2. Limbic System
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the function the limbic system?
Hippocampus, amygdala & more! Regulates emotions, motivation, memory & some behaviors like:
Feeding & thirst
Seeking pleasure & rewards
Forming memories (esp. emotional ones)
Reacting to danger (fight or flight)
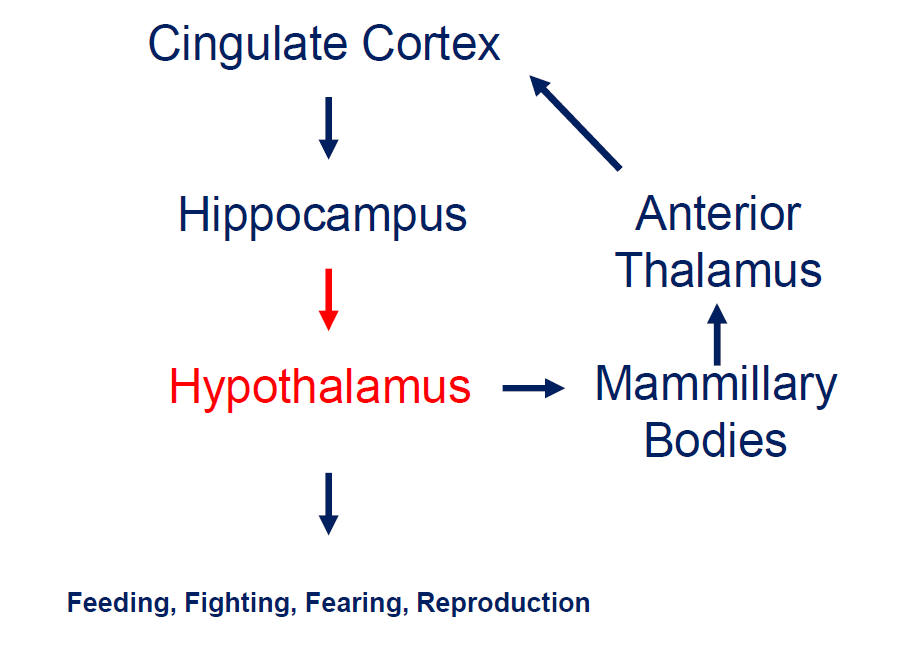
What is the limbic circuit?
What is the function of the cingulate cortex? Anterior vs Posterior?
helps people understand how to alter behavior in a variety of situations, recognize alternatives
PACE - Posterior for Autobiographical & Cognitive, Anterior for Emotion
Posterior cingulate cortex (PCC): Focuses on autobiographical memory, spatial memory, active when dreaming.
Imagine using the PCC to PACE yourself back through your memories and experiences.
Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC): Plays a bigger role in processing emotions, error detection, anticipation of tasks, attention, motivation.
What is the function of the parahippocampal cortex?
important for memory storage, encoding, and retrieval
What structure is the major input to the basal ganglia?
striatum
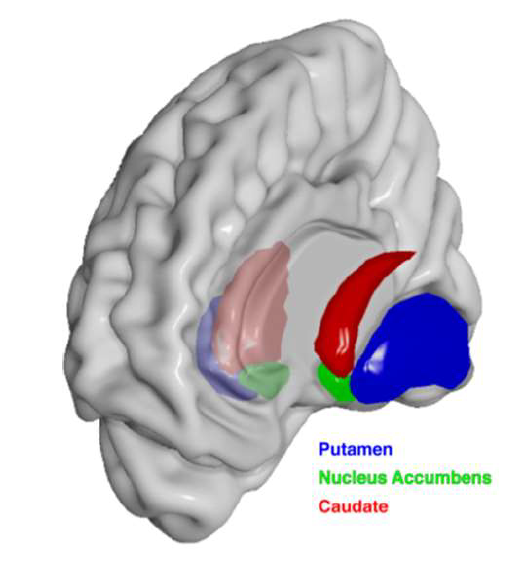
What is the function of the nucleus accumbens (ventral striatum)?
Plays a major role in the brain's reward system, motivating us to seek pleasurable experiences.
