Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas, Spleen
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Largest gland in the body
Liver
Liver is intra/retroperitoneal
Intraperitoneal
Does the liver have a role in immunity
Yes, it is a major lymph producing organ
Name the 4 anatomical lobes of the liver
1. Right
2. Left
3. Quadrate
4. Caudate
How many functional lobes of the liver are there
8
What separates out the liver into functional lobes
Divided based on blood supply
Significance of having 8 functional lobes to the liver
Individual sections can be surgically removed without disturbing any other functional lobe
What is the Porta hepatis
This is the “hilum” of the liver where abdominal structures can enter or leave
What blood vessels don’t pass through the porta hepatis
The hepatic veins drain blood away from the liver and when blood is exiting it does not pass through the porta hepatis
Instead the hepatic veins drain posteriorly to the inferior vena cava
Ligamentum venosum is a remnant of what embryological structure
ductus venosus
Round ligament of the liver / Ligamentum teres hepatis is a remnant of what embryological structure
umbilical vein
Round ligament of the liver / Ligamentum teres hepatis is formed from what structure
Thick, free, inferior border of the falciform ligament
What is the bare area of the liver
Diaphragmatic area on the liver not covered in visceral peritoneum
Liver & diaphragm in direct contact
What does the portal triad consist of
Common bile duct
Hepatic artery proper
Hepatic portal vein
The common hepatic artery is a direct branch from what
the celiac trunk
The common hepatic trunk changes its name to ______ when
Changes name to hepatic artery proper when the gastroduodenal artery branches off
Hepatic artery proper divides at the what to become what
Hepatic artery proper divides at the porta hepatis to become:
▪ Right hepatic artery
▪ Left hepatic artery
The liver receives blood from what two different sources
Arterial → Hepatic arteries (20-25%)
Venous → Hepatic portal vein (75-80%)
The hepatic portal vein carries what where
The hepatic portal vein carries all nutrients (carried in venous blood) from the gastrointestinal tract directly to the liver
Comes mainly from stomach - very high in nutrients
Blood in the hepatic portal vein has a slightly lower/higher oxygen content than the venous blood in the systemic/caval system
Blood in the hepatic portal vein has a slightly higher oxygen content than the venous blood in the systemic/caval system
Hepatic portal vein forms when the following two veins unite
Superior mesenteric vein
Splenic vein
The hepatic veins drain blood from where to where
Away from the liver and back to the systemic system
Name the veins of the liver
The central veins of the liver unite together and drain to form the left, right and middle hepatic veins respectively
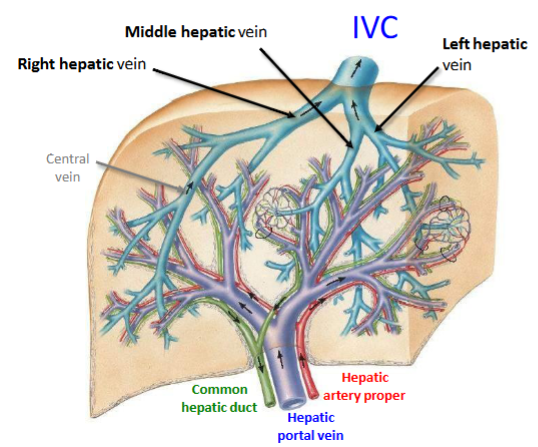
What keeps the liver in position
The relationship between the hepatic veins and the inferior vena cava helps to keep the liver in position - the liver doesn’t have much connective tissue
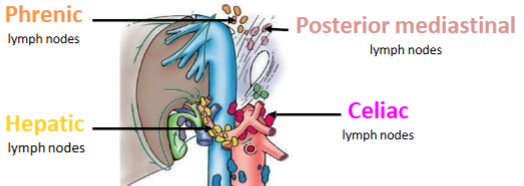
Name the lymph nodes of the liver
Liver: Summary
Arterial Supply:
Venous Drainage:
Lymphatics:
Innervation:
Liver: Summary
Arterial Supply: Celiac trunk
Venous Drainage: Hepatic veins → Inferior vena cava → Systemic (caval) venous system
Lymphatics: Drain by following two routes, either Phrenic or Posterior Mediastinal lymph nodes or Hepatic or Celiac lymph nodes
Innervation: Vagus Nerve & Hepatic nerve plexus (part of the celiac plexus!)
