Lipids and Lipoproteins
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
organic substances that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic substances
“like dissolves like”
ether or chloroform > organic solvents
lipids cannot be directly distributed > use lipoproteins to transport lipids
Lipids
Lipids are transported in the blood by major lipoprotein which is (4)
ULTRACENTRIFUGATION - categorized by density
Chylomicrons
VLDL
LDL
HDL
Rich source of energy and efficient way to store excess calories > fats
provide stability to the cell membrane > phospholipids
also a precursor of steroid hormones > estrogen testosterone
Lipids
Forms of Lipids (5)
arrange according to abundance
phospholipid most abundant and so on
Phospholipids
Cholesterol
Triglycerides
Fatty acids
Fat-Soluble Vitamins - A,D,E,K
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
also known as -
conjugated lipids
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
most abundant form of lipids that originates in the - and -
liver
intestine
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
With similar structure as - except that two fatty acids and a phosphate group is attached to -
triglycerides
glycerol backbone
*triglycerides have 3 fatty acids and does not have phosphate
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
reference value
150 to 380 mg/dL
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Functions of Phospholipids
→decreases surface tension within the alveolar space, allowing effective gas exchange and prevent alveolar collapse during expiration
Surfactant
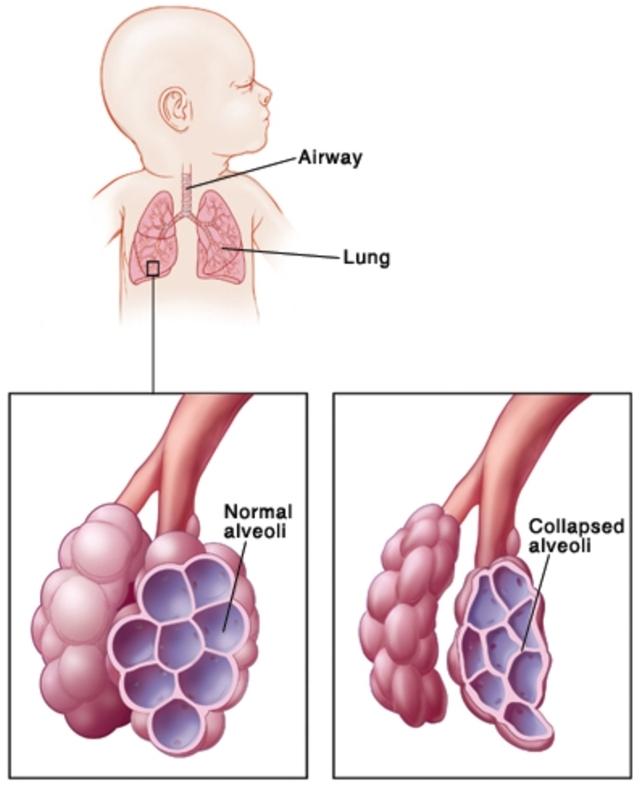
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Functions of Phospholipids
→participate in - and -
cellular metabolism and blood coagulation
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Functions of Phospholipids
→important substrates for lipoprotein-metabolizing enzymes like (2)
LCAT > Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase
LPL > Lipoprotein lipase
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Functions of Phospholipids
→ Deficiency of surfactant lead to -
neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Forms of Phospholipids (3)
Lecithin / Phosphatidylcholine - 70%
Sphingomyelin - 20%
Cephalin - 10%
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Forms of Phospholipids
→is the only phospholipid in membranes that is not derived from glycerol but from an amino alcohol
Sphingomyelin
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Forms of Phospholipids
→amino alcohol from which sphingosine is derived
sphingosine
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Forms of Phospholipids
→Sphingomyelin accumulates in the liver and spleen of patients with _ (lipid storage disorder)
Niemann-Pick Disease
PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Forms of Phospholipids
→Cephalin - 10% (3)
Phosphatidylethanolamine
Phosphatidylserine
Lysolecithin + inositol phosphatide
PHOSPHOLIPID
FETAL LUNG MATURATION
→ estimated from the evaluation of pulmonary surfactant in amniotic fluid
Lecithin/Sphingomyelin (L/S) Ratio
PHOSPHOLIPID
FETAL LUNG MATURATION
→Method for estimating Lecithin/Sphingomyelin (L/S) Ratio
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) followed by densitometric quantitation
PHOSPHOLIPID
Phospholipids can be measured in disorders characterized by - and -
altered phospholipids cmposition and lipoprotein distribution
CHOLESTEROL
also known as -
3-hydroxy-5,6-cholestene
CHOLESTEROL
synthesized in the - and is found on the surface layer of -
liver
lipoproteins
CHOLESTEROL
not catabolized by most cells, not a source of -
fuel
CHOLESTEROL
transport and excretion is promoted by _