Lesion → anhedonia
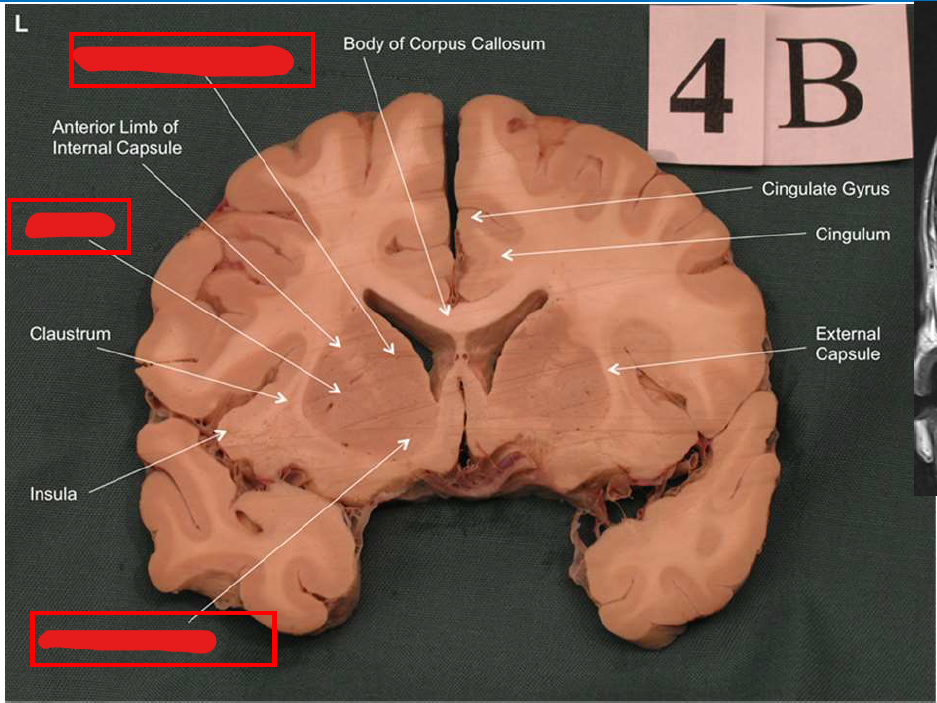
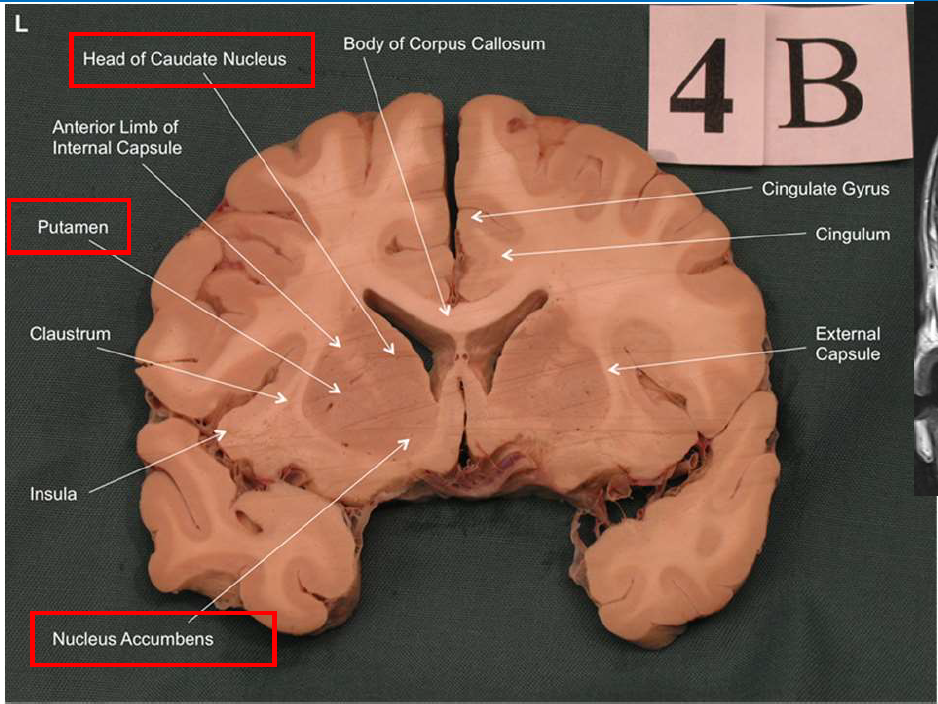
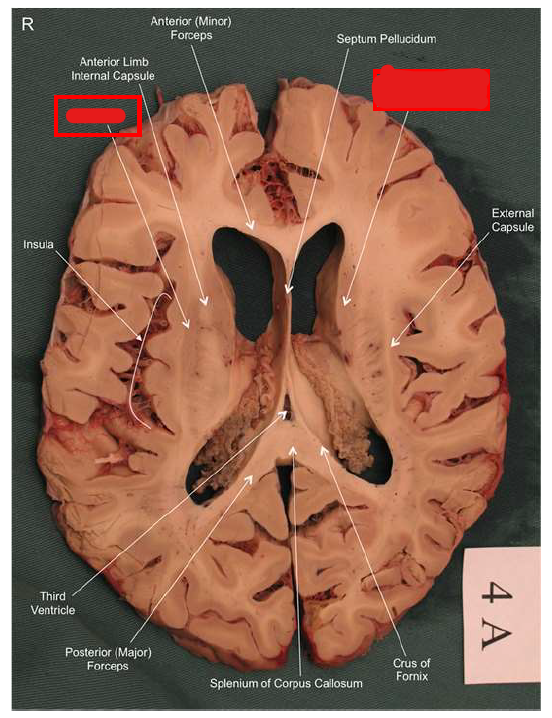
