anatomy 2 midterm 2
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
pulmonary ventilation
air flows between atmosphere and alveoli of lungs
external (pulmonary) respiration
exchange between alveoli and blood in pulmonary capillaries; gain O2 and lose CO2
internal (tissue) respiration
exchange of gas between blood in capillaries and tissue cells; consume O2 and create CO2 (cellular respiration)
upper respiratory system
nose, pharynx, and associated structures
lower respiratory system
larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs
conducting zone
pathway of cavities and tubes outside and inside lungs; nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and terminal bronchioles; NO exchange
respiratory zone
tubes and tissues in lungs where gas exchange happens; bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli
nasal cavity functions
filtering incoming air, detecting olfactory stimuli, modifying speech vibrations passing through nasal sinuses
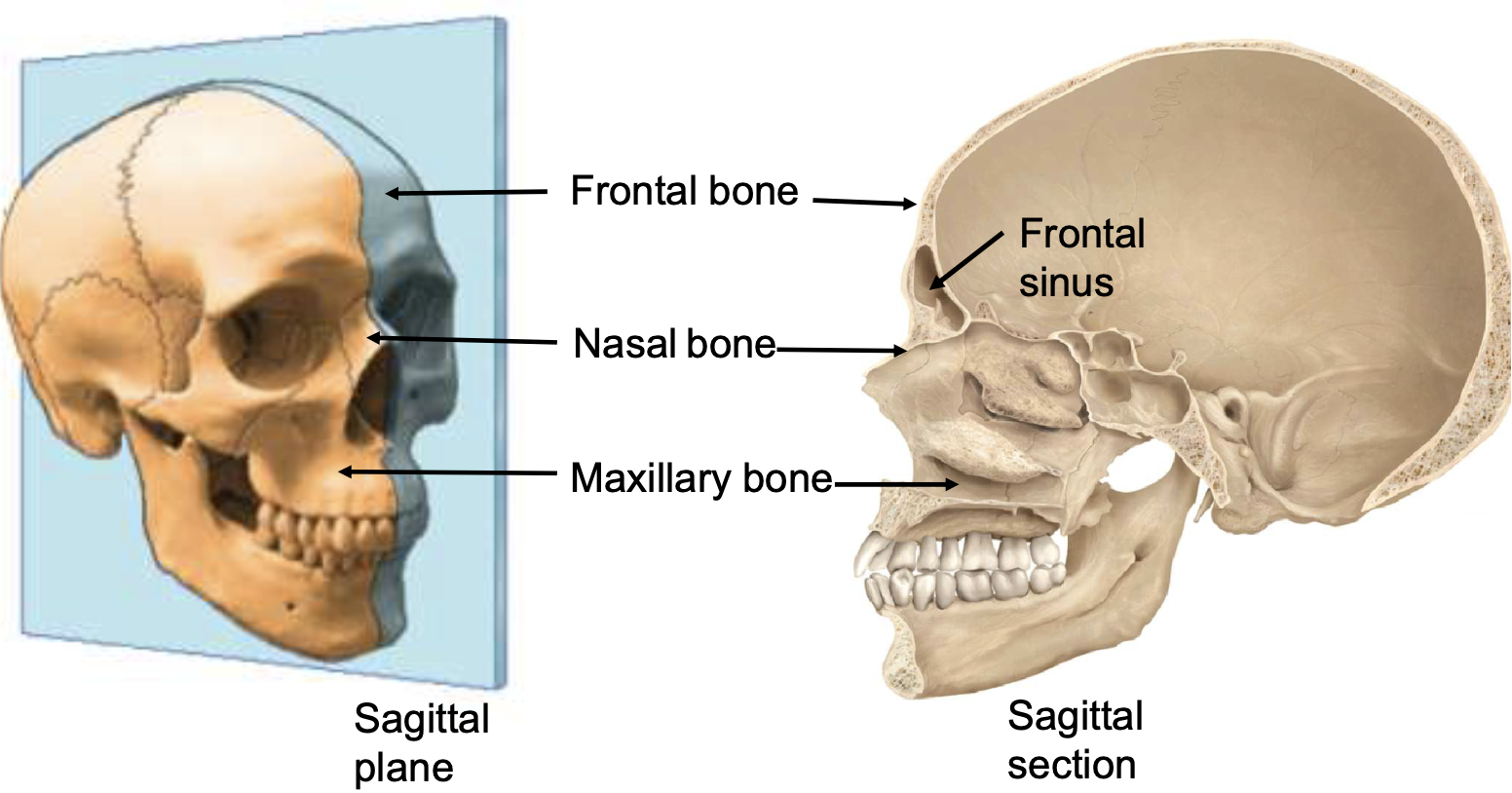
internal anatomy of nose
frontal bone, frontal sinus, nasal bone, maxillary bone