Role of gallbladder
Store & concentrate bile
Emulsification
The breakdown of large fat globules into smaller, uniformly distributed particles prior to being digested by specific enzymes
Role of bile
Bile is a yellow-brown (or green) fluid that aids in the emulsification of fat
Bile is produced & secreted in the liver by ……….
Hepatocytes
What transports bile from the liver and deposit it into the gastrointestinal tract.
Biliary ducts
What part of the GI tract is bile released into
2nd part of the duodenum
Do biliary ducts secrete bile as a constant flow into the GI tract or intermittently
Intermittently when needed
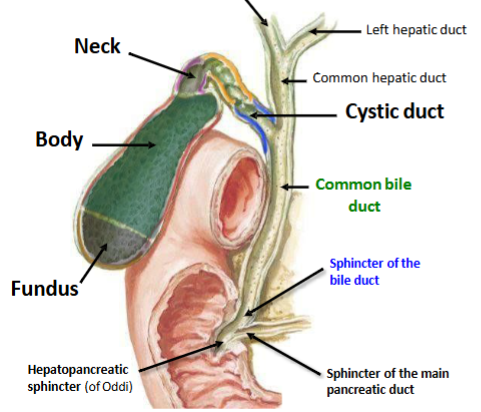
3 parts of gall bladder
Fundus
Body
Neck
arterial supply of gallbladder
Cystic artery from right hepatic artery from common hepatic artery from celiac trunk
(The cystic artery is highly variable, however, it most commonly branches directly from the right hepatic artery)
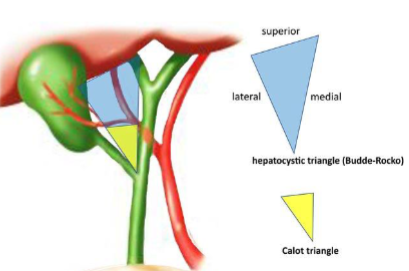
The cystic artery travels in a significant triangle called
cystohepatic triangle (Triangle of Calot)
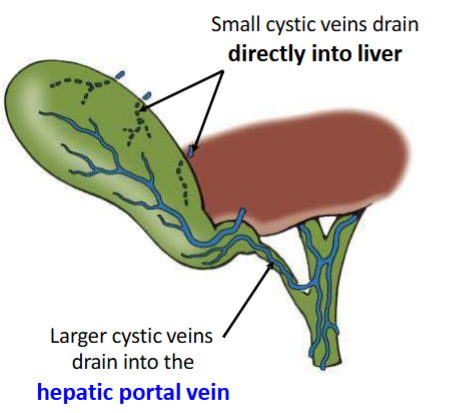
Venous drainage of the gallbladder
cystic veins drain blood away from the gallbladder
Where do cystic veins drain to
The gallbladder is in direct contact with what part of the liver
The gallbladder is in direct contact with the visceral (inferior) surface of the liver and is firmly adhered
Most small veins from the body of the gallbladder pass directly into the
hepatic sinusoids that are within the liver