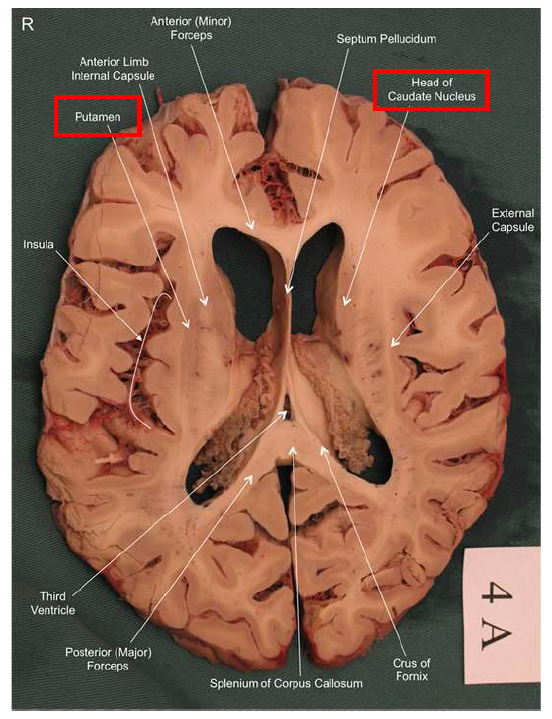
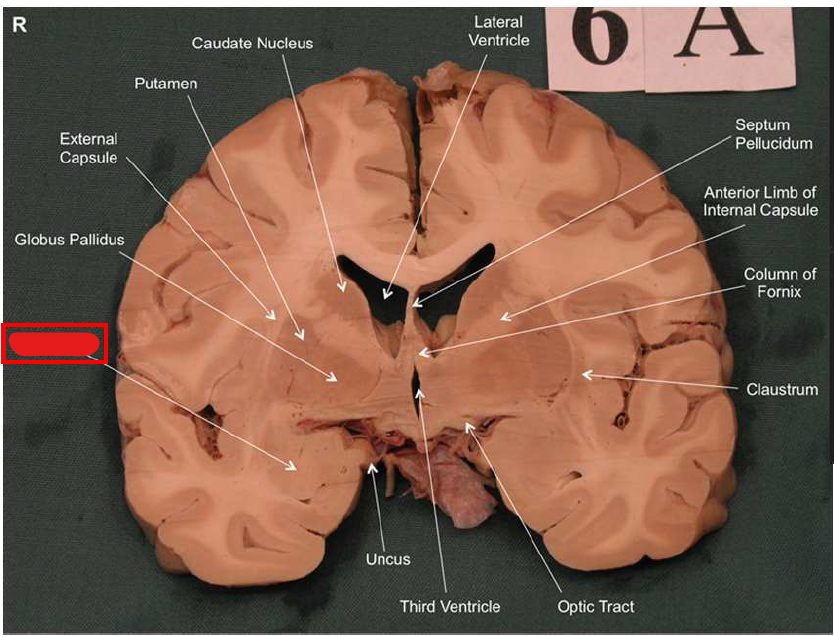
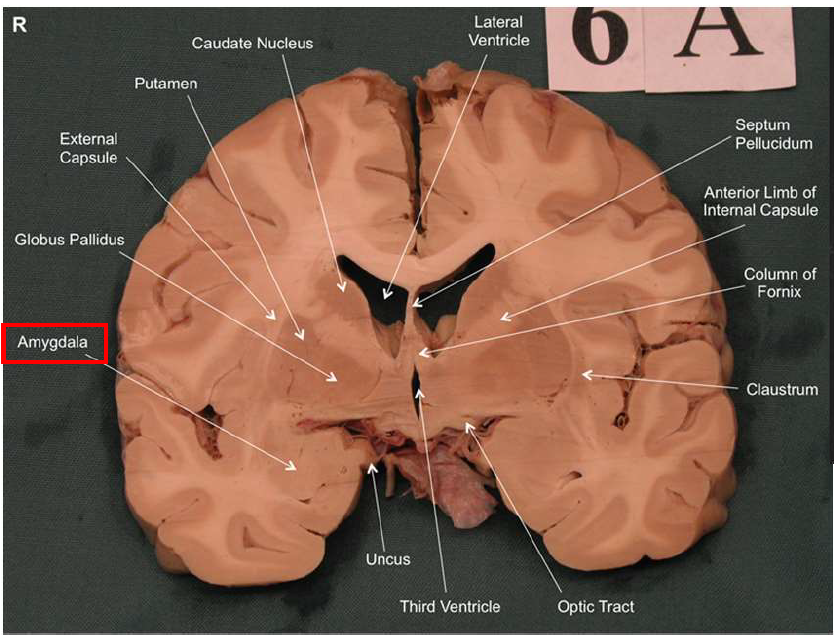
What is the function of the amygdala?