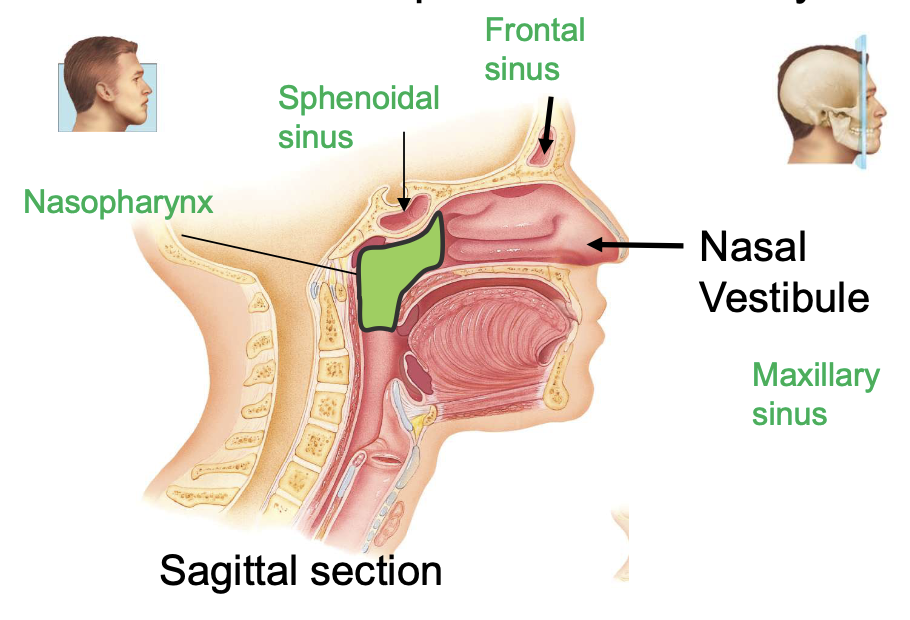
internal portion of nose communicates with
paranasal sinuses and nasopharynx
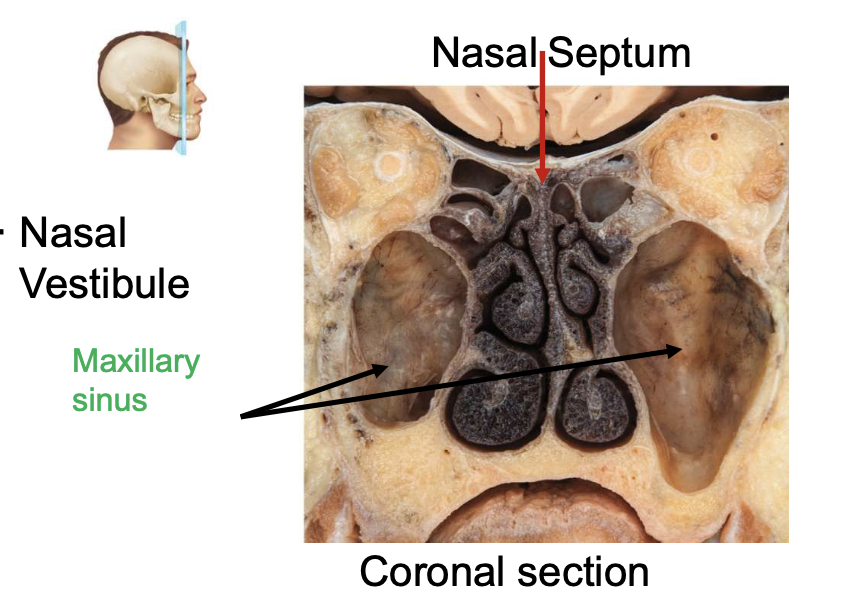
nasal cavity is divided into R and L sides by the
nasal septum
mucous membranes in nose contain [blank] that moisten the air and trap dust particles
goblet cells
drainage from [blank] goes into nasal cavity
nasolacrimal ducts
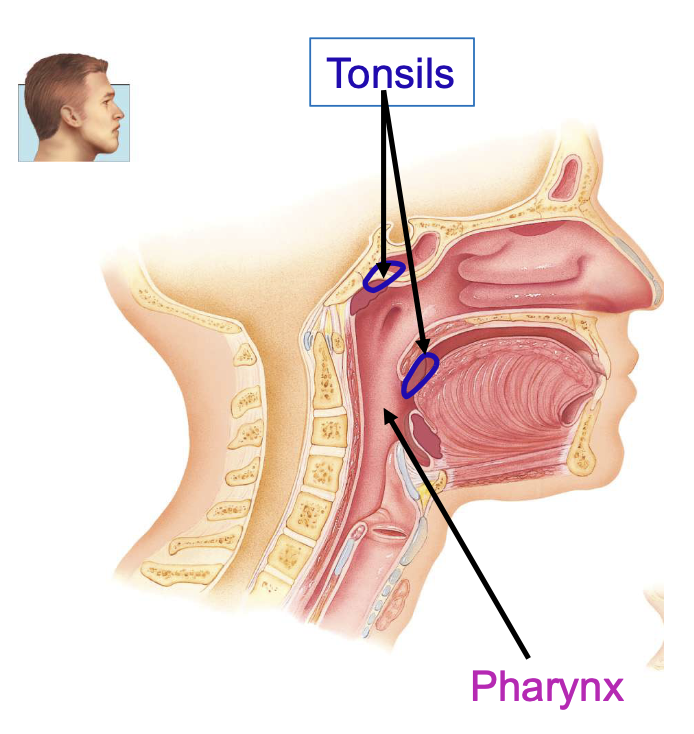
pharynx functions
passageway for air and food, resonating chamber for speech, houses tonsils
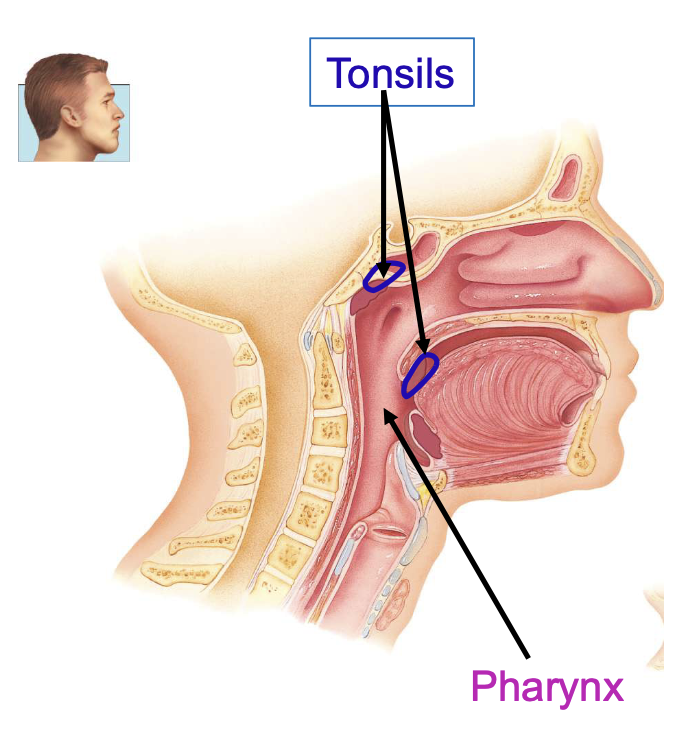
tonsil functions
participate in immunological rxns against foreign invaders
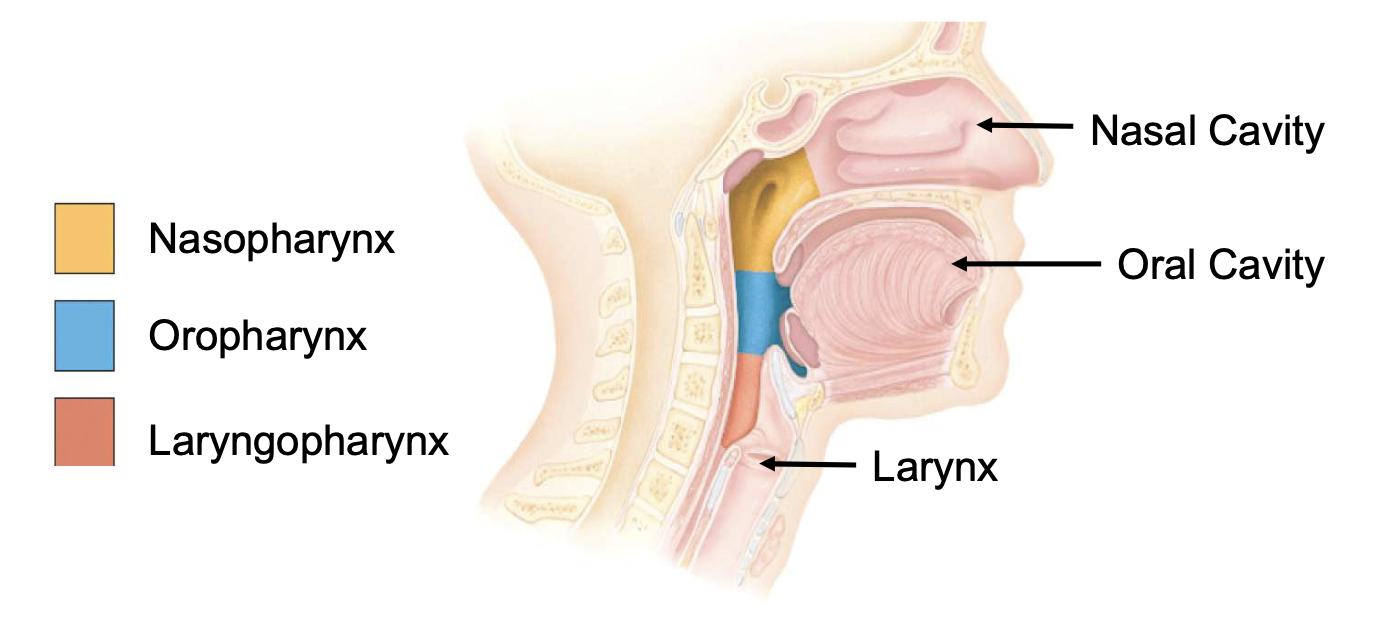
anatomic regions of pharynx
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
larynx parts
thyroid cartilage, epiglottis, cricoid cartilage, arytenoid + corniculate + cuneiform cartilages
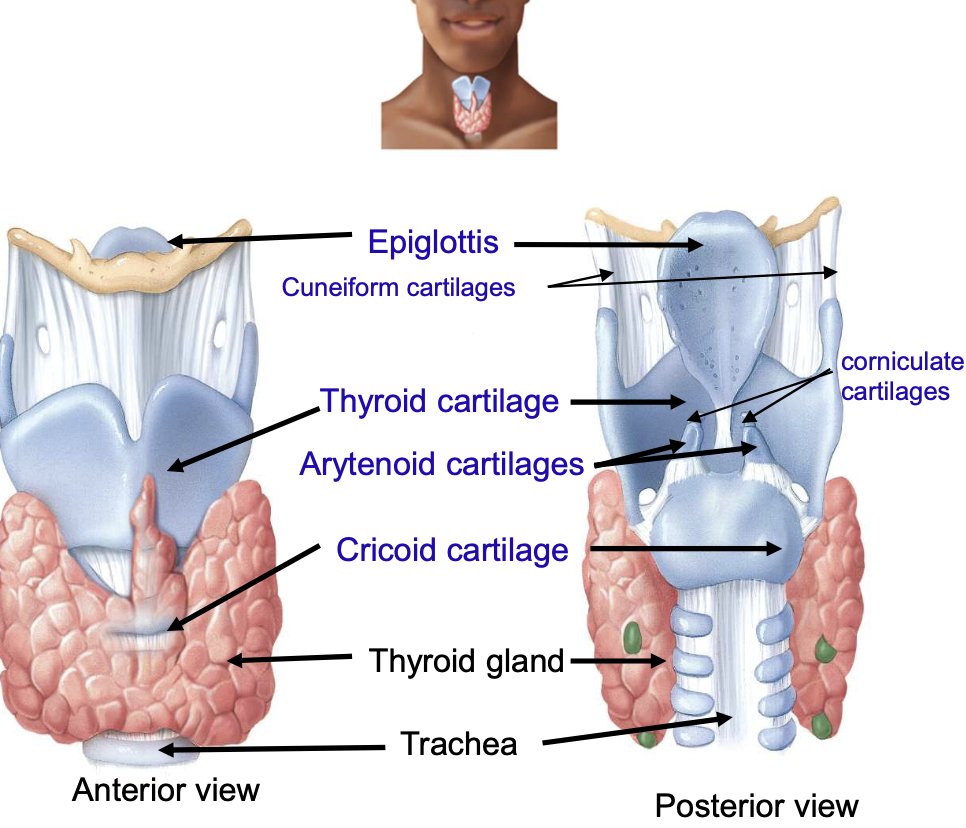
adam’s apple is actually
the thyroid cartilage
epiglottis function
prevent food from entering the larynx
cricoid cartilage connects w/
the larynx and trachea; ring of hyaline cartilage
landmark for tracheotomy
