Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
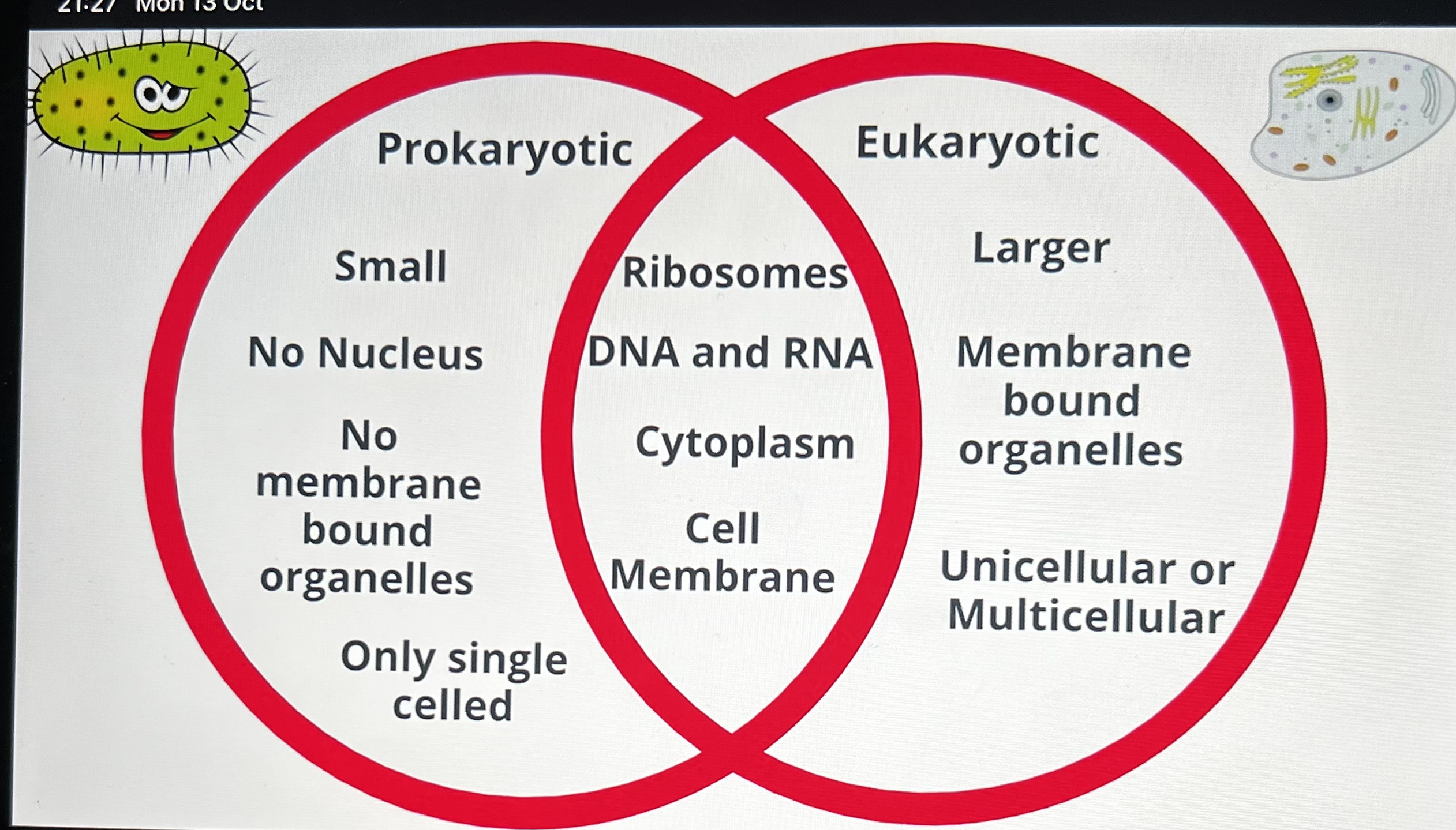
State the 2 types of cells
Eukaryotic {animals and plants}
Prokaryotic cells {bacteria and fungi}
What is the difference between a eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus
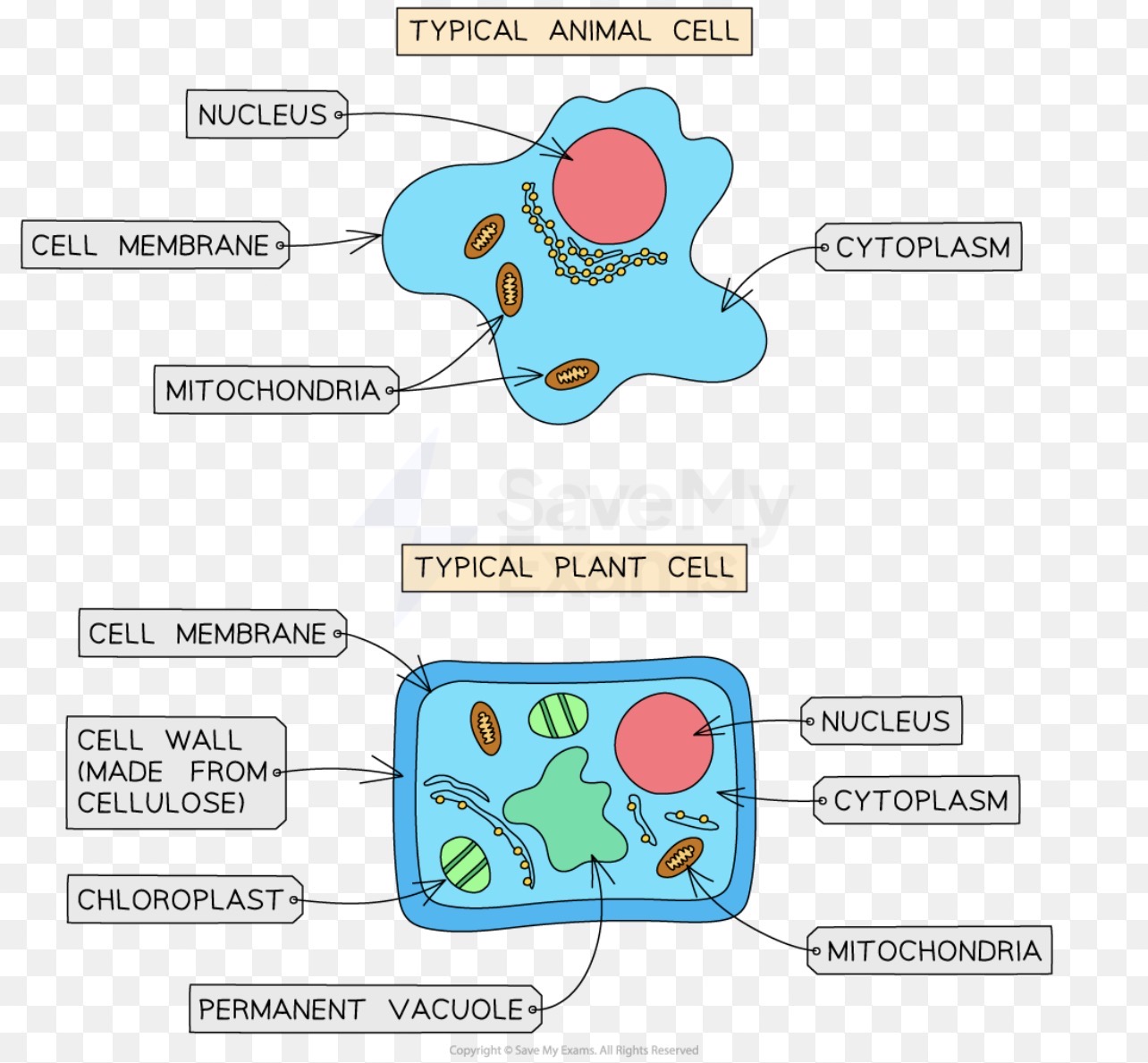
Define and state what these sub cellular structures are and do: Animal and plant
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Cell wall
Large vacuole
Partially permeable cell membrane
Chloroplast
Nucleus: acts as the control centre of the cell and contains DNA which is arranged into chromosomes
Cytoplasm: gel like substance where most of the chemical reactions happen. Contains enzymes which control these chemical reactions