Emotions & Memory Hub
Processes emotions (esp. fear & pleasure)
Helps us remember emotional experiences
Imagine the amygdala as a fire alarm in your brain. When it senses danger (fire!), it triggers the alarm (fight-or-flight response) almost instantaneously and remembers the event vividly (emotional memory)
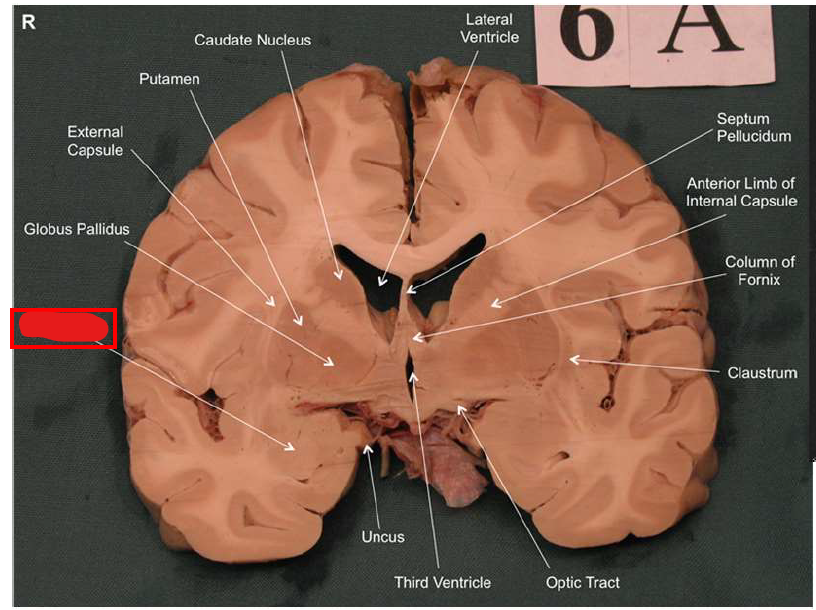
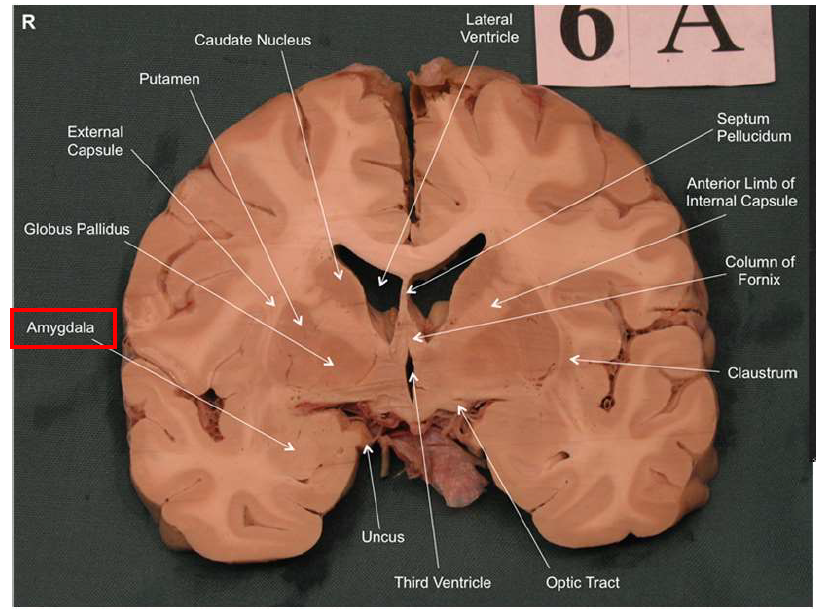
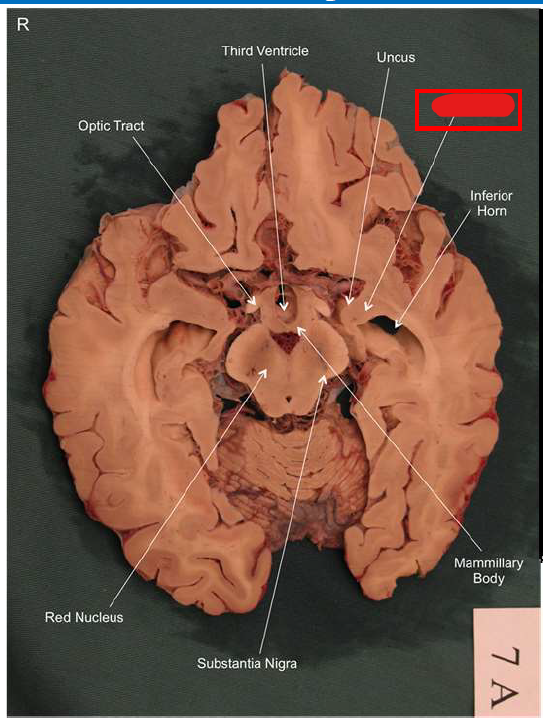
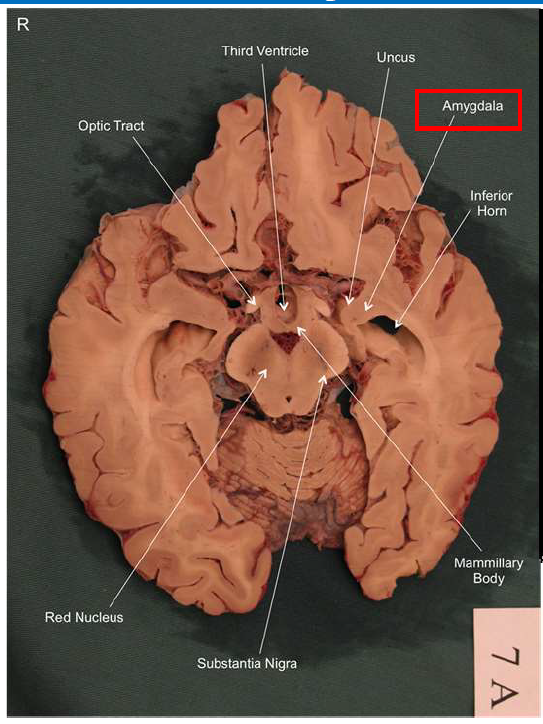
What is the function of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex?
CEO of the Brain!
Working memory (holding info in mind)
Planning & decision-making
Reasoning & problem-solving
Inhibiting impulses & controlling emotions
Attention & focus
Memory control processes that cause confabulation are associated with which part of the brain?
right lateral prefrontal cortex
What is the function of the orbitofrontal cortex?
Judge for Rewards & Decisions
Values rewards (like a critic)
Helps choose best option
Learns from experience
Regulates emotions tied to rewards
What is the function of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex?