cricoid cartilage
arytenoid, corniculate and cuneiform cartilage purpose
moves vocal cords
larynx contains [blank] which produce sound when they vibrate
true vocal cords
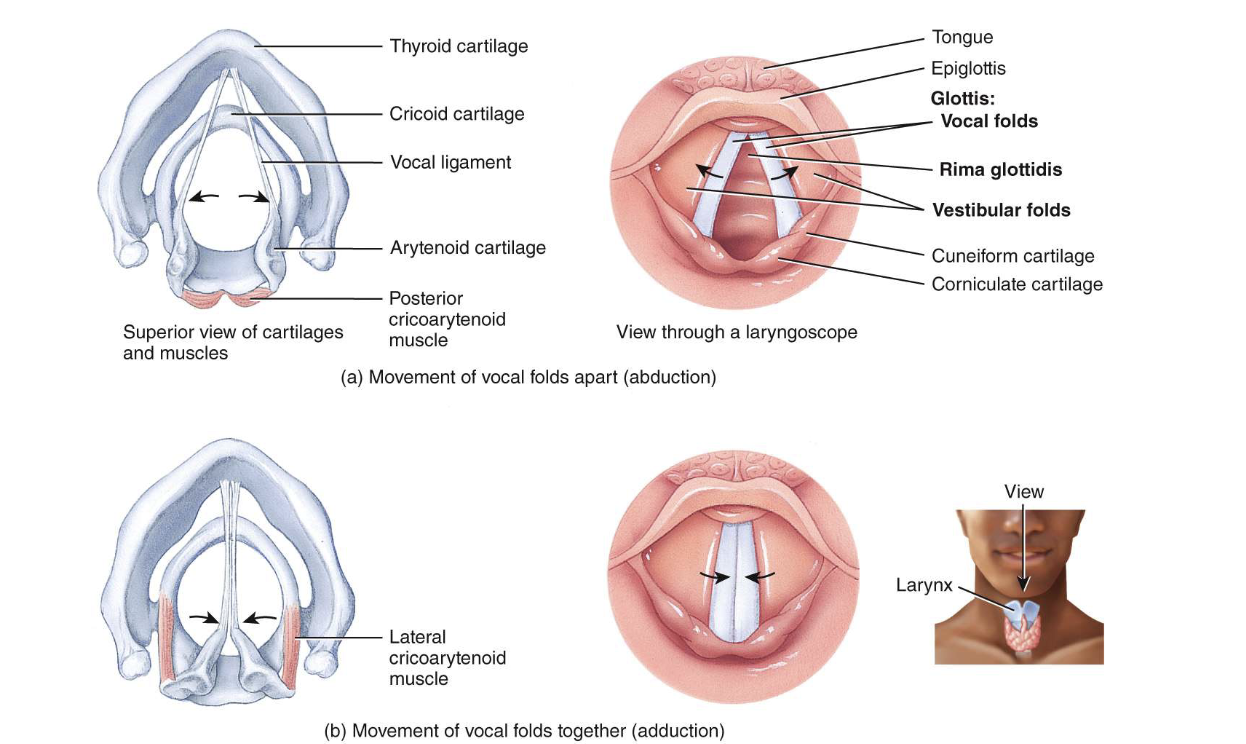
[blank] vocal folds prod. high pitches, [blank] vocal cords prod. low pitches
taunt; relaxed
vocal cords vibrate to make all vocal sounds and voiced sounds like
b, d, g, z
vocal cords do not vibrate for voiceless sounds like
p, t, k , s
your lungs give you air to make every sound, especially [blank] b/c it’s all air
h
laryngitis
inflammation of larynx (acute or chronic)
acute inflammation of larynx can be caused by
respiratory infections or irritants
chronic inflammation of larynx can be caused by
long term smoking
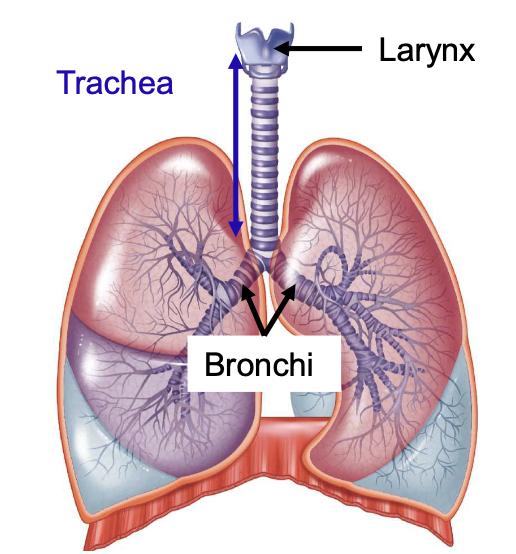
trachea (windpipe) is [blank] to the esophagus
anterior + extends from larynx to the main bronchi

trachea consists of
smooth muscle and c-shaped rings of cartilage, lined w/ pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
c-shapes cartilage rings (tracheal rings)
keep the airway open
endotracheal intubation
machine is breathing for you