estrogen
CHOLESTEROL
reference value
<200 mg/dL (desirable)
CHOLESTEROL
Interpretation of Result
200 to 239 mg/dL (borderline)
≥ 240 mg/dL (high cholesterol)
CHOLESTEROL
Functions of cholesterol
→ precursor of major steroids (4)
glucocorticoids
mineralocorticoids
androgens
estrogens
CHOLESTEROL
Functions of cholesterol
→important constituent in the assembly of - and -
cell membranes
bile acids
CHOLESTEROL
Functions of cholesterol
→cholesterol after being converted to - can also be transformed to - in the skin by irradiation from sunlight
7-dehydrocholesterol
vitamin D3
CHOLESTEROL
Diagnostic significance
→evaluates the risk of (3)
atherosclerosis
myocardial infarction
coronary arterial occlusions
CHOLESTEROL
Diagnostic significance
→used as (3) function tests and for - studies
thyroid, liver, renal function tests
DM studies
CHOLESTEROL
Forms of Cholesterol (2)
Cholesterol Ester (70%)
Unesterified/Free Cholesterol (30%)
CHOLESTEROL
Forms of Cholesterol
→found in plasma and serum
→bound to fatty acid
→inactive form with protective property and stored in cells
Cholesterol Ester (70%)
CHOLESTEROL
Forms of Cholesterol
→found in plasma, serum, and RBCs
→active form of cholesterol with cytotoxic property
Unsterified/Free Cholesterol (30%)
CHOLESTEROL
is a detoxification step to reduce the accumulation of free cholesterol
Esterification
CHOLESTEROL
Esterification is a detoxification step to reduce the accumulation of free cholesterol through _
acyltransferases
CHOLESTEROL
METHODS OF CHOLESTEROL DETERMINATION
→_ is measured rather that its forms
Total cholesterol
CHOLESTEROL
METHODS OF CHOLESTEROL DETERMINATION
→TC can be assayed using _ samples
non-fasting
CHOLESTEROL
METHODS OF CHOLESTEROL DETERMINATION
→It increases with - , with women having lower values than men before age -
age
45
CHOLESTEROL
METHODS OF CHOLESTEROL DETERMINATION
→Serum TC increases at - between 45 to 65 years ols
2 mg/dL/year
CHOLESTEROL
METHODS OF CHOLESTEROL DETERMINATION
→Decreased levels of _ among menopausal women contribute to increase of serum cholesterol
estrogen
CHOLESTEROL
METHODS OF CHOLESTEROL DETERMINATION
→specimen:
plasma/serum
CHOLESTEROL
METHODS OF CHOLESTEROL DETERMINATION (2)
chemical method
enzymatic method
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→ Principle:
Dehydration and oxidation of cholesterol to form a colored compound
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→General methods (4)
one-step
two-step
three-step
four-step
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→General methods > ONE-STEP
colorimetry > Pearson, Stern, & Mac Gavack
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→General methods > TWO-STEP
extract + colorimetry > Bloors
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→General methods > THREE-STEP
saponification + extraction + colorimetry > Abell-Kendall
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→General methods > FOUR-STEP
saponification + extraction + colorimetry + precipitation > Schoenheimer, Sperry, Parekh, and Jung
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→Reagents for the steps: (4)
Liebermann-Burchardt > colorimetry
Petroleum ether > saponification
Alcoholic potassium hydroxide > saponification
Digitonin > precipitation
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→Color Developer Mixture (3)
Glacial acetic acid
acetic anhydride
Concentrated sulfuric acid
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→Precautions
Avoid hemolysis > may falsely - total cholesterol
Avoid icteric specimen > causes - to - mg increase in cholesterol/ mg bilirubin above normal
Avoid - contamination
Precise and accurate timing for - must be observed
