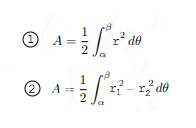Engng Math 145 Polar Coordinates
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Polar coordinates
(r, θ), where r is distance from origin to point & θ is angle between x-axis and line.
Measuring conventions
θ > 0: measure angle anti-clockwise
θ < 0: measure angle clockwise
(-r, θ) = (r, θ+π)
(0, θ) is a single point
Conversion from Cartesian to Polar coordinates
Cartesian→Polar:
Use r = sqrt(x2 + y2) & tanθ = y/x
Polar→Cartesian:
Use x = rcosθ & y = rsinθ
Plot point in Cartesian before determining Polar.
Polar curves
Graph of a polar eqn r = f(θ) consists of all points P that have at least one polar representation (r, θ), with coordinates r & θ that satisfy the polar eqn.
Differentiation with polar curves
For polar curve r=f(θ) can be seen as parametric curve, where
x = rcosθ = f(θ)cos(θ) & y = rsinθ = f(θ)sin(θ), therefore →

Integration with polar curves
For lines θ=a & θ=b and curve r=f(θ)
For lines θ=a & θ=b and curves r1=f(θ) & r2=g(θ), r1 > r2