Classroom and Behavioral Management Strategies for Exceptional Learners: Exam 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Dependent Variable
The behavior to be changed through intervention.
Escape Conditioning
Avoidance of unpleasant stimuli by learning new behaviors to help terminate the occurring unpleasant stimuli.
AB Design
Baseline data in A phase, intervention data in B phase.
Behavior
Observable actions.
Stimulus Response Chain
A change in environment with each step in the expected behavior.
Backwards Chaining
Teacher helps with learned behavior until student can do it on their own.
Shaping
Training a learned behavior that would not normally occur.
Satiation
Student has been fulfilled by reinforcement and it no longer works.
Deprivation
Student has been deprived of something, and it makes it easier to use it as a reinforcer.
Sensory Reinforcers
Auditory (ears), visual (eyes), olfactory (nose), taste (mouth), tactile (touch), proprioceptive (sense of self/position of body).
Variable Duration Schedule
The required amount of time that the student engages in the behavior to receive reinforcement varies around some average.
Baseline Data
Data recorded before intervention.
A Phase
Baseline Data
B Phase
Intervention Data
Variability
Fluctuations across the baseline data.
Interval Recording
Measuring the occurrence of nonoccurrence of a behavior within specified intervals; a mark is made if the behavior occurred during any part of interval (partial) or entire interval (whole); the percentage of intervals marked is computed.
ABAB (Reversal) Design
Sequential application and withdrawal of intervention following initial baseline.
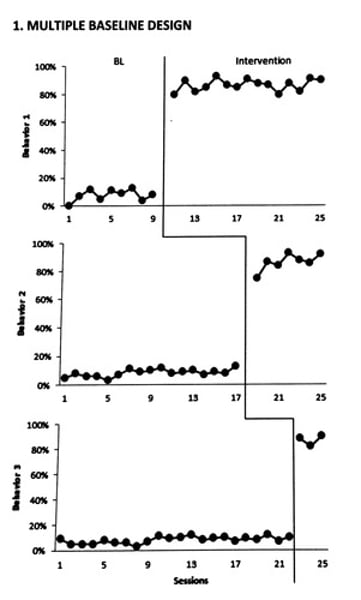
Multiple Baseline Design
Simultaneous analysis of behaviors, students, or settings.
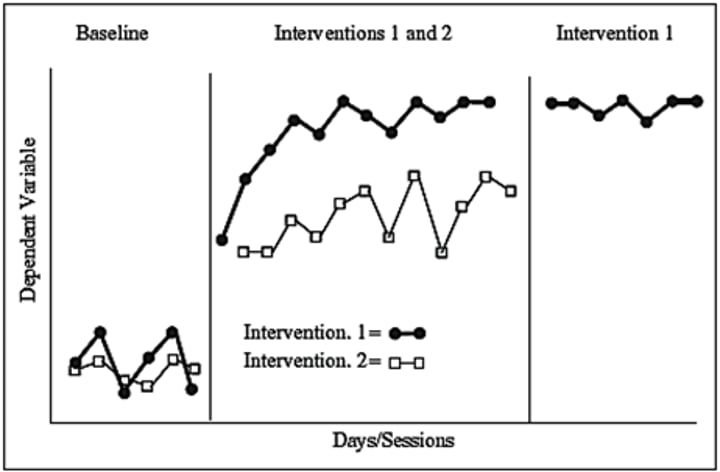
Alternating Treatments Design
Random alternation of two or more to compare their effectiveness.
Subjective Descriptions
Relates to personal viewpoints, experiences, or perspectives.
Objective Descriptions
Refers to factual data that is not influenced by personal beliefs or biases.
Setting Events
What occurred before the behavior that increased the likelihood that the interfering behavior would occur.
Three Term Contingency
Antecedent, Behavior, Consequence (ABC's of Behavior)
Antecedent (A)
What occurred right before the behavior.
Behavior (B)
The action of the student.
Consequences (C)
What occurs after the behavior.
Contingency
The relationship between the behavior and the environment.
Reinforcer
Event that follows a behavior and INCREASES the probability of future occurrence.
Punisher
Event that follows a behavior and DECREASES the probability of future occurrence.
Positive Reinforcement
Stimulus was added and the behavior increased.
Negative Reinforcement
Stimulus was removed and the behavior increased.
Positive Punishment
Stimulus was added and the behavior decreased.
Negative Punishment
Stimulus was removed and the behavior decreased.
Premack Principle
Reinforcement is individualized based on the preferences of the student.
Continuous Schedule
Each target behavior is immediately reinforced.
Fixed Ratio Schedule
Reinforcement occurs each time a set number of behaviors are performed.
Variable Ratio Schedule
The number of responses required to receive reinforcement varies around some average.
Fixed Interval Schedule
Student must perform behavior in a fixed amount of time after reinforcement becomes available.
Variable Interval Schedule
The time for the student to perform behavior after reinforcement becomes available is varied.
Fixed Duration Schedule
Reinforcement is provided after the student engages in the specified behavior for a continuous amount of time.
Stability
Consistent data across the baseline.
Trend
Clear direction of the data (increasing, constant, decreasing).
Independent Variable
Actual intervention/program being implemented.
School-Wide Positive Behavior Support
A systematic three-tired model that addresses a continuum from prevention of behavior problems to highly individualized supports for students who display that most challenging behaviors.
1. school-wide
2. classroom or group
3. individual-intensive
Primary Reinforcer
Stimulus that is naturally rewarding, such as food or water.
Conditioned Reinforcer
A stimulus that has acquired reinforcing properties through prior learning.
Frequency Recording
Counting number of times a target behavior occurs.
Duration Recording
Measuring how long a behavior lasts.
Latency Recording
Measuring how long it takes a behavior to be performed.
Permanent Product
Counting the by-products of a student's behavior (# of pencils snapped, problems completed)
Time Sampling
Same as interval recording except that the observer look at the child at the end of the interval and records if the behavior is or is not occurring at that instant.
Changing Criterion Design
Successive increase or decrease in criteria for reinforcement in a step-wise fashion.
Changing Conditions Design (ABAC)
Successive change in conditions for performance of behavior to evaluate comparative effects of intervention.