Avoid hemolysis > may falsely INCREASE total cholesterol
Avoid icteric specimen > causes 5 to 6 mg increase in cholesterol/ mg bilirubin above normal
Avoid WATER contamination
Precise and accurate timing for COLOR DEVELOPMENT must be observed
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→ ABELL-KENDALL (3 steps)
Saponification
Extraction
Colorimetry
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→ABELL-KENDALL
Step 1: Saponification
Reagent
Purpose
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→ABELL-KENDALL
Step 1: Saponification
Reagent > Alcoholic KOH
Purpose > Convert cholesterol esters into free cholesterol and fatty acids
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→ABELL-KENDALL
Step 1: Extraction
Reagent
Purpose
Reagent > Petroleum Ether
Purpose > Separate cholesterol from protein carriers
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - CHEMICAL METHOD
→ABELL-KENDALL
Step 1: Colorimetry
Reagent
Purpose
Reagent > Acetic anhydride
Purpose > Liebermann-Burchardt reaction - colorimetric step, meausres GREEN COLOR absorbance at 410 nm
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→it measures total cholesterol in -
serum/plasma
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→rapid, uses - quantities of sample
→does not require -
microliter quantities
preliminary extraction
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→elevated levels of - can lead to low Total Cholesterol
ascorbic acid
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→Chromogen:
Phenol + 4-aminoantipyrine
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→ Hemoglobin has a - activity that can diminish the hydrogen peroxide produced in the reaction
pseudo-peroxidase
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→Bilirubin exceeding 5 mg/dL decreases total cholesterol by -
5% to 15%
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→3 steps
Cholesterol esterase
Cholesterol oxidase
Peroxidase
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→Step 1: Cholesterol esterase
cholesterol esters →free cholesterol + fatty acids
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→Step 2: Cholesterol oxidase
→reacts only to free cholesterol
→free cholesterol + O2 → cholest-4-en-3-one + H2O2
CHOLESTEROL
Methods of cholesterol determination - ENZYMATIC METHOD
→Step 3: Peroxidase
H2)2 + phenol + 4-aminoantipyrine → quinoneimine dye + H2O
CHOLESTEROL
CDC REFERENCE METHOD (2)
Abell, Levy, and Brodie Method
Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS)
CHOLESTEROL
CDC REFERENCE METHOD - ABELL, LEVY, and BRODIE METHOD
→uses hexane extraction after hydrolysis with alcoholic - followed by reaction with - color reagent
→end color:
→uses hexane extraction after hydrolysis with alcoholic KOH followed by reaction with LIEBERMANN-BURCHARDT color reagent
→end color: GREEN
CHOLESTEROL
CDC REFERENCE METHOD - ISOTOPE DILUTION MASS SPECTROMETRY (IDMS)
→- order method for serum cholesterol developed by NIST
→- method for cholesterol
highest
gold standard
CHOLESTEROL
INCREASED (6)
Hyperlipoproteinemia (Types II, III, V)
Biliary cirrhosis
Nephrotic syndrome
Poorly controlled DM
Alcoholism
Primary hypothyroidism
CHOLESTEROL
DECREASED (5)
Severe hepatocellular disease
Malnutrition
Severe burns
Hyperthyroidism
Malabsorption syndrome
TRIGLYCERIDES
also known as -
triacylglycerol / neutral fats
TRIGLYCERIDES
formed from one - molecule with three - attached via - bonds
glycerol
fatty acids
ester bond
TRIGLYCERIDES
main storage form of - in man > adipose tissue
constitutes - % of stored fat
lipids
95%
TRIGLYCERIDES
when they are metabolized, their _ are released to the cells and converted into energy
fatty acids
TRIGLYCERIDES