tracheostomy
not able to breathe through nasal cavity b/c of blockage
trachea divides into the [blank]
right and left main bronchi
bronchial tree consists of
trachea, main bronchi, lobar (secondary) bronchi, segmental (tertiary) bronchi, bronchioles, terminal bronchioles
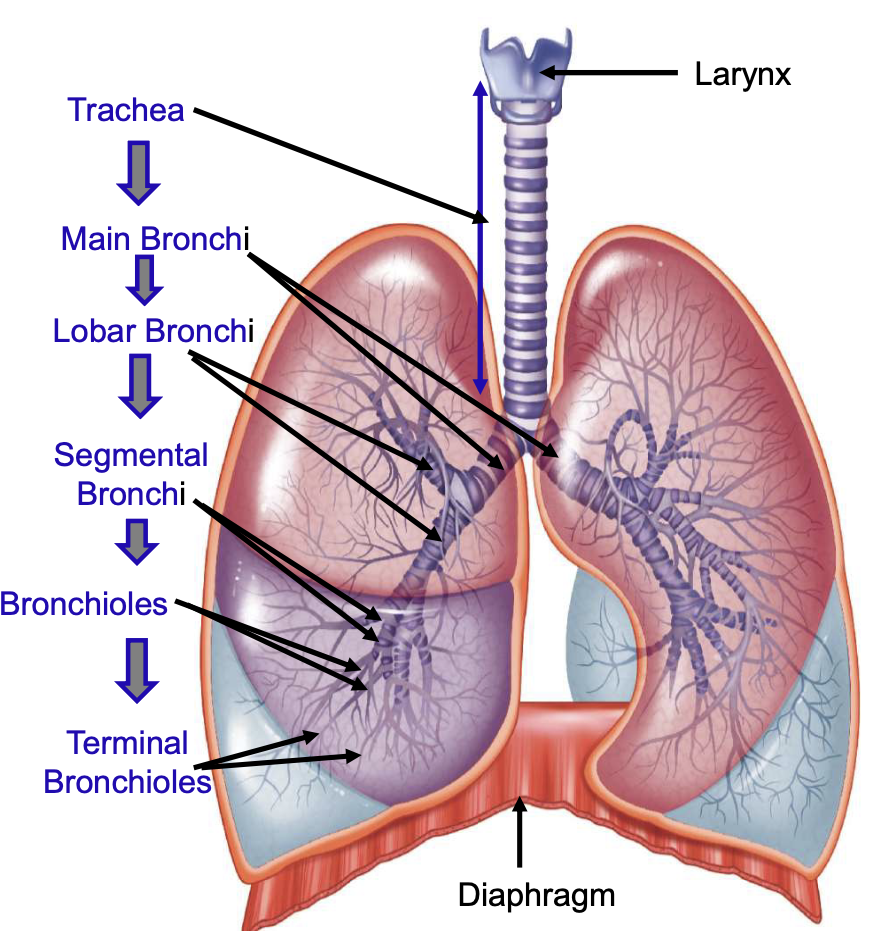
going down trachea, mucus membrane changes from ciliated pseudo stratified epithelium w/ many goblet cells to
non-ciliated cuboidal epithelium in the smallest bronchioles
terminal bronchioles contain [blank] cells among epithelial cells
exocrine bronchiolar (Clara)
Clara cell function
protects against toxins and produce surfactant
c-rings of trachea are replaces by plates of cartilage and eventually [blank] completely in the bronchioles
disappears
as the amount off cartilage decreases, the amount of smooth muscle [blank] in bronchioles
increases
epithelium of respiratory membrane removes inhaled particles by
using mucus prod. goblet cells and using cilia to move mucus and trapped particles to pharynx for removal
in areas w/ conciliated simple cuboidal epithelium, what happens to particles?