Conductor for Social & Emotional Decisions
Makes social judgments and decisions
Processes and regulates emotions (esp. in social situations)
Involved in social reward processing
Contributes to self-perception
Stimulation of _ via the ipsilateral frontal cortex elicits aggression
amygdala
Why do children have less control over their emotions?
axons that send info from cortex to limbic system are not fully developed
neurons of the prefrontal cortex that provide rational control over emotions doesn’t mature until early 20s
What is Kluver-Bucy syndrome?
Rare brain disorder caused by bilateral lesion of the amygdala. Due to lobectomies, encephalitis from Herpes simplex, stroke, or Alzhemier’s. Causes abnormal behaviors and memory problems:
Putting objects in mouth (hyperorality)
Excessive touching of objects (hypermetamorphosis)
Increased sex drive (hypersexuality)
Binge eating/purging (bulimia)
Difficulty recognizing objects (visual agnosia)
Memory problems (amnesia)
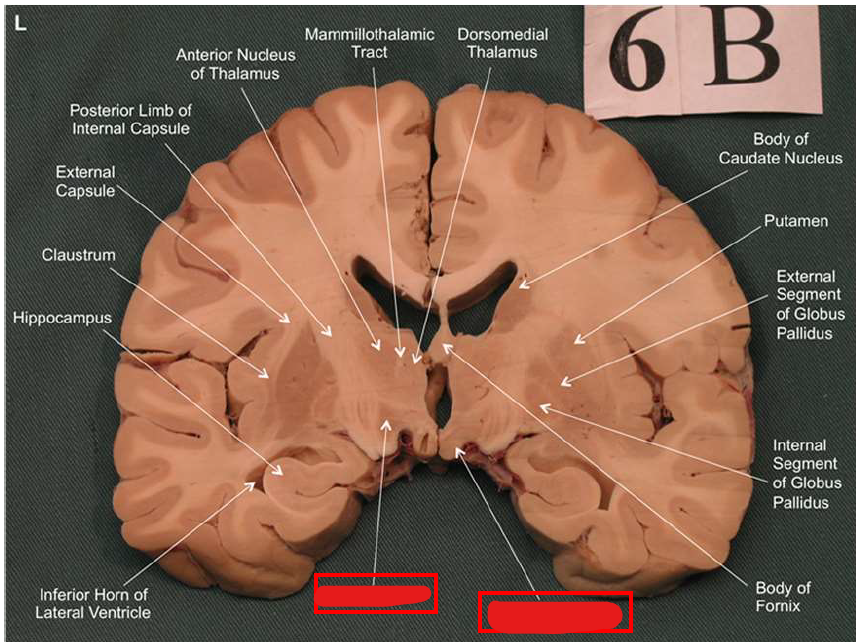
