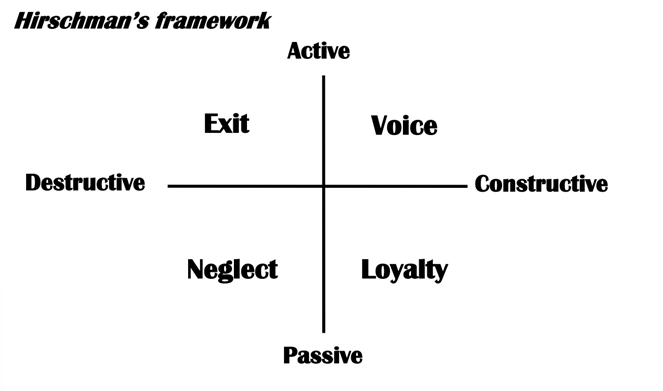
Can lead to…
abusing others
-production deviance
-theft
-sabotage
-withdrawal behaviors
Stereotyping
Making assumptions about a person based on category or group membership without verifying whether the assumption
Perspective Taking
The active cognitive process of imagining the world from another’s vantage point or imagining oneself in another’s shoes to understand their visual viewpoint, thoughts, motivations, intentions, and/or emotions
Decreases: stereotyping & discrimination
Increases: liking, coordination, & cooperation
Extrinsic Motivation
Pay for performance, piece-rates, commissions, promotions etc.
Being motivated by incentives
Intrinsic Motivation
Opportunites for challenge, growth, etc.
Fairness, equity, etc.
Being motivated by internal values
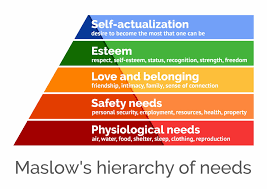
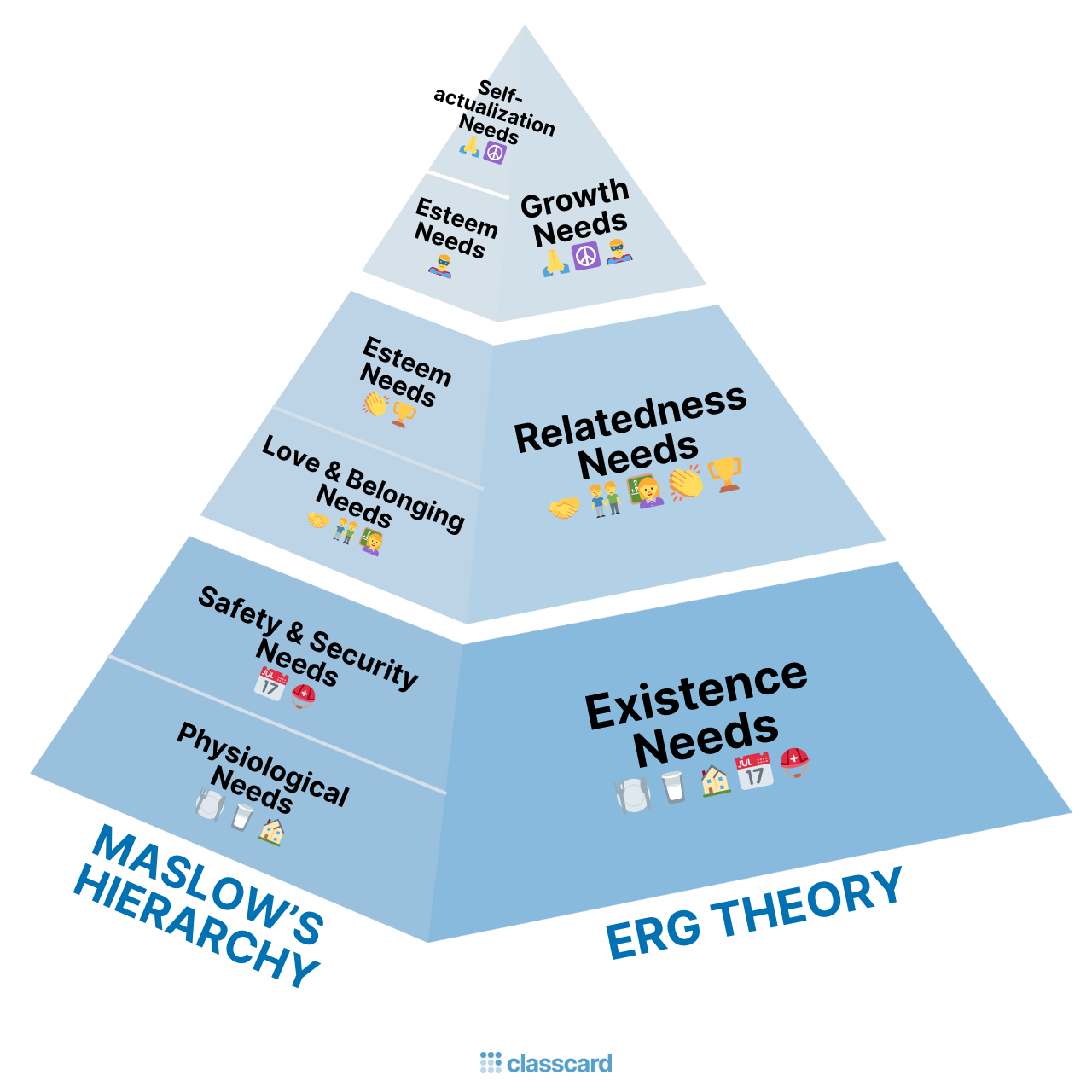
Maslows Theory of Motivation
Certain fundamental human needs must be met in a hierarchical order to facilitate motivation
1. Physiological needs
2. Safety needs
3. Social needs
4. Esteem needs
5. Self-actualization needs
ERG Theory
Motivators (2 factor theory)
Achievement, personal growth, challenging work
—> Presence leads to increased motivation, but absence is not necessarily demotivating
Hygiene Factors (2 factor theory)
A salary, benefits, safe and clean working environment, etc.
—>Prescence does not motivate, but absence is demotivating