Most veins around the neck of the gallbladder drain into the
hepatic portal vein
Gallbladder: Summary
Arterial supply:
Venous drainage:
Lymphatics:
Innervation:
Gallbladder: Summary
Arterial supply: Celiac trunk
Venous drainage: Direct or via the hepatic portal vein → Portal venous system
Lymphatics: Ultimately drain by following the arteries towards → Celiac lymph nodes
Innervation: Vagus nerve & celiac nerve plexus
The gallbladder receives general somatic afferent (GSA) innervation through what nerve
the right phrenic nerve
What kind of pain is associated with the right phrenic nerve innervating the gallbladder
referred pain
Irritation of what structures lead to pain in each patch
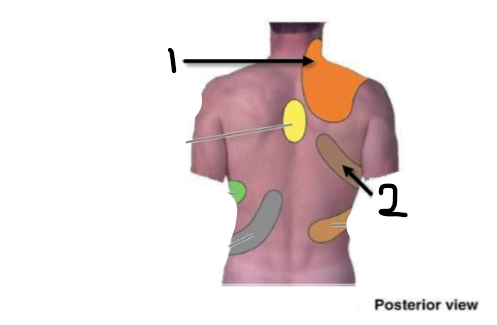
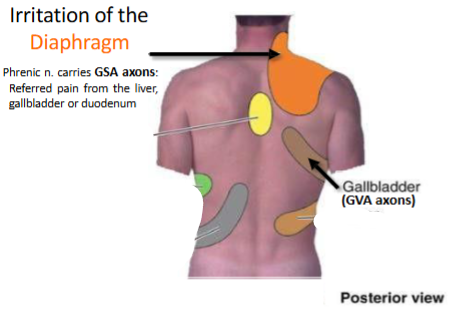
(diaphragm can be felt on either side)
What nerve & nerve roots supply the diaphragm
Phrenic nerve

Name the parts of the pancreas
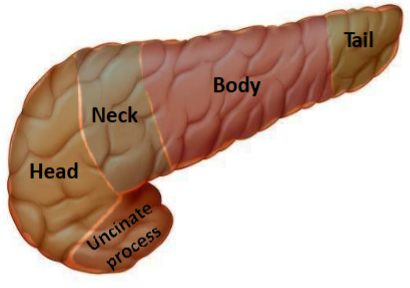
Where is the head & neck & the uncinate process of the pancreas in relation to the superior mesenteric artery
Head = right of it
Uncinate process = Posterior to it
Body = left of it
Where is the neck of the pancreas in relation to a specific part of the stomach
directly behind the PYLORUS of the stomach
The pancreas is mostly retroperitoneal. What is the intraperitoneal part of the pancreas
The tail
The tail of the pancreas lies within what ligament
lies within the splenorenal ligament
link between the Transpyloric plane and the pancreas
The pancreas (especially its neck) lies along the transpyloric plane.