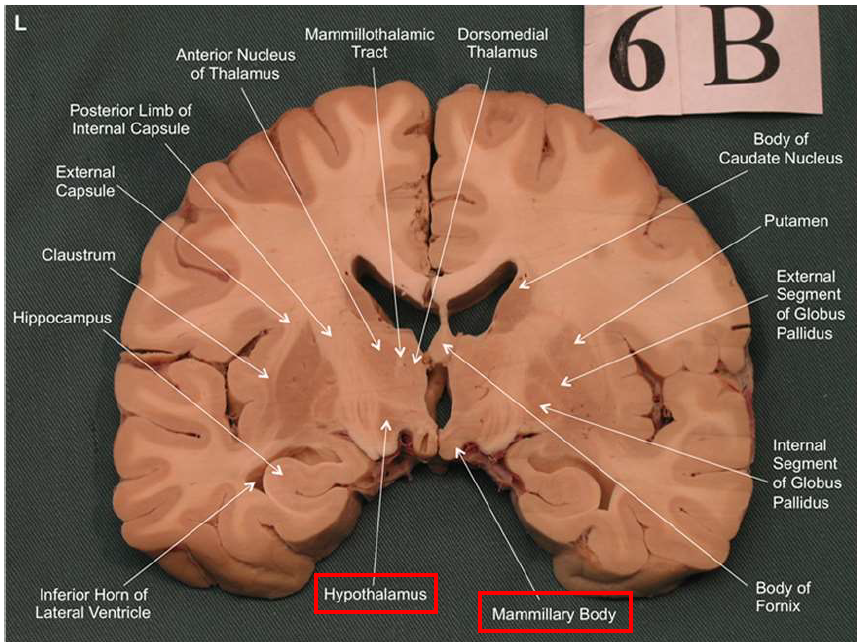
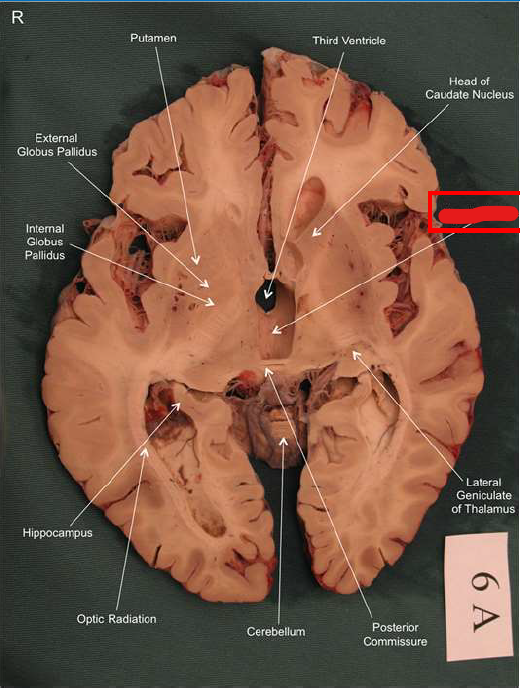
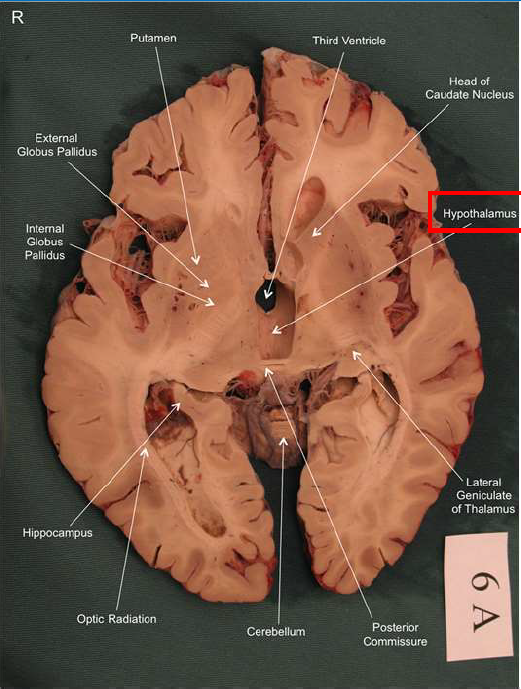
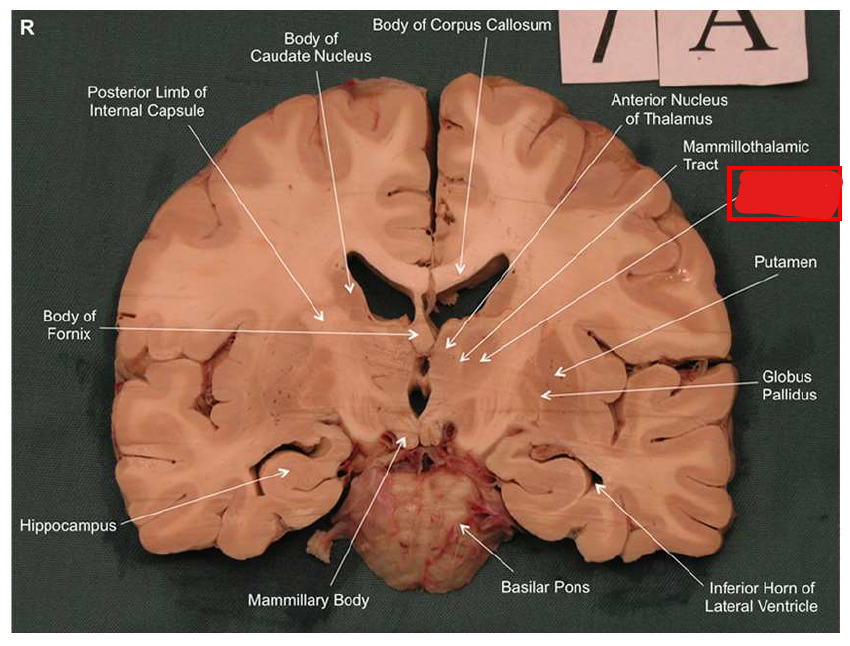
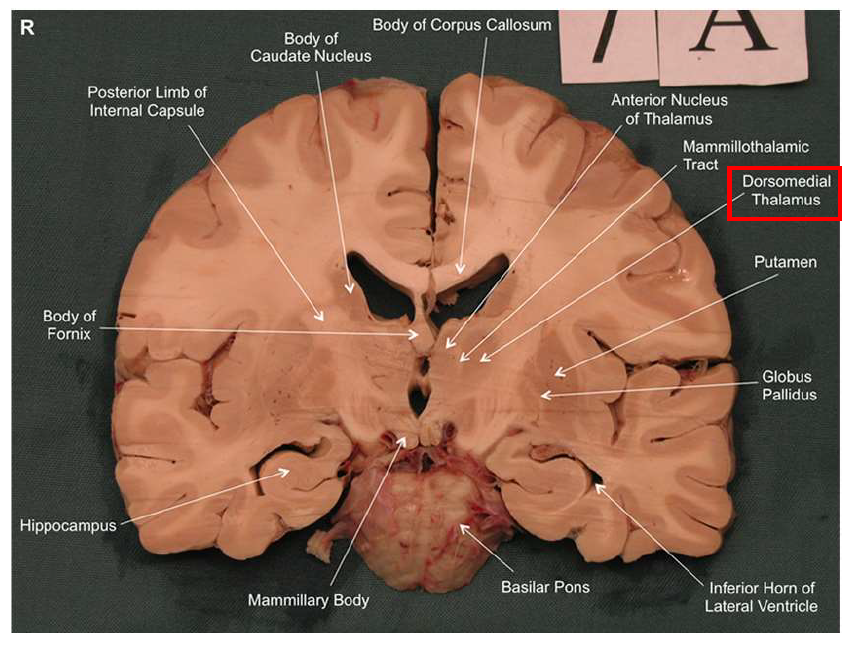
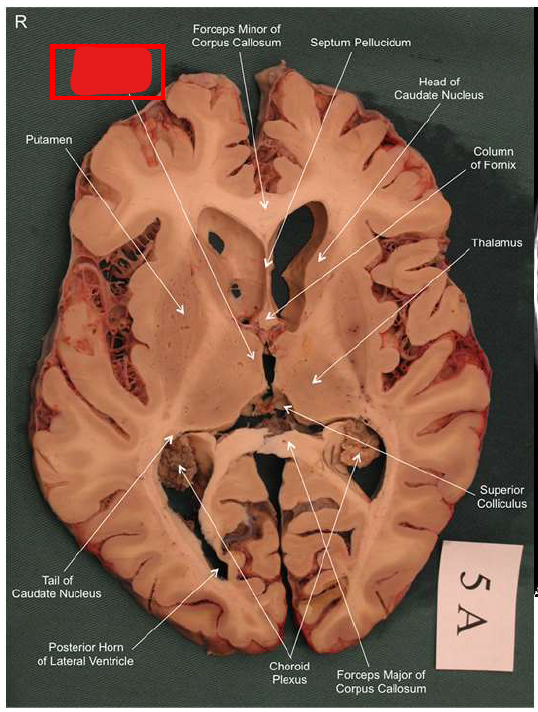
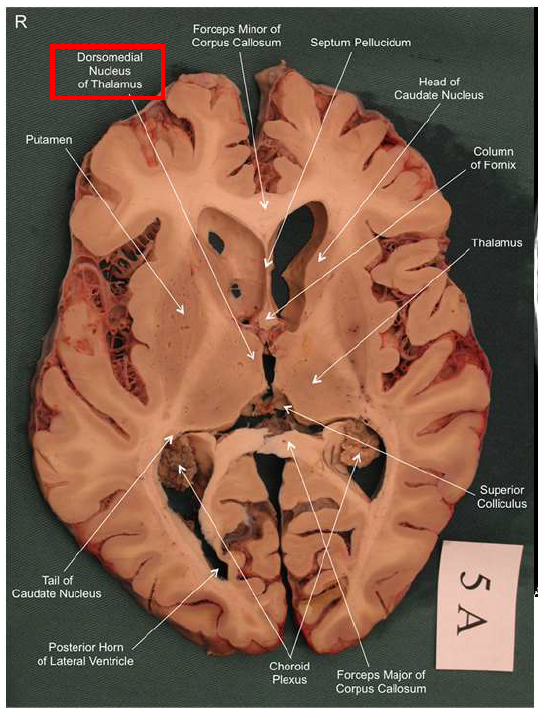
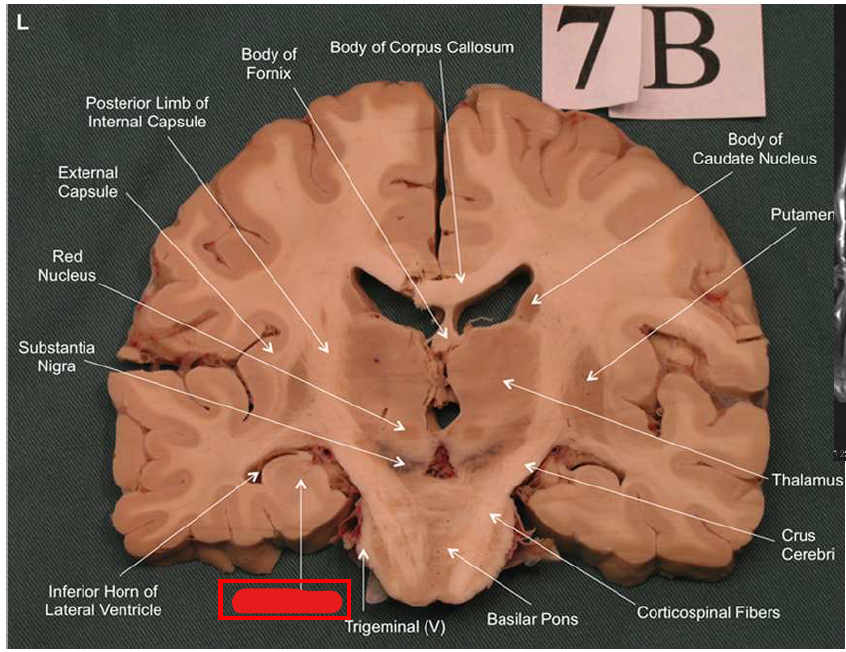
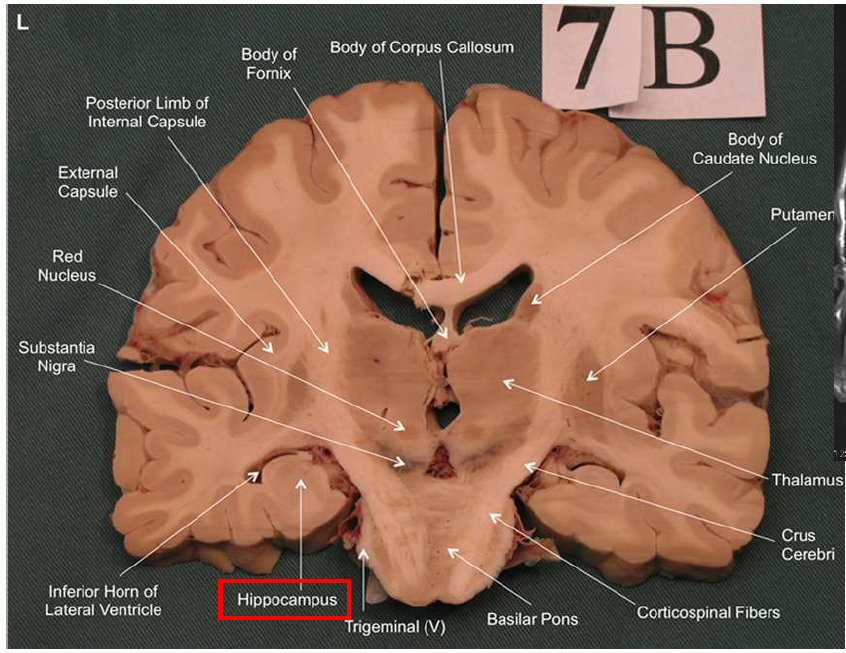
What structure has the function of reducing unpleasant effects of stress, psychological resistance, and formation of new memories?