their breakdown is facilitated by (4)
lipase
lipoprotein lipase
epinephrine
cortisol
TRIGLYCERIDES
an average person ingests, absorbs, resynthesizes and transports - grams of fat daily
60 to 130 grams
TRIGLYCERIDES
FASTING:
10 to 12 hours
TRIGLYCERIDES
Reference Range:
<150 mg/dL
TRIGLYCERIDES
Interpretation (3)
150 to 199 mg/dL > Borderline high
200 to 499 mg/dL > High TAG
>500 mg/dL > Very high TAG
TRIGLYCERIDES
Diagnostic significance
→evaluates suspected - and measures the body's bility to -
atherosclerosis
metabolize fat
TRIGLYCERIDES
Diagnostic significance
→FASTING TAG of _ > at risk for coronary artery disease
≥ 200 mg/dL
TRIGLYCERIDES
Diagnostic significance
→ are the most important lipids for the managemnet of CAD (2)
TAG
Cholesterol
TRIGLYCERIDES
METHODS
→ Specimen:
Plasma or serum
TRIGLYCERIDES
METHODS
→Interferences (3)
ascorbic acid
bilirubin
hemolysis
TRIGLYCERIDES
METHODS
→TAG level increases to - between 45 and 65 years old
2 mg/dL/year
TRIGLYCERIDES
METHODS
→if processing will be delayed and lipemic serum will be frozeb, the specimen should be - and - before test
warm thoroughly and mixed
TRIGLYCERIDES
METHODS (2)
Chemical Methods
Colorimetric > Van Handel & Silversmith
Fluorometric > Hantzsch Condensation Method
Enzymatic Method
Glycerol Kinase Method
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
>4 Steps
Extraction Phase
Saponification Phase
Oxidation Pahse
Colorimetry
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
→ Step 1: Extraction Phase
Reagent:
Purpose:
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
→ Step 1: Extraction Phase
Reagent: CHLOROFORM
Purpose: Separates TAG from protein carrier
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
→ Step 2: Saponification Phase
Reagent:
Purpose:
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
→ Step 2: Saponification Phase
Reagent: Alcoholic KOH
Purpose: Hydrolysis; divides TAG to fatty acids and glycerol
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
→ Step 3: Oxidation Phase
Reagent:
Purpose:
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
→ Step 3: Oxidation Phase
Reagent: Sodium Periodate
Purpose: Converts glycerol to something that can be measured
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
→ Step 4: Colorimetry
Reagent:
Purpose:
TRIGLYCERIDES
CHEMICAL METHOD - Van Handel & Silversmith
→ Step 4: Colorimetry
Reagent: Color reagent
Purpose: Formation of pink color at 410 nm
TRIGLYCERIDES
ENZYMATIC METHOD
→ ALL 3 reactions has initial reaction that uses - and -
lipase & glycerokinase
TAG is converted by lipase into glycerol + fatty acids
Glycerol + ATP is converted by glycerokinase into glycerophosphate + ADP
TRIGLYCERIDES
ENZYMATIC METHOD (Reaction 1)
→ Initial reaction +
Glycerophosphate + O2 is converted by GLYCERPHOSPHATE OXIDASE into dihydroxyacetone + H2O2
Two H2O2 + Phenol + 4-aminoantipyrine is converted by PEROXIDASE into quinoneimine dye + four H2O
TRIGLYCERIDES
ENZYMATIC METHOD (Reaction 2)
→Initial reaction +
Glycerophosphate + NAD is converted by GLYCEROPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE into dihydroxyacetone phosphate + NADH + H4
NADH + tetrazolium dye is converted by DIAPHORASE into formazan + NAD
TRIGLYCERIDES
ENZYMATIC METHOD (Reaction 3)
→Initial reaction + -
ADP + Phosphoenolpyruvate is converted by PYRUVATE KINASE into ATP and pyruvate
Pyruvate +NADH + H is converetd by LACTATE DEHUYDROGENASE into Lactate = NAD+
TRIGLYCERIDES
Clinical Significance
→Decreased (5)
Malabsorption syndrome
Hyperthyroidism
Malnutrition
Burns
Brain Infarction
FATTY ACIDS
major constituents of - and -
triglycerides
phospholipids
FATTY ACIDS
mainly derived from hydrolysis of - in adipose tissues
TAG