The body and tail of the pancreas extend slightly above this plane.
The head of the pancreas is positioned slightly below it, nestled within the curve of the duodenum.
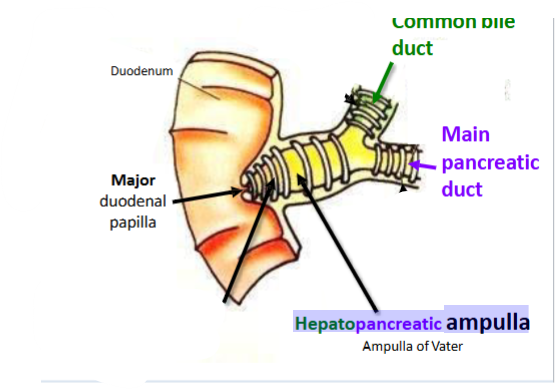
What ducts are associated with the pancreas
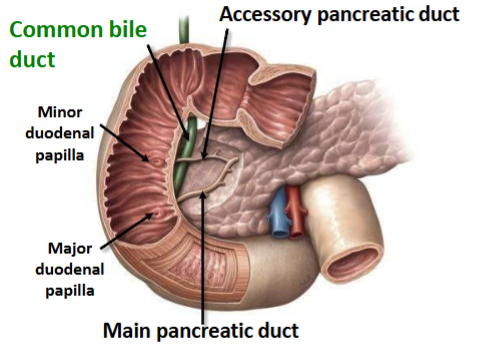
Which duct joins with the common bile duct
The main pancreatic duct
(Main) Pancreatic Duct unites with the common bile duct opens into the GI tract with the common bile duct via the _________
(Major) duodenal papilla
The Accessory Pancreatic Duct IF present & patent opens into the GI tract via the _______
minor duodenal papilla
What is a Papilla
Defined as a small rounded protuberance on an organ of the body
What is an Ampulla
Dilated end of a vessel named after ancient flasks

Name an ampulla associated with the pancreas
Hepatopancreatic ampulla
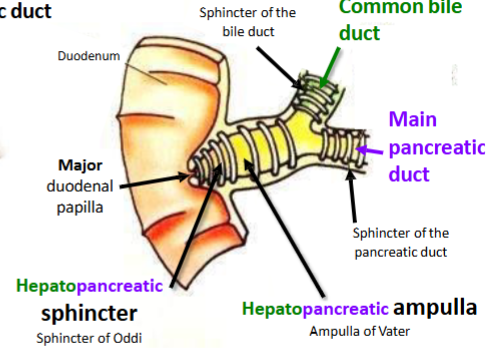
What is a Sphincter
Defined as a ring of muscle surrounding and serving to guard or close an opening
Name a sphincter associated with the pancreas
Hepatopancreatic sphincter - Sphincter of Oddi
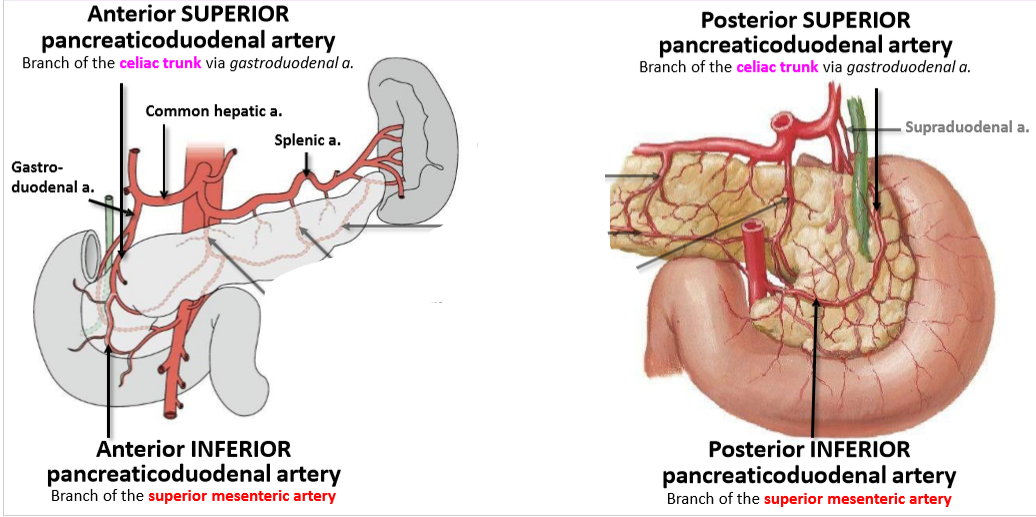
What does the Dual Arterial Supply of the pancreas consist of (& what they branch from)
4 in total:
Anterior SUPERIOR pancreaticoduodenal artery - Branch of the celiac trunk via gastroduodenal a.
Anterior INFERIOR pancreaticoduodenal artery - Branch of the superior mesenteric artery
Posterior SUPERIOR pancreaticoduodenal artery - Branch of the celiac trunk via gastroduodenal a.