they are removed by macrophages
each lung is enclose and protected by a double-layer serous membrane called the [blank]
pleural membrane
outer layer of pleural membrane
partial pleura; attached to wall of thoracic cavity
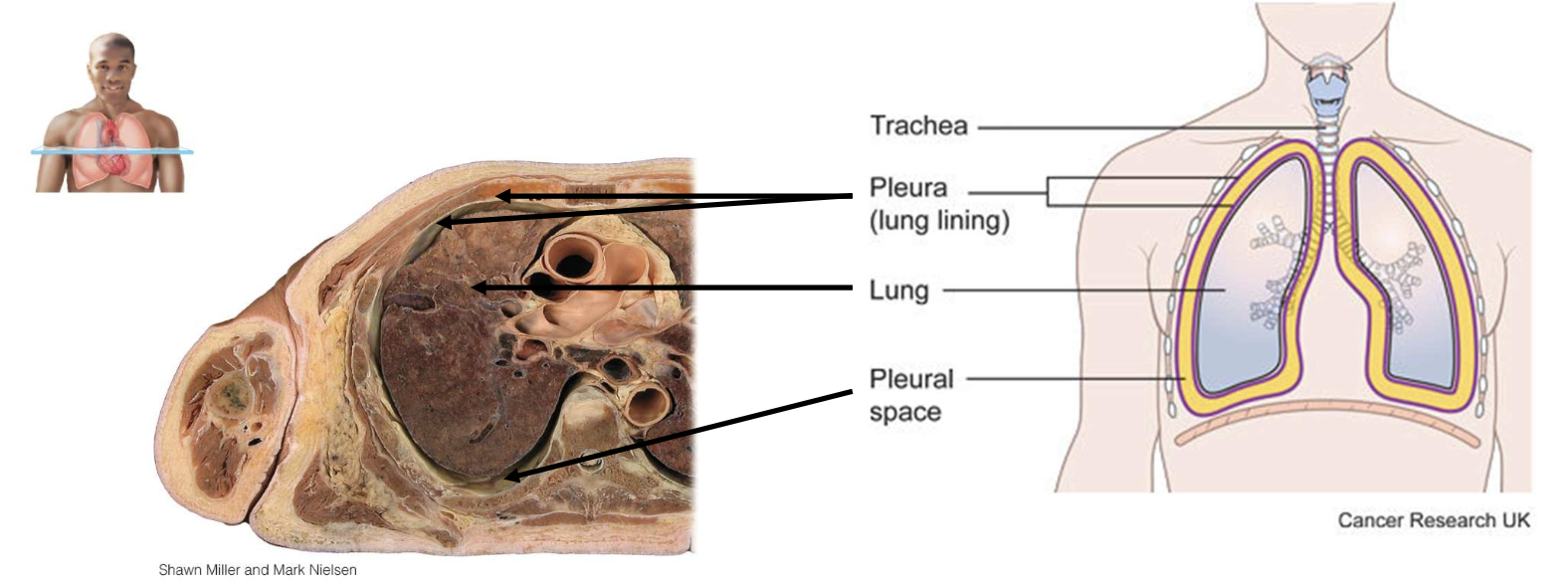
inner layer of pleural membrane
visceral pleura; covering lungs themselves
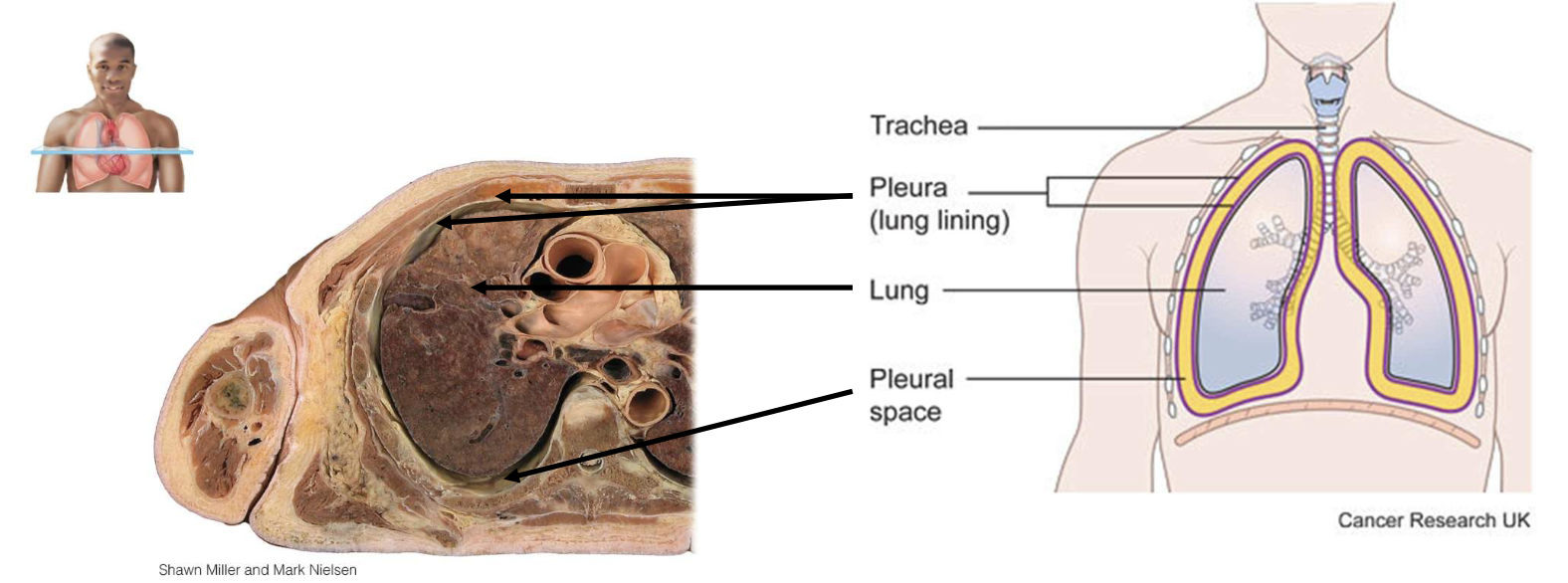
lubricating fluid in pleural cavity
reduces friction between membranes, allowing them to slide easily over one another while breathing
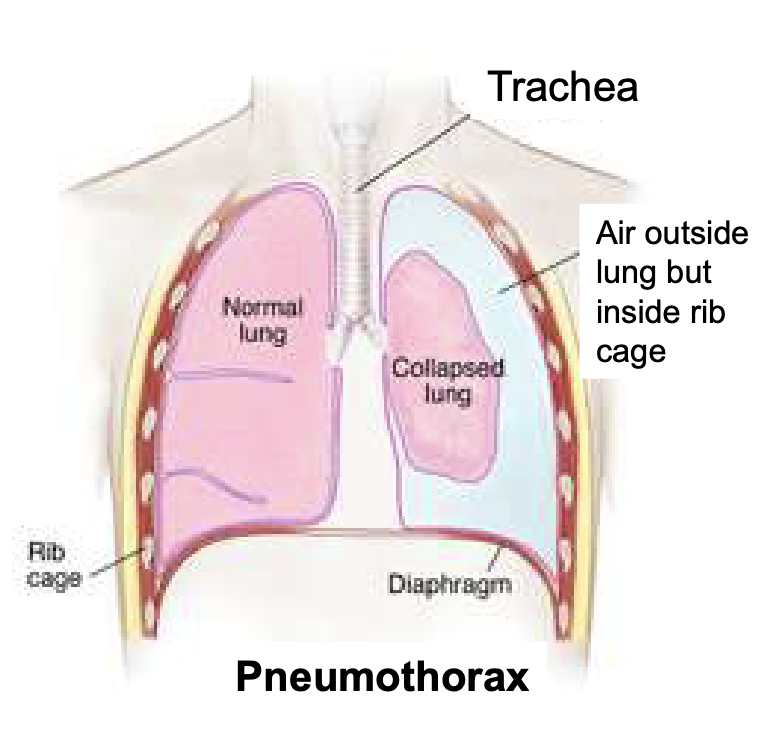
filling of the pleural cavity w/ air due to chest injury
pneumothorax; air entering intrapleural space from outside or from alveoli
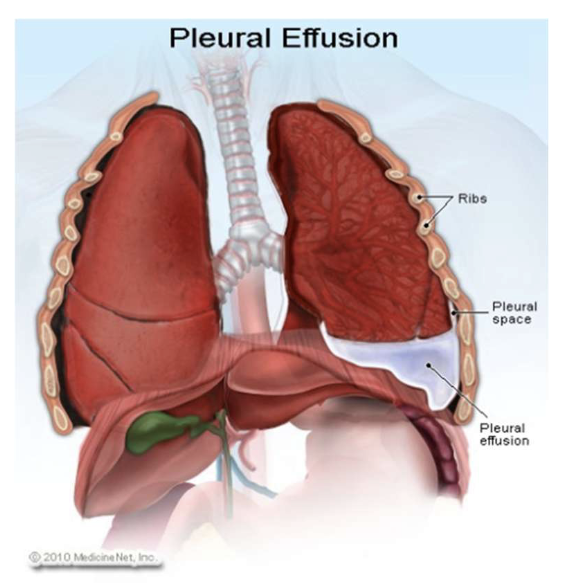
pleural effusion
accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural space
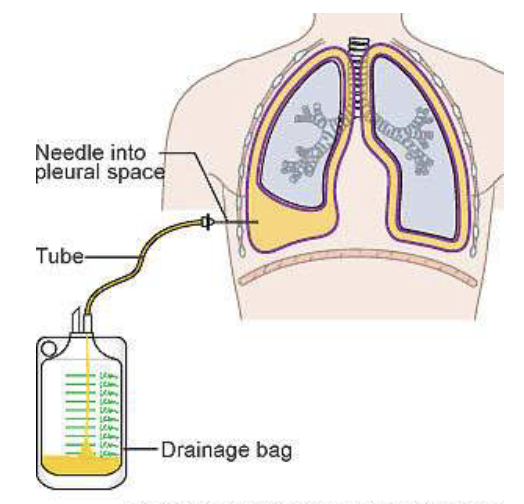
thoracentesis
removal of excessive fluid in pleural cavity w/ a needle
which lung is longer and narrower (R or L)
