xray production
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
decreased or stopped
The production of x-rays requires a rapidly moving stream of electrons that are suddenly …..
cathode
The negative electrode is heated
thermionic emission
the electrons are emitted called
attracted
The electrons are …. to the anode, move rapidly toward the positive electrode, and are stopped or decelerated
deceleration
Sudden ….. of electrons creates x-ray and heat energy
xray tube
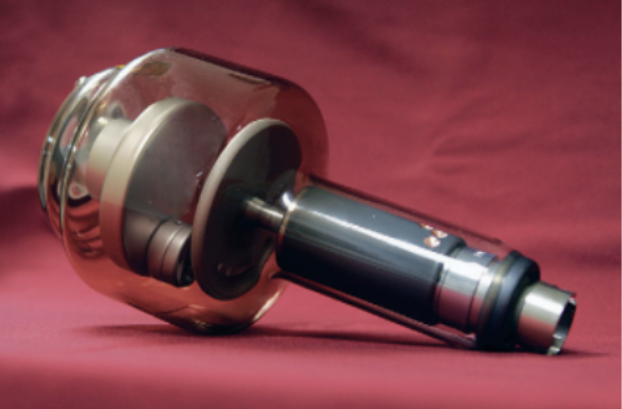

metal or glass
the kind of envelope the xray tube could be
vacuum
interior of the xray tube
cathode
negatively charge electrode
anode
positively charged electrode
coiled tungsten wire
cathode is made this type of wire
small and large
size of the two coiled wires in the cathode
cathode
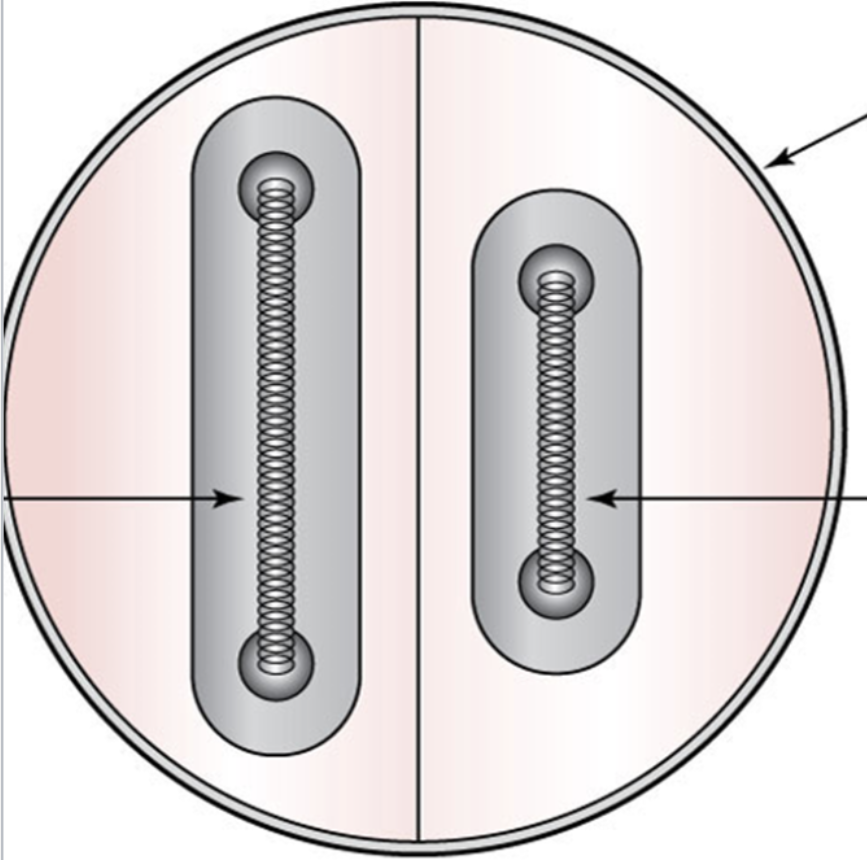
space charge effect
when there is cloud of excess electrons coming out of the cathode
focusing cup
focuses the stream of electrons from the filament toward the anode target
anode
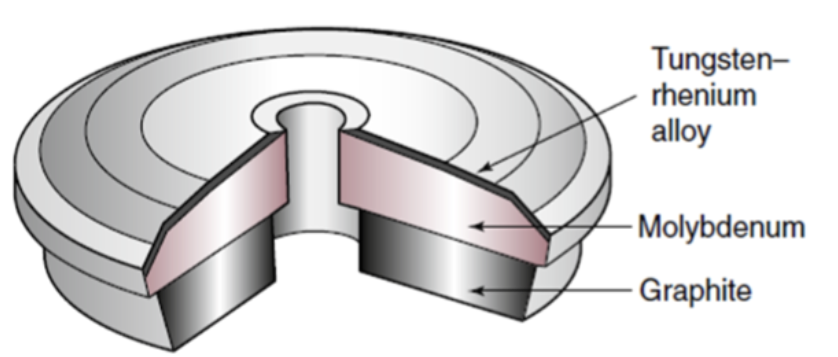

rotates
the anode …
stator, rotor
the rotation anode requires a …. and a …. to rotate
tungsten
anode is made of
melting point
tungsten has a high ….
target
decelerates the anode and stops electrons
xrays
energy gets converted to heat and
focal spot
area hit by electrons on the anode
electron bombardment
…. creates very high heat production
heat tolerance
a moving anode surface permits greater
50,000-150,000
xray production is high voltage process with a range of what volts
W=IxV
electrical power expressed in kW
high voltage and low voltage
2 main divisions of the the xray circuit
primary and secondary
high voltage circuits
filament
low voltage circuit
mutual induction and transformer law
transformers used to regulate voltage
step up
transformer that increases voltage and decreases current
step down
transformer that decreases voltage and increases current
autotransformer
controlled by the kVp you select
autotranformer
determines the induced voltage going to the primary side of the high-tension transformer
capacitors
charge storage components and when placed in the circuit with the inverter the stored chargers are released in a sequential fashion that result in a current waveform with a very small voltage fluctuation, known as ripple
diodes
use solid-state, semiconductor materials that permit current flow in only one direction
mutual induction
the process of an electrical current coming into a set of coils on the input side (primary
side) will create an electrical current and voltage in the secondary coil windings, the output side.
circuit
a fixed path that electricity flows through and its purpose is to precisely control the flow and intensity of electrons as they travel through the circuit pathways and components.
rectification
changing alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC)
Resistance
electric friction that inherently impedes the flow of electrons along its pathway.
resistors
regulate the amount of current passing through the cathode filament during exposure and are used to control amperage.
step down transformers
have more core windings on the primary side than on the secondary side and reduce the incoming voltage to a lower value
step up transformers
have fewer core windings on the primary side than on the secondary side and increase the incoming voltage to a higher value
transformer
Regulates voltage in an x-ray system. The ratio of wire windings between the primary and secondary sides determines whether the transformer is a step-up or step-down transformer.