Posterior INFERIOR pancreaticoduodenal artery Branch of the superior mesenteric artery
The pancreatic veins drain blood from the pancreas and as they are part of what system of veins
the portal system
Pancreatic veins drain where
will first drain to the liver before heading to the heart
What 2 veins merge to form the hepatic portal vein
The splenic vein & The superior mesenteric vein
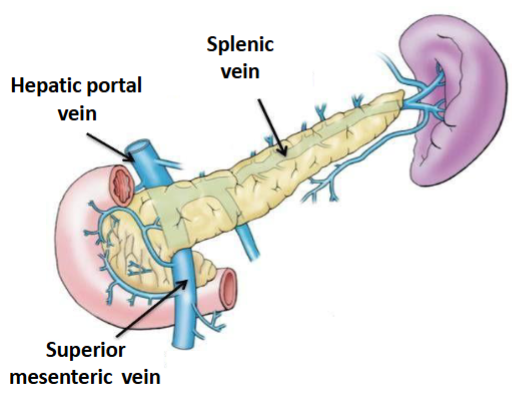
Majority of veins follow the arteries, therefore most veins will drain into what vein
The splenic vein → hepatic portal vein
Some veins, particularly around the head of the pancreas, will drain via the _______
superior mesenteric vein → hepatic portal vein
Pancreas: Summary
Arterial Supply:
Venous drainage:
Lymphatics:
Innervation:
Pancreas: Summary
Arterial Supply: Celiac trunk and Superior mesenteric artery
Venous drainage: Ultimately to the Hepatic portal vein → Portal venous system
Lymphatics: Ultimately drain by following the arteries → Celiac lymph nodes, or → Superior mesenteric lymph nodes
Innervation: Vagus & greater splanchnic
Largest lymphatic organ in the body
Spleen
The spleen is what shape
The spleen is ovoid in shape
The spleen is a pulpy mass in what quadrant
LUQ
The spleen lies on what anatomical line
midaxillary line
The spleen is a retro/intraperitoneal organ
intraperitoneal organ
Roles of spleen
Largest lymphatic organ in the body
Acts as a blood reservoir
Is the spleen a vital organ
No
The spleen is vulnerable to damage when what ribs are hit
Ribs 9, 10, 11
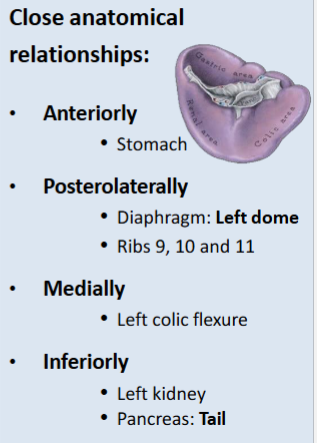
Spleen close anatomical relationships:
Anteriorly:
Posterolateral:
Medially:
Inferiorly:
How does the splenic artery travel to the spleen (in what)
Splenic artery travels in the splenorenal ligament with the tail of the pancreas
Celiac trunk arises from the abdominal aorta at what vertebral level
T12
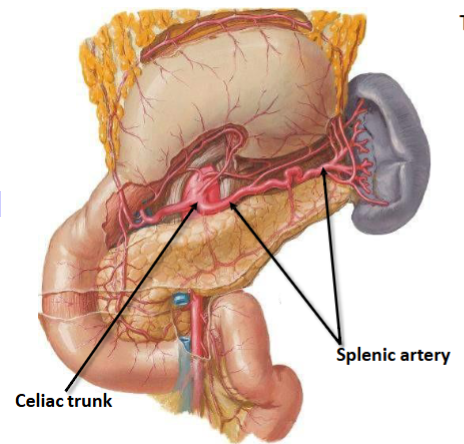
What is the largest branch of the celiac trunk
The splenic artery
Course of the splenic artery (with reference to the pancreas)
Courses along the superior border of the pancreas
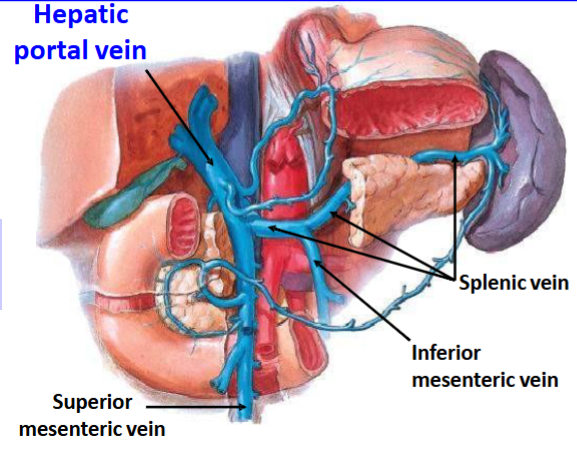
The splenic vein is formed by what
many tributaries that leave the hilum of the spleen
The splenic vein runs __________ to the pancreas
Posterior
Relation of the splenic vein with the superior & inferior mesenteric veins
The inferior mesenteric vein usually drains into the splenic v.