Mitochondria: contain enzymes needed in aerobic respiration
Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis
Cell wall: made of cellulose. Supports and strengthens the plant cell
Large vacuole: contains cell sap, which is a weak solution of sugars and salt
Partially permeable Cell membrane: controls what goes in and out of the cell
Chloroplast:site of photosynthesis {production of food for plant}. It contains a green substance called chlorophyll
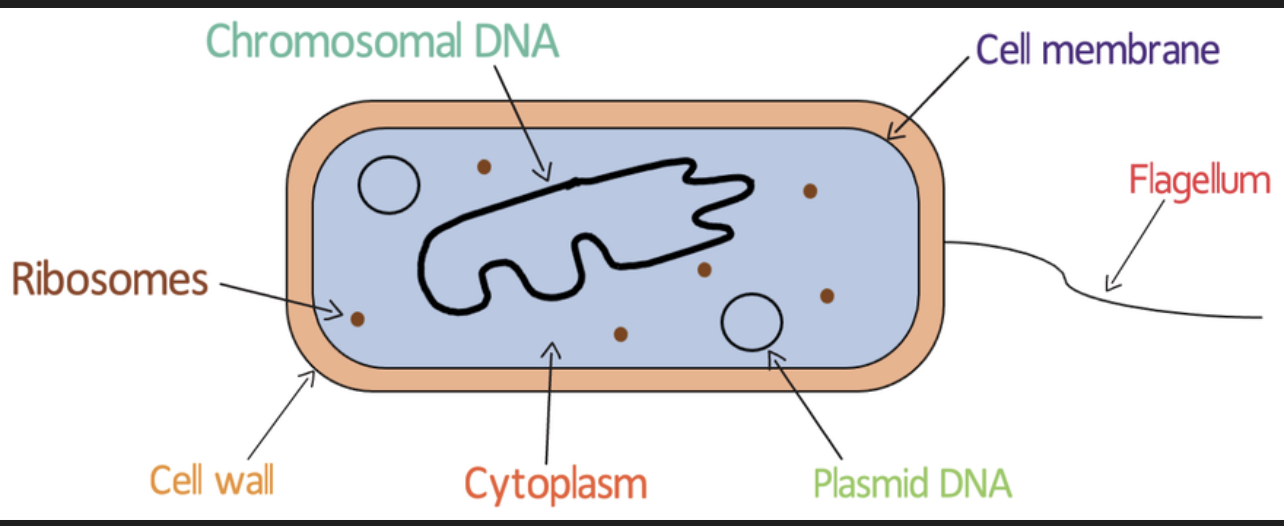
How do prokaryotic cells store their genetic material {DNA}?since they DO NOT HVAE A NUCLEUS
They store their genetic material {DNA} as:
One long circular chromosome which floats free in the cytoplasm
Plasmids
What are plasmids? {sub cellular structures in prokaryotic cells}
Plasmids are small loops of EXTRA DNA
They carry genes that provide genetic advantages e.g. drug resistance
They can be passed between prokaryotic cells
NOT ALL PROKARYOTIC CELLS CONTAIN PLASMIDS
What other sub cellular structures do Prokaryotic cells have?
Partially permeable Cell membrane: controls what goes in and out of the cell
Ribosomes: site of protein synthesis
Flagella:a long tail like structure which allows the prokaryotic cells to move toward nutrients or away from harmful substances
Cell wall: made of cellulose. Supports and strengthens the plant cell