Equity Theory
People evaluate the ratio of inputs they bring to a job (ability, experience, effort) to the outputs they receive (pay, promotions, etc.)
-If one perceives inequity, or imbalance in this ratio, they tend to be less motivated
-People refer to past precedents and other people to assess equity vs. inequity
Expectancy Theory
Motivation is a function of expectancy, instrumentality, valence
Expectancy: effort à performance
Instrumentality: performance à outcomes
Valence: value of outcome/reward (highly desirable to highly undesirable)
Goal-setting Theory
Motivation and performance can be maximized by assigning specific levels of performance for workers to attain
Rather than just “do your best”
50 years of empirical support and data on goal setting
Goals activate a psychological drive to reach the goal, even without extrinsic rewards
Goals direct attention
Goals lead people to develop strategies to achieve them
Goals increase persistence
SMART Goals
Specific
Measurable
Aggressive
Realistic
Time-bound
Job Characteristics Model of Intrinsic Motivation
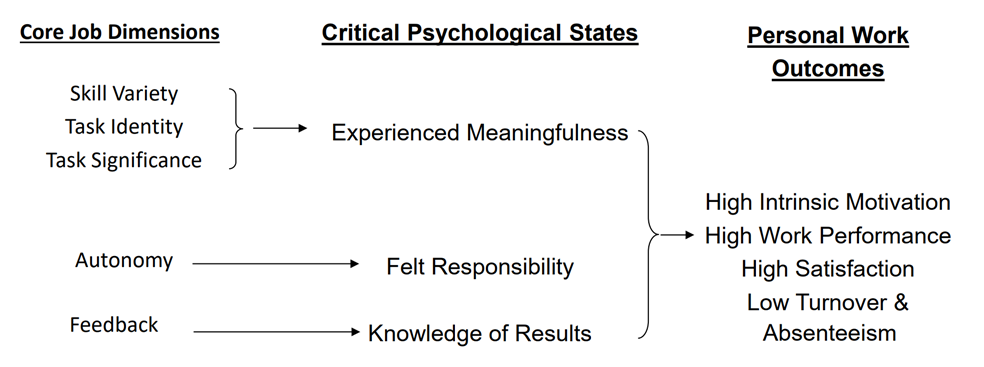
MPS = ((Skill Variety + Task Identity + Task Significance)/3) x Autonomy x Feedback
Pay for Performance
Pay may motivate up to a point, after which other concerns become more important
-Compensation = s + b * x
-Collective-based systems may work better
-Individual employees are rewarded in proportion to their performance/contributions