hippocampus
What is the difference between declarative and procedural memory?
Feature | Declarative Memory | Procedural Memory |
|---|---|---|
Type of information | Facts, events, experiences | Skills and procedures |
Retrieval | Conscious effort | Automatic, triggered by cues |
Examples | Recalling historical dates, remembering birthdays, describing events | Riding a bike, tying shoes, playing an instrument |
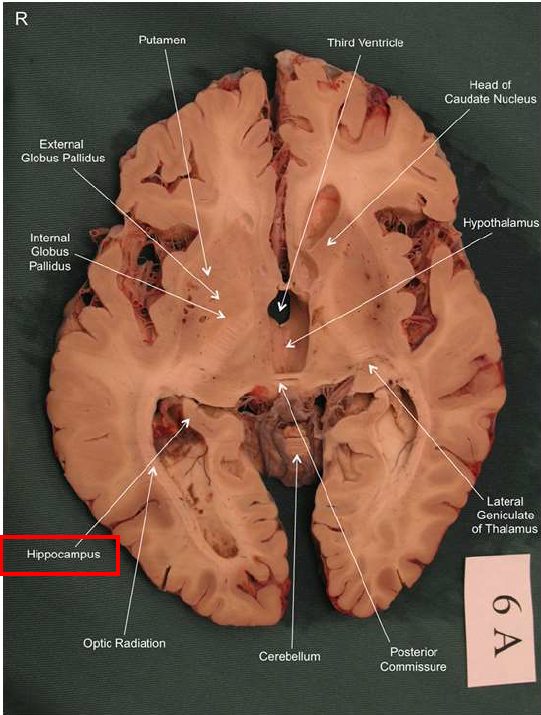
What is the fornix of the hippocampus?
Hippocampus output pathway (C-shaped)
Connects hippocampus to hypothalamus/mamillary bodies
Carries information to and from hippocampus
Important for memory consolidation and retrieval
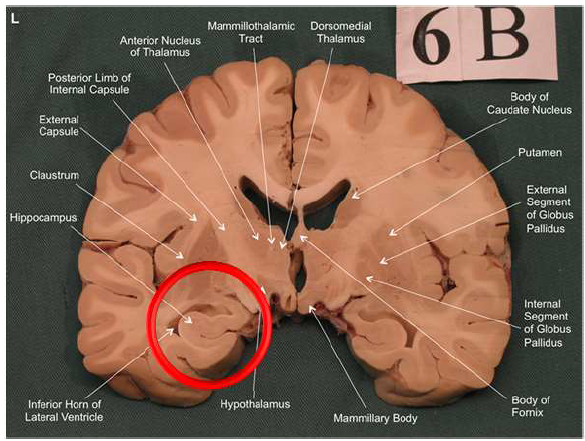
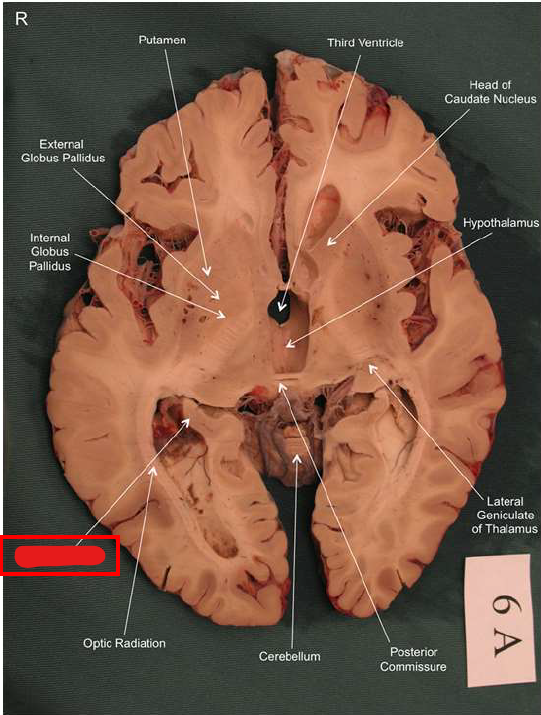
What is this?
hippocampal fornix
How does the hippocampus form memories?
Association areas activate the hippocampus, which reverberates in the Papez circuit until information is stored permanently
Hippocampus → fornix → mamillary bodies → anterior thalamic nucleus → cingulate cortex → hypothalamus
What is Korsakoff syndrome?
Memory disorder from thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency. Often linked to chronic alcoholism.
Symptoms: anterograde amnesia (can't form new memories), confabulation (making up memories), disorientation, apathy.