3.7.3 evolution may lead to speciation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What may cause changes in phenotype
Genetic and environmental factors
What may cause genetic variation
Mutations
Crossing over of non-sister chromatids during prophase I
Independent segregation during metaphase 1
Random fertilisation
Independent segregation and crossing over leads to genetic variation of …
Gametes
Random fertilisation leads to genetic variation of…
Zygotes
Mutations lead to genetic variation of…
Individuals within a species
Explain natural selection
Genetic variation means that some organisms will have an advantageous allele which makes them better adapted to survive.
Therefore they pass these favourable alleles onto their offspring
Allelic frequency of favourable alleles increases
Define evolution
The formation of new species from pre-existing species over time, as a result of changes to gene pools and allele frequencies from generation to generation
What are the three types of selection
Stabilising, directional, disruptive
Directional selection
favours individuals with a phenotype at one extreme, causing a shift in a population’s traits over time
Define disruptive selection
Draw the graph
natural selection that maintains high frequencies of two different sets of alleles
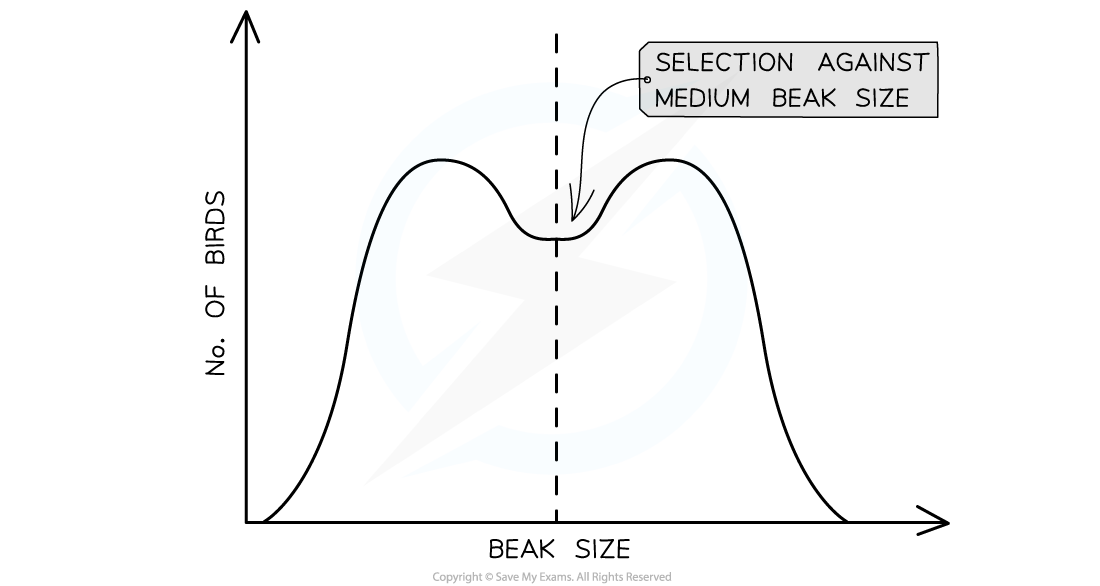
Speciation
The evolution of a new species from an existing one
Reproductive isolation
when changes in alleles or phenotypes prevent certain individuals from breeding successfully with others in the same population
What is allopatric speciation?
occurs when a population is separated by a geographical barrier
Barriers can be natural or man made
Separated groups are reproductively separated, so no gene flow
Different selection pressures act on each group changing allele frequencies via natural selection
What is sympatric speciation
When population living in the same area are separated by ecological or behavioural factors
What is genetic drift
When chance affects which individuals in a population survive
Usually affects very small populations
Large populations mainly affected by natural selection.
Why does genetic drift mainly affect small populations
Random chance has a much larger impact on smaller populations
What is bottleneck?
Extreme example of genetic drift when size of population is suddenly reduced
Results in quick and drastic loss of genetic variation within a population
Remaining members of population become ancestors of all following generations