left lung
which lung is wider (R or L)
right lung
interior portion of the lung
base
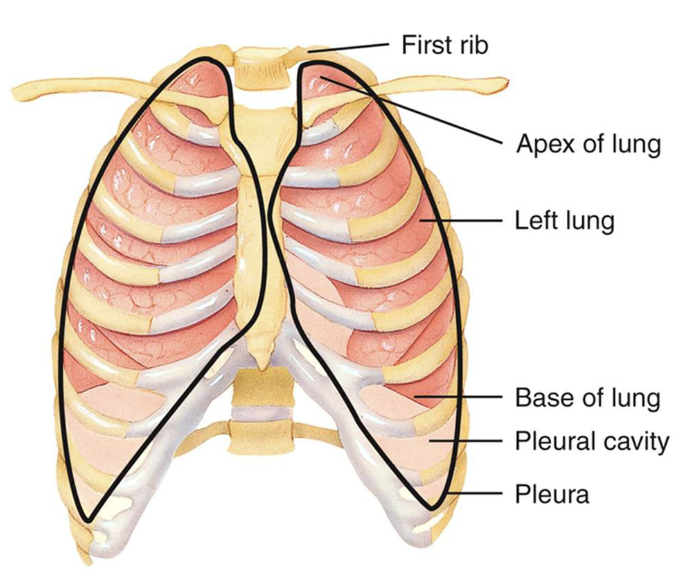
narrow, superior portion of the lung
apex
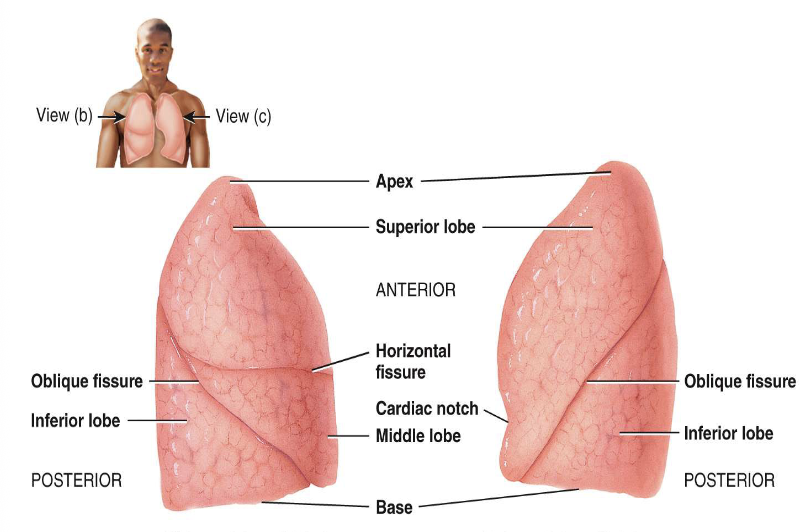
how many lobes and fissures does the right lung have
3 lobes; 2 fissures
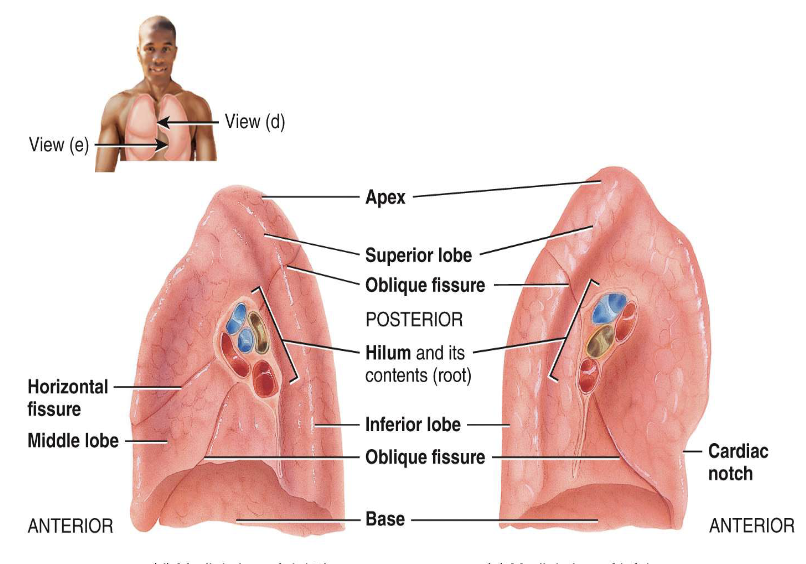
how many lobes and fissures does the left lung have
2 lobes; 1 fissure and a depression (cardiac notch)
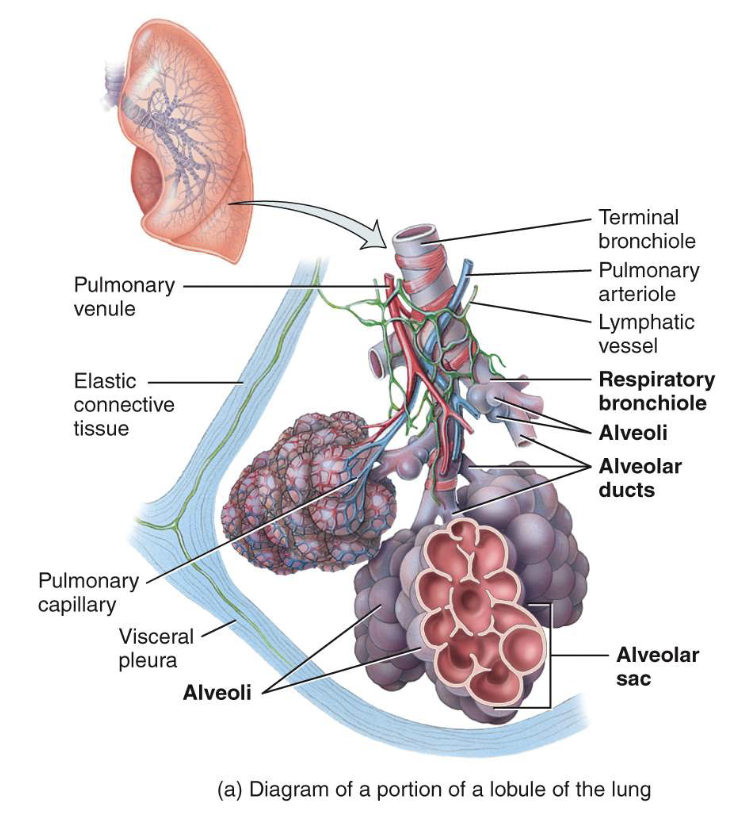
what are lobules
small compartments in a bronchopulmonary segment
lobules contain
lymphatics, arterioles, venues, terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, alveoli
alveolar wall consists of
pneumocyte type I, pneumocyte type II, and alveolar macrophages
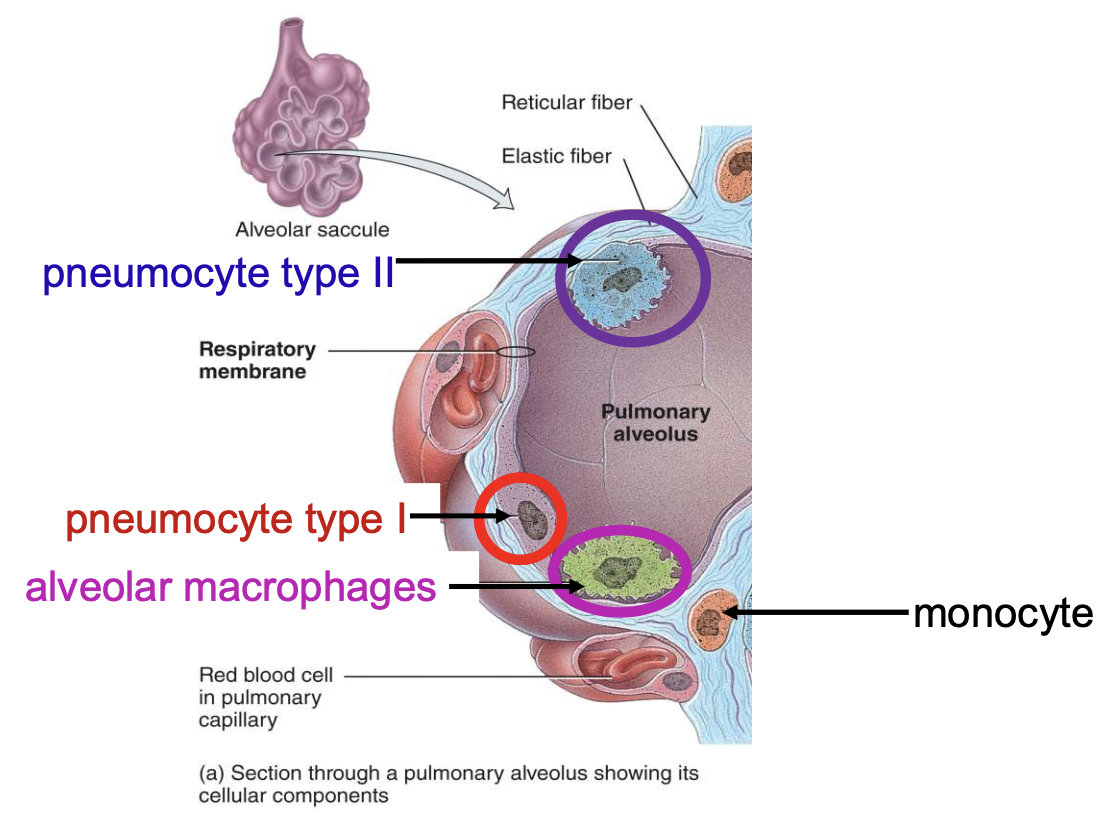
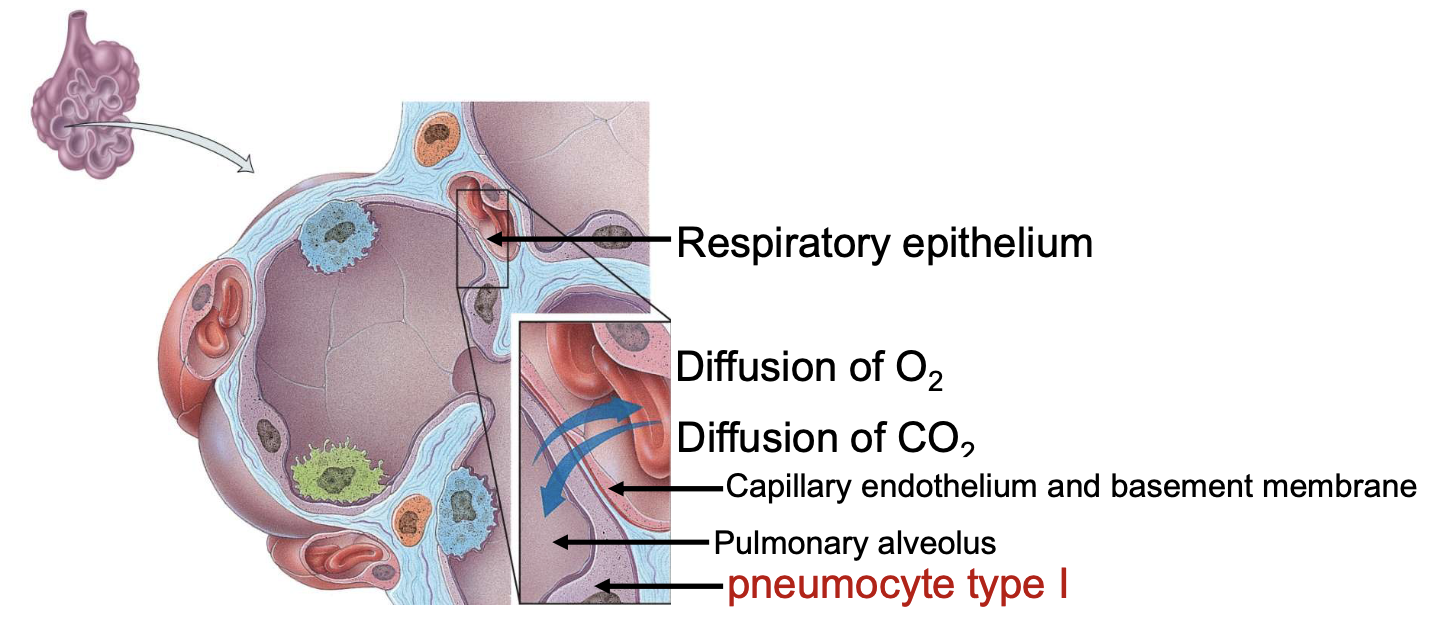
pneumocyte type I is responsible for
gas exchange
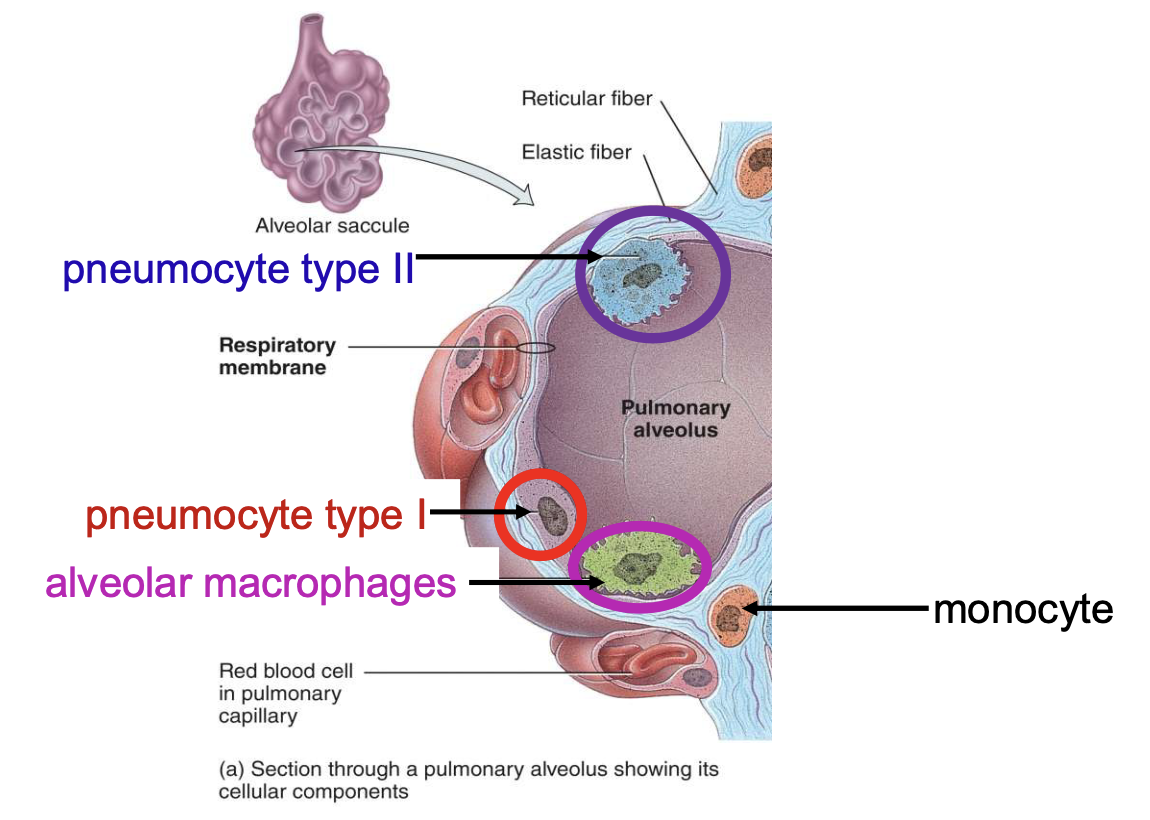
pneumocyte type II is a
surfactant
respiratory membrane is composed of
a layer of pneumocytes (type I and type II) and alveolar macrophages (alveolar wall), an epithelial basement membrane under the alveolar wall, a capillary basement membrane fused to the epithelial basement membrane, the capillary endothelium
what is a surfactant
a mucous membrane that lowers surface tension of alveolar fluid and prevents alveoli from collapsing on top of each other w/ each expiration
blood enters lungs via
pulmonary arteries and bronchial arteries
pulmonary arteries provide [blank] circulation
pulmonary
bronchial arteries provide [blank] circulation
systemic
ventilation-perfusion coupling
lungs perform vasoconstriction in response to hypoxia and diverts pulmonary blood to well ventilated areas
respiration occurs in 3 steps:
pulmonary ventilation, external respiration and internal respiration
pulmonary ventilation (breathing)
inhaling (inflow) and exhaling (outflow) of air; exchange between atmosphere and alveoli
air flows between atmosphere and alveoli b/c of
pressure differences created by contraction and relaxation of respiratory muscles
boyle’s law
pressure more = air volume less, air volume more = pressure less
first step of inhalation
contraction of diaphragm
inhalation occurs when
alveolar (intrapulmonic) pressure falls below atmospheric pressure
diaphragm and external intercostal muscles increases size of thorax, therefore [blank]
decreasing the intrapleural (interthroacic) pressure so lungs expand
expansion of lungs [blank] alveolar pressure so that [blank]
decreases; air moves along pressure gradient from atmosphere into lungs
exhalation occurs when
alveolar pressure is higher than atmospheric pressure
relaxation of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles results in [blank] which [blank]
elastic recoil of chest wall and lungs; increases intrapleural pressure, decreases lung volume, increases alveolar pressure so air moves from lungs to atmosphere