The splenic vein unites with the superior mesenteric vein to form the Hepatic Portal Vein
Spleen summary:
Arterial Supply:
Venous drainage:
Lymphatics:
Innervation:
Spleen summary:
Arterial Supply: Celiac trunk
Venous drainage: Ultimately to the Hepatic portal vein → Portal venous system
Lymphatics: Ultimately drain by following the arteries towards → Celiac lymph nodes
Innervation: Vagus & greater & lesser splanchnics
Boundaries of the Cystohepatic Triangle / Triangle of Calot
Superior border: Inferior border of the Liver
Medial border: Common hepatic duct
Lateral border: Cystic duct
What is a Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder
Why would a Cholecystectomy be done
The gallbladder is not a vital organ, therefore if gallstones have a high risk of reoccurrence and regularly cause severe biliary colic then an individual may elect to undergo a cholecystectomy to remove the gallbladder
Important to identify the cystohepatic triangle in a Cholecystectomy why?
to determine if there is a variation the cystic artery or biliary apparatus
Once identified, the cystic duct and cystic artery are ligated and divided to prevent bleeding and the release of bile
What are Cholelithiasis
small lumps of solid stone-like deposits which form in the gallbladder (gallstones)
How do Cholelithiasis form
Crystals form when there are high concentrations of cholesterol
Who is at risk of gallstones
Individuals who are regularly dehydrated
Relatively common in females
Cholelithiasis are asymptomatic, however, symptoms may include:
• Pain in the right upper quadrant (RUQ)
• Pain may be referred to the right neck/shoulder region
• Nausea
• Cholecystitis → Inflammation of the gallbladder
• Jaundice
Where do Cholelithiasis sometimes become painfully lodged
hepatopancreatic ampulla is a common constriction site where cholelithiasis often become painfully lodged
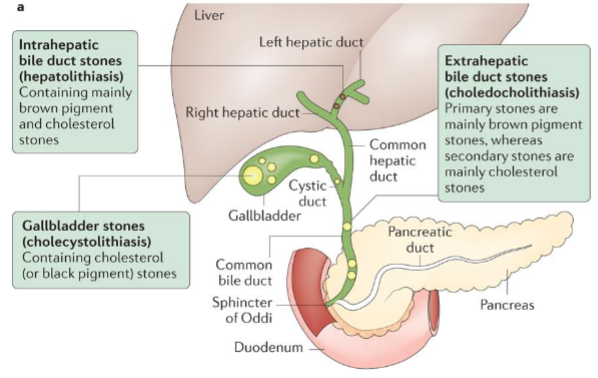
Difference between intrahepatic bile duct stones (hepatolithiasis), extrahepatic bile duct stones (choledocholithiasis) & gallbladder stones (cholecystolithiasis)
most commonly injured abdominal organ
The spleen
Despite being protected by the rib cage, a traumatic blow to the left side may fracture the ribs and result in fragments of bone lacerating the spleen
→ Example could be becoming impacted against the steering wheel during a road traffic accident
If the spleen ruptures, this will lead to
Shock
• Intraperitoneal hemorrhage – profuse internal bleeding
Splenectomy
Surgical removal of the spleen to prevent bleeding to death
Splenomegaly
Pathological enlargement of the spleen (up to 10x normal size) accompanied by high blood pressure
What is bigger ratio wise - liver in adult/liver in embryo
